776
Biological RHYTHMS: circadian rhythms of BODIES
All living beings on Earth — from plants to higher mammals, are subject to circadian rhythms. In humans, depending on the time of day cyclically change the physiological state, intellectual capacity and even mood. Scientists have proved that the cause of the fluctuations in concentrations of hormones in the blood.
In recent years, the science of biorhythms, chronobiology has been done to establish the mechanism of diurnal hormonal cycles. Scientists have discovered the brain's "circadian center," and the so-called "clock genes" biological rhythms health.

CHRONOBIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF THE DAILY RHYTHMS OF THE BODY
In 1632, the English scientist John Wren in his "Treatise on herbs" ("Herbal Treatise") was the first to describe the daily cycles of tissue fluids in the human body, which he, following the terminology of Aristotle, called "gomory" (lat. humor — liquid). Each of the "tides" of the tissue fluid, according to Wren, lasted six hours.
Humoral cycle began at nine o'clock in the evening and highlighting the first gomory bile — "сhole" (gr. cholе — bile) and lasted until three in the morning. Then came the phase of black bile — "melancholy" (gr. melas — black, chole — bile), followed by phlegm — "phlegma" (gr. phlegma — mucus, sputum), and finally, the fourth humora — blood.
Of course, correlate with Gomori now known bodily fluids and tissue secrets impossible. Modern medical science has no connection with the mystical physiology humorama does not recognize. And yet Venom described patterns of change of mood, intellectual ability and physical condition have a very scientific basis.
The science that studies circadian rhythms of the body, called chronobiologia (gr. chronos — time). Its basic idea formulated Wali distinguished German and American scientists of Professor jürgen Ashoff and Colin Pittendrigh, who in the early 80-ies of the last century was even nominated for the Nobel prize. But the highest scientific award they, unfortunately, never received.
The main concept of chronobiology — day cycles, the duration of which is periodic about (lat. circa) day (lat. dies). Therefore, successive daily cycles are called circadian rhythms. These rhythms are directly connected with cyclic changes in illumination, that is, with the rotation of the Earth around its axis. They are all living beings on Earth: plants, microorganisms, invertebrates and vertebrates, up to higher mammals and man.
Each of us known circadian cycle "sleep — wakefulness". In 1959, Ashoff found a pattern that of Pittendrigh proposed to call the "rule Asifa". Under this name it entered chronobiology and the history of science.
The rule reads as follows: "At night the animals active period (Wake) of a more continuous with constant lighting, the daytime animals Wake longer under constant darkness." Indeed, as later established, Ashoff, long-term isolation of man or animals in the dark cycle "sleep — wakefulness" is lengthened by increasing the duration of the phase of wakefulness. The rule Asifa implies that light determines circadian oscillation of the body.
HORMONES AND BIORHYTHMS
During the circadian day (awake) our physiology is mainly configured for processing the accumulated nutrients to get energy for an active daily life. On the contrary, during the circadian night the nutrients accumulate, there are restoration and fix tissues. As it turned out, these changes in the intensity of metabolism are regulated by the endocrine system, i.e. hormones. In endocrine control mechanism of the circadian cycles have a lot in common with humoral theory Wren.
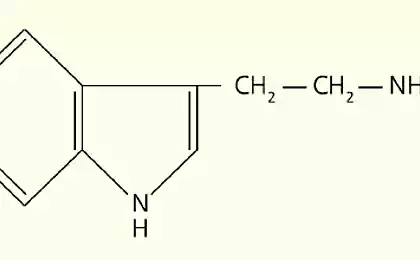
In the evening, before nightfall, the blood of the so-called upper appendage of the brain — the pineal gland is the "night hormone" — melatonin. This amazing substance is produced by the pineal gland only in the dark, and the time of its presence in the blood is directly proportional to the duration of the light of the night. In some cases, insomnia in the elderly is associated with insufficiency of secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland. Preparations of melatonin are often used as hypnotics.
Melatonin reduces body temperature, in addition, it regulates the duration and change of sleep phases. The fact that human sleep is an alternation of slow-wave and paradoxical phases.
Non-REM sleep is characterized by low frequency activity of the cortex of hemispheres. This is the "dream legs", a time when the brain is fully rest. During paradoxical sleep the oscillation frequency of the electrical activity of the brain increases, and we see dreams. This phase is close to wakefulness and serves as "a springboard" in awakening. Slow-wave and paradoxical phases succeed one another 4-5 times during the night, in time with the changes in melatonin concentration.
The onset of light nights accompanied by other hormonal changes: increased growth hormone and decreased production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) others brain called the pituitary gland. HGH stimulates anabolic processes such as cell proliferation and accumulation of nutrients (glycogen) in the liver.
No wonder they say: "Children grow in their sleep." ACTH causes the release into blood of epinephrine and other "stress hormones" (glucocorticoids) from the adrenal cortex, so reducing its level allows to remove the fluorescent excitation and peacefully to sleep. In the moment of falling asleep from the pituitary gland highlighted opioid hormones, having narcotic effect, the endorphins and enkephalins. That is why the process of falling asleep is accompanied by pleasant sensations.
Before the awakening of a healthy body should be ready for active wakefulness, at this time, the adrenal cortex begins to produce stimulating the nervous system and hormones — glucocorticoids.
Most active of them is cortisol, which leads to increased pressure, increased heart rate, increased vascular tone and reduce blood clotting. That's why clinical statistics show that acute heart attacks and intracerebral hemorrhagic strokes are heavily concentrated in the early morning. Now we are developing drugs that reduce blood pressure, which can reach a peak concentration in the blood only in the morning, preventing deadly attacks.
Why do some people stand up "no light, no dawn", and the other off to sleep until noon? It turns out that the well-known phenomenon of "owls and larks" is quite a scientific explanation which is based on the works of Jami, Seizer of the Research center for sleep (Sleep Research Center) at Stanford University in California.
It found that the minimum concentration of cortisol in the blood usually is in the middle of a night's sleep, and its peak is reached before the awakening. "The lark" the maximum release of cortisol occurs earlier than most people — at 4-5 o'clock in the morning. Therefore, the "larks" are more active in the morning hours, but quickly get tired in the evening. They are usually early starts tend to sleep, because the sleep hormone melatonin into the bloodstream long before midnight.
In "owls" the situation is reversed: melatonin is secreted later, closer to midnight, and the peak of cortisol release has been shifted to the 7-8 o'clock in the morning. The specified time frame is individual and can vary depending on the severity of the morning ("larks") and evening ("owls") chronotypes.

"CIRCADIAN CENTER" IS IN THE BRAIN
What is this body which controls the circadian fluctuations of hormones concentration in the blood? On this question, scientists for a long time could not find the answer. But none of them had any doubt that "circadian center" should be located in the brain.
Its existence was predicted and the founders of chronobiology, Pittendrigh and Asoff. The attention of physiologists has attracted has long been known to anatomists structure of the brain — the suprachiasmatic nucleus, situated above the (lat. super) a chiasm (from the Greek. chiasmos) of the optic nerves. It has a cigar-shaped and consists, for example, in rodents of only 10,000 neurons, very little. Another, closely located, -, paraventrikulyarnoe, contains hundreds of thousands of neurons. The length of the suprachiasmatic nucleus is also small — no more than half of a millimeter, and the volume is 0,3 mm3 .
In 1972 two groups of American researchers managed to show that the suprachiasmatic nucleus is the control center of the biological clock of the body. To do this, they destroyed the core in the brain of mice by microsurgical.
Robert Moore and Victor Eichler found that in animals with non-functioning suprachiasmatic the nucleus disappears cyclical release into blood of stress hormones — adrenaline and glucocorticoids.
Another research group under the leadership of Frederick Stephan and Irving Zucker studied locomotor activity of rodents with a remote "circadian". Usually small rodents after waking up all the time are in motion.
In the laboratory to record the movement of the wheel in which the animal runs on the spot, be connected by a cable. Mice and hamsters in a wheel with a diameter of 30 cm run 15-20 km per day! According to the data graphs, which are called hectogramme.
It turned out that the destruction of the suprachiasmatic nucleus leads to the disappearance of the circadian locomotor activity of animals: periods of sleep and wakefulness, they have become chaotic. They cease to sleep during the circadian night, that is, in the daytime, and stay awake during the circadian day, i.e. after dark.
Suprachiasmatic nucleus — the structure is unique. If you remove it from the brain of rodents and place them in "comfortable" with a warm nutrient medium saturated with oxygen, then a few months in the neurons of the nucleus will cyclically vary the frequency and amplitude of the polarization membrane and the production of different signaling molecules — neurotransmitters that transmit the nerve impulse from one cell to another.
Suprachiasmatic which helps the kernel to retain such stable cycles? Neurons in this very densely adjoin to each other, forming a large number of cell-cell contacts (synapses). Due to this, changes in electrical activity of one neuron are transmitted instantly to all the cells of the nucleus, that is, synchronized activity of cell population.
In addition, neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus are associated with a special kind of contacts, which are called annular. They represent the areas of the membranes of contiguous cells, which are embedded in a protein tube, the so-called connexin. On these tubes from one cell to another moving streams of ions, which also sinhroniziruete "work" of neurons of the nucleus. Compelling evidence of this mechanism was presented by American Professor Barry Connors at the annual Convention of neuroscientists "Neuroscience-2004" held in October 2004 in San Diego (USA).
In all likelihood, the suprachiasmatic nucleus plays an important role in protecting the body against the formation of malignant tumors. The proof of this in 2002 showed French and British researchers under the leadership of Professor Francis Levi and Michael Hastings.
The mice with destroyed suprachiasmatic a-planted tumors of bone (osteosarcoma Glasgow) and pancreas (adenocarcinoma). It turned out that the mice without the "circadian center," the speed of development of tumors in 7 times higher than their conventional counterparts.
The relationship between the disturbances of the circadian rhythm and cancer in humans point epidemiological studies. They show that the incidence of breast cancer in women, long-working the night shift, according to various estimates, up to 60% higher than that of women working in the daytime.
CLOCK GENES
The uniqueness of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the fact that his cells are the so-called clock genes. These genes were first discovered in fruit fly Drosophila the counterpart of the brain of vertebrates is the head ganglia, protocerebrum. The clock genes in the mammals according to their nucleotide sequence was very similar to fruit fly genes.
There are two family of clock genes: periodic (Пер1, 2, 3) and cryptochrome (Кри1 and 2).
The products of these genes, Per and Cry proteins, have an interesting feature. In the cytoplasm of neurons they form the molecular complexes, which penetrate into the nucleus and inhibit the activation of clock genes and, of course, the production of their corresponding proteins.
As a result, the concentration of Per and Cry proteins in the cytoplasm of cells is reduced, which again leads to "unlock" and activate genes, which begin to produce new portions of the proteins. This ensures cyclic operation clock genes. It is assumed that the clock genes as it were, setting the biochemical processes occurring in the cell, the circadian mode, but how synchronization occurs, it is not yet clear.
Interestingly, in animals, of the genome where genetic engineering methods, the researchers removed one of the clock genes Per 2 spontaneously develop tumors blood — lymphoma.

DAYLIGHT AND BIORHYTHMS
Circadian rhythms 'invented' by nature to adapt the organism to alternating light and dark time of day, and therefore can not be associated with the perception of light. Information about daylight enters the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the light-sensitive membrane (retina) of the eye.
Light information from photoreceptors of the retina, the rods and cones at the end of a ganglion cells is transmitted in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Ganglion cells do not simply transmit information in the form of nerve impulses, they synthesize a light-sensitive enzyme — melanopsin. Therefore, even in conditions where rods and cones are not functioning (e.g., congenital blindness), these cells are able to perceive light, but not visual information and transmit it to the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
You might think that in the dark no circadian activity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus should be observed. But it is not so: even in the absence of light information in the daily cycle remains stable — changes only its duration.
In the case when the information about the light in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is not received, the circadian period in humans compared to the astronomical day is lengthened. To prove this, in 1962, "father of chronobiology" Professor jürgen Ashoff, which was discussed above, for a few days was placed in a completely dark apartment two volunteers — their sons.
It turned out that the cycle "sleep — wakefulness" after people in the darkness lasted for half an hour. Sleep in complete darkness becomes a fragmentar NYM, surface, it is dominated by slow-wave phase. People no longer feel the dream is like a deep trip, he seems to be daydreaming. After 12 years, the Frenchman Michel Siffre repeated these experiments on himself and you came to similar results. Interestingly, at night the animals cycle in the dark, on the contrary, is declining and is 23.4 hours. The meaning of such shifts in circadian rhythms is still not clear.
The changing photoperiod affects the activity of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. If animals, which for several weeks was kept in stable conditions (12 hours light and 12 hours dark), then put in the other light cycles (e.g., 18 hours in light and 6 hours dark), they had been a violation of the periodicity of active wakefulness and sleep. Similar happens with a person when you change illumination.
Cycle "sleep — Wake" in wild animals coincides with periods of daylight. In modern human society "24/7" (24 hours per day, 7 days per week) mismatch of biological rhythms actual daily cycle leads to a "circadian stress", which, in turn, can cause development of many diseases, including depression, insomnia, disorders of the cardiovascular system and cancer.
There is even such a thing as seasonal affective disease seasonal depression associated with the decrease of day length in the winter. It is known that in Northern countries such as Scandinavia, where the mismatch in the duration of daylight active period is especially noticeable among the population is very large, the frequency of depression and suicides.
If you have seasonal depression in the patient's blood increases the levels of the main adrenal hormone, cortisol, which strongly depresses the immune system. And lowered immunity will inevitably lead to increased susceptibility to infectious diseases. So it is possible that a short day is one of the reasons for the surge in the incidence of viral infections in the winter.
CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS OF ORGANS AND TISSUES
Today found that suprachiasmatic nucleus sends signals to the brain centers responsible for the cyclical production of hormones controls the daily activity of the organism.
One of these regulatory centers is paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, where the signal "start" synthesis of growth hormone or ACTH is transferred to the pituitary gland. So suprachiasmatic nucleus can be called the "conductor" of circadian activity of the organism. But other cells are subject to their own circadian rhythms. It is known that in the cells of the heart, liver, lung, pancreas, kidney, muscle, and connective tissue work the clock genes.
The activity of these peripheral systems is subject to its own circadian rhythms, which generally coincide with the cycles of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, but shifted in time. The question of how the "conductor of the circadian orchestra" controls the functioning of the "musicians" who remains a key problem of modern chronobiology.
Cyclical parts of our bodies quite easy to withdraw from the control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. In 2000-2004, a series of sensational works of the Swiss and American research groups, led by Julia Silarom and Michael Menaker.
In experiments conducted by scientists, night rodents were fed only in the daytime. For mice it is as unnatural for a human, which would give the opportunity to eat only at night. The result of the activity of circadian clock genes in the inner organs of animals gradually rebuilt completely and ceased to coincide with circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Return to normal synchronized biorhythms occurred immediately after the start feeding them in their normal waking hours, i.e. night time. The mechanisms of this phenomenon are still unknown. But one thing is for sure: to bring the whole body under control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus just — we just have to radically change diet, started dinner at night. Therefore, a strict regime of eating no empty sound. It is especially important to follow it in childhood, because the biological clock "starts" at a very early age.
Heart, like all internal organs, also has its own circadian activity. In vitro it exhibits a significant circadian fluctuations, resulting in a cyclic variation of its contractile function and oxygen consumption. The biorhythms of the heart coincide with the activity of "heart" clock genes.
In the hypertrophied heart (which is muscle mass increased due to growth of cells) fluctuations in the activity of the heart and "heart" clock genes disappear. It is therefore possible, and otherwise fail in the daily activity of the cells of the heart may cause its hypertrophy and the subsequent development of heart failure. So violation of the day regimen and nutrition are likely to be the cause of heart disease.
Circadian rhythms are subject to not only the endocrine system and internal organs, cells activity in peripheral tissues is also the specific circadian program. This field of research is only beginning to develop, but has already accumulated interesting data. So, in the cells of the internal organs of rodents, the synthesis of new DNA molecules predominantly occurs at the beginning of circadian night, then have the morning and cell division begins actively at the beginning of the circadian day, or evening.
Cyclically changes the growth rate of the cells of the oral mucosa of man. That is especially important, according to circadian rhythms and changing the activity of proteins responsible for cell proliferation, such as topoisomerase II α protein, which often serves as a "target" of the action of chemotherapy drugs.
This fact is of exceptional importance for the treatment of malignant tumors. As shown by clinical observations, chemotherapy in circadian period corresponding to the peak generation topoisomerase, is much more effective than one-time or continuous infusion of chemotherapy drugs at an arbitrary time.
None of the scientists is not in doubt that circadian rhythms one of the basic biological mechanisms, through which over millions of years of evolution all the inhabitants of the Land have adapted to the daily light cycle. Although man is vysokoprepodobny creature that allowed him to become the most numerous species among the mammals, civilization inevitably destroys its biological rhythm.
And while plants and animals follow a natural circadian rhythm, a person has much more complicated. Circadian stress is a feature of our time, to resist them is extremely difficult. However, in our power to respect the "biological clock" of health, clearly following the sleep, wakefulness, and eating.
Illustration of "the Life of plants and the biological clock"
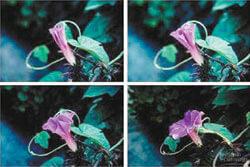
Not only animals, but also plants live by the "biological clock". The day the flowers close and open the petals depending on the lighting — it is known to all. However, not everyone knows that the education of nectar is also subject to circadian rhythms. And bees pollinate the flowers only during certain hours — at the time of generation of the greatest amount of nectar. This observation was done at the beginning of chronobiology in the early twentieth century by German scientists Karl von Frisch and Ingeborg the Belinga.
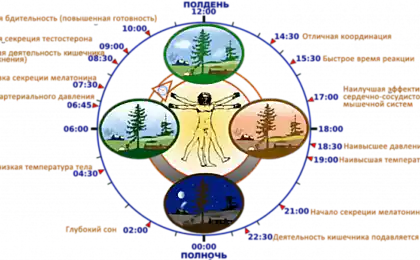
Illustration "the Diagram of the "ideal" diurnal rhythms of synthesis of "waking hormone" cortisol and the "sleep hormone" melatonin."
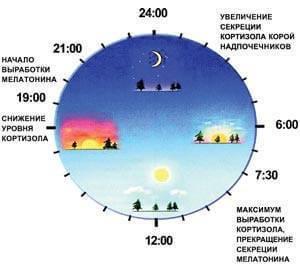
Most people have a level of cortisol in the blood begins to increase from midnight and reaches a maximum at 6-8 o'clock in the morning. By this time almost stops the production of melatonin. After approximately 12 hours the cortisol concentration begins to decline, and after 2 hours starts the synthesis of melatonin. But this time frame is very conditional. "The lark," for example, cortisol reaches the maximum level earlier — to the 4-5 o'clock in the morning, "owls" later — 9-11 hours. Depending on chronotype and shift the peaks of emission of melatonin.
Illustration "the Graph of the number of heart attacks with lethal outcome."
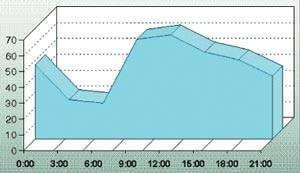
The chart shows the number of heart attacks with lethal outcome among patients admitted to the clinic of the Medical College of the University of Kentucky (USA) in 1983, the time of day. As can be seen from the graph, the peak in the number of heart attacks falls on the time interval from 6 to 9 o'clock in the morning. This is due to circadian activation of the cardiovascular system before awakening.
Illustration of the "suprachiasmatic nucleus."
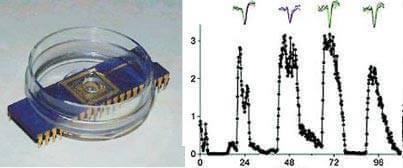
If suprachiasmatic nucleus placed in a "comfortable" physiological conditions (left picture) and record the electrical activity of its neurons during the day, it will look like the periodic increase of the amplitude of discharges (action potential) with peaks every 24 hours (right figure).
Illustration "Night animals — hamsters during wakefulness are in constant motion."

In the laboratory for registration of motor activity of rodents to the wheel, in which the animal runs on the spot, be connected by a cable. According to the data graphs, which are called hectogramme.
Illustration of the "Main "conductor" of biological rhythms is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SHA) is located in the hypothalamus, an evolutionarily ancient part of the brain."
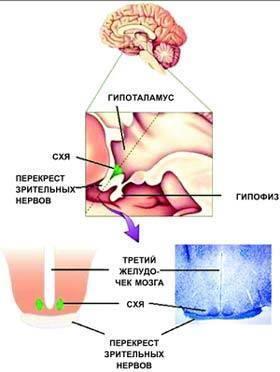
The hypothalamus is framed in the top drawing, made with a longitudinal section of the human brain. Suprachiasmatic nucleus lies above the optic chiasm, through which it receives light information from the retina. The lower right drawing is a cross — section of the mouse hypothalamus, painted in blue. On the left lower image the same image is presented schematically. Paired spherical formation, a cluster of neurons forming the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Illustration "the Diagram of synthesis of "night hormone" melatonin."
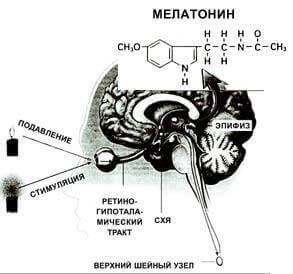
Melatonin induces sleep, and its fluctuations during the day lead to a change of sleep phases. Melatonin secretion is subject to circadian rhythm and is light-dependent: it stimulates dark and light, on the contrary, suppresses. Information about light in mammals is supplied to the epiphysis in a complex way: from the retina to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (retino-hypothalamic tract), then from the suprachiasmatic nucleus to the upper cervical node and from the upper cervical node in the pineal gland. In fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds, the illumination can govern the production of melatonin via the pineal gland directly because light easily passes through the thin skull of these animals. Hence another name for the pineal gland — "the third eye". As melatonin controls the sleep and change of sleep phases, is not yet clear.
Illustration for "suprachiasmatic nucleus is the controller of the circadian rhythm of the various organs and tissues."
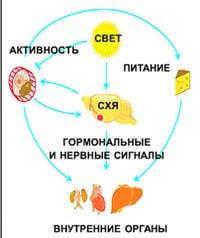
It carries out its functions, regulating hormone production by the pituitary and adrenal glands, and also through direct transmission of the signal by the spikes of neurons. The circadian activity of peripheral organs can be withdrawn from under the control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, violating the diet — eating at night.published
Author: Vladimir Grinevich
This simple procedure will help you to quickly clean the lymphatic system, the Fascia — the "secret" on your body
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/1828813710663547
In recent years, the science of biorhythms, chronobiology has been done to establish the mechanism of diurnal hormonal cycles. Scientists have discovered the brain's "circadian center," and the so-called "clock genes" biological rhythms health.

CHRONOBIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF THE DAILY RHYTHMS OF THE BODY
In 1632, the English scientist John Wren in his "Treatise on herbs" ("Herbal Treatise") was the first to describe the daily cycles of tissue fluids in the human body, which he, following the terminology of Aristotle, called "gomory" (lat. humor — liquid). Each of the "tides" of the tissue fluid, according to Wren, lasted six hours.
Humoral cycle began at nine o'clock in the evening and highlighting the first gomory bile — "сhole" (gr. cholе — bile) and lasted until three in the morning. Then came the phase of black bile — "melancholy" (gr. melas — black, chole — bile), followed by phlegm — "phlegma" (gr. phlegma — mucus, sputum), and finally, the fourth humora — blood.
Of course, correlate with Gomori now known bodily fluids and tissue secrets impossible. Modern medical science has no connection with the mystical physiology humorama does not recognize. And yet Venom described patterns of change of mood, intellectual ability and physical condition have a very scientific basis.
The science that studies circadian rhythms of the body, called chronobiologia (gr. chronos — time). Its basic idea formulated Wali distinguished German and American scientists of Professor jürgen Ashoff and Colin Pittendrigh, who in the early 80-ies of the last century was even nominated for the Nobel prize. But the highest scientific award they, unfortunately, never received.
The main concept of chronobiology — day cycles, the duration of which is periodic about (lat. circa) day (lat. dies). Therefore, successive daily cycles are called circadian rhythms. These rhythms are directly connected with cyclic changes in illumination, that is, with the rotation of the Earth around its axis. They are all living beings on Earth: plants, microorganisms, invertebrates and vertebrates, up to higher mammals and man.
Each of us known circadian cycle "sleep — wakefulness". In 1959, Ashoff found a pattern that of Pittendrigh proposed to call the "rule Asifa". Under this name it entered chronobiology and the history of science.
The rule reads as follows: "At night the animals active period (Wake) of a more continuous with constant lighting, the daytime animals Wake longer under constant darkness." Indeed, as later established, Ashoff, long-term isolation of man or animals in the dark cycle "sleep — wakefulness" is lengthened by increasing the duration of the phase of wakefulness. The rule Asifa implies that light determines circadian oscillation of the body.
HORMONES AND BIORHYTHMS
During the circadian day (awake) our physiology is mainly configured for processing the accumulated nutrients to get energy for an active daily life. On the contrary, during the circadian night the nutrients accumulate, there are restoration and fix tissues. As it turned out, these changes in the intensity of metabolism are regulated by the endocrine system, i.e. hormones. In endocrine control mechanism of the circadian cycles have a lot in common with humoral theory Wren.
In the evening, before nightfall, the blood of the so-called upper appendage of the brain — the pineal gland is the "night hormone" — melatonin. This amazing substance is produced by the pineal gland only in the dark, and the time of its presence in the blood is directly proportional to the duration of the light of the night. In some cases, insomnia in the elderly is associated with insufficiency of secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland. Preparations of melatonin are often used as hypnotics.
Melatonin reduces body temperature, in addition, it regulates the duration and change of sleep phases. The fact that human sleep is an alternation of slow-wave and paradoxical phases.
Non-REM sleep is characterized by low frequency activity of the cortex of hemispheres. This is the "dream legs", a time when the brain is fully rest. During paradoxical sleep the oscillation frequency of the electrical activity of the brain increases, and we see dreams. This phase is close to wakefulness and serves as "a springboard" in awakening. Slow-wave and paradoxical phases succeed one another 4-5 times during the night, in time with the changes in melatonin concentration.
The onset of light nights accompanied by other hormonal changes: increased growth hormone and decreased production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) others brain called the pituitary gland. HGH stimulates anabolic processes such as cell proliferation and accumulation of nutrients (glycogen) in the liver.
No wonder they say: "Children grow in their sleep." ACTH causes the release into blood of epinephrine and other "stress hormones" (glucocorticoids) from the adrenal cortex, so reducing its level allows to remove the fluorescent excitation and peacefully to sleep. In the moment of falling asleep from the pituitary gland highlighted opioid hormones, having narcotic effect, the endorphins and enkephalins. That is why the process of falling asleep is accompanied by pleasant sensations.
Before the awakening of a healthy body should be ready for active wakefulness, at this time, the adrenal cortex begins to produce stimulating the nervous system and hormones — glucocorticoids.
Most active of them is cortisol, which leads to increased pressure, increased heart rate, increased vascular tone and reduce blood clotting. That's why clinical statistics show that acute heart attacks and intracerebral hemorrhagic strokes are heavily concentrated in the early morning. Now we are developing drugs that reduce blood pressure, which can reach a peak concentration in the blood only in the morning, preventing deadly attacks.
Why do some people stand up "no light, no dawn", and the other off to sleep until noon? It turns out that the well-known phenomenon of "owls and larks" is quite a scientific explanation which is based on the works of Jami, Seizer of the Research center for sleep (Sleep Research Center) at Stanford University in California.
It found that the minimum concentration of cortisol in the blood usually is in the middle of a night's sleep, and its peak is reached before the awakening. "The lark" the maximum release of cortisol occurs earlier than most people — at 4-5 o'clock in the morning. Therefore, the "larks" are more active in the morning hours, but quickly get tired in the evening. They are usually early starts tend to sleep, because the sleep hormone melatonin into the bloodstream long before midnight.
In "owls" the situation is reversed: melatonin is secreted later, closer to midnight, and the peak of cortisol release has been shifted to the 7-8 o'clock in the morning. The specified time frame is individual and can vary depending on the severity of the morning ("larks") and evening ("owls") chronotypes.

"CIRCADIAN CENTER" IS IN THE BRAIN
What is this body which controls the circadian fluctuations of hormones concentration in the blood? On this question, scientists for a long time could not find the answer. But none of them had any doubt that "circadian center" should be located in the brain.
Its existence was predicted and the founders of chronobiology, Pittendrigh and Asoff. The attention of physiologists has attracted has long been known to anatomists structure of the brain — the suprachiasmatic nucleus, situated above the (lat. super) a chiasm (from the Greek. chiasmos) of the optic nerves. It has a cigar-shaped and consists, for example, in rodents of only 10,000 neurons, very little. Another, closely located, -, paraventrikulyarnoe, contains hundreds of thousands of neurons. The length of the suprachiasmatic nucleus is also small — no more than half of a millimeter, and the volume is 0,3 mm3 .
In 1972 two groups of American researchers managed to show that the suprachiasmatic nucleus is the control center of the biological clock of the body. To do this, they destroyed the core in the brain of mice by microsurgical.
Robert Moore and Victor Eichler found that in animals with non-functioning suprachiasmatic the nucleus disappears cyclical release into blood of stress hormones — adrenaline and glucocorticoids.
Another research group under the leadership of Frederick Stephan and Irving Zucker studied locomotor activity of rodents with a remote "circadian". Usually small rodents after waking up all the time are in motion.
In the laboratory to record the movement of the wheel in which the animal runs on the spot, be connected by a cable. Mice and hamsters in a wheel with a diameter of 30 cm run 15-20 km per day! According to the data graphs, which are called hectogramme.
It turned out that the destruction of the suprachiasmatic nucleus leads to the disappearance of the circadian locomotor activity of animals: periods of sleep and wakefulness, they have become chaotic. They cease to sleep during the circadian night, that is, in the daytime, and stay awake during the circadian day, i.e. after dark.
Suprachiasmatic nucleus — the structure is unique. If you remove it from the brain of rodents and place them in "comfortable" with a warm nutrient medium saturated with oxygen, then a few months in the neurons of the nucleus will cyclically vary the frequency and amplitude of the polarization membrane and the production of different signaling molecules — neurotransmitters that transmit the nerve impulse from one cell to another.
Suprachiasmatic which helps the kernel to retain such stable cycles? Neurons in this very densely adjoin to each other, forming a large number of cell-cell contacts (synapses). Due to this, changes in electrical activity of one neuron are transmitted instantly to all the cells of the nucleus, that is, synchronized activity of cell population.
In addition, neurons of the suprachiasmatic nucleus are associated with a special kind of contacts, which are called annular. They represent the areas of the membranes of contiguous cells, which are embedded in a protein tube, the so-called connexin. On these tubes from one cell to another moving streams of ions, which also sinhroniziruete "work" of neurons of the nucleus. Compelling evidence of this mechanism was presented by American Professor Barry Connors at the annual Convention of neuroscientists "Neuroscience-2004" held in October 2004 in San Diego (USA).
In all likelihood, the suprachiasmatic nucleus plays an important role in protecting the body against the formation of malignant tumors. The proof of this in 2002 showed French and British researchers under the leadership of Professor Francis Levi and Michael Hastings.
The mice with destroyed suprachiasmatic a-planted tumors of bone (osteosarcoma Glasgow) and pancreas (adenocarcinoma). It turned out that the mice without the "circadian center," the speed of development of tumors in 7 times higher than their conventional counterparts.
The relationship between the disturbances of the circadian rhythm and cancer in humans point epidemiological studies. They show that the incidence of breast cancer in women, long-working the night shift, according to various estimates, up to 60% higher than that of women working in the daytime.
CLOCK GENES
The uniqueness of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the fact that his cells are the so-called clock genes. These genes were first discovered in fruit fly Drosophila the counterpart of the brain of vertebrates is the head ganglia, protocerebrum. The clock genes in the mammals according to their nucleotide sequence was very similar to fruit fly genes.
There are two family of clock genes: periodic (Пер1, 2, 3) and cryptochrome (Кри1 and 2).
The products of these genes, Per and Cry proteins, have an interesting feature. In the cytoplasm of neurons they form the molecular complexes, which penetrate into the nucleus and inhibit the activation of clock genes and, of course, the production of their corresponding proteins.
As a result, the concentration of Per and Cry proteins in the cytoplasm of cells is reduced, which again leads to "unlock" and activate genes, which begin to produce new portions of the proteins. This ensures cyclic operation clock genes. It is assumed that the clock genes as it were, setting the biochemical processes occurring in the cell, the circadian mode, but how synchronization occurs, it is not yet clear.
Interestingly, in animals, of the genome where genetic engineering methods, the researchers removed one of the clock genes Per 2 spontaneously develop tumors blood — lymphoma.

DAYLIGHT AND BIORHYTHMS
Circadian rhythms 'invented' by nature to adapt the organism to alternating light and dark time of day, and therefore can not be associated with the perception of light. Information about daylight enters the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the light-sensitive membrane (retina) of the eye.
Light information from photoreceptors of the retina, the rods and cones at the end of a ganglion cells is transmitted in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Ganglion cells do not simply transmit information in the form of nerve impulses, they synthesize a light-sensitive enzyme — melanopsin. Therefore, even in conditions where rods and cones are not functioning (e.g., congenital blindness), these cells are able to perceive light, but not visual information and transmit it to the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
You might think that in the dark no circadian activity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus should be observed. But it is not so: even in the absence of light information in the daily cycle remains stable — changes only its duration.
In the case when the information about the light in the suprachiasmatic nucleus is not received, the circadian period in humans compared to the astronomical day is lengthened. To prove this, in 1962, "father of chronobiology" Professor jürgen Ashoff, which was discussed above, for a few days was placed in a completely dark apartment two volunteers — their sons.
It turned out that the cycle "sleep — wakefulness" after people in the darkness lasted for half an hour. Sleep in complete darkness becomes a fragmentar NYM, surface, it is dominated by slow-wave phase. People no longer feel the dream is like a deep trip, he seems to be daydreaming. After 12 years, the Frenchman Michel Siffre repeated these experiments on himself and you came to similar results. Interestingly, at night the animals cycle in the dark, on the contrary, is declining and is 23.4 hours. The meaning of such shifts in circadian rhythms is still not clear.
The changing photoperiod affects the activity of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. If animals, which for several weeks was kept in stable conditions (12 hours light and 12 hours dark), then put in the other light cycles (e.g., 18 hours in light and 6 hours dark), they had been a violation of the periodicity of active wakefulness and sleep. Similar happens with a person when you change illumination.
Cycle "sleep — Wake" in wild animals coincides with periods of daylight. In modern human society "24/7" (24 hours per day, 7 days per week) mismatch of biological rhythms actual daily cycle leads to a "circadian stress", which, in turn, can cause development of many diseases, including depression, insomnia, disorders of the cardiovascular system and cancer.
There is even such a thing as seasonal affective disease seasonal depression associated with the decrease of day length in the winter. It is known that in Northern countries such as Scandinavia, where the mismatch in the duration of daylight active period is especially noticeable among the population is very large, the frequency of depression and suicides.
If you have seasonal depression in the patient's blood increases the levels of the main adrenal hormone, cortisol, which strongly depresses the immune system. And lowered immunity will inevitably lead to increased susceptibility to infectious diseases. So it is possible that a short day is one of the reasons for the surge in the incidence of viral infections in the winter.
CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS OF ORGANS AND TISSUES
Today found that suprachiasmatic nucleus sends signals to the brain centers responsible for the cyclical production of hormones controls the daily activity of the organism.
One of these regulatory centers is paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, where the signal "start" synthesis of growth hormone or ACTH is transferred to the pituitary gland. So suprachiasmatic nucleus can be called the "conductor" of circadian activity of the organism. But other cells are subject to their own circadian rhythms. It is known that in the cells of the heart, liver, lung, pancreas, kidney, muscle, and connective tissue work the clock genes.
The activity of these peripheral systems is subject to its own circadian rhythms, which generally coincide with the cycles of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, but shifted in time. The question of how the "conductor of the circadian orchestra" controls the functioning of the "musicians" who remains a key problem of modern chronobiology.
Cyclical parts of our bodies quite easy to withdraw from the control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. In 2000-2004, a series of sensational works of the Swiss and American research groups, led by Julia Silarom and Michael Menaker.
In experiments conducted by scientists, night rodents were fed only in the daytime. For mice it is as unnatural for a human, which would give the opportunity to eat only at night. The result of the activity of circadian clock genes in the inner organs of animals gradually rebuilt completely and ceased to coincide with circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Return to normal synchronized biorhythms occurred immediately after the start feeding them in their normal waking hours, i.e. night time. The mechanisms of this phenomenon are still unknown. But one thing is for sure: to bring the whole body under control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus just — we just have to radically change diet, started dinner at night. Therefore, a strict regime of eating no empty sound. It is especially important to follow it in childhood, because the biological clock "starts" at a very early age.
Heart, like all internal organs, also has its own circadian activity. In vitro it exhibits a significant circadian fluctuations, resulting in a cyclic variation of its contractile function and oxygen consumption. The biorhythms of the heart coincide with the activity of "heart" clock genes.
In the hypertrophied heart (which is muscle mass increased due to growth of cells) fluctuations in the activity of the heart and "heart" clock genes disappear. It is therefore possible, and otherwise fail in the daily activity of the cells of the heart may cause its hypertrophy and the subsequent development of heart failure. So violation of the day regimen and nutrition are likely to be the cause of heart disease.
Circadian rhythms are subject to not only the endocrine system and internal organs, cells activity in peripheral tissues is also the specific circadian program. This field of research is only beginning to develop, but has already accumulated interesting data. So, in the cells of the internal organs of rodents, the synthesis of new DNA molecules predominantly occurs at the beginning of circadian night, then have the morning and cell division begins actively at the beginning of the circadian day, or evening.
Cyclically changes the growth rate of the cells of the oral mucosa of man. That is especially important, according to circadian rhythms and changing the activity of proteins responsible for cell proliferation, such as topoisomerase II α protein, which often serves as a "target" of the action of chemotherapy drugs.
This fact is of exceptional importance for the treatment of malignant tumors. As shown by clinical observations, chemotherapy in circadian period corresponding to the peak generation topoisomerase, is much more effective than one-time or continuous infusion of chemotherapy drugs at an arbitrary time.
None of the scientists is not in doubt that circadian rhythms one of the basic biological mechanisms, through which over millions of years of evolution all the inhabitants of the Land have adapted to the daily light cycle. Although man is vysokoprepodobny creature that allowed him to become the most numerous species among the mammals, civilization inevitably destroys its biological rhythm.
And while plants and animals follow a natural circadian rhythm, a person has much more complicated. Circadian stress is a feature of our time, to resist them is extremely difficult. However, in our power to respect the "biological clock" of health, clearly following the sleep, wakefulness, and eating.
Illustration of "the Life of plants and the biological clock"

Not only animals, but also plants live by the "biological clock". The day the flowers close and open the petals depending on the lighting — it is known to all. However, not everyone knows that the education of nectar is also subject to circadian rhythms. And bees pollinate the flowers only during certain hours — at the time of generation of the greatest amount of nectar. This observation was done at the beginning of chronobiology in the early twentieth century by German scientists Karl von Frisch and Ingeborg the Belinga.
Illustration "the Diagram of the "ideal" diurnal rhythms of synthesis of "waking hormone" cortisol and the "sleep hormone" melatonin."

Most people have a level of cortisol in the blood begins to increase from midnight and reaches a maximum at 6-8 o'clock in the morning. By this time almost stops the production of melatonin. After approximately 12 hours the cortisol concentration begins to decline, and after 2 hours starts the synthesis of melatonin. But this time frame is very conditional. "The lark," for example, cortisol reaches the maximum level earlier — to the 4-5 o'clock in the morning, "owls" later — 9-11 hours. Depending on chronotype and shift the peaks of emission of melatonin.
Illustration "the Graph of the number of heart attacks with lethal outcome."

The chart shows the number of heart attacks with lethal outcome among patients admitted to the clinic of the Medical College of the University of Kentucky (USA) in 1983, the time of day. As can be seen from the graph, the peak in the number of heart attacks falls on the time interval from 6 to 9 o'clock in the morning. This is due to circadian activation of the cardiovascular system before awakening.
Illustration of the "suprachiasmatic nucleus."

If suprachiasmatic nucleus placed in a "comfortable" physiological conditions (left picture) and record the electrical activity of its neurons during the day, it will look like the periodic increase of the amplitude of discharges (action potential) with peaks every 24 hours (right figure).
Illustration "Night animals — hamsters during wakefulness are in constant motion."

In the laboratory for registration of motor activity of rodents to the wheel, in which the animal runs on the spot, be connected by a cable. According to the data graphs, which are called hectogramme.
Illustration of the "Main "conductor" of biological rhythms is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SHA) is located in the hypothalamus, an evolutionarily ancient part of the brain."

The hypothalamus is framed in the top drawing, made with a longitudinal section of the human brain. Suprachiasmatic nucleus lies above the optic chiasm, through which it receives light information from the retina. The lower right drawing is a cross — section of the mouse hypothalamus, painted in blue. On the left lower image the same image is presented schematically. Paired spherical formation, a cluster of neurons forming the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Illustration "the Diagram of synthesis of "night hormone" melatonin."

Melatonin induces sleep, and its fluctuations during the day lead to a change of sleep phases. Melatonin secretion is subject to circadian rhythm and is light-dependent: it stimulates dark and light, on the contrary, suppresses. Information about light in mammals is supplied to the epiphysis in a complex way: from the retina to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (retino-hypothalamic tract), then from the suprachiasmatic nucleus to the upper cervical node and from the upper cervical node in the pineal gland. In fish, amphibians, reptiles and birds, the illumination can govern the production of melatonin via the pineal gland directly because light easily passes through the thin skull of these animals. Hence another name for the pineal gland — "the third eye". As melatonin controls the sleep and change of sleep phases, is not yet clear.
Illustration for "suprachiasmatic nucleus is the controller of the circadian rhythm of the various organs and tissues."

It carries out its functions, regulating hormone production by the pituitary and adrenal glands, and also through direct transmission of the signal by the spikes of neurons. The circadian activity of peripheral organs can be withdrawn from under the control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, violating the diet — eating at night.published
Author: Vladimir Grinevich
This simple procedure will help you to quickly clean the lymphatic system, the Fascia — the "secret" on your body
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/1828813710663547