1353
Prisoners of war in the USSR
Subject German prisoners of war for a long time considered to be sensitive and was on ideological grounds covered with darkness. Most of it involved and engaged German historians. In Germany, published the so-called "series of stories of war» («Reihe Kriegsgefangenenberichte»), published by non-official persons on their own funds. Joint analysis of domestic and foreign archives, conducted over the past decade, sheds light on many of the events of those years.
GUPVI (General Administration of prisoners of war and interned Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR) never led personal records of prisoners of war. In the army posts and camps to count the number of people it was set out very badly, and the movement of prisoners from one camp to make it difficult. It is known that at the beginning of 1942 the number of German prisoners of war was only about 9 000 people. For the first time a huge number of Germans (more than 100 000 soldiers and officers) were taken prisoner at the end of the Battle of Stalingrad. Remembering the atrocities of the Nazis, with them not particularly ceremony. A huge crowd of naked, sick and emaciated people make winter crossings of several tens of kilometers a day, spent the night under the open sky and ate almost nothing. All this has led to what are alive at the end of the war left no more than 6 000 people. In total, according to official statistics, the domestic, were taken prisoner 2,389,560 German soldiers, of which 356,678 people died. But on the other (German) sources in Soviet captivity was not less than three million Germans, of which one million prisoners died. A column of German prisoners on the march somewhere on the Eastern Front
The Soviet Union was divided into 15 economic regions. Twelve of them on the basis of the Gulag were created hundreds of prisoner of war camps. During the war, their position has been particularly severe. There were shortages of food, medical care remained at a low level due to lack of qualified doctors. An appliance in the camps were extremely poor. The prisoners were placed in unfinished buildings. The cold, cramped and dirt were commonplace. The mortality rate reached 70%. Only in the post-war years managed to reduce these figures. The rules, established by the order of the NKVD, for each prisoner of war, was supposed to 100 grams of fish, 25 grams of meat and 700 grams of bread. In practice, where they rarely respected. It was mentioned a lot of crimes service protection from theft products and ending with non-extradition of water.
Herbert Bamberg, a German soldier who was in captivity near Ulyanovsk, wrote in his memoirs: "In the camp, the prisoners were fed only once a day, a liter of soup ladle millet porridge and a quarter of bread. I agree that the local population of Ulyanovsk, most likely, too starved ».
Often, if the required type of product was not, it was replaced with bread. For example, 50 grams of meat equated with 150 grams of bread, 120 grams of cereals - 200 grams of bread.
Every nationality in accordance with the traditions of a creative hobby. To survive, the Germans organized theater groups, choirs, literary groups. In the camps were allowed to read newspapers and play games neazartnye. Many prisoners were made chess, cigarette cases, boxes, toys and different mebel.V during the war, despite the twelve-time labor of German prisoners did not play a big role in the national economy of the USSR due to poor organization of labor. After the war, the Germans were involved in the rehabilitation of destroyed during the war factories, railways, dams and ports. They restored the old and building new homes in many cities of our country. For example, with their help, it was built the main building of Moscow State University in Moscow. In Yekaterinburg, entire neighborhoods were built hands of war. In addition, they were used in the construction of roads in remote places, the extraction of coal, iron ore and uranium. Particular attention was paid to highly qualified specialists in various fields, doctors, engineers. As a result, their activity was introduced many important innovations.
Despite the fact that the Geneva Convention on the treatment of prisoners of war in 1864, Stalin did not recognize, in the USSR there was an order to preserve the life of the German soldiers. There is no doubt that they were treated far more humanely than the Soviet people came to Germany.
Plaine for the soldiers of the Wehrmacht brought great disappointment to Nazi ideals crushed old life positions, brought uncertainty of the future. Along with the fall in living standards it was a strong test of personal human qualities. Not survive strong body and spirit, and learned to walk over the corpses of others.
Eyhenberg Henry wrote: "In general, the problem of the stomach has been above all, for a bowl of soup or a piece of bread sold body and soul. Hunger spoiled people, corrupted them and turned into beasts. Ordinary steel products stolen from his comrades ».
Any unofficial relations between the Soviet people and prisoners were seen as a betrayal. Soviet propaganda long and hard exhibited all Germans beasts in human form, producing them extremely hostile attitude.
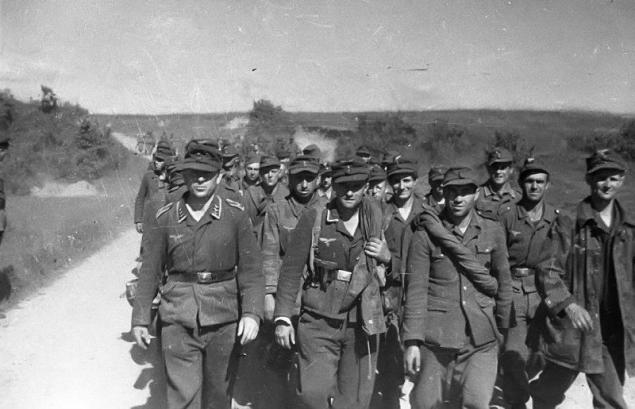

A column of German prisoners of war carried through the streets of Kiev. All along the way the column was being watched residents and off-duty soldiers (right)
According to the memoirs of one prisoner: "During the work orders in the same village, an elderly woman did not believe me that I am German. She told me: "What are you German? You also do not have horns! »
Along with the soldiers and officers of the German army in captivity were also representatives of the elite army of the Third Reich - the German generals. The first 32 general headed by Commander of the Sixth Army, Friedrich Paulus captured in the winter of 1942-1943 directly from Stalingrad. Total in Soviet captivity was visited 376 German generals, of whom 277 have returned home, and 99 died (18 of them generals were hanged as war criminals). Attempts to escape among the generals were not available.
In 1943-1944, together with GUPVI Main Political Administration of the Red Army led by the hard work of creating anti-fascist organizations among the prisoners. In June 1943, it was formed by the National Committee "Free Germany." 38 people entered his first composition. The lack of senior officers and generals has caused many German POWs doubt the prestige and importance of the organization. Soon the desire to join the SSS declared Major General Martin Lattmann (commander of the 389 th Infantry Division), Major General Otto Korfes (commander of the 295th Infantry Division), and Lieutenant-General Alexander von Daniels (commander of the 376th Infantry Division). < br />
17 generals, led by Paulus wrote them an answer: "They want to make an appeal to the German people and the German army, claiming bias of the German leadership and the Nazi government. What do officers and generals belonging to the "Union" is treason. We deeply regret that they went this way. We no longer consider them their comrades, and we strongly reject them ».
Paulus was the instigator of the statement posted on a special cottage in Dubrovo of Moscow, where underwent psychological treatment. Hoping that Paulus will choose a heroic death to captivity, Hitler promoted him to field marshal, and the third in February 1943 symbolically buried him as a "fallen hero's death with the heroic soldiers of the Sixth Army." Moscow, however, to attempt to connect to the anti-fascist work of Paulus. "Processing" General carried out by a special program developed and approved Kruglov Beria. A year later, Paulus openly about the transition to the anti-Hitler coalition. The main role was played by the victory of our army on the front and "conspiracy of generals" July 20, 1944, when the Führer on schastlivoysluchaynosti escaped death.
August 8, 1944, when Berlin was hanged each Paulus, Field Marshal von Witzleben, he openly said on the radio «Freies Deutschland»: «Recent events have made for the continuation of the war the German equivalent victim senseless. For Germany the war was lost. Germany must renounce Adolf Hitler and establish a new state power that will stop the war and create conditions for our people later in life and the establishment of peaceful, even friendly
relations with our present enemies ».
Subsequently Paulus wrote: "It became clear that Hitler not only could not win the war, but it does not have to win, it would be in the interest of humanity and in the interests of the German people».
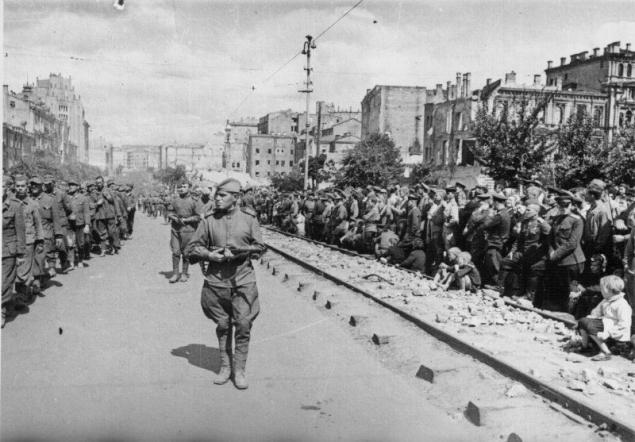

The return of German prisoners of war from Soviet captivity. The Germans arrived at the border transit camp Friedland
Speech by Field Marshal received a wide response. Family Paulus offered to renounce it publicly condemn this act and change the name. When they flatly refused to comply with the requirements, the son of Alexander Paulus was imprisoned in the fortress-prison Kiistrin, and his wife Elena Constance Paulus - the concentration camp Dachau. August 14, 1944 Paulus formally entered into CHO and began an active anti-Nazi activities. Despite his requests to return to his home in the GDR it was only in late 1953.
From 1945 to 1949 in the home has been returned more than one million sick and disabled prisoners. In the late forties to release prisoners of the Germans stopped, and many also have given 25 years in the camps, declaring them war criminals. Before the Soviet government allies citing the need for further restoration of the ruined country. After a visit to our country the German Chancellor Adenauer in 1955 issued a decree "On the early release and repatriation of German prisoners convicted of war crimes." After that, many Germans were able to return to his home.

Source:
GUPVI (General Administration of prisoners of war and interned Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR) never led personal records of prisoners of war. In the army posts and camps to count the number of people it was set out very badly, and the movement of prisoners from one camp to make it difficult. It is known that at the beginning of 1942 the number of German prisoners of war was only about 9 000 people. For the first time a huge number of Germans (more than 100 000 soldiers and officers) were taken prisoner at the end of the Battle of Stalingrad. Remembering the atrocities of the Nazis, with them not particularly ceremony. A huge crowd of naked, sick and emaciated people make winter crossings of several tens of kilometers a day, spent the night under the open sky and ate almost nothing. All this has led to what are alive at the end of the war left no more than 6 000 people. In total, according to official statistics, the domestic, were taken prisoner 2,389,560 German soldiers, of which 356,678 people died. But on the other (German) sources in Soviet captivity was not less than three million Germans, of which one million prisoners died. A column of German prisoners on the march somewhere on the Eastern Front
The Soviet Union was divided into 15 economic regions. Twelve of them on the basis of the Gulag were created hundreds of prisoner of war camps. During the war, their position has been particularly severe. There were shortages of food, medical care remained at a low level due to lack of qualified doctors. An appliance in the camps were extremely poor. The prisoners were placed in unfinished buildings. The cold, cramped and dirt were commonplace. The mortality rate reached 70%. Only in the post-war years managed to reduce these figures. The rules, established by the order of the NKVD, for each prisoner of war, was supposed to 100 grams of fish, 25 grams of meat and 700 grams of bread. In practice, where they rarely respected. It was mentioned a lot of crimes service protection from theft products and ending with non-extradition of water.
Herbert Bamberg, a German soldier who was in captivity near Ulyanovsk, wrote in his memoirs: "In the camp, the prisoners were fed only once a day, a liter of soup ladle millet porridge and a quarter of bread. I agree that the local population of Ulyanovsk, most likely, too starved ».
Often, if the required type of product was not, it was replaced with bread. For example, 50 grams of meat equated with 150 grams of bread, 120 grams of cereals - 200 grams of bread.
Every nationality in accordance with the traditions of a creative hobby. To survive, the Germans organized theater groups, choirs, literary groups. In the camps were allowed to read newspapers and play games neazartnye. Many prisoners were made chess, cigarette cases, boxes, toys and different mebel.V during the war, despite the twelve-time labor of German prisoners did not play a big role in the national economy of the USSR due to poor organization of labor. After the war, the Germans were involved in the rehabilitation of destroyed during the war factories, railways, dams and ports. They restored the old and building new homes in many cities of our country. For example, with their help, it was built the main building of Moscow State University in Moscow. In Yekaterinburg, entire neighborhoods were built hands of war. In addition, they were used in the construction of roads in remote places, the extraction of coal, iron ore and uranium. Particular attention was paid to highly qualified specialists in various fields, doctors, engineers. As a result, their activity was introduced many important innovations.
Despite the fact that the Geneva Convention on the treatment of prisoners of war in 1864, Stalin did not recognize, in the USSR there was an order to preserve the life of the German soldiers. There is no doubt that they were treated far more humanely than the Soviet people came to Germany.
Plaine for the soldiers of the Wehrmacht brought great disappointment to Nazi ideals crushed old life positions, brought uncertainty of the future. Along with the fall in living standards it was a strong test of personal human qualities. Not survive strong body and spirit, and learned to walk over the corpses of others.
Eyhenberg Henry wrote: "In general, the problem of the stomach has been above all, for a bowl of soup or a piece of bread sold body and soul. Hunger spoiled people, corrupted them and turned into beasts. Ordinary steel products stolen from his comrades ».
Any unofficial relations between the Soviet people and prisoners were seen as a betrayal. Soviet propaganda long and hard exhibited all Germans beasts in human form, producing them extremely hostile attitude.

A column of German prisoners of war carried through the streets of Kiev. All along the way the column was being watched residents and off-duty soldiers (right)
According to the memoirs of one prisoner: "During the work orders in the same village, an elderly woman did not believe me that I am German. She told me: "What are you German? You also do not have horns! »
Along with the soldiers and officers of the German army in captivity were also representatives of the elite army of the Third Reich - the German generals. The first 32 general headed by Commander of the Sixth Army, Friedrich Paulus captured in the winter of 1942-1943 directly from Stalingrad. Total in Soviet captivity was visited 376 German generals, of whom 277 have returned home, and 99 died (18 of them generals were hanged as war criminals). Attempts to escape among the generals were not available.
In 1943-1944, together with GUPVI Main Political Administration of the Red Army led by the hard work of creating anti-fascist organizations among the prisoners. In June 1943, it was formed by the National Committee "Free Germany." 38 people entered his first composition. The lack of senior officers and generals has caused many German POWs doubt the prestige and importance of the organization. Soon the desire to join the SSS declared Major General Martin Lattmann (commander of the 389 th Infantry Division), Major General Otto Korfes (commander of the 295th Infantry Division), and Lieutenant-General Alexander von Daniels (commander of the 376th Infantry Division). < br />
17 generals, led by Paulus wrote them an answer: "They want to make an appeal to the German people and the German army, claiming bias of the German leadership and the Nazi government. What do officers and generals belonging to the "Union" is treason. We deeply regret that they went this way. We no longer consider them their comrades, and we strongly reject them ».
Paulus was the instigator of the statement posted on a special cottage in Dubrovo of Moscow, where underwent psychological treatment. Hoping that Paulus will choose a heroic death to captivity, Hitler promoted him to field marshal, and the third in February 1943 symbolically buried him as a "fallen hero's death with the heroic soldiers of the Sixth Army." Moscow, however, to attempt to connect to the anti-fascist work of Paulus. "Processing" General carried out by a special program developed and approved Kruglov Beria. A year later, Paulus openly about the transition to the anti-Hitler coalition. The main role was played by the victory of our army on the front and "conspiracy of generals" July 20, 1944, when the Führer on schastlivoysluchaynosti escaped death.
August 8, 1944, when Berlin was hanged each Paulus, Field Marshal von Witzleben, he openly said on the radio «Freies Deutschland»: «Recent events have made for the continuation of the war the German equivalent victim senseless. For Germany the war was lost. Germany must renounce Adolf Hitler and establish a new state power that will stop the war and create conditions for our people later in life and the establishment of peaceful, even friendly
relations with our present enemies ».
Subsequently Paulus wrote: "It became clear that Hitler not only could not win the war, but it does not have to win, it would be in the interest of humanity and in the interests of the German people».

The return of German prisoners of war from Soviet captivity. The Germans arrived at the border transit camp Friedland
Speech by Field Marshal received a wide response. Family Paulus offered to renounce it publicly condemn this act and change the name. When they flatly refused to comply with the requirements, the son of Alexander Paulus was imprisoned in the fortress-prison Kiistrin, and his wife Elena Constance Paulus - the concentration camp Dachau. August 14, 1944 Paulus formally entered into CHO and began an active anti-Nazi activities. Despite his requests to return to his home in the GDR it was only in late 1953.
From 1945 to 1949 in the home has been returned more than one million sick and disabled prisoners. In the late forties to release prisoners of the Germans stopped, and many also have given 25 years in the camps, declaring them war criminals. Before the Soviet government allies citing the need for further restoration of the ruined country. After a visit to our country the German Chancellor Adenauer in 1955 issued a decree "On the early release and repatriation of German prisoners convicted of war crimes." After that, many Germans were able to return to his home.

Source: