779
The temperature rhythm of our body: to understand and use
Real health is properly organized mode of life. Without respect and consideration biorhythms nakakoy progress and improved health is impossible. Human nature is complex, and we have not one, but several pacemakers that can be synchronized, and can be no (desenhos).
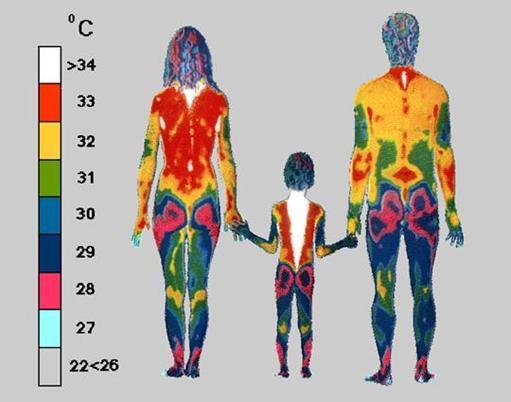
I want to tell about one important driver of rhythm of temperature. It is important to know how the underlying rhythmic organization of physiological functions (sleep, nutrition, physical activity, stress) affects the health, working capacity and resistance to various influences.
Drivers rhythms: light and temperature Adaptation of human organism to changing environmental conditions (changing time of day, seasons, solar activity, etc.) is provided by biological rhythms or “internal clock”. Formed in the course of evolution, circadian rhythms of organisms synchronized with the duration of photoperiod. As one of the fundamental properties of living matter, biological rhythms manifest in the functioning of all body systems (nervous, endocrine, reproductive, cardiovascular, etc.).
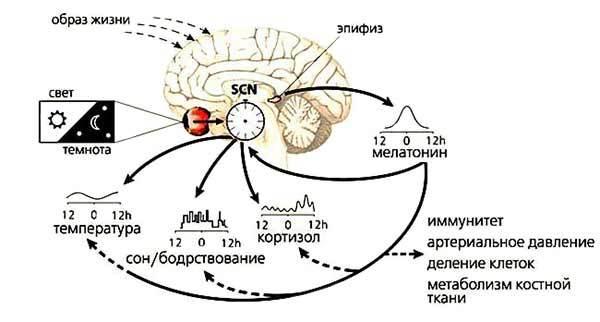
Biorhythms are divided into circadian (diurnal) circannual (year), ultradian (lasting more than a day), infradian (lasting less than a day), etc. Center of the regulation of biorhythms is considered in the hypothalamus. Generator of circadian rhythms is localized in the supra-hezmattash nuclei (SHA) of the anterior hypothalamus. The suprachiasmatic nucleus receives information about light through retinohypothalamic tract. Circadian pacemaker responds to different light — wavelengths, duration and time of exposure.The main external synchronizer of circadian rhythm is the cycle of light—dark, but even in the absence of external light (solar) exposures (a bunker, a submarine, a cave, etc.) circadian rhythms persist, varying in duration, due to internal periodicity.Moreover, melatonin is due to the hypothermic properties has a direct influence on the circadian rhythm of body temperature.
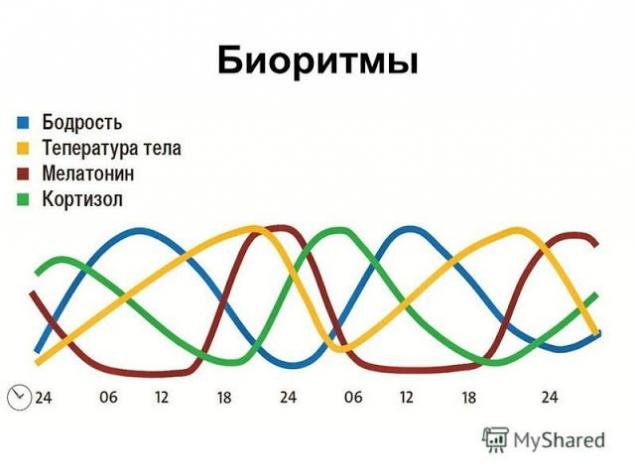
Although the suprachiasmatic nucleus (the driver of which is light) definitely play a crucial role in the regulation of circadian time systems, there is evidence of the existence of other pacemakers in mammals. For example, in monkeys, squirrel monkeys with damaged suprachiasmatic nuclei disappear rhythms of feeding, drinking and activity, but what remains the daily cycle of body temperature. This shows that temperature fluctuations are controlled by some other driver of a rhythm.
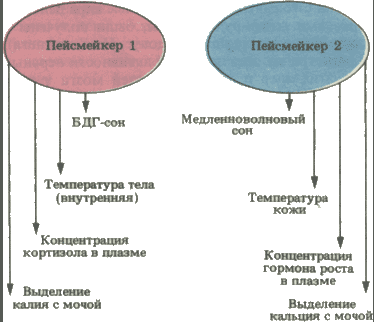
The fact that the subjects showed a spontaneous desynchronization, i.e. a mismatch of circadian rhythm of body temperature cycle and sleep-Wake indicates the existence of at least two drivers. There are specific sets of rhythms that these experiments never desynchronized and therefore should be subject to a common pacemaker. In one such set consists of the rhythms of sleep and wakefulness, body temperature, concentration of HGH in blood and calcium in urine. It is assumed (though not proven) that this group of rhythms is controlled supremeamanda kernel. The second group of indicators, varying in concert even when desynchronization occurs other functions of the body, consists of sleep cycles with REM, internal body temperature, cortisol levels in the blood and potassium in the urine. Pacemaker controlling these rhythms seem to be more stable than the one that affects the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness. In cases when the rhythms became svobodnensky, i.e. in the absence of external premathematical, this band rarely deviated.
Temperature mode is configured when the flights are much later than the light. Even if a person is completely cut off from any external signals such as daylight hours, weather changes, meal time and other, it will still be daily fluctuations in temperature. However, in this situation, the variations are rhythmic, but their cycle is not exactly 24 hours. Rhythmic fluctuations of body temperature in conditions of isolation from external factors usually occur within 24 – 25 hours, and this period of time is called the circadian periodicity. That is, all the daily fluctuations in temperature is entirely based on endogenous biological rhythms that are synchronized with the period of rotation of Earth around its axis. If a person moves through space, crossing time zones meridians, after arrival at permanent residence for 1 – 2 weeks daily fluctuations in body temperature will sync with the new local time (!).
Body temperature
Body temperature is a complex indicator of the thermal state of the body of animals, including humans. Is one of the main and oldest of the biomarkers. Our body temperature is easily measurable and is a very useful indicator. The problem now is that the variation is minimized, resulting in numerous failures. We day and night in all seasons of the year are in the same zone of temperature comfort and is not very good. Very often the temperature rhythm starts to interfere with the light and this leads to desynchronization, which is the cause of many problems.
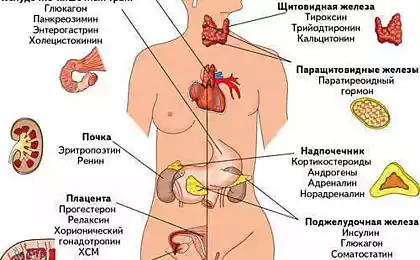
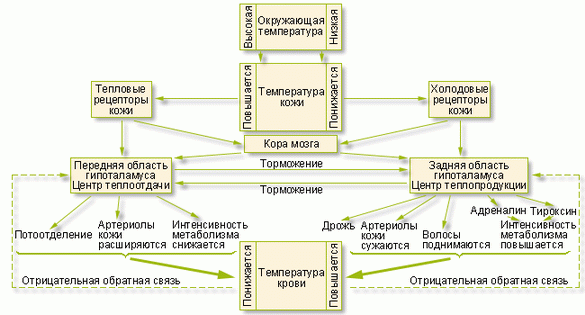
So, let's see, how does the temperature cycle.Chief, as always, is the hypothalamus. In the implementation of the hypothalamic regulation of body temperature involves the endocrine glands, mainly the thyroid and adrenal glands. The thyroid gland and its hormones increase thermogenesis and increase metabolism by raising the temperature. The adrenal glands produce adrenaline, which also increases the oxidative processes in tissues, particularly in muscles, increases heat generation, and narrows the skin blood vessels, reducing heat transfer.
The nerve cells of the hypothalamus are receptors that directly respond to body temperature by increasing or decreasing the secretion of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which in turn regulates the activity of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are responsible for the intensity of metabolism. To a lesser extent in temperature regulation involves the hormone estradiol (plays a major role in thermoregulation of bodies in women during the menstrual cycle), increase its level leads to a decrease in basal temperature.
Circadian rhythms are prominent among the biological rhythms of the person. Modern authors call them the totality and coherence — temporal organization, stressing that it play a special role, as when you sync vnutripolostnyh processes and the interaction of the organism with the environment. Among the parameters of the rhythm occupies a special place mesor and amplitude. Mesor (average daily level) reflects the center line, around which there are oscillations of physiological functions throughout the day. Amplitude (amplitude of oscillations) is the most plastic figure functional morphology and one of the first changes under the influence of various factors. The amplitude can serve as an indicator of the adaptation process.
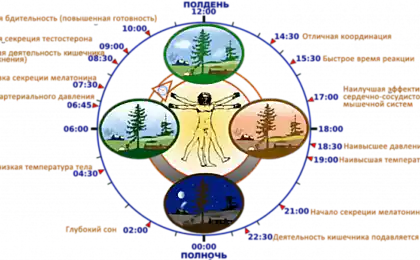
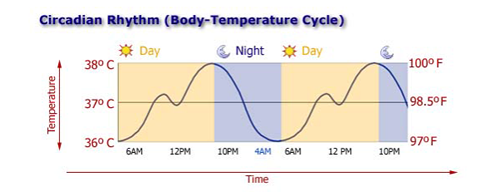
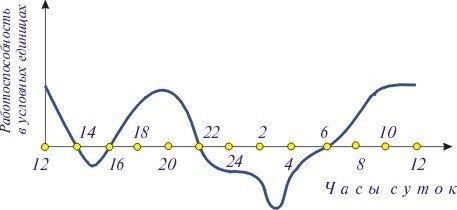
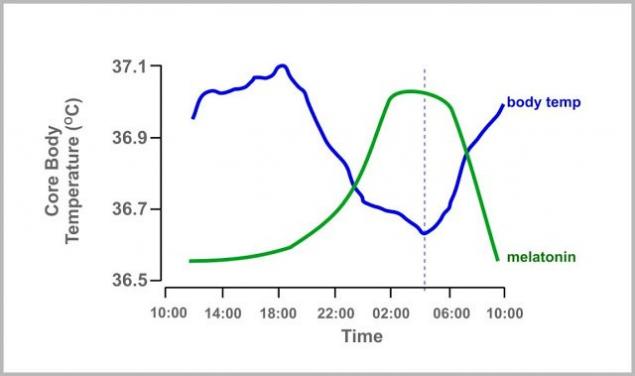
"Thermostat" (hypothalamus) is located in the brain and is constantly engaged in thermoregulation. During the day the body temperature in humans varies, reflecting the circadian rhythms. The body temperature of each person in the course of the day fluctuates in a small range, remaining in the range of 35.5 to 37.0°C for a healthy person. Following the circadian rhythms, the lowest body temperature observed in the morning, about 6 hours, and the maximum value is reached in the evening. Like many other biorhythms, the temperature follows a daily cycle of the Sun, and not the level of our activity. People working by night and sleeping by day, demonstrate the same cycle of temperature change, the rest.
Temperature cycle
1. Morning and awakening.
Experiments American psychologists, conducted under the guidance of Professor Zeisler, showed that sleep and waking are closely linked to body temperature. In the morning the body temperature rises. Scientists have found that hunter-gatherer mode of sleep and wakefulness correlated not only with the order of the day and night (which is trivial and needs no proof), but also the ambient temperature. The latter conclusion is less obvious, but is confirmed by measurements. Awakening and San, and Zimanov occurs when the ambient temperature is minimal. The awakening shows a sharp decrease in the temperature of the fingers, reflecting a narrowing of the peripheral vessels, which is accompanied by increased blood flow to the brain, and thus indicates the transition from sleep to wakefulness. At San minimum temperature of the environment is an hour after dawn, and Zimanov — an hour before dawn. Time to fall asleep and those and others comes at a time of sharp decline of the ambient temperature, and not the onset of darkness. This explains the slightly different mode of the day in these largely similar traditional societies. Probably shift sleep at the coldest time of day helps to save energy costs, because more affordable, in the traditional setting.
Charging and moderate physical activity in the morning contribute to a rise in body temperature and higher activity. I am also a supporter of healthy protein Breakfast because protein has the highest thermogenic effect compared to other nutrients. Thus, waking up the man is always on the rise of the temperature curve. Therefore, the duration of sleep depends on which phase of the temperature cycle has the moment of falling asleep: the next rise in body temperature will Wake you up even if you haven't slept for several days.
2. Day and activity
As for our activity, mental and physical activity increases with body temperature. Physical activity helps to maintain mental alertness throughout the day. Thus, the athletes know that the "warming-up" improves performance, and optimal levels of hyperthermia (T core body = 38.7 and 39.2 C°), provide maximum efficiency in the exercises for strength, speed, flexibility and agility. And while performing intermittent exercise rise in body temperature to the level of 38.7-39,2°C is "normal" and even desirable for efficiency of muscular work. If a person experiences intense physical activity, the optimum temperature is raised (for strength training). Body temperature reaches a maximum in the evening, night falls quickly and rises on awakening.
Studies also show that changes in usual body temperature caused by heat or cold, can have a significant impact not only on mood but also on cognitive function. Cognition is the process that controls how we react to the environment and the ability to store memories and to perform mental tasks such as arithmetic. And this ability is diminished if the body temperature deviates from the norm. Extreme temperature or prolonged exposure to uncomfortable weather can change the temperature of the body, disrupt homeostatic control (the body's ability to maintain its temperature). Studies have also shown that when the ambient temperature drops, the body temperature falls, and this has a negative impact on cognitive abilities. Scientists from the University of Kent (USA) placed subjects in a water temperature of 13 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes. After that, most of the body temperature fell to a level of 35-36 degrees Celsius, slightly below the normal range of 36.5-37.2 degrees Celsius. The participants rested for 15 minutes, and then the researchers asked them to perform the Stroop Test (in the frame is written the name of the color, but the form of response should specify the font color that the written word). Despite the seeming simplicity, the test requires some cognitive tension. Participants were asked to name the font color as quickly as possible. It turned out that test was much more difficult for the participants, placed in cold water. This study shows that low body temperature has a significant influence on attention to detail, which is considered a marker of cognition.
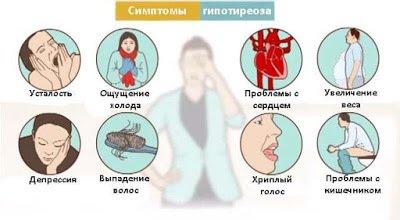
Reduced the body temperature of a day is a common symptom of hypothyroidism. The regular decrease of temperature is one of the first signs of disturbance in the thyroid gland. Subclinical hypothyroidism is often accompanied by chronic fatigue, decreased temperature, weight gain, weakness. Normal axillary body temperature is determined in the morning immediately after waking up for diagnosis of hypothyroidism, is in the range 97,4 ─ 98.2 degrees Fahrenheit (36,3 ─ 36,8 C). Women should determine the body temperature during the first 5 days of the cycle and then averaging the values. The temperature is below 36.3 From points to the lack of thyroid function (hypothyroidism). If the calculated average temperature by the above procedure and it will be less than 36.5 C then you have a very high probability of hypothyroidism. The question is, is this a violation of primary failure of thyroid gland or it refers to "problems" in the pituitary or adrenal insufficiency.
3. The evening and falling asleep
18-19 hours there is a maximum body temperature, after which it begins to decline. Well, if the bedtime coincides with a lowered body temperature. Individual lag time speedy fall of temperature (extreme inflection point on the curve) corresponds to the optimal time for falling asleep. So you can easily sleep and faster to sleep. So improve sleep all of the procedures associated with the cooling of the body. Also important light, yellow low light helps produce melatonin, which causes drowsiness and controls body temperature.
We have said that during the day the body temperature is cyclical, and fluctuations with an amplitude of about 1 °C. People tend to fall asleep when you lower your body temperature and Wake up when it is lifting. 19:00 the highest blood pressure and highest temperature of the body. Internal signal for bedtime is the decrease of the body temperature.
Our body through the hands, face and feet, the body generates heat when it is time for sleep. Cooling continues until about four in the morning. However, if something prevents the decrease in body temperature, sleep quality deteriorates immediately. People can't sleep, suffer from insomnia. In this regard, the scientist advises to choose wisely linens, giving preference to natural fabrics. A mattress made from foam or other synthetic materials, needs a mattress pad made from natural wool. And those who are experiencing trouble falling asleep, and completely unable to keep during the day the pillow in the refrigerator. Before bedtime you can also hold hands under cold water for several minutes. Then immediately go to bed.
However, many people get a good night sleep after a warm bath, and doctors this effect is well known. Perhaps the fact that heating causes vasodilatation of hands and feet, with a strong exchangers. When a person leaves the bath, dilated vessels of the extremities vigorously give off heat and cooling the body.
There is another explanation. Kangaroo rats have a local heating region of hypothalamus increases the duration of slow sleep phase. Perhaps the fact that overheated the hypothalamus includes an additional cooling system of the brain. If this mechanism is true for humans and the blood flowing through the vertebral artery from the heated body to the brain mainly enters the region of the hypothalamus, with him is the same as the opossum: the hypothalamus includes the cooling system that causes sleep, or rather, its non-REM phase.
A curious description of the mechanism of yawning from the point of view of cooling the brain. So, relatively recently as a system of rapid cooling of the brain by scientists was considered an act of yawning, which also helped to explain the relationship of yawning falling asleep and hypoxia. The dependence of the frequency of yawning from the ambient temperature seen for a long time. In addition, the influence of yawning on the heat-dependent epilepsy, migraine and multiple sclerosis pointed to the important role of this act in thermoregulation of the brain. The alleged connection of yawning is cooling the brain has been proven in 2010 when the researchers introduced into the rat brain temperature sensors and found that the increase in brain temperature by only 0.1°C instantly provoked in rodents bouts of yawning, followed by observed decrease in brain temperature by 0.5°C. However, these observations could not justify it anatomically — like yawning removes excess heat from the brain? The act of yawning begins with the opening of the mouth and expansion of the nasopharynx that leads to its filling with cold air through the mouth.Try to yawn. Felt a chill and a strong tension in the center of the head?
It turned out that at the peak of the yawn, the lower jaw pulls the pterygoid muscles, and those, in turn, retard the sphenoid bone, carrying with it the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. The volume of the sinuses in an adult is up to 34 CC, and the tension of the rear walls during yawning increases their size by a third. Any negative pressure in the sinuses "suck" cold air from the nasopharynx. This air causes evaporation of moisture on the walls of the sinus, thereby cooling the capillaries of the mucous membrane. Chilled so the blood is then collected into the veins of the pterygoid plexus. With the completion of yawning, jaw clenching, and chewing muscles compress the pterygoid plexus (step 4) causing the outflow of the cooled blood in the sinuses of the Dura mater. This blood in turn cools the cerebrospinal fluid, which flows also increase during the yawn — in this act, it acts as a coolant of the Central nervous system. Thus cooling of the brain happens immediately after the act of yawning.
4. Night and recovery
Most people sleep better in a cool room. During sleep the body cools at 4.00-5.00 — the lowest temperature of the body. The ideal temperature in the bedroom — 18-21 °C. in people with severe cases of insomnia circadian rhythm of body temperature; it varies slightly and no specific patterns. Or rhythm exists, but the period is far from 24 hours. With such a rhythm can sleep through the night only on days when the temperature decrease falls on evening hours.
The body temperature (and brain) is subject to a circadian rhythm, and when she falls, I want to sleep. In addition, night temperature reduced nighttime-burning, autophagy, and production of growth hormone. Cooling of the brain is not simply due to falling asleep, but stimulates it. Probably, it is known to many household way of dealing with insomnia: it is necessary to properly freeze. The group of American scientists from the Pennsylvania University of Pittsburgh (University of Pittsburgh) have managed to develop a methodology that allows quite effective to get rid of insomnia. Special caps, cooling of the frontal departments of a bark brain of the patient, can significantly improve the quality and productivity of a night's rest. The study, which is in question here, the American experts under the guidance of Dr. Eric Nofzinger (Eric Nofzinger) studied the effect of low temperature on the activity of areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as on the metabolic processes in patients suffering from insomnia. Meanwhile, the scientists relied on data obtained in previous studies, according to which the activity of metabolic processes in the frontal divisions of the cortex of the brain of a healthy person is reduced during sleep. At the same time, it has been proven that patients suffering from insomnia in night-time leisure activity for a specified part of the brain remains elevated.
Adequate sleep is very important to the alternation of slow and fast sleep, paired with alternating low and high temperatures.
Numerous experiments indicate that changes in brain temperature is not accidental. In rats it always increases in response to external stimuli: pain, social contact with other individuals, sexual arousal. Moreover, the temperature of each part of the brain in response to different stimuli is increased to a certain value, as if committed to him.
For example, the nucleus accumbens of the rat brain, this temperature is 38.5°C. And in a phase of slow sleep is cooling on the order of several tenths of a degree to several degrees in different parts of the brain in different animals. Obviously, the brain temperature changes is not passive, but adjusts the activity of the nervous tissue. No wonder about the man, sober-minded, saying that he had a cool head. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! © econet
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2017/03/temperaturnyj-ritm-nashego-organizma-ponyat-i-ispolzovat.html

I want to tell about one important driver of rhythm of temperature. It is important to know how the underlying rhythmic organization of physiological functions (sleep, nutrition, physical activity, stress) affects the health, working capacity and resistance to various influences.
Drivers rhythms: light and temperature Adaptation of human organism to changing environmental conditions (changing time of day, seasons, solar activity, etc.) is provided by biological rhythms or “internal clock”. Formed in the course of evolution, circadian rhythms of organisms synchronized with the duration of photoperiod. As one of the fundamental properties of living matter, biological rhythms manifest in the functioning of all body systems (nervous, endocrine, reproductive, cardiovascular, etc.).

Biorhythms are divided into circadian (diurnal) circannual (year), ultradian (lasting more than a day), infradian (lasting less than a day), etc. Center of the regulation of biorhythms is considered in the hypothalamus. Generator of circadian rhythms is localized in the supra-hezmattash nuclei (SHA) of the anterior hypothalamus. The suprachiasmatic nucleus receives information about light through retinohypothalamic tract. Circadian pacemaker responds to different light — wavelengths, duration and time of exposure.The main external synchronizer of circadian rhythm is the cycle of light—dark, but even in the absence of external light (solar) exposures (a bunker, a submarine, a cave, etc.) circadian rhythms persist, varying in duration, due to internal periodicity.Moreover, melatonin is due to the hypothermic properties has a direct influence on the circadian rhythm of body temperature.


Although the suprachiasmatic nucleus (the driver of which is light) definitely play a crucial role in the regulation of circadian time systems, there is evidence of the existence of other pacemakers in mammals. For example, in monkeys, squirrel monkeys with damaged suprachiasmatic nuclei disappear rhythms of feeding, drinking and activity, but what remains the daily cycle of body temperature. This shows that temperature fluctuations are controlled by some other driver of a rhythm.
The fact that the subjects showed a spontaneous desynchronization, i.e. a mismatch of circadian rhythm of body temperature cycle and sleep-Wake indicates the existence of at least two drivers. There are specific sets of rhythms that these experiments never desynchronized and therefore should be subject to a common pacemaker. In one such set consists of the rhythms of sleep and wakefulness, body temperature, concentration of HGH in blood and calcium in urine. It is assumed (though not proven) that this group of rhythms is controlled supremeamanda kernel. The second group of indicators, varying in concert even when desynchronization occurs other functions of the body, consists of sleep cycles with REM, internal body temperature, cortisol levels in the blood and potassium in the urine. Pacemaker controlling these rhythms seem to be more stable than the one that affects the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness. In cases when the rhythms became svobodnensky, i.e. in the absence of external premathematical, this band rarely deviated.

Temperature mode is configured when the flights are much later than the light. Even if a person is completely cut off from any external signals such as daylight hours, weather changes, meal time and other, it will still be daily fluctuations in temperature. However, in this situation, the variations are rhythmic, but their cycle is not exactly 24 hours. Rhythmic fluctuations of body temperature in conditions of isolation from external factors usually occur within 24 – 25 hours, and this period of time is called the circadian periodicity. That is, all the daily fluctuations in temperature is entirely based on endogenous biological rhythms that are synchronized with the period of rotation of Earth around its axis. If a person moves through space, crossing time zones meridians, after arrival at permanent residence for 1 – 2 weeks daily fluctuations in body temperature will sync with the new local time (!).

Body temperature
Body temperature is a complex indicator of the thermal state of the body of animals, including humans. Is one of the main and oldest of the biomarkers. Our body temperature is easily measurable and is a very useful indicator. The problem now is that the variation is minimized, resulting in numerous failures. We day and night in all seasons of the year are in the same zone of temperature comfort and is not very good. Very often the temperature rhythm starts to interfere with the light and this leads to desynchronization, which is the cause of many problems.
So, let's see, how does the temperature cycle.Chief, as always, is the hypothalamus. In the implementation of the hypothalamic regulation of body temperature involves the endocrine glands, mainly the thyroid and adrenal glands. The thyroid gland and its hormones increase thermogenesis and increase metabolism by raising the temperature. The adrenal glands produce adrenaline, which also increases the oxidative processes in tissues, particularly in muscles, increases heat generation, and narrows the skin blood vessels, reducing heat transfer.
The nerve cells of the hypothalamus are receptors that directly respond to body temperature by increasing or decreasing the secretion of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) which in turn regulates the activity of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are responsible for the intensity of metabolism. To a lesser extent in temperature regulation involves the hormone estradiol (plays a major role in thermoregulation of bodies in women during the menstrual cycle), increase its level leads to a decrease in basal temperature.
Circadian rhythms are prominent among the biological rhythms of the person. Modern authors call them the totality and coherence — temporal organization, stressing that it play a special role, as when you sync vnutripolostnyh processes and the interaction of the organism with the environment. Among the parameters of the rhythm occupies a special place mesor and amplitude. Mesor (average daily level) reflects the center line, around which there are oscillations of physiological functions throughout the day. Amplitude (amplitude of oscillations) is the most plastic figure functional morphology and one of the first changes under the influence of various factors. The amplitude can serve as an indicator of the adaptation process.
"Thermostat" (hypothalamus) is located in the brain and is constantly engaged in thermoregulation. During the day the body temperature in humans varies, reflecting the circadian rhythms. The body temperature of each person in the course of the day fluctuates in a small range, remaining in the range of 35.5 to 37.0°C for a healthy person. Following the circadian rhythms, the lowest body temperature observed in the morning, about 6 hours, and the maximum value is reached in the evening. Like many other biorhythms, the temperature follows a daily cycle of the Sun, and not the level of our activity. People working by night and sleeping by day, demonstrate the same cycle of temperature change, the rest.
Temperature cycle
1. Morning and awakening.
Experiments American psychologists, conducted under the guidance of Professor Zeisler, showed that sleep and waking are closely linked to body temperature. In the morning the body temperature rises. Scientists have found that hunter-gatherer mode of sleep and wakefulness correlated not only with the order of the day and night (which is trivial and needs no proof), but also the ambient temperature. The latter conclusion is less obvious, but is confirmed by measurements. Awakening and San, and Zimanov occurs when the ambient temperature is minimal. The awakening shows a sharp decrease in the temperature of the fingers, reflecting a narrowing of the peripheral vessels, which is accompanied by increased blood flow to the brain, and thus indicates the transition from sleep to wakefulness. At San minimum temperature of the environment is an hour after dawn, and Zimanov — an hour before dawn. Time to fall asleep and those and others comes at a time of sharp decline of the ambient temperature, and not the onset of darkness. This explains the slightly different mode of the day in these largely similar traditional societies. Probably shift sleep at the coldest time of day helps to save energy costs, because more affordable, in the traditional setting.
Charging and moderate physical activity in the morning contribute to a rise in body temperature and higher activity. I am also a supporter of healthy protein Breakfast because protein has the highest thermogenic effect compared to other nutrients. Thus, waking up the man is always on the rise of the temperature curve. Therefore, the duration of sleep depends on which phase of the temperature cycle has the moment of falling asleep: the next rise in body temperature will Wake you up even if you haven't slept for several days.
2. Day and activity
As for our activity, mental and physical activity increases with body temperature. Physical activity helps to maintain mental alertness throughout the day. Thus, the athletes know that the "warming-up" improves performance, and optimal levels of hyperthermia (T core body = 38.7 and 39.2 C°), provide maximum efficiency in the exercises for strength, speed, flexibility and agility. And while performing intermittent exercise rise in body temperature to the level of 38.7-39,2°C is "normal" and even desirable for efficiency of muscular work. If a person experiences intense physical activity, the optimum temperature is raised (for strength training). Body temperature reaches a maximum in the evening, night falls quickly and rises on awakening.

Studies also show that changes in usual body temperature caused by heat or cold, can have a significant impact not only on mood but also on cognitive function. Cognition is the process that controls how we react to the environment and the ability to store memories and to perform mental tasks such as arithmetic. And this ability is diminished if the body temperature deviates from the norm. Extreme temperature or prolonged exposure to uncomfortable weather can change the temperature of the body, disrupt homeostatic control (the body's ability to maintain its temperature). Studies have also shown that when the ambient temperature drops, the body temperature falls, and this has a negative impact on cognitive abilities. Scientists from the University of Kent (USA) placed subjects in a water temperature of 13 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes. After that, most of the body temperature fell to a level of 35-36 degrees Celsius, slightly below the normal range of 36.5-37.2 degrees Celsius. The participants rested for 15 minutes, and then the researchers asked them to perform the Stroop Test (in the frame is written the name of the color, but the form of response should specify the font color that the written word). Despite the seeming simplicity, the test requires some cognitive tension. Participants were asked to name the font color as quickly as possible. It turned out that test was much more difficult for the participants, placed in cold water. This study shows that low body temperature has a significant influence on attention to detail, which is considered a marker of cognition.
Reduced the body temperature of a day is a common symptom of hypothyroidism. The regular decrease of temperature is one of the first signs of disturbance in the thyroid gland. Subclinical hypothyroidism is often accompanied by chronic fatigue, decreased temperature, weight gain, weakness. Normal axillary body temperature is determined in the morning immediately after waking up for diagnosis of hypothyroidism, is in the range 97,4 ─ 98.2 degrees Fahrenheit (36,3 ─ 36,8 C). Women should determine the body temperature during the first 5 days of the cycle and then averaging the values. The temperature is below 36.3 From points to the lack of thyroid function (hypothyroidism). If the calculated average temperature by the above procedure and it will be less than 36.5 C then you have a very high probability of hypothyroidism. The question is, is this a violation of primary failure of thyroid gland or it refers to "problems" in the pituitary or adrenal insufficiency.

3. The evening and falling asleep
18-19 hours there is a maximum body temperature, after which it begins to decline. Well, if the bedtime coincides with a lowered body temperature. Individual lag time speedy fall of temperature (extreme inflection point on the curve) corresponds to the optimal time for falling asleep. So you can easily sleep and faster to sleep. So improve sleep all of the procedures associated with the cooling of the body. Also important light, yellow low light helps produce melatonin, which causes drowsiness and controls body temperature.
We have said that during the day the body temperature is cyclical, and fluctuations with an amplitude of about 1 °C. People tend to fall asleep when you lower your body temperature and Wake up when it is lifting. 19:00 the highest blood pressure and highest temperature of the body. Internal signal for bedtime is the decrease of the body temperature.
Our body through the hands, face and feet, the body generates heat when it is time for sleep. Cooling continues until about four in the morning. However, if something prevents the decrease in body temperature, sleep quality deteriorates immediately. People can't sleep, suffer from insomnia. In this regard, the scientist advises to choose wisely linens, giving preference to natural fabrics. A mattress made from foam or other synthetic materials, needs a mattress pad made from natural wool. And those who are experiencing trouble falling asleep, and completely unable to keep during the day the pillow in the refrigerator. Before bedtime you can also hold hands under cold water for several minutes. Then immediately go to bed.
However, many people get a good night sleep after a warm bath, and doctors this effect is well known. Perhaps the fact that heating causes vasodilatation of hands and feet, with a strong exchangers. When a person leaves the bath, dilated vessels of the extremities vigorously give off heat and cooling the body.
There is another explanation. Kangaroo rats have a local heating region of hypothalamus increases the duration of slow sleep phase. Perhaps the fact that overheated the hypothalamus includes an additional cooling system of the brain. If this mechanism is true for humans and the blood flowing through the vertebral artery from the heated body to the brain mainly enters the region of the hypothalamus, with him is the same as the opossum: the hypothalamus includes the cooling system that causes sleep, or rather, its non-REM phase.
A curious description of the mechanism of yawning from the point of view of cooling the brain. So, relatively recently as a system of rapid cooling of the brain by scientists was considered an act of yawning, which also helped to explain the relationship of yawning falling asleep and hypoxia. The dependence of the frequency of yawning from the ambient temperature seen for a long time. In addition, the influence of yawning on the heat-dependent epilepsy, migraine and multiple sclerosis pointed to the important role of this act in thermoregulation of the brain. The alleged connection of yawning is cooling the brain has been proven in 2010 when the researchers introduced into the rat brain temperature sensors and found that the increase in brain temperature by only 0.1°C instantly provoked in rodents bouts of yawning, followed by observed decrease in brain temperature by 0.5°C. However, these observations could not justify it anatomically — like yawning removes excess heat from the brain? The act of yawning begins with the opening of the mouth and expansion of the nasopharynx that leads to its filling with cold air through the mouth.Try to yawn. Felt a chill and a strong tension in the center of the head?
It turned out that at the peak of the yawn, the lower jaw pulls the pterygoid muscles, and those, in turn, retard the sphenoid bone, carrying with it the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. The volume of the sinuses in an adult is up to 34 CC, and the tension of the rear walls during yawning increases their size by a third. Any negative pressure in the sinuses "suck" cold air from the nasopharynx. This air causes evaporation of moisture on the walls of the sinus, thereby cooling the capillaries of the mucous membrane. Chilled so the blood is then collected into the veins of the pterygoid plexus. With the completion of yawning, jaw clenching, and chewing muscles compress the pterygoid plexus (step 4) causing the outflow of the cooled blood in the sinuses of the Dura mater. This blood in turn cools the cerebrospinal fluid, which flows also increase during the yawn — in this act, it acts as a coolant of the Central nervous system. Thus cooling of the brain happens immediately after the act of yawning.
4. Night and recovery
Most people sleep better in a cool room. During sleep the body cools at 4.00-5.00 — the lowest temperature of the body. The ideal temperature in the bedroom — 18-21 °C. in people with severe cases of insomnia circadian rhythm of body temperature; it varies slightly and no specific patterns. Or rhythm exists, but the period is far from 24 hours. With such a rhythm can sleep through the night only on days when the temperature decrease falls on evening hours.
The body temperature (and brain) is subject to a circadian rhythm, and when she falls, I want to sleep. In addition, night temperature reduced nighttime-burning, autophagy, and production of growth hormone. Cooling of the brain is not simply due to falling asleep, but stimulates it. Probably, it is known to many household way of dealing with insomnia: it is necessary to properly freeze. The group of American scientists from the Pennsylvania University of Pittsburgh (University of Pittsburgh) have managed to develop a methodology that allows quite effective to get rid of insomnia. Special caps, cooling of the frontal departments of a bark brain of the patient, can significantly improve the quality and productivity of a night's rest. The study, which is in question here, the American experts under the guidance of Dr. Eric Nofzinger (Eric Nofzinger) studied the effect of low temperature on the activity of areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as on the metabolic processes in patients suffering from insomnia. Meanwhile, the scientists relied on data obtained in previous studies, according to which the activity of metabolic processes in the frontal divisions of the cortex of the brain of a healthy person is reduced during sleep. At the same time, it has been proven that patients suffering from insomnia in night-time leisure activity for a specified part of the brain remains elevated.

Adequate sleep is very important to the alternation of slow and fast sleep, paired with alternating low and high temperatures.
Numerous experiments indicate that changes in brain temperature is not accidental. In rats it always increases in response to external stimuli: pain, social contact with other individuals, sexual arousal. Moreover, the temperature of each part of the brain in response to different stimuli is increased to a certain value, as if committed to him.
For example, the nucleus accumbens of the rat brain, this temperature is 38.5°C. And in a phase of slow sleep is cooling on the order of several tenths of a degree to several degrees in different parts of the brain in different animals. Obviously, the brain temperature changes is not passive, but adjusts the activity of the nervous tissue. No wonder about the man, sober-minded, saying that he had a cool head. published
Author: Andrey Blueskin
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! © econet
Source: www.beloveshkin.com/2017/03/temperaturnyj-ritm-nashego-organizma-ponyat-i-ispolzovat.html