179
Personalized medicine: DNA treatment

Description: How a genetic passport and gut bacteria become key to health A review of revolutionary methods for 2025: from genome editing to predicting diseases decades before they appear.
Genetic Designer: CRISPR 2.0
A new version of CRISPR-Cas9 with the addition of cytosine improved the accuracy of gene editing by 3,000 times, minimizing ophtharget effects. The technology is already being used to:
- Treatment of hemophilia through correction of blood stem cells
- Creating organ donor pigs with human compatibility genes
- Regeneration of heart tissue after a heart attack

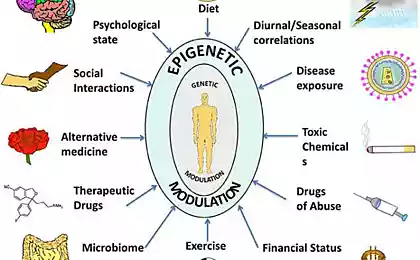
Microbiome as a Diagnostic
Analysis of gut bacteria now predicts risks:
- Alzheimer's disease - 15 years before symptoms
- Type 2 Diabetes by Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes
- Autoimmune diseases – through Akkermansia imbalance
The Anti-Age Revolution: Timekeeping of DNA
The MethylAge epigenetic clock analyzes 353 DNA methylation sites, determining biological age with a margin of error of 1.5 years. Clinics offer:
- Personalized telomerase therapy
- APOE4 gene correction for dementia prevention
- Microbiome cocktails against cellular aging
Case: Patient 0
A 45-year-old man with a genetic predisposition to cancer received:
Parameter TherapyResult for 1 year Gene BRCA1CRISPR-correction Risk reduced from 85% to 2% Microbiome Transplantation Inflammation by 70%EpigeneticsMethylation Diet Bioage reduced by 3.2 years

Ethical coordinates
Personalized medicine faces dilemmas:
- Price: complete genomic analysis + therapy = $12,000
- Privacy: 1 genome = 100 GB of data
- Risks of CRISPR: 0.7% of cases of chromosomal abnormalities
Glossary
Ophtharget effect Non-targeted editing of CRISPR genes
DNA methylation Epigenetic modification that affects gene expression
Fecal transplantation Transferring the donor’s microbiome to the recipient
APOE4 Genetic variant associated with Alzheimer’s disease
How ChatGPT change peace: from written text to management business
Journey to Mars: When will man first set foot on the red planet?