1498
Photo-excursion on the bus plant
Photo-excursion on the bus to the famous Yaroslavl plant, one of the biggest tire factories in the central region of Russia. Reports of the workshops, which produce and test the tire brand «Cordiant» for cars.
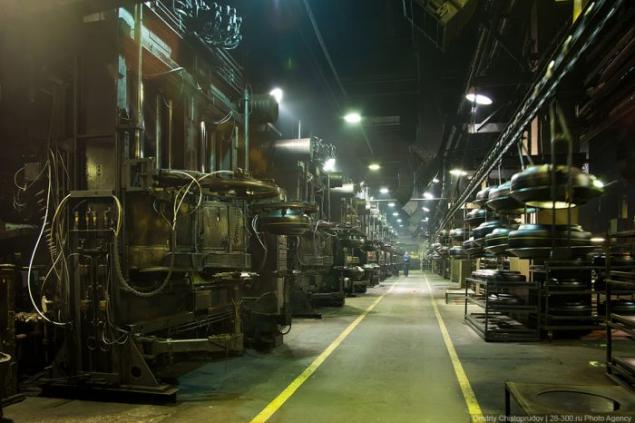

I previously knew that the tire - not a simple thing. It turned out that the production is even more difficult than I imagined. And most importantly, I have learned the secret, where are the antennae on the new tires and why they are needed!
A bit of history: Not many people know that long ago the tires were wooden or metal (so I was told at the institute). The world's first rubber tire was made by Robert William Thomson in 1846, but the author of the tire considered Scotsman John Dunlop, who in 1887 came up to put on the wheel tricycle his 10-year-old son broad hoops made out of a hose for watering the garden, and inflate of air. It is with the bike and began the era of pneumatic tires.
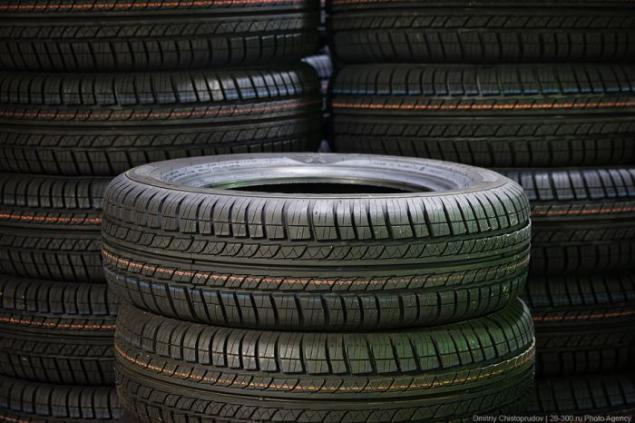

The main materials for the production of tires are rubber, which is made from natural and synthetic rubbers, and cord.
Manufacturing begins with the tire rubber compounding, which can include up to 10 chemicals from sulfur and carbon and ending with rubber. From a mixture of special machines to make different extrusion billets for the future tire.
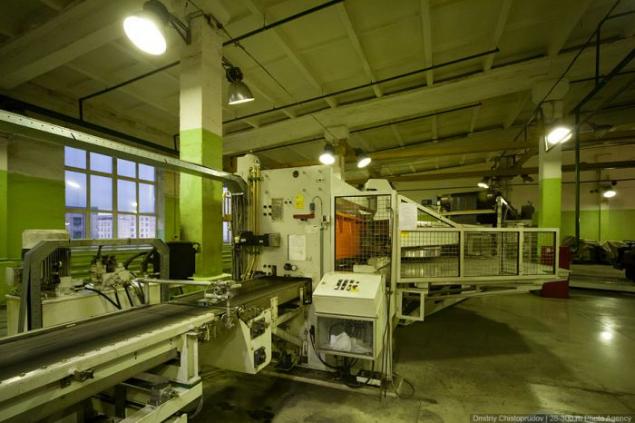

For example, looking next on the conveyor cord.
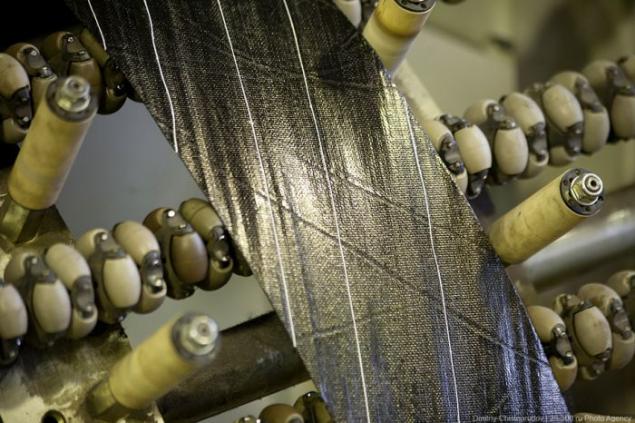

On the cull section blank you can see a "skeleton tires" - frame, which is made of high-strength steel cord. Many minded car owners believe that it's time to throw the bus only when it is erased before the cord.
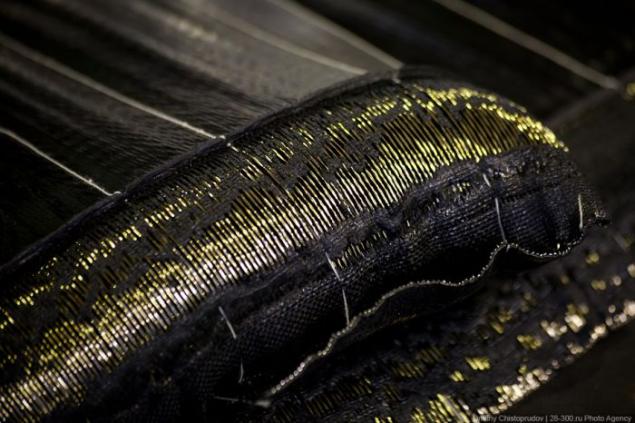

The machines are manufactured components for assembly. The extrusion process is similar for the majority of products and components look about the same - at the exit of the machine turns a long rubber band.
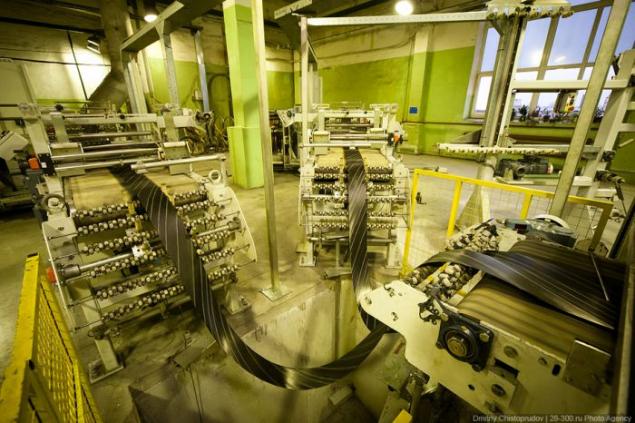

Rubber vulcanization up very sticky, so the material is wound into reels paving each turn with a protective layer.
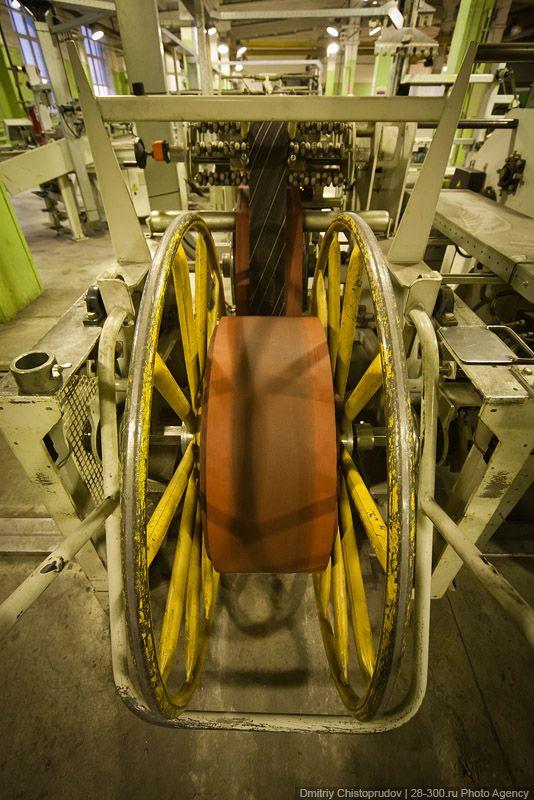

All components are sorted by size tires on each reel glued bar code so that you can at any time to understand what type of tires manufactured material.
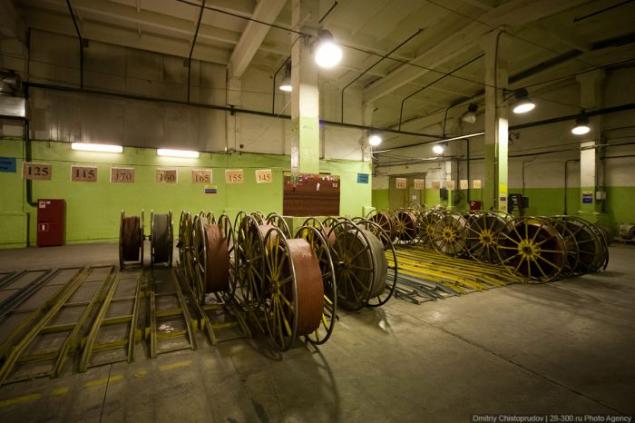

Machines with the giant coils made bead rings. Onboard ring - an important element of the tire, which is made of a plurality of coils of rubberized bead wire. This inextensible, tough part of the tire, with which the fixation on the rim of the disc.
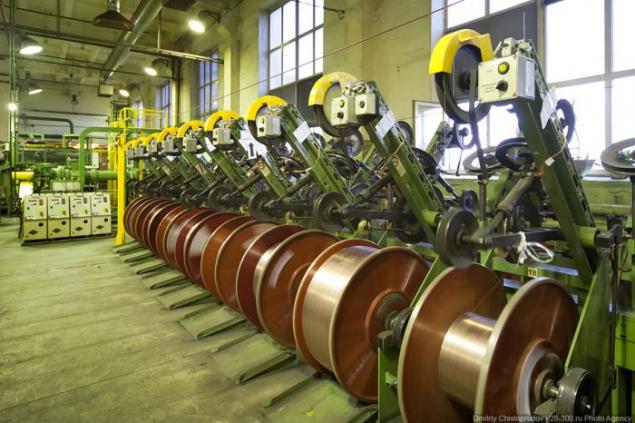

Many, many strands woven into a series that further obrezinivayutsya.
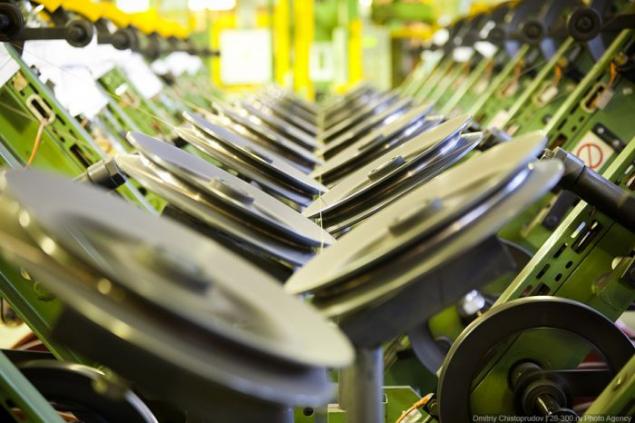

This machine rounds out the rubberized wire into the ring for the desired planting size of the disk. On the left in the frame - ribbon wire to the right - finished rings.

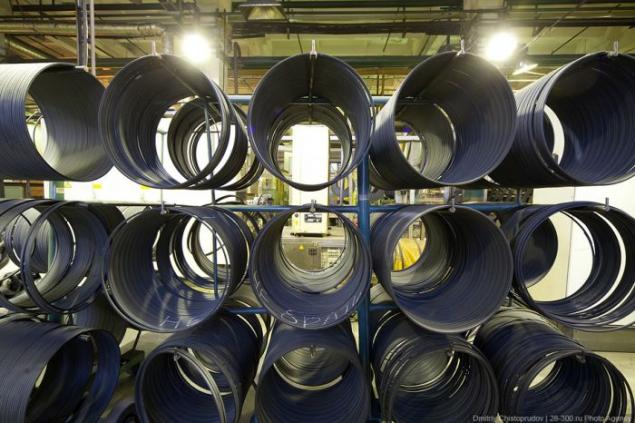
Ready bead rings.

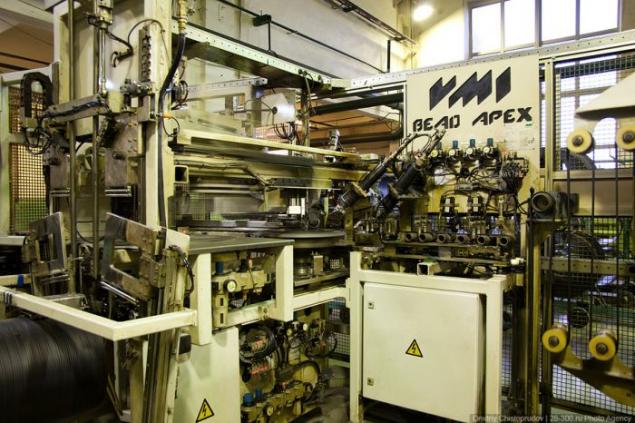
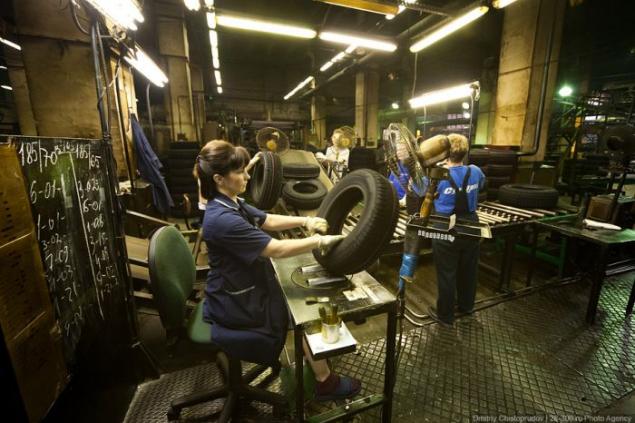
On the assembly machines are connected to the bus all the details together. Required components with spools are loaded on the conveyor belt.
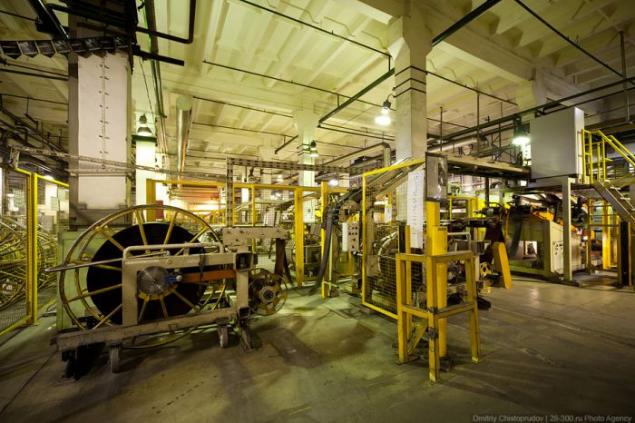

It looks like the tread of the workpiece. Before curing it is simply a thick rubber band without tread. Colored lines - special coding to be able to quickly and clearly understand what a tire radius, width and height of the profile, etc. (a kind of barcode tires).
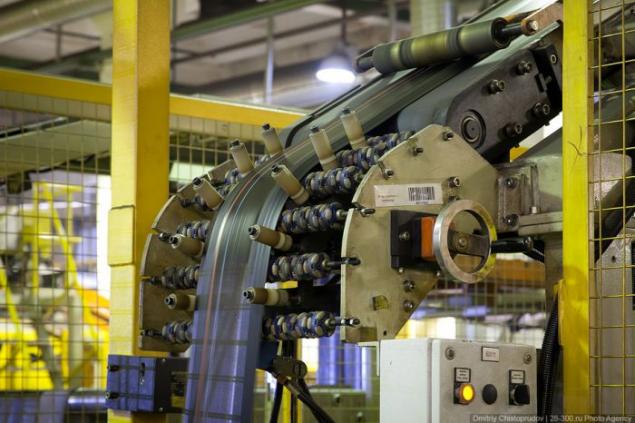

Babina the workpiece is unwound, the component goes on the conveyor, and a protective layer (brown belt, the material does not stick together) is wound on another reel.
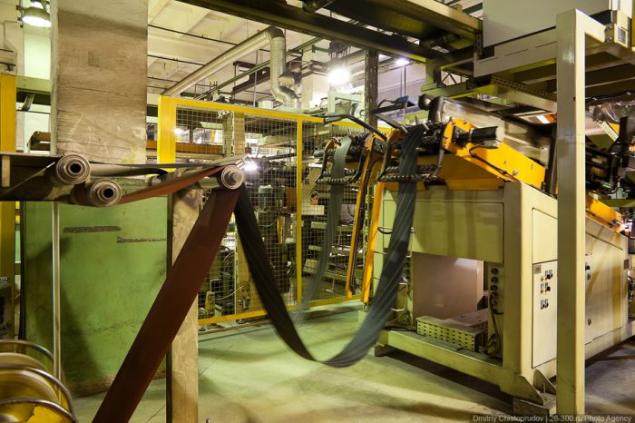

Then begins the stage of "Glory robots!". Everything happens very quickly and you can not immediately figure out what's what. On the building drum successively superimposed layers with different conveyor belts.
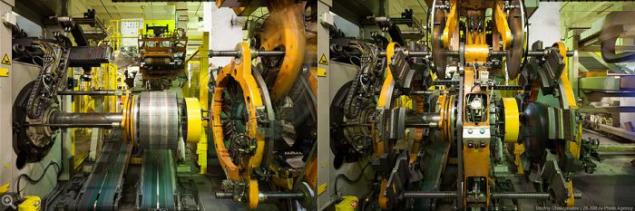
Then comes the big robot and cleverly air balloons blank, something crushes, compresses and wraps it turns semi-finished tire.

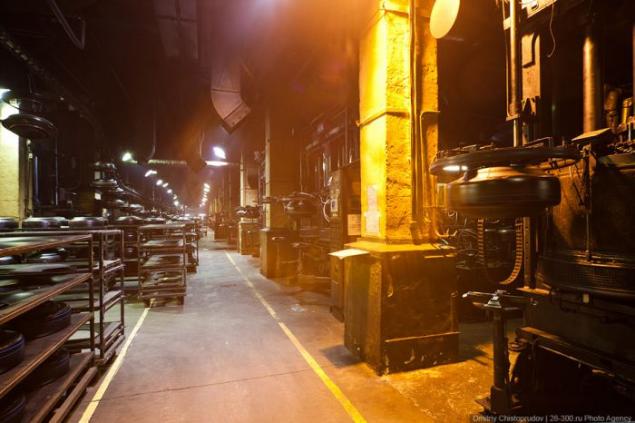
On conveyor lines blanks are sent to the shop vulcanization.
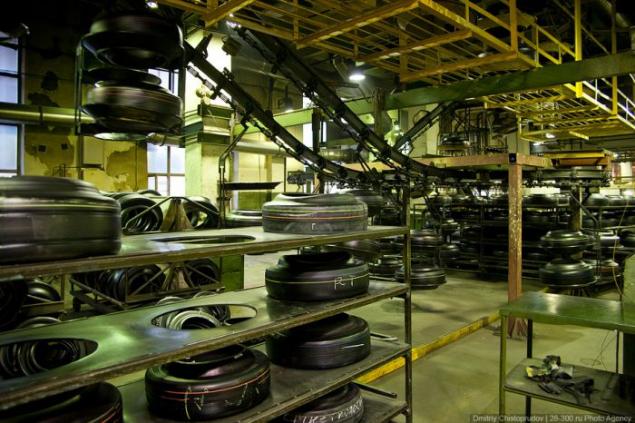
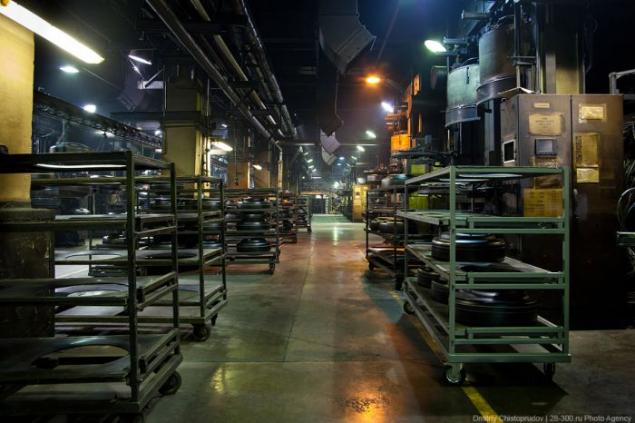


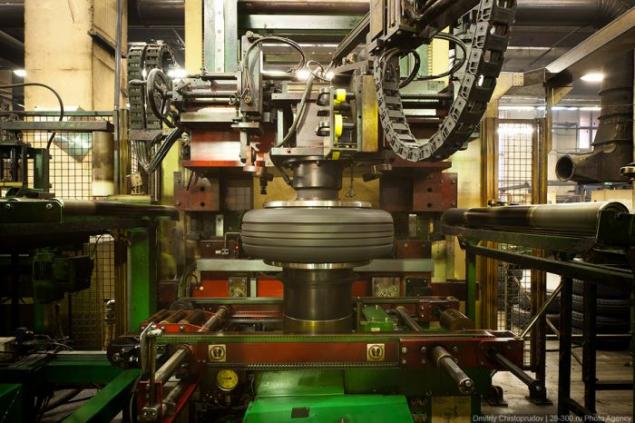
Here, the tire is subjected to hot-heat steam under high pressure. Rubber, carbon black and additives "baked" into a single unit, and the external and internal surface of the tire by a mold applied tread pattern, labels and other technical profiles.
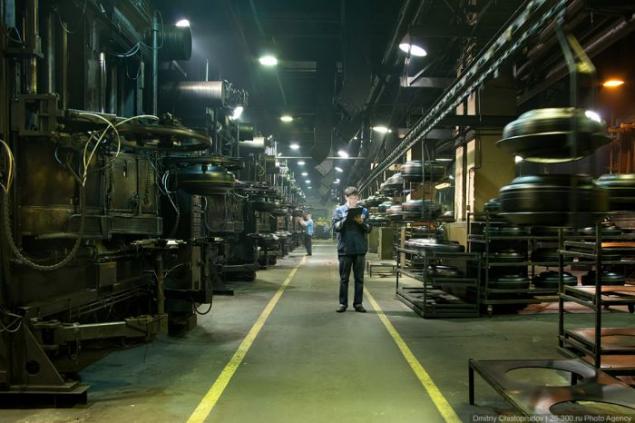

The whole series of workshop settings with vulcanization molds for different types of tire.
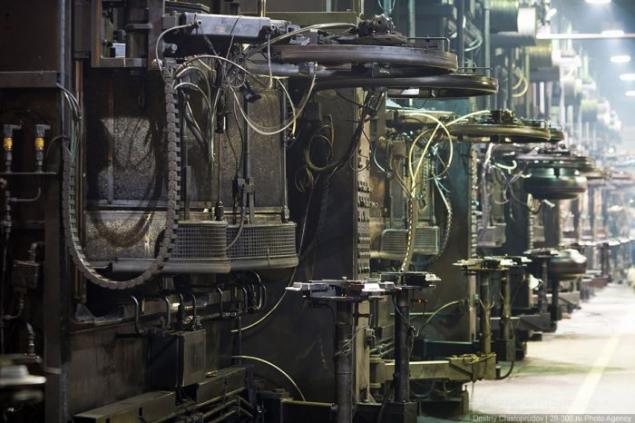

On the left is the curing process, and the right of an empty chamber with a diaphragm, which inflates the tire under high pressure.
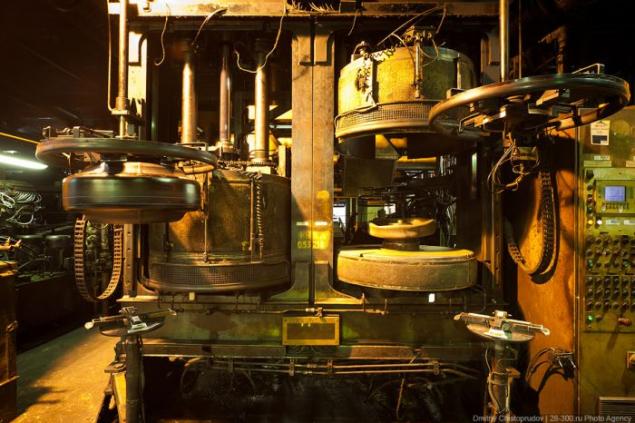

The blank in the chamber, seen from the top of the mold. Under pressure on the sidewalls and tread drawn embossed pattern. There is a chemical reaction (curing), which gives the rubber elasticity and strength.
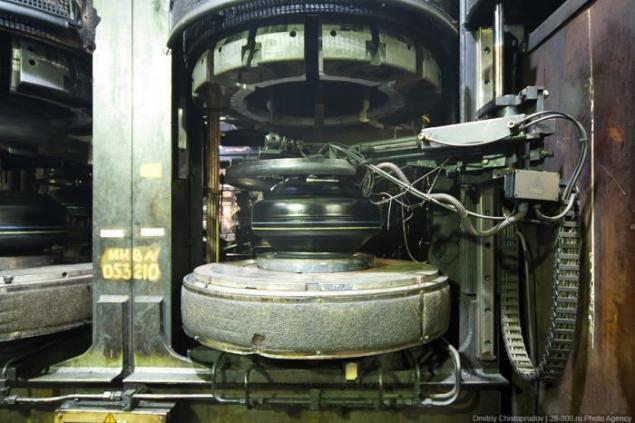

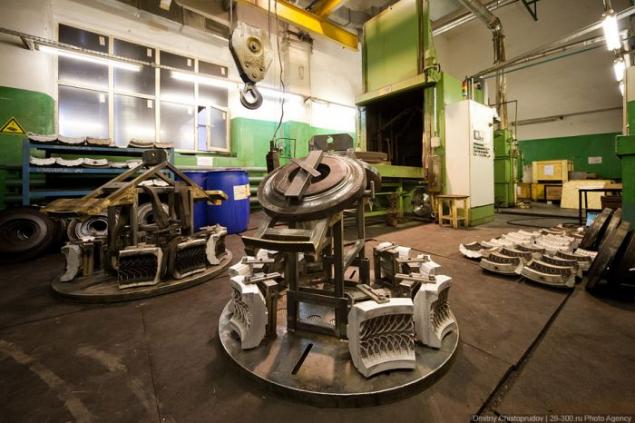
It looks like mold disassembled. Over time, from the heat and pressure of the mold is contaminated and should be cleaned.
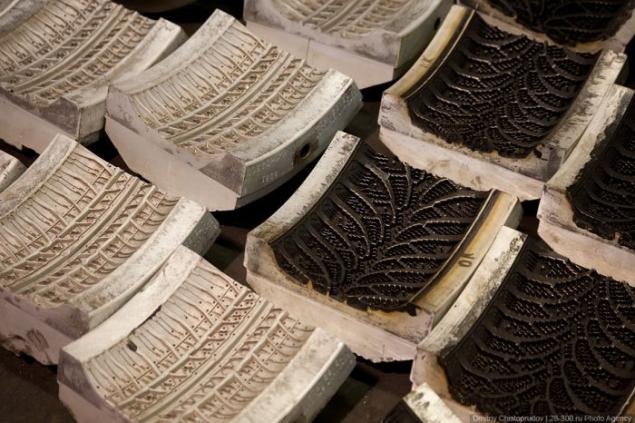

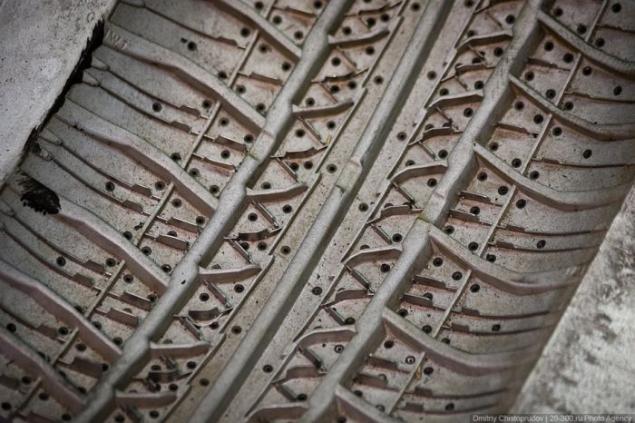
First clogged channels for discharging air during vulcanization. It is because these channels are formed and those mysterious "antennae" on the new tires.

Molds for the sidewalls.
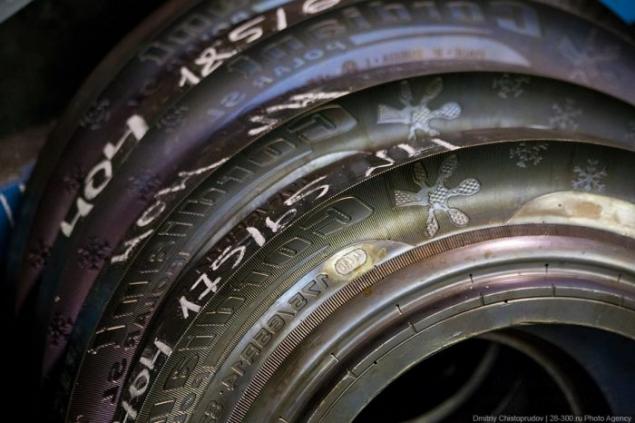

The shop, which is contaminated with mold clean.

Background:
In June 1943, as a result of German air raids, the factory was completely destroyed. But in late September, the consequences of the bombing were eliminated, the plant recovered.
1950s. For the first time in the USSR, the plant started producing tubeless tires for passenger car "Victory", "Volga", "ZIM».
The end of the '50s. The country is experiencing a "tire crisis", a simple transport increased due to the shortage of tires.
1966 released 100 millionth tire.
1969 YaShZ first of the domestic factories were given the right to issue new tires for the car "Zhiguli».
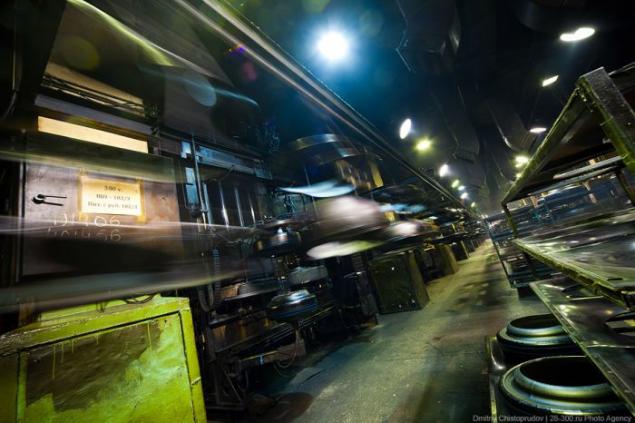

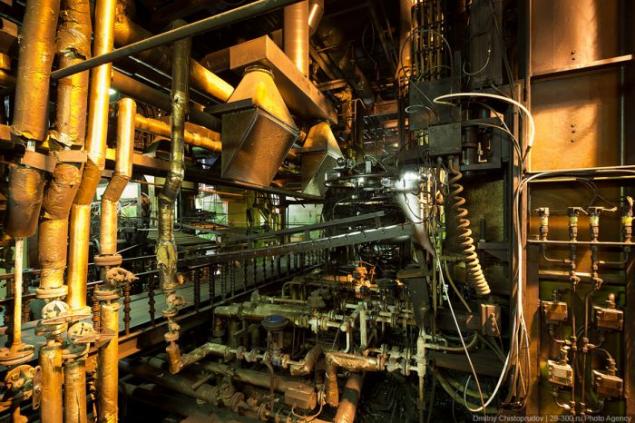
Inside installations curing insanely beautiful!
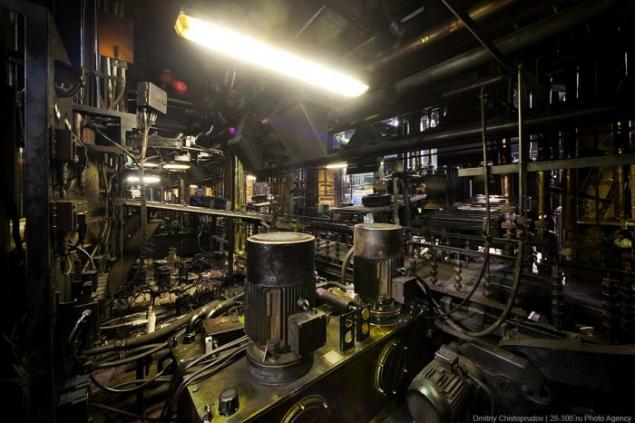

Here's where you had to shoot the Terminator.



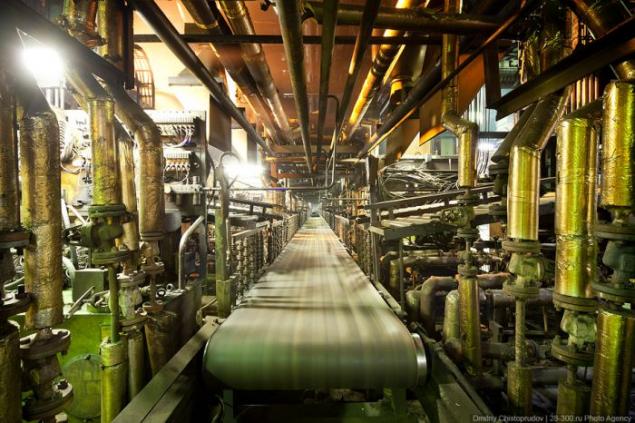
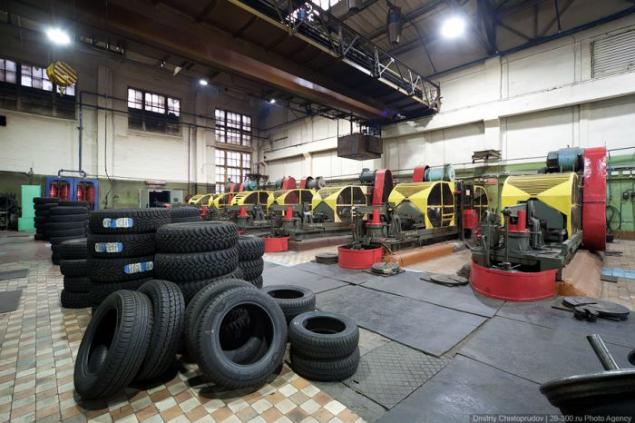
Ready tires supplied to the common pipeline and sent to the final quality control before sending tires to consumers.


Under the control performed a visual inspection of tires.

Next to the work of the robot is switched on again, check that the dynamic characteristics of each tire.

All new models are sure to stand and laboratory and road tests in the factory experimental test center that carried out on special machines, which simulate operating conditions, several times higher than on the effects of road.

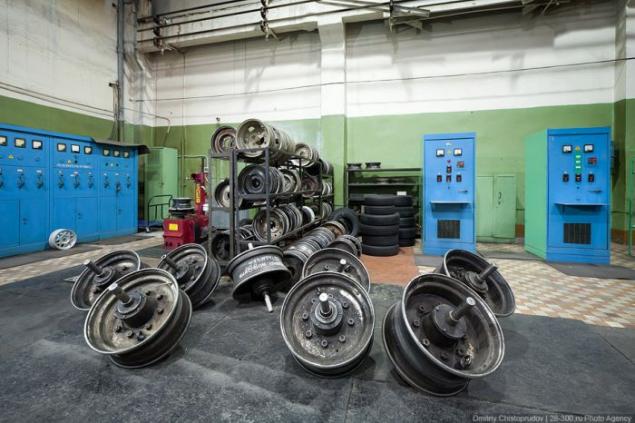
Wheels for all types of tires.

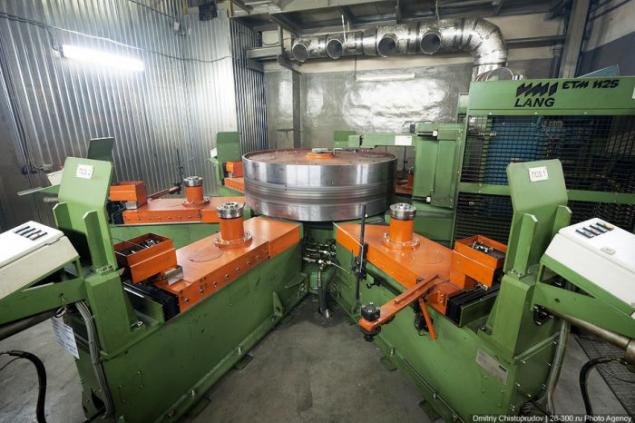
And look for a test bench just six tires at the same time.

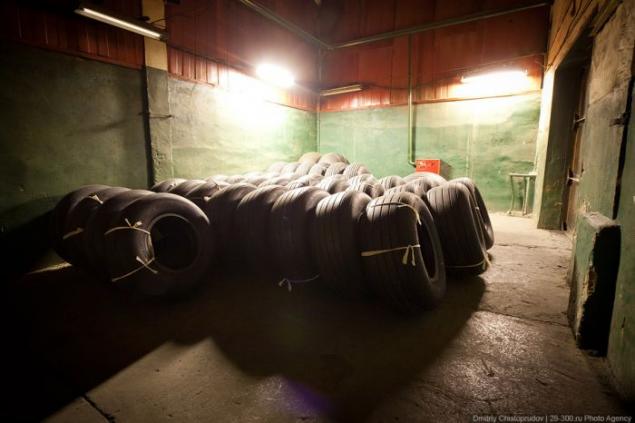
And this is - aircraft tires. How to produce them - a big secret! The enterprises of the company "SIBUR - Russian Tyres", producing tire brand Cordiant made not only the products for a wide range of consumers, but also special products, such as tires for fighter of the 5th generation, known as T-50 or PAK-FA.

To look at the production of aircraft tires need to obtain approval by the FSB.
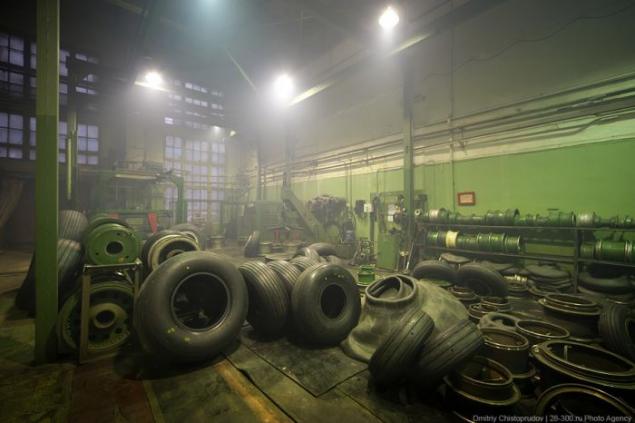

This workshop established stands where mimic the speed and the load on the tire during takeoff and landing aircraft.
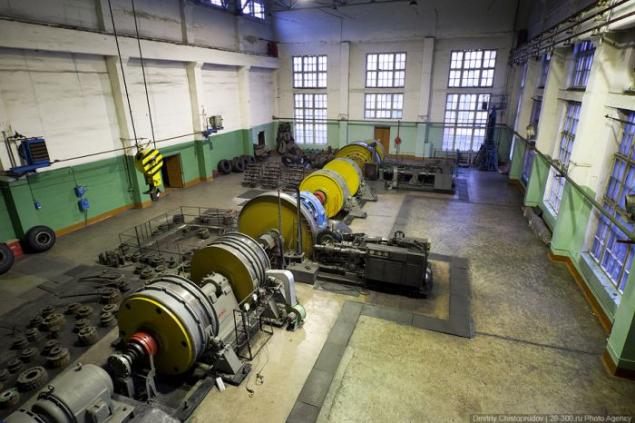
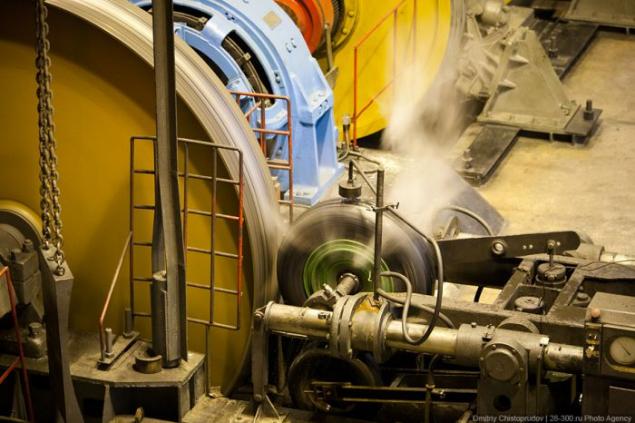


So manufactures tires Cordiant.
"The modern assembly equipment - is a fully automated production, in which a person is given only minimal role. Automated production reduces human factor influence on the quality of the tire, which leads to a significant improvement in the performance of the final product. »


I previously knew that the tire - not a simple thing. It turned out that the production is even more difficult than I imagined. And most importantly, I have learned the secret, where are the antennae on the new tires and why they are needed!
A bit of history: Not many people know that long ago the tires were wooden or metal (so I was told at the institute). The world's first rubber tire was made by Robert William Thomson in 1846, but the author of the tire considered Scotsman John Dunlop, who in 1887 came up to put on the wheel tricycle his 10-year-old son broad hoops made out of a hose for watering the garden, and inflate of air. It is with the bike and began the era of pneumatic tires.

The main materials for the production of tires are rubber, which is made from natural and synthetic rubbers, and cord.
Manufacturing begins with the tire rubber compounding, which can include up to 10 chemicals from sulfur and carbon and ending with rubber. From a mixture of special machines to make different extrusion billets for the future tire.

For example, looking next on the conveyor cord.

On the cull section blank you can see a "skeleton tires" - frame, which is made of high-strength steel cord. Many minded car owners believe that it's time to throw the bus only when it is erased before the cord.

The machines are manufactured components for assembly. The extrusion process is similar for the majority of products and components look about the same - at the exit of the machine turns a long rubber band.

Rubber vulcanization up very sticky, so the material is wound into reels paving each turn with a protective layer.

All components are sorted by size tires on each reel glued bar code so that you can at any time to understand what type of tires manufactured material.

Machines with the giant coils made bead rings. Onboard ring - an important element of the tire, which is made of a plurality of coils of rubberized bead wire. This inextensible, tough part of the tire, with which the fixation on the rim of the disc.

Many, many strands woven into a series that further obrezinivayutsya.

This machine rounds out the rubberized wire into the ring for the desired planting size of the disk. On the left in the frame - ribbon wire to the right - finished rings.

Ready bead rings.

On the assembly machines are connected to the bus all the details together. Required components with spools are loaded on the conveyor belt.

It looks like the tread of the workpiece. Before curing it is simply a thick rubber band without tread. Colored lines - special coding to be able to quickly and clearly understand what a tire radius, width and height of the profile, etc. (a kind of barcode tires).

Babina the workpiece is unwound, the component goes on the conveyor, and a protective layer (brown belt, the material does not stick together) is wound on another reel.

Then begins the stage of "Glory robots!". Everything happens very quickly and you can not immediately figure out what's what. On the building drum successively superimposed layers with different conveyor belts.

Then comes the big robot and cleverly air balloons blank, something crushes, compresses and wraps it turns semi-finished tire.

On conveyor lines blanks are sent to the shop vulcanization.


Here, the tire is subjected to hot-heat steam under high pressure. Rubber, carbon black and additives "baked" into a single unit, and the external and internal surface of the tire by a mold applied tread pattern, labels and other technical profiles.

The whole series of workshop settings with vulcanization molds for different types of tire.

On the left is the curing process, and the right of an empty chamber with a diaphragm, which inflates the tire under high pressure.

The blank in the chamber, seen from the top of the mold. Under pressure on the sidewalls and tread drawn embossed pattern. There is a chemical reaction (curing), which gives the rubber elasticity and strength.

It looks like mold disassembled. Over time, from the heat and pressure of the mold is contaminated and should be cleaned.

First clogged channels for discharging air during vulcanization. It is because these channels are formed and those mysterious "antennae" on the new tires.

Molds for the sidewalls.

The shop, which is contaminated with mold clean.

Background:
In June 1943, as a result of German air raids, the factory was completely destroyed. But in late September, the consequences of the bombing were eliminated, the plant recovered.
1950s. For the first time in the USSR, the plant started producing tubeless tires for passenger car "Victory", "Volga", "ZIM».
The end of the '50s. The country is experiencing a "tire crisis", a simple transport increased due to the shortage of tires.
1966 released 100 millionth tire.
1969 YaShZ first of the domestic factories were given the right to issue new tires for the car "Zhiguli».

Inside installations curing insanely beautiful!

Here's where you had to shoot the Terminator.



Ready tires supplied to the common pipeline and sent to the final quality control before sending tires to consumers.


Under the control performed a visual inspection of tires.

Next to the work of the robot is switched on again, check that the dynamic characteristics of each tire.

All new models are sure to stand and laboratory and road tests in the factory experimental test center that carried out on special machines, which simulate operating conditions, several times higher than on the effects of road.

Wheels for all types of tires.

And look for a test bench just six tires at the same time.

And this is - aircraft tires. How to produce them - a big secret! The enterprises of the company "SIBUR - Russian Tyres", producing tire brand Cordiant made not only the products for a wide range of consumers, but also special products, such as tires for fighter of the 5th generation, known as T-50 or PAK-FA.

To look at the production of aircraft tires need to obtain approval by the FSB.

This workshop established stands where mimic the speed and the load on the tire during takeoff and landing aircraft.


So manufactures tires Cordiant.
"The modern assembly equipment - is a fully automated production, in which a person is given only minimal role. Automated production reduces human factor influence on the quality of the tire, which leads to a significant improvement in the performance of the final product. »
























