2117
It was mobile communications in the USSR (7 pics + text)
The world's first fully automatic mobile communication has been established and put into operation in the Soviet Union. And within a few years, the Soviet Union was the world leader in mobile communications.
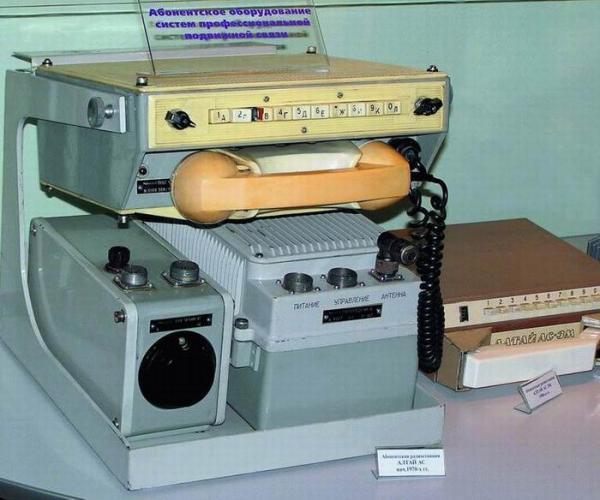

"Altai". The world's first.
Work on the system of automatic mobile communications called "Altai", it began in 1958. In the city of Voronezh in Voronezh Research Institute of Communications (VNIIS) were created by the subscriber stations (in other words, the actual phones) and base stations for communicating with them. Antenna systems have been developed at the Moscow State Specialized Design Institute (SSDI), the same place where born Soviet television. Above the other components of the "Altai" working people of Leningrad, and later joined the company from Belarus and Moldova. Experts from different parts of the Soviet Union have joined forces to create a completely unique at the time the product - automatic mobile communications.
"Altai" was to become a full-fledged phone installed in your car. According to it, just be able to talk as the usual phone (ie, the sound travels in both directions at the same time, the so-called full duplex). To make a call to another "Altai" or regular phone, it was enough just to dial a number - like on a desktop telephone, without switching channels or talk with the dispatcher.
To realize this possibility when the then technical level was not easy. Digital communication, of course, was not yet; voice broadcasting the usual way. But apart from the voice, it was necessary to transmit special signals, by which the system could find itself free radio, to communicate, to transmit the dialed telephone number, etc.
It seems natural to us now simply dial a number on a cell phone buttons. And in 1963, when Moscow launched a pilot zone of the "Altai", this phone in the car makes an indelible impression. The developers tried to make it as much as possible like the usual machines: the "Altai" was a tube, and in some models - even drive to dial. However, the disc was soon abandoned and replaced it with the buttons as tapped in the car appeared uncomfortable.
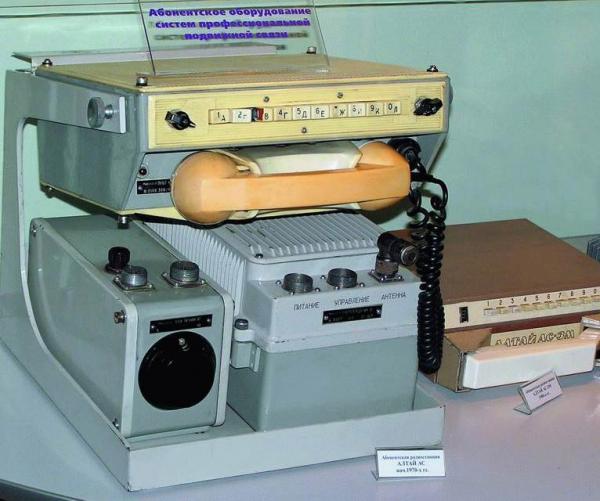

"Altai". Phone 60s.
Party and economic leaders were delighted by the new system. Car telephones soon appeared in "Zilahi" and "The Seagull" the upper echelons of the Soviet leadership. They were followed and "Volga" Directors of the most important companies.
"Altai" certainly was not a complete cellular system. Initially, a city with suburbs serviced by only a single base station with sixteen radio channels. But for a small number of senior officers, which was available as a mobile telephone, it initially lacked.
The system uses a frequency range of 150 MHz - is the frequency of the same order as the TV meter range. Therefore, an antenna mounted on a high tower, enabling the linking to a distance of tens of kilometers.
A similar system in the US, IMTS (Improved Mobile Telephone Service), was launched in the experimental area a year later. And its commercial launch took place only in 1969. Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union by 1970 "Altai" has been installed and successfully operating for approximately 30 cities!
Speaking of the system IMTS. The description of this system is a very interesting paragraph.
In the 70s and the early 80s, before the introduction of cellular phones, there were «waiting lists» of up to three years for those wishing to have mobile telephone service. These potential subscribers were literally waiting for other subscribers to disconnect their subscription in order to obtain a mobile telephone number and mobile phone service.
I translate:
In the 70s and early 80s before using cellular existed "waiting lists" of up to 3 years, for those who have mobile communications. Potential subscribers were forced to wait until the current subscribers disconnected from the network to get a phone number and the mobile phone network service.
Queues! Lists! Number plates! Here it is, Cursed Scoop © !!!
Of course, such severe restrictions were caused by a limited number of radio channels. But I especially pay attention to it, that the readers would understand that such a system could not be mass purely for technical reasons, not because of someone's malicious intent.
For this reason, the system phones were very expensive (from 2 to 4 thousand dollars) and minute call cost from 70 cents to 1.2 US dollar. Most phones were taken on loan from the company rather than purchased.
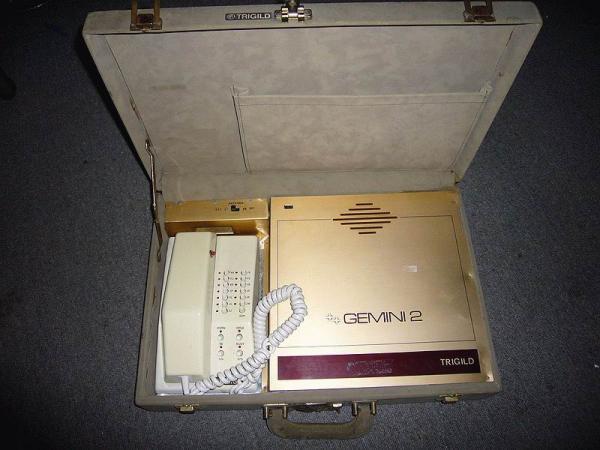

Telephone Systems IMTS. Beginning 70.
And by the way, this system is still in operation in Canada and the United States.
Now, in Moscow, Leningrad, Tashkent, Rostov, Kiev, Voronezh, and many other cities (and regions) of the USSR Party and economic leaders can safely talk on the phone from the car. Our country, as it is strange to hear now confidently in the lead in mobile communications.
In the 1970s, the system "Altai" actively developed. Have been allocated a new radio channels (22 "barrel" to 8 channels) in the range of 330 MHz - ie at slightly longer wavelengths than decimeter TV, thereby providing a considerable range and simultaneously serve more subscribers. Thanks to the first chip subscriber stations became more compact - although still remained car (you can carry the phone with the battery in a heavy suitcase).
By the mid-70s, gradually geography of system "Altai" has expanded to 114 cities in the Soviet Union.
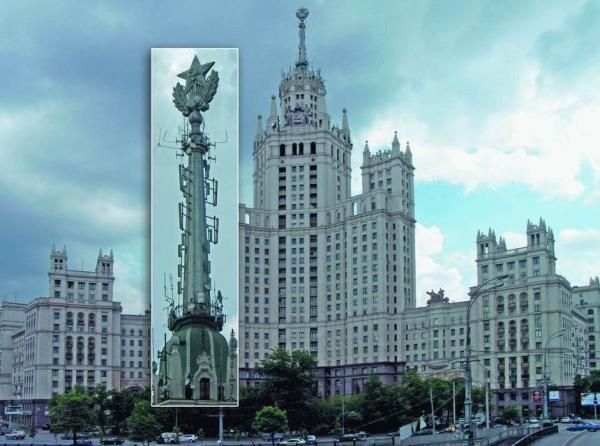
Specific work on the modernization of the equipment had to spend to the Moscow Olympics in 1980. Moreover, it is the base station for the Olympics "Altai" moved to the Ostankino television tower. Prior to that, she held the top two floors of a tall building on the waterfront Tinkers.

At the Olympics-80 connection modernized system "Altai-3M" is used very broadly and showed their best side. So, almost all the journalistic coverage of the events being held across the "Altai". Soviet signalmen have won the Olympics with the Soviet athletes; Olympic medals, although they did not get, but the USSR State Prize received many leading developers.
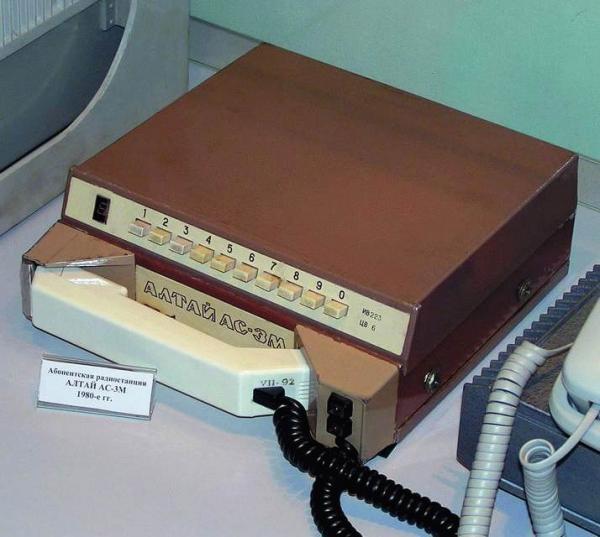

"Altai 3M." End of the 70s - 80s.
However, during the Olympic Games began to appear and limitations "Altai". Sometimes journalists complained of a bad connection; engineers recommended them to rearrange a little car, and everything was adjusted immediately.
All in all, the beginning of the 80s the number of subscribers of the Altai was about 25 thousand.
To set the phone without wires became popular, it was necessary to further develop the system - in particular, the transition to the now familiar use of multiple base stations, covering the territory of the neighboring areas. And Soviet engineers were well prepared for this development. Unfortunately, not everything depended on this readiness.
Volemot that came too late.
In the early 1980s, experts VNIIS and other companies were willing to work on a new generation communication system. It was called "Volemot" (a contraction of the names of towns, where the developers: Voronezh, Leningrad, Molodechno, Ternopil). Especially "Volemot" had the opportunity to make full use of a plurality of base stations; During a call you can switch from one of them to another without losing the connection.
This feature, known today as the "handover" and allows you to talk on the move without any problems, did "Volemot" full service provider. Also supports auto-roaming: The unit "Volemot", registered in the network of the city, could be used in another. At the same time it uses all the same range of 330 MHz, and each base station can, if necessary, "cover" link tens of square kilometers.
Volemot "could become a mass communication in rural areas," true friend "of farmers, cottagers and tourists. For this purpose he came to better than Western cellular systems developed in the same period (AMPS, NMT), because it was easy to let it on a very wide area. But to serve a plurality of users on a small area (the city) "Volemot" inferior AMPS and NMT, however, the further development, however, could solve this problem.
Mobile communications was quite possible to enter in the Soviet way of life in communist ideology. Initially, telephones could, for example, be installed in rural and suburban towns to share and issued in tourist rental clubs (during the campaign). The service call with "Volemot" could appear in the long-distance train or bus. And, of course, no threat to "national security" did not arise - mobile communication devices without encryption is very easy to listen to. Therefore, in the future it could well be available for all citizens.
However, a few years for the project "Volemot" failed to obtain the necessary financing and development of the system was very slow. Meanwhile, cellular systems in the West actively developed and gaining popularity. For the beginning - the middle of the 1980s the former leadership was missed.
"Volemot" yet been completed by the end of the 1980s and was ready to start the deployment, but at a time "process has already started" and the opportunity to catch up with Europe and the United States it was not walking.
Nevertheless, the system has been launched in a number of cities in the early '90s and is still in effect, as well as "Altai". Today, their main positioning - professional communication for various services, from taxis to the "ambulance».
But despite this, a complete cellular managed to appear in the USSR. The first statement - Leningrad "Delta Telecom" started on 9 September 1991 for three and a half months before the collapse of the Soviet Union. This means that work on installing it began six months or a year before the event, when followed in December in the Bialowieza Forest events are not predicted even CIA analysts.
Something interesting. The first cell phones.

Mobile (or rather - the car!) Phone early 80s the company Nokia - Mobira Senator. Weight of the device - 15 kilogram.

Mobira Talkman - phone second half of the 80's - early 90's. His weight has only 3 kg.

First cell phone digging Motorola - DynaTAC 8000X, was released for sale March 6, 1983. Its development was worth about $ 100 million (at the time!).
Phone weighed 794 grams and has dimensions of 33h4.4h8.9 cm. Battery lasts for 1 hour of talk time or 8 hours of standby time. He had a daughter with 30 rooms and one melody.
This phone is worth $ 3,995. In the mobile communications market lasted 10 years.
In a network first US commercial cellular companies «Ameritech Mobile» license fee was $ 50 plus one minute call cost the user from 24 to 40 cents (depending on the time of call). A year after the launch of its network had 12 million subscribers.

"Altai". The world's first.
Work on the system of automatic mobile communications called "Altai", it began in 1958. In the city of Voronezh in Voronezh Research Institute of Communications (VNIIS) were created by the subscriber stations (in other words, the actual phones) and base stations for communicating with them. Antenna systems have been developed at the Moscow State Specialized Design Institute (SSDI), the same place where born Soviet television. Above the other components of the "Altai" working people of Leningrad, and later joined the company from Belarus and Moldova. Experts from different parts of the Soviet Union have joined forces to create a completely unique at the time the product - automatic mobile communications.
"Altai" was to become a full-fledged phone installed in your car. According to it, just be able to talk as the usual phone (ie, the sound travels in both directions at the same time, the so-called full duplex). To make a call to another "Altai" or regular phone, it was enough just to dial a number - like on a desktop telephone, without switching channels or talk with the dispatcher.
To realize this possibility when the then technical level was not easy. Digital communication, of course, was not yet; voice broadcasting the usual way. But apart from the voice, it was necessary to transmit special signals, by which the system could find itself free radio, to communicate, to transmit the dialed telephone number, etc.
It seems natural to us now simply dial a number on a cell phone buttons. And in 1963, when Moscow launched a pilot zone of the "Altai", this phone in the car makes an indelible impression. The developers tried to make it as much as possible like the usual machines: the "Altai" was a tube, and in some models - even drive to dial. However, the disc was soon abandoned and replaced it with the buttons as tapped in the car appeared uncomfortable.

"Altai". Phone 60s.
Party and economic leaders were delighted by the new system. Car telephones soon appeared in "Zilahi" and "The Seagull" the upper echelons of the Soviet leadership. They were followed and "Volga" Directors of the most important companies.
"Altai" certainly was not a complete cellular system. Initially, a city with suburbs serviced by only a single base station with sixteen radio channels. But for a small number of senior officers, which was available as a mobile telephone, it initially lacked.
The system uses a frequency range of 150 MHz - is the frequency of the same order as the TV meter range. Therefore, an antenna mounted on a high tower, enabling the linking to a distance of tens of kilometers.
A similar system in the US, IMTS (Improved Mobile Telephone Service), was launched in the experimental area a year later. And its commercial launch took place only in 1969. Meanwhile, in the Soviet Union by 1970 "Altai" has been installed and successfully operating for approximately 30 cities!
Speaking of the system IMTS. The description of this system is a very interesting paragraph.
In the 70s and the early 80s, before the introduction of cellular phones, there were «waiting lists» of up to three years for those wishing to have mobile telephone service. These potential subscribers were literally waiting for other subscribers to disconnect their subscription in order to obtain a mobile telephone number and mobile phone service.
I translate:
In the 70s and early 80s before using cellular existed "waiting lists" of up to 3 years, for those who have mobile communications. Potential subscribers were forced to wait until the current subscribers disconnected from the network to get a phone number and the mobile phone network service.
Queues! Lists! Number plates! Here it is, Cursed Scoop © !!!
Of course, such severe restrictions were caused by a limited number of radio channels. But I especially pay attention to it, that the readers would understand that such a system could not be mass purely for technical reasons, not because of someone's malicious intent.
For this reason, the system phones were very expensive (from 2 to 4 thousand dollars) and minute call cost from 70 cents to 1.2 US dollar. Most phones were taken on loan from the company rather than purchased.

Telephone Systems IMTS. Beginning 70.
And by the way, this system is still in operation in Canada and the United States.
Now, in Moscow, Leningrad, Tashkent, Rostov, Kiev, Voronezh, and many other cities (and regions) of the USSR Party and economic leaders can safely talk on the phone from the car. Our country, as it is strange to hear now confidently in the lead in mobile communications.
In the 1970s, the system "Altai" actively developed. Have been allocated a new radio channels (22 "barrel" to 8 channels) in the range of 330 MHz - ie at slightly longer wavelengths than decimeter TV, thereby providing a considerable range and simultaneously serve more subscribers. Thanks to the first chip subscriber stations became more compact - although still remained car (you can carry the phone with the battery in a heavy suitcase).
By the mid-70s, gradually geography of system "Altai" has expanded to 114 cities in the Soviet Union.
Specific work on the modernization of the equipment had to spend to the Moscow Olympics in 1980. Moreover, it is the base station for the Olympics "Altai" moved to the Ostankino television tower. Prior to that, she held the top two floors of a tall building on the waterfront Tinkers.

At the Olympics-80 connection modernized system "Altai-3M" is used very broadly and showed their best side. So, almost all the journalistic coverage of the events being held across the "Altai". Soviet signalmen have won the Olympics with the Soviet athletes; Olympic medals, although they did not get, but the USSR State Prize received many leading developers.

"Altai 3M." End of the 70s - 80s.
However, during the Olympic Games began to appear and limitations "Altai". Sometimes journalists complained of a bad connection; engineers recommended them to rearrange a little car, and everything was adjusted immediately.
All in all, the beginning of the 80s the number of subscribers of the Altai was about 25 thousand.
To set the phone without wires became popular, it was necessary to further develop the system - in particular, the transition to the now familiar use of multiple base stations, covering the territory of the neighboring areas. And Soviet engineers were well prepared for this development. Unfortunately, not everything depended on this readiness.
Volemot that came too late.
In the early 1980s, experts VNIIS and other companies were willing to work on a new generation communication system. It was called "Volemot" (a contraction of the names of towns, where the developers: Voronezh, Leningrad, Molodechno, Ternopil). Especially "Volemot" had the opportunity to make full use of a plurality of base stations; During a call you can switch from one of them to another without losing the connection.
This feature, known today as the "handover" and allows you to talk on the move without any problems, did "Volemot" full service provider. Also supports auto-roaming: The unit "Volemot", registered in the network of the city, could be used in another. At the same time it uses all the same range of 330 MHz, and each base station can, if necessary, "cover" link tens of square kilometers.
Volemot "could become a mass communication in rural areas," true friend "of farmers, cottagers and tourists. For this purpose he came to better than Western cellular systems developed in the same period (AMPS, NMT), because it was easy to let it on a very wide area. But to serve a plurality of users on a small area (the city) "Volemot" inferior AMPS and NMT, however, the further development, however, could solve this problem.
Mobile communications was quite possible to enter in the Soviet way of life in communist ideology. Initially, telephones could, for example, be installed in rural and suburban towns to share and issued in tourist rental clubs (during the campaign). The service call with "Volemot" could appear in the long-distance train or bus. And, of course, no threat to "national security" did not arise - mobile communication devices without encryption is very easy to listen to. Therefore, in the future it could well be available for all citizens.
However, a few years for the project "Volemot" failed to obtain the necessary financing and development of the system was very slow. Meanwhile, cellular systems in the West actively developed and gaining popularity. For the beginning - the middle of the 1980s the former leadership was missed.
"Volemot" yet been completed by the end of the 1980s and was ready to start the deployment, but at a time "process has already started" and the opportunity to catch up with Europe and the United States it was not walking.
Nevertheless, the system has been launched in a number of cities in the early '90s and is still in effect, as well as "Altai". Today, their main positioning - professional communication for various services, from taxis to the "ambulance».
But despite this, a complete cellular managed to appear in the USSR. The first statement - Leningrad "Delta Telecom" started on 9 September 1991 for three and a half months before the collapse of the Soviet Union. This means that work on installing it began six months or a year before the event, when followed in December in the Bialowieza Forest events are not predicted even CIA analysts.
Something interesting. The first cell phones.

Mobile (or rather - the car!) Phone early 80s the company Nokia - Mobira Senator. Weight of the device - 15 kilogram.

Mobira Talkman - phone second half of the 80's - early 90's. His weight has only 3 kg.

First cell phone digging Motorola - DynaTAC 8000X, was released for sale March 6, 1983. Its development was worth about $ 100 million (at the time!).
Phone weighed 794 grams and has dimensions of 33h4.4h8.9 cm. Battery lasts for 1 hour of talk time or 8 hours of standby time. He had a daughter with 30 rooms and one melody.
This phone is worth $ 3,995. In the mobile communications market lasted 10 years.
In a network first US commercial cellular companies «Ameritech Mobile» license fee was $ 50 plus one minute call cost the user from 24 to 40 cents (depending on the time of call). A year after the launch of its network had 12 million subscribers.