596
Some facts from the microcosm
Recently, a good post dedicated to black holes and general relativity. I would like to blow up the brain even more to some people, showing some of the achievements of modern quantum mechanics.
Quanta - the minimum portions of energy.
Any energy can radiate absorbed and does not in any quantity but only in proportion to the minimum energy of a single photon. The photon energy depends on the wave of Dina. The smaller the wavelength and the higher the frequency the higher the energy of a single photon. Quantum of electromagnetic radiation is called a photon.
Particle or Wave?
Einstein's famous formula linked mass and energy. Electromagnetic radiation is a particle and a wave at the same time.
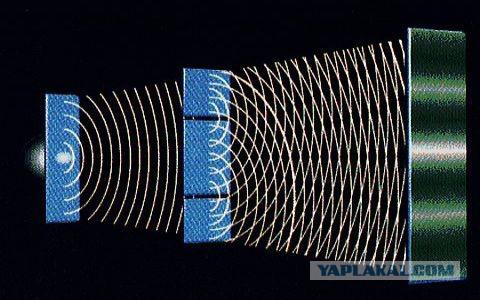
There is a remarkable experiment associated with the passage of light through the plate with one or two slots. If we put a light source on the screen, which is located between the screen plate with a slit, we can see that the light passing through the slit lit one strip on the screen. However, if the plate are two parallel slots, the picture on the screen will be already consist of a series of light and dark areas. This fact proves the electromagnetic nature of light as the light passes through the various different ways in different parts of the slit screen extinguish or reinforce each other.
Matter also wave
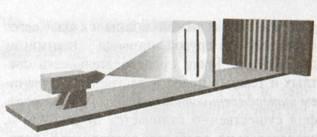
What is most interesting, if in the previous experiment, we will replace the light source to the source of the electrons (full of material particles having a well measured weight), we will see on the screen the same interferential picture. You can certainly assume that this effect as that associated with the interaction of electrons with each other. Change the photon source so that it emits electrons one by one (for example, one electron every 10 seconds). Still, on the screen we will see interferential picture. Remove one slit, the interference disappears. Electron wave too!
Bol, the electrons pass through one of the slits, as it knows there is another slot or not. Alternatively, the electron going through both slits simultaneously.
Journey to Andromeda
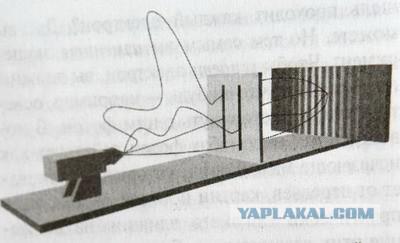
Moreover, not only the electron passes through both slits simultaneously. He also goes to the destination for all possible paths simultaneously.
That is, the electron travels to the Andromeda nebula, flies around the galaxy, and returns to the destination through the left slit. Simultaneously, this electron passes through the gap at the lower right path. There are an infinite number of possible paths through which passed a single electron to the selected target.
What about Newton?
But if we take a bunch of particles, each of which behaves like a wave, while traveling from point A to point B on a pile of paths simultaneously and combine them into an understandable, we object, such as a tennis ball, it appears that all of these paths are mutually reduced. And there will be only one path we can observe in the usual world. The path, which is fully described by Newtonian mechanics.
Does God dice?
In 1927, Heisenberg proved that whatever particle or the process we do not nablyuli, There is a limit to the accuracy of the definition of two related variables. For example, we can not at the same time to know exactly the position of a particle and its momentum (speed). The more accurately we measure the speed, the less accurately we know the position, and vice versa.
Suppose we measure the position of an electron with a very high accuracy. This means that the velocity of the electron in this state to find out exactly what we can not. That is the speed of the probabilistic distributed over a certain period of possible speeds. Alternatively, the electron moves with an infinite number of speeds simultaneously.
It is understood that the uncertainty principle is a property of the world, regardless of the methods for measuring and monitoring.
The unusual nature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and its memorable name made him the source of a series of jokes. It is alleged that the popular graffiti physical faculty campus is: "There may have been a Heisenberg».
In another joke about the uncertainty principle of quantum physics expert stops on the highway police officer and asks: "Do you know how fast you were going, sir?". What physicist replied: "No, but I know where I am!»
Is there a "great nothingness»
Since Einstein's famous formula linked mass and energy, the uncertainty principle applies with respect to the wave perturbations (such as solenoid). The amplitude of the wave and the rate of change of amplitude likewise connected reverse ratio of proportionality. The more precisely we know one thing, the large range of available variation of another.
Now consider a perfect vacuum. Without mother, without waves. You can definitely say that at some point the wave amplitude = 0. But this means that the rate of change of the wave lies within wide limits (and less than the relevant time, the greater the rate of change). So the next time it will not be zero. That is the energy of a small portion of the vacuum in some small amount of time may have a non-zero energy. And since there are lots of energy, in this moment it can be born a pair of particles (particle and antiparticle), which immediately annihilate in order to keep the overall energy balance.
As a result, the vacuum - there are a bunch of particles that are born and die are transformed into each other, while maintaining the overall balance of power.
Again black holes.
Now imagine that two such particles born in the vicinity of the event horizon of a black hole. Since, according to the uncertainty principle, the two particles can not be in one place, then it is one particle would be born inside the event horizon, and the other outside it. Thus, one particle can be absorbed by the black hole, and the other to fly off of it. Due to the fact that the mass of the black hole can be reduced, and the black hole emits weak radiation (Hawking radiation).
However, as seen from the process, such particles can not make the information inside the black hole.
Alive or dead?
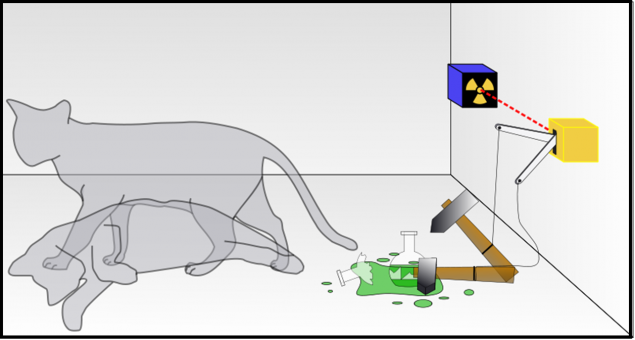
A thought experiment. Take the most usual code and lock it in a drawer with a certain device, consisting of a single atom of a radioactive substance (with a half life of 1 hour), the collapse of the detector coupled with a hammer, smashing the vial for a cat with a deadly poison. If the detector detects the collapse of the disintegration of the atom (the probability of decay of an atom within an hour - 50%) of the hammer smashes a vial of poison, and the cat dies.
Lock the cat in a box and run an experiment.
After an hour, until we observe the results of the experiment, the core is stored in a quantum superposition of two competitions. That is the core of both decayed and not decayed.
And our cat at the time and is alive and dead at the same time! But as soon as we open the box and observe the condition of the cat, the fact of observation "collapses" the wave function of our cat to a state - alive or dead.
Sources:
The book "The Elegant Universe," Brian Green book "A Brief History of Time," Stephen Hawking, Internet, Wikipedia. Pictures from the Internet.
That's all I wanted to say.
Source:
Quanta - the minimum portions of energy.
Any energy can radiate absorbed and does not in any quantity but only in proportion to the minimum energy of a single photon. The photon energy depends on the wave of Dina. The smaller the wavelength and the higher the frequency the higher the energy of a single photon. Quantum of electromagnetic radiation is called a photon.
Particle or Wave?
Einstein's famous formula linked mass and energy. Electromagnetic radiation is a particle and a wave at the same time.
There is a remarkable experiment associated with the passage of light through the plate with one or two slots. If we put a light source on the screen, which is located between the screen plate with a slit, we can see that the light passing through the slit lit one strip on the screen. However, if the plate are two parallel slots, the picture on the screen will be already consist of a series of light and dark areas. This fact proves the electromagnetic nature of light as the light passes through the various different ways in different parts of the slit screen extinguish or reinforce each other.

Matter also wave
What is most interesting, if in the previous experiment, we will replace the light source to the source of the electrons (full of material particles having a well measured weight), we will see on the screen the same interferential picture. You can certainly assume that this effect as that associated with the interaction of electrons with each other. Change the photon source so that it emits electrons one by one (for example, one electron every 10 seconds). Still, on the screen we will see interferential picture. Remove one slit, the interference disappears. Electron wave too!
Bol, the electrons pass through one of the slits, as it knows there is another slot or not. Alternatively, the electron going through both slits simultaneously.

Journey to Andromeda
Moreover, not only the electron passes through both slits simultaneously. He also goes to the destination for all possible paths simultaneously.
That is, the electron travels to the Andromeda nebula, flies around the galaxy, and returns to the destination through the left slit. Simultaneously, this electron passes through the gap at the lower right path. There are an infinite number of possible paths through which passed a single electron to the selected target.

What about Newton?
But if we take a bunch of particles, each of which behaves like a wave, while traveling from point A to point B on a pile of paths simultaneously and combine them into an understandable, we object, such as a tennis ball, it appears that all of these paths are mutually reduced. And there will be only one path we can observe in the usual world. The path, which is fully described by Newtonian mechanics.
Does God dice?
In 1927, Heisenberg proved that whatever particle or the process we do not nablyuli, There is a limit to the accuracy of the definition of two related variables. For example, we can not at the same time to know exactly the position of a particle and its momentum (speed). The more accurately we measure the speed, the less accurately we know the position, and vice versa.
Suppose we measure the position of an electron with a very high accuracy. This means that the velocity of the electron in this state to find out exactly what we can not. That is the speed of the probabilistic distributed over a certain period of possible speeds. Alternatively, the electron moves with an infinite number of speeds simultaneously.
It is understood that the uncertainty principle is a property of the world, regardless of the methods for measuring and monitoring.
The unusual nature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and its memorable name made him the source of a series of jokes. It is alleged that the popular graffiti physical faculty campus is: "There may have been a Heisenberg».
In another joke about the uncertainty principle of quantum physics expert stops on the highway police officer and asks: "Do you know how fast you were going, sir?". What physicist replied: "No, but I know where I am!»
Is there a "great nothingness»
Since Einstein's famous formula linked mass and energy, the uncertainty principle applies with respect to the wave perturbations (such as solenoid). The amplitude of the wave and the rate of change of amplitude likewise connected reverse ratio of proportionality. The more precisely we know one thing, the large range of available variation of another.
Now consider a perfect vacuum. Without mother, without waves. You can definitely say that at some point the wave amplitude = 0. But this means that the rate of change of the wave lies within wide limits (and less than the relevant time, the greater the rate of change). So the next time it will not be zero. That is the energy of a small portion of the vacuum in some small amount of time may have a non-zero energy. And since there are lots of energy, in this moment it can be born a pair of particles (particle and antiparticle), which immediately annihilate in order to keep the overall energy balance.
As a result, the vacuum - there are a bunch of particles that are born and die are transformed into each other, while maintaining the overall balance of power.
Again black holes.
Now imagine that two such particles born in the vicinity of the event horizon of a black hole. Since, according to the uncertainty principle, the two particles can not be in one place, then it is one particle would be born inside the event horizon, and the other outside it. Thus, one particle can be absorbed by the black hole, and the other to fly off of it. Due to the fact that the mass of the black hole can be reduced, and the black hole emits weak radiation (Hawking radiation).
However, as seen from the process, such particles can not make the information inside the black hole.
Alive or dead?
A thought experiment. Take the most usual code and lock it in a drawer with a certain device, consisting of a single atom of a radioactive substance (with a half life of 1 hour), the collapse of the detector coupled with a hammer, smashing the vial for a cat with a deadly poison. If the detector detects the collapse of the disintegration of the atom (the probability of decay of an atom within an hour - 50%) of the hammer smashes a vial of poison, and the cat dies.
Lock the cat in a box and run an experiment.
After an hour, until we observe the results of the experiment, the core is stored in a quantum superposition of two competitions. That is the core of both decayed and not decayed.
And our cat at the time and is alive and dead at the same time! But as soon as we open the box and observe the condition of the cat, the fact of observation "collapses" the wave function of our cat to a state - alive or dead.
Sources:
The book "The Elegant Universe," Brian Green book "A Brief History of Time," Stephen Hawking, Internet, Wikipedia. Pictures from the Internet.
That's all I wanted to say.

Source: