529
The walls of the frame house: the correct pie of warming
Canadian technology is one of the most popular methods of building a timber frame house. In our review we highlighted the most key moments, including the rules of construction of the frame system, characteristics of which depends on the efficiency of insulation and easy facade.

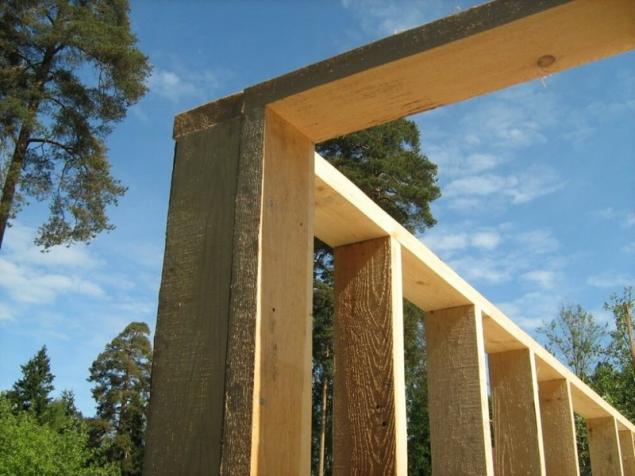
Carrying system frame buildingsfor the Correct device thermal protection frame buildings is defined by each of the stages of construction, starting with the Foundation. Then how well will be fixed to the base support system and how she can have a configuration that will play a crucial role for effective insulation, wind and noise.
Base system device frame walls consist of vertical boards with an aspect ratio of about 3-5:1. The thicker its cross-sectional structure, the better they conduct heat less than this should be step installation. In addition, there may be a need for additional connections. In particular, in the frame practiced the addition of diagonal struts and ties between the individual panels.

The quality of thermal insulation can be estimated by the total area of the wooden elements in longitudinal cut of the wall. It is believed that the wood content in the thermal barrier shall not exceed 18-20% of the total area of the wall. If necessary, you can reduce wood content, developing its own framework that focuses on the shape of the building and the conditions for its operation.
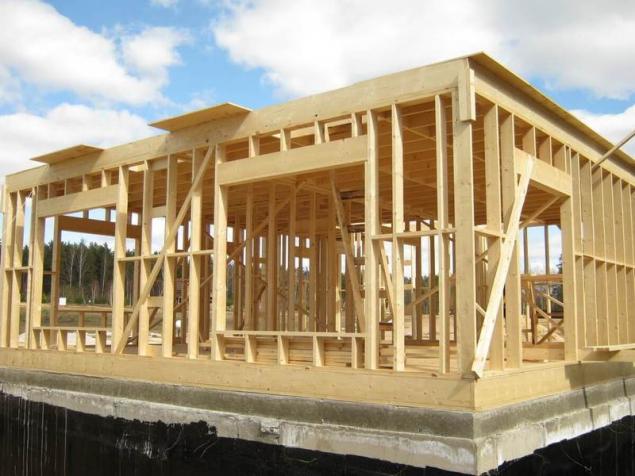

Material for the frame serve only the highest quality lumber very low humidity — no more than 11-12%. When humidity increases by only 3% thermal conductivity of wood is doubled. You should also choose a so-called core Board which is the predominant direction of the fibers across the path of heat transfer — thermal conductivity struts in their correct orientation can be reduced to 2 times depending on the wood.
From materials are also widely used calibrated timber, which, although has an average thermal conductivity due to the oncoming direction of the fibers, but can be used in smaller quantities due to the higher strength and stability. Similarly is the case with solid wood. Although they are denser and better conducting heat, sometimes reducing cold bridges carries a much greater benefit.

In the construction of passive houses frame sometimes do multi-row: internal subsystem complementary rails, which are attached to the strut outer sheathing. In this case, the cross section of the cold bridges is reduced significantly and is approximately equal to the total area between the two rows. This greatly facilitates the calculation of the thickness of the insulation, however, at least 2/3 of its total volume should fall on the outer layer of insulation.
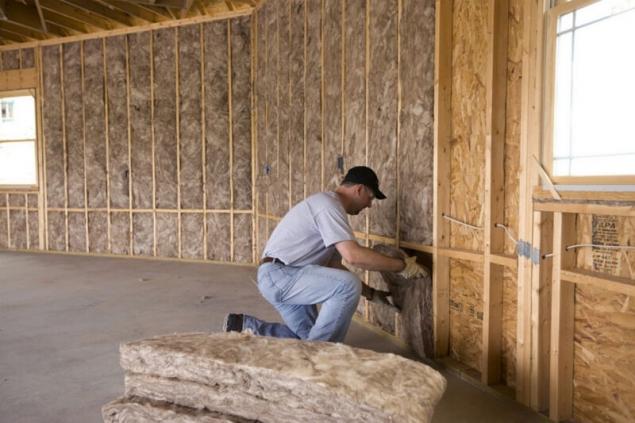
Insulation materialsWith proper design of the frame comes a time when the presence of thermal bridges can be neglected for hedging through increasing a layer of insulation 5-10%. However, how to determine whether the thickness and thermal resistance to reduce heat loss to the required values?
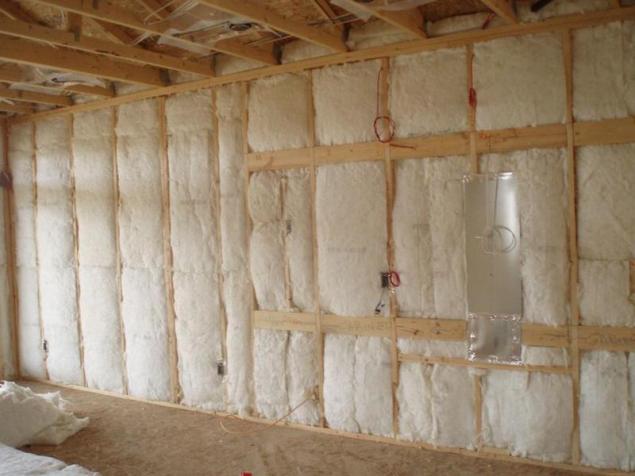

Considered energy-efficient building that loses no more than 100 kWh of thermal energy per square meter of the total area in one year. Sometimes the total heat loss determined by the maximum capacity of the heating equipment. Knowing the height of the enclosing walls and the length of the perimeter, simply calculate the total area of enclosing surfaces, to separate them by types and to calculate what proportion of the walls in heat exchange with outdoor environment. Given that the heating period is not less than 180 days, it is easy to determine which value should be limited to the specific thermal conductivity of the walls to support the original heat balance.
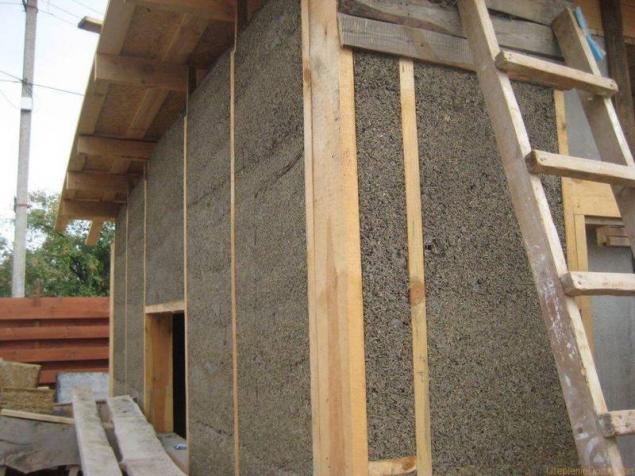

To find the required thickness of insulation, consider its heat-conductivity and the temperature difference, which depends on the internal climate and the level of the thermometer in the coldest five-day week. Also note that the thermal conductivity of the insulation over time may increase or change during the year. If the calculation of heat losses was carried out not on the basis of the maximum power of heating, the temperature difference can be determined by the average temperature around January-February.
Protection of thermal insulationSome insulation materials require protection from moisture, blowing, or perhaps direct sunlight. Some of these tasks might fall on the finish layer, but the primary protection is provided by special membrane materials.
One of the most commonly used in the canadian frame of insulation materials — stone wool — has the ability to dramatically reduce the resistance to heat transfer when wet. Source of water can be precipitation or condensation of water vapor. In the first case used a special synthetic burlap, air-permeable and water vapor, but retains water.

The penetration of steam inside cannot be restricted completely, because the building needed to implement the natural gas exchange with the environment. However, you can limit the amount of water vapor to such values when it will not be enough to raise the relative humidity in the cooled internal air to 85-90%. Typically, such a calculation is carried out for the point of the section of the rows of the frame or carrier system with external insulation. However, the same method can be applied for layer-by-layer calculation of the displacement of the dew point during the year within homogeneous walls.
The hydraulic protection of enclosing structuresof Certain types of materials for insulation has a closed cell structure and is therefore absolutely not absorb water. In this case, the calculated range of displacement of the dew point in whole is placed in a layer of the insulation, because there is moisture to condense may not, simply due to the lack of water vapor.

However, this approach should be particularly cautious. In particular, for single frames require the additional calculation of the displacement of the dew point in the cold bridges, because the main route for leakage of steam will remain gaps between the frame and the insulation.
The formation of moisture on the frame elements might bring harm not only in the long term. A sharp change in wood moisture activates the processes of warping, what with the lack of rigidity of the supporting structure can damage the finish or to open additional paths to the outflow of heat.

To isolate the frame from direct contact with moisture simply. The wood kiln-dried, treated with antiseptic and a hydrophobizing impregnation can be for many decades to be muffled isolated from the external environment that will only increase its durability. In addition obmazochnoy waterproofing the frame can be covered by several layers of thin styrene or vinyl acetate packaging films.
Preparation for finishingAfter installation and protect the insulation comes the turn to build the carrier subsystem for ventilated cladding or plane under the finish wet facade. In the latter case, wind and hydroprotection of a heater can be provided with a layer of plaster finishes and/or paint.
Installation in both cases is on different circuits. To ensure the necessary strength of the sheathing for installation of panel materials, a step of installation of racks of a skeleton in advance choose often enough. After the temporary fastening of waterproof membrane stapled to the edges of the frame, encouraging her remote strips with a thickness of about 25-30 mm. In this case, it provides space for draining trapped inside the water and ventilation. If desired, the adjacent strips can be sealed with fresh oil paint or mastic.
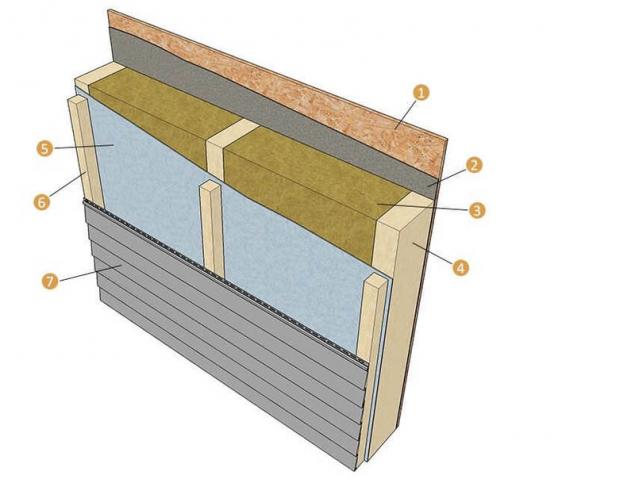
Cake wall-frame house: 1 — the inner lining of OSB; 2 — steam; 3 — insulation; 4 — wooden frame; 5 — super-diffused membrane; 6 — counter lathing; 7 — facade finishing (siding, paneling, block-house)
When the device solid sheathing for stucco use sheet materials which are an excellent vapor barrier. The high concentration of moisture can cause condensation drops, the removal of which provides for the produh between the hydraulic protection and leaves. Leaves, in turn, eliminate the blowing insulation.
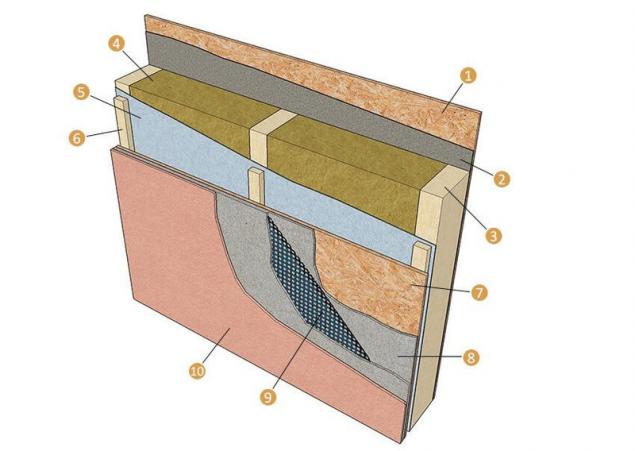
Plaster walls of a frame house: 1 — the inner lining of OSB; 2 — steam; 3 — wooden frame; 4 — insulation; 5 — super-diffused membrane; 6 — counter lathing; 7 — the external skin OSB; 8 — base plaster; 9 — plaster grid; 10 — plaster
In some cases, a system external cladding is fixed on top of the sheet materials. Such a decision may be taken due to the high offset range of the dew point. Possible condensation in the ventilated layer does not promise any particular problems when you use water-resistant sheets. However, in this case the junction to the plinth and the cornice has a more complex device. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.rmnt.ru/story/isolation/1322186.htm

Carrying system frame buildingsfor the Correct device thermal protection frame buildings is defined by each of the stages of construction, starting with the Foundation. Then how well will be fixed to the base support system and how she can have a configuration that will play a crucial role for effective insulation, wind and noise.
Base system device frame walls consist of vertical boards with an aspect ratio of about 3-5:1. The thicker its cross-sectional structure, the better they conduct heat less than this should be step installation. In addition, there may be a need for additional connections. In particular, in the frame practiced the addition of diagonal struts and ties between the individual panels.

The quality of thermal insulation can be estimated by the total area of the wooden elements in longitudinal cut of the wall. It is believed that the wood content in the thermal barrier shall not exceed 18-20% of the total area of the wall. If necessary, you can reduce wood content, developing its own framework that focuses on the shape of the building and the conditions for its operation.

Material for the frame serve only the highest quality lumber very low humidity — no more than 11-12%. When humidity increases by only 3% thermal conductivity of wood is doubled. You should also choose a so-called core Board which is the predominant direction of the fibers across the path of heat transfer — thermal conductivity struts in their correct orientation can be reduced to 2 times depending on the wood.
From materials are also widely used calibrated timber, which, although has an average thermal conductivity due to the oncoming direction of the fibers, but can be used in smaller quantities due to the higher strength and stability. Similarly is the case with solid wood. Although they are denser and better conducting heat, sometimes reducing cold bridges carries a much greater benefit.

In the construction of passive houses frame sometimes do multi-row: internal subsystem complementary rails, which are attached to the strut outer sheathing. In this case, the cross section of the cold bridges is reduced significantly and is approximately equal to the total area between the two rows. This greatly facilitates the calculation of the thickness of the insulation, however, at least 2/3 of its total volume should fall on the outer layer of insulation.
Insulation materialsWith proper design of the frame comes a time when the presence of thermal bridges can be neglected for hedging through increasing a layer of insulation 5-10%. However, how to determine whether the thickness and thermal resistance to reduce heat loss to the required values?

Considered energy-efficient building that loses no more than 100 kWh of thermal energy per square meter of the total area in one year. Sometimes the total heat loss determined by the maximum capacity of the heating equipment. Knowing the height of the enclosing walls and the length of the perimeter, simply calculate the total area of enclosing surfaces, to separate them by types and to calculate what proportion of the walls in heat exchange with outdoor environment. Given that the heating period is not less than 180 days, it is easy to determine which value should be limited to the specific thermal conductivity of the walls to support the original heat balance.

To find the required thickness of insulation, consider its heat-conductivity and the temperature difference, which depends on the internal climate and the level of the thermometer in the coldest five-day week. Also note that the thermal conductivity of the insulation over time may increase or change during the year. If the calculation of heat losses was carried out not on the basis of the maximum power of heating, the temperature difference can be determined by the average temperature around January-February.
Protection of thermal insulationSome insulation materials require protection from moisture, blowing, or perhaps direct sunlight. Some of these tasks might fall on the finish layer, but the primary protection is provided by special membrane materials.
One of the most commonly used in the canadian frame of insulation materials — stone wool — has the ability to dramatically reduce the resistance to heat transfer when wet. Source of water can be precipitation or condensation of water vapor. In the first case used a special synthetic burlap, air-permeable and water vapor, but retains water.

The penetration of steam inside cannot be restricted completely, because the building needed to implement the natural gas exchange with the environment. However, you can limit the amount of water vapor to such values when it will not be enough to raise the relative humidity in the cooled internal air to 85-90%. Typically, such a calculation is carried out for the point of the section of the rows of the frame or carrier system with external insulation. However, the same method can be applied for layer-by-layer calculation of the displacement of the dew point during the year within homogeneous walls.
The hydraulic protection of enclosing structuresof Certain types of materials for insulation has a closed cell structure and is therefore absolutely not absorb water. In this case, the calculated range of displacement of the dew point in whole is placed in a layer of the insulation, because there is moisture to condense may not, simply due to the lack of water vapor.

However, this approach should be particularly cautious. In particular, for single frames require the additional calculation of the displacement of the dew point in the cold bridges, because the main route for leakage of steam will remain gaps between the frame and the insulation.
The formation of moisture on the frame elements might bring harm not only in the long term. A sharp change in wood moisture activates the processes of warping, what with the lack of rigidity of the supporting structure can damage the finish or to open additional paths to the outflow of heat.

To isolate the frame from direct contact with moisture simply. The wood kiln-dried, treated with antiseptic and a hydrophobizing impregnation can be for many decades to be muffled isolated from the external environment that will only increase its durability. In addition obmazochnoy waterproofing the frame can be covered by several layers of thin styrene or vinyl acetate packaging films.
Preparation for finishingAfter installation and protect the insulation comes the turn to build the carrier subsystem for ventilated cladding or plane under the finish wet facade. In the latter case, wind and hydroprotection of a heater can be provided with a layer of plaster finishes and/or paint.
Installation in both cases is on different circuits. To ensure the necessary strength of the sheathing for installation of panel materials, a step of installation of racks of a skeleton in advance choose often enough. After the temporary fastening of waterproof membrane stapled to the edges of the frame, encouraging her remote strips with a thickness of about 25-30 mm. In this case, it provides space for draining trapped inside the water and ventilation. If desired, the adjacent strips can be sealed with fresh oil paint or mastic.

Cake wall-frame house: 1 — the inner lining of OSB; 2 — steam; 3 — insulation; 4 — wooden frame; 5 — super-diffused membrane; 6 — counter lathing; 7 — facade finishing (siding, paneling, block-house)
When the device solid sheathing for stucco use sheet materials which are an excellent vapor barrier. The high concentration of moisture can cause condensation drops, the removal of which provides for the produh between the hydraulic protection and leaves. Leaves, in turn, eliminate the blowing insulation.

Plaster walls of a frame house: 1 — the inner lining of OSB; 2 — steam; 3 — wooden frame; 4 — insulation; 5 — super-diffused membrane; 6 — counter lathing; 7 — the external skin OSB; 8 — base plaster; 9 — plaster grid; 10 — plaster
In some cases, a system external cladding is fixed on top of the sheet materials. Such a decision may be taken due to the high offset range of the dew point. Possible condensation in the ventilated layer does not promise any particular problems when you use water-resistant sheets. However, in this case the junction to the plinth and the cornice has a more complex device. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //www.rmnt.ru/story/isolation/1322186.htm
How to make a flat floor on adjustable lags with their hands
Kinesiology: an algorithm for the treatment of allergies