191
How to live to 170 years and enjoy life

Imagine a world where one hundred years of age is considered the middle of life, and 170 years is not a fantasy, but an achievable reality. Modern science is bringing us closer to this future faster than we can imagine.
Jeanne Calman lived 122 years and 164 days, becoming the longest-lived person in history. But what if her record is just the beginning? Recent advances in gerontology, genetics and biohacking open up incredible prospects for radical life extension.
Scientific fact: Studies show that the theoretical maximum of human life can reach 150-200 years if the aging process slows down at the cellular level.
A revolution in understanding ageing
For a long time, aging was considered an inevitable biological process. Today, scientists see it as a disease that can be treated and prevented. The key to longevity lies in understanding the nine major mechanisms of aging identified by modern science.
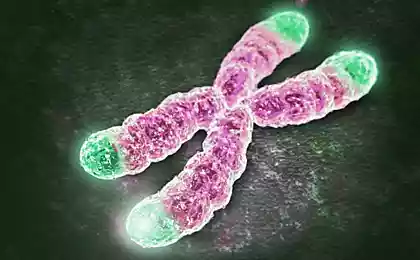
Telomeres are time meters of our cells
Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with each cell division. When they become critically short, the cell stops dividing and dies. The 2009 Nobel Prize was awarded for the discovery of a mechanism for protecting chromosomes by telomeres.
Practical advice: Regular moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (150 minutes per week) can slow telomere shortening by 10 to 15 years of biological age.
Mitochondrial Therapy of the Future
Mitochondria, the energy stations of our cells, are getting worse with age. The accumulation of damage in mitochondrial DNA leads to reduced energy and accelerated aging. New therapies aim to repair and replace damaged mitochondria.

Secrets of the planet's centenarians
The study of “blue zones” – regions with the highest concentration of centenarians – reveals amazing patterns. Okinawa in Japan, Sardinia in Italy, the Nicoya Peninsula in Costa Rica – what unites these places?
Okinawans follow the principle of "hara hachi bu" - eat up to 80% saturation. This simple rule can extend life by 10 to 20 years by activating cellular renewal mechanisms.
The Five Pillars of Super Longevity
1. Calorie restriction with optimal nutrition: Reducing the calorie content of the diet by 15-20% while preserving all the necessary nutrients activates longevity genes and triggers the processes of autophagy - cellular "cleaning".
2. Interval fasting: Periods without food lasting 14-16 hours stimulate the production of growth hormone and improve insulin sensitivity.
3. High-intensity interval training: HIIT training just 2-3 times a week for 20 minutes can reverse age-related changes in mitochondria.
4. Quality sleep and circadian rhythms: 7-9 hours of deep sleep in total darkness is critical for repairing DNA and removing toxins from the brain.
5. Social connections and purpose in life: Strong social ties and a sense of meaning in life can add up to 7 years of life, according to large-scale epidemiological studies.
Amazing discovery: People with a strong sense of purpose in life have a 44% lower risk of dementia and a 23% lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
Advanced anti-aging technologies
Modern medicine is developing revolutionary approaches to slow aging. Gene therapy is already showing impressive results in animal experiments.
NAD+ Therapy and Sirtuins
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a key molecule involved in cell energy metabolism. With age, its level decreases, which leads to a decrease in the activity of sirtuins - longevity proteins. NAD+ precursor supplements show promising results in clinical trials.
Biohacking today: Taking niacinamide riboside (a form of vitamin B3) at a dose of 250-300 mg can increase NAD+ levels by 40-60% after 2-4 weeks.
Senolytics - destroyers of old cells
Senescent cells are “zombie cells” that have stopped dividing but continue to release inflammatory substances. Senolytics - drugs that selectively destroy such cells, show impressive results in tissue rejuvenation.

Personalized Longevity Program
The journey to 170 begins with a personalized approach based on genetic testing, biomarkers of aging, and ongoing health monitoring.
Biomarkers of biological age
Modern tests can determine your actual biological age to within a few years. Analysis of DNA methylation, telomere length, level of inflammatory markers allows you to create an accurate picture of the state of the body.
A study of more than 13,000 people found that those whose biological age was 5 years below chronological age had a 25% lower risk of death from all causes.
Protocol 170+: Your Action Plan
Food: Mediterranean diet with elements of the ketogenic diet 2-3 days a week. Excluding processed foods, adding polyphenols (resveratrol, curcumin, quercetin).
Movement: A combination of strength training (3 times a week), cardio (2 times a week) and yoga or tai chi (15 minutes daily).
Additions: Omega-3, vitamin D3, magnesium, coenzyme Q10, alpha-lipoic acid under the supervision of a specialist.
Stress management: Meditation for at least 10 minutes daily, breathing techniques, time in nature.
Monitoring: Regular tests every 3-6 months, including a full range of longevity biomarkers.
Future perspective: Scientists predict that the first person to live to 200 years old has already been born. CRISPR technologies, artificial organs and nanomedicine could make this a reality by 2070-2080.
Conclusion: A New Era of Humanity
We are on the verge of the greatest revolution in human history: the victory over aging. The combination of the ancient wisdom of centenarians and advanced scientific technology opens the way to a radical extension of life.
The path to 170 years is not just about adding years to life, but adding life to years. This is an opportunity to see your great-grandchildren grow up, witness incredible scientific discoveries and live several full-fledged careers.
Start your journey to super longevity today. Every day of delay is a missed opportunity to extend your life for months and years. The future of longevity begins here and now.
Glossary
telomeres
Protective structures at the ends of chromosomes, shortening with each cell division and determining the lifespan of the cell.
mitochondria
Cell organelles responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP are often referred to as "cell energy stations."
sirtuins
A family of proteins that regulate the cellular processes of aging and stress resistance, activated when calorie restriction.
NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme involved in energy metabolism and activation of sirtuins, the level of which decreases with age.
Senescent cells
Aged cells that have stopped dividing but continue to release inflammatory substances, contributing to the aging process.
Senolytics
Drugs that can selectively destroy senescent cells, potentially slowing the aging process.
Autophagy
A cellular “self-cleaning” process in which a cell destroys damaged components and recycles them into energy.
Biomarkers of ageing
Measurable indicators of biological processes that allow to determine the real biological age of the organism.
Blue Zones
Geographical regions with the highest number of centenarians and the highest life expectancy in the world.
CRISPR
Gene-editing technology to accurately alter DNA sequences to treat diseases and potentially prolong life.
Does going sideways mean the end of a relationship?
11 Signs You Are Still Dependent on Your Parents