580
The mask of agar agar — instant anti-aging effect
INCI: Agar
Synonyms: Seaweed, Aagar-agar, gum agal agal, layor carang, agar-agar, kanten, Japanese gelatin, gelatin Bengal
Family: Gelidiales (Gelidiaceae)
Botanical description: red algae Gelidium amansii is found and mined on the Pacific coast of Asia from the Great Sunda Islands to Japan, along the Pacific coast of Mexico and California and the coast of the Indian ocean. It's delicate, very delicate branched plant, reaching a length of about 20 — 24 cm
In Russia the highest value as a producer of agar-agar has ahnfeltia (Ahnfelria plicara [Huds.] Fries) from the family Phyllophoraceae.
Product description: agar-Agar from Malay agar-agar (seaweed) is a natural gelling agent obtained from various species of marine and oceanic algae (Gracilaria, Gelidium, Ceramium, Ahnfeltia, etc.) growing in the White sea and the Pacific ocean. When mixed with water, the agar-agar forms a gel is completely harmless to the body even with regular use. Has thickening properties, high plagiarise ability and is a vegetable substitute for gelatin. Consists mainly of polysaccharides (a mixture of polysaccharides agarose and agaropectin). In aqueous solutions forms a strong jelly, which have a vitreous fracture.
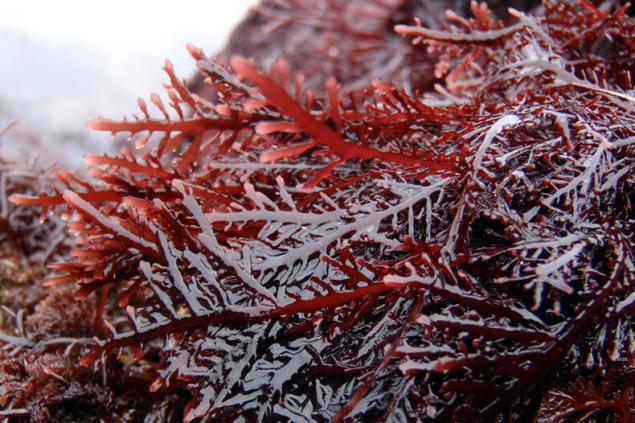

Agar-agar — a classic representative of the class of thickeners, stabilizers, emulsifiers.
Obtain: Get it from seaweed, mainly gelidiales. The red Alga Gelidium amansii is found along the coast of the Pacific ocean. In Mexico, California, Chile, China since ancient times, the swimmers produce brittle branched thalli of this Alga. Then according to traditional recipes dried it in the sun and treated to produce agar.
Produced by the following techniques: washing and cleaning algae — treatment with alkali and water — extraction — filtration — hardening — pressing — drying — grinding. Agar-agar is approximately 80% of the carbohydrates and also it contains proteins and fiber. Algae, giving the agar-agar, extremely rich in iodine, calcium, iron and other valuable substances and trace elements.
Picking and harvesting of agar-Agar: seaweed extracted from the sea floor from may to September, divers using nets or special rakes and thoroughly flushed with fresh water from dirt and small organisms, usually in abundance on the surface of algae. For the subsequent bleaching of the material collected are laid out on mats, where it is frequently washed by fresh water and dried, all the while turning.
Dried seaweed agar-Agar usually while stored in warehouses before they are actually processed in agar. For this they are again moistened and boiled in large vats with water. After adding acid, then heated again at the same geleobraznye substances are dissolved, and strain off from the remaining sediment. Agar is isolated by freezing, after thawing it is a leathery-leaf mass. Then it again dried, and the product is ready to use.
Parts used: thallus (thallus) of algae.
The quality of agar-agar are classified in two classes:
Features:
Appearance: dried fiber, yellowish-white powder or plates
Color: from white to light yellow, yellow, dark yellow, light brown
Smell: does not have
Taste: has
pH: 5,9 – 9,0
Solubility: insoluble in cold water. It is fully soluble only at temperatures from 95 to 100 degrees.
The hot solution is clear and viscous limited. When cooled to temperatures of 35-40 degrees, it becomes pure and strong gel that is termoobrabotki. When heated to 85-95 degrees it again becomes liquid again turns into a gel at 35-40 degrees.
Compared to other generousity (such as carrageenan, pectin, gelatin), agar has the best performance density and gelification. Calificaci independent of pH, sugar concentration and the presence of potassium cations.
Gels prepared using agar are termoobrabotki (jelly melts and freezes again), but on heating acidic solutions of agar-agar at high temperatures can occur by hydrolytic cleavage. Therefore, it is recommended to add acid/acid after dissolving the agar-agar at temperatures up to 60 degrees.
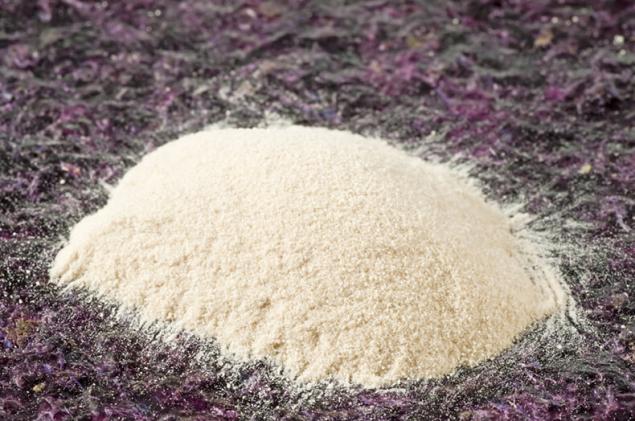

Chemical composition: Contains about 1.5-4% of mineral salts, 10-20 % water and 70-80% of polysaccharides, which identified D - and L-galactose, 3,6-anhydrogalactose, pentoses, D-glucuronic and pyruvic acid.
The molecules of agar are formed by agaroses (galactosyl as a frame) and agaropectin. Agarose is a non-ionic polysaccharide without alkanolamide sulfate and gel-forming part. Agaropectin is a complex of polysaccharides with alkanolamides and pyruvic acid group.
Action: detoxifying, anti-inflammatory, sorbtsionnoe, helatiruyushchey, soothing, nourishing, moisturizing
Masks with agar relieve swelling, improve the complexion. In the agar well to make the mask Express care.
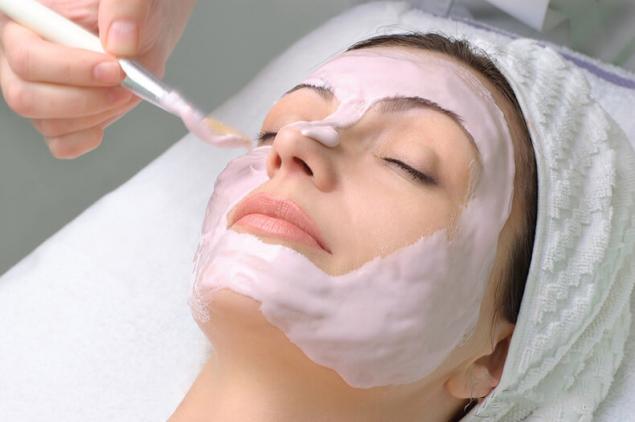

Mask to improve the complexion and hydration (agar+xanthan)
Composition (for 50 ml):

Preparation:
1. The aqueous phase is divided into 2 parts. In a large pour the agar-agar and put in a water bath. To introduce the xanthan gum, solid oil, then the liquid and leave to cool, stirring occasionally.
How to color your hair without chemicals: only natural productsFenugreek for rapid growth and volume of hair
2. To prepare the active phase on chitosane and slightly warm in a water bath (just put in the water where basking agar with the oils, but the fire not include). With a minute to hold and pour into agar jelly. The idea is that both phases should be possible to match the temp-re.
3. Add the essential oil.published
Source: /users/15106
Synonyms: Seaweed, Aagar-agar, gum agal agal, layor carang, agar-agar, kanten, Japanese gelatin, gelatin Bengal
Family: Gelidiales (Gelidiaceae)
Botanical description: red algae Gelidium amansii is found and mined on the Pacific coast of Asia from the Great Sunda Islands to Japan, along the Pacific coast of Mexico and California and the coast of the Indian ocean. It's delicate, very delicate branched plant, reaching a length of about 20 — 24 cm
In Russia the highest value as a producer of agar-agar has ahnfeltia (Ahnfelria plicara [Huds.] Fries) from the family Phyllophoraceae.
Product description: agar-Agar from Malay agar-agar (seaweed) is a natural gelling agent obtained from various species of marine and oceanic algae (Gracilaria, Gelidium, Ceramium, Ahnfeltia, etc.) growing in the White sea and the Pacific ocean. When mixed with water, the agar-agar forms a gel is completely harmless to the body even with regular use. Has thickening properties, high plagiarise ability and is a vegetable substitute for gelatin. Consists mainly of polysaccharides (a mixture of polysaccharides agarose and agaropectin). In aqueous solutions forms a strong jelly, which have a vitreous fracture.

Agar-agar — a classic representative of the class of thickeners, stabilizers, emulsifiers.
Obtain: Get it from seaweed, mainly gelidiales. The red Alga Gelidium amansii is found along the coast of the Pacific ocean. In Mexico, California, Chile, China since ancient times, the swimmers produce brittle branched thalli of this Alga. Then according to traditional recipes dried it in the sun and treated to produce agar.
Produced by the following techniques: washing and cleaning algae — treatment with alkali and water — extraction — filtration — hardening — pressing — drying — grinding. Agar-agar is approximately 80% of the carbohydrates and also it contains proteins and fiber. Algae, giving the agar-agar, extremely rich in iodine, calcium, iron and other valuable substances and trace elements.
Picking and harvesting of agar-Agar: seaweed extracted from the sea floor from may to September, divers using nets or special rakes and thoroughly flushed with fresh water from dirt and small organisms, usually in abundance on the surface of algae. For the subsequent bleaching of the material collected are laid out on mats, where it is frequently washed by fresh water and dried, all the while turning.
Dried seaweed agar-Agar usually while stored in warehouses before they are actually processed in agar. For this they are again moistened and boiled in large vats with water. After adding acid, then heated again at the same geleobraznye substances are dissolved, and strain off from the remaining sediment. Agar is isolated by freezing, after thawing it is a leathery-leaf mass. Then it again dried, and the product is ready to use.
Parts used: thallus (thallus) of algae.
The quality of agar-agar are classified in two classes:
- high — color white or light yellow, may be slightly grayish hue;
- the first color from yellow to dark yellow.
Features:
Appearance: dried fiber, yellowish-white powder or plates
Color: from white to light yellow, yellow, dark yellow, light brown
Smell: does not have
Taste: has
pH: 5,9 – 9,0
Solubility: insoluble in cold water. It is fully soluble only at temperatures from 95 to 100 degrees.
The hot solution is clear and viscous limited. When cooled to temperatures of 35-40 degrees, it becomes pure and strong gel that is termoobrabotki. When heated to 85-95 degrees it again becomes liquid again turns into a gel at 35-40 degrees.
Compared to other generousity (such as carrageenan, pectin, gelatin), agar has the best performance density and gelification. Calificaci independent of pH, sugar concentration and the presence of potassium cations.
Gels prepared using agar are termoobrabotki (jelly melts and freezes again), but on heating acidic solutions of agar-agar at high temperatures can occur by hydrolytic cleavage. Therefore, it is recommended to add acid/acid after dissolving the agar-agar at temperatures up to 60 degrees.

Chemical composition: Contains about 1.5-4% of mineral salts, 10-20 % water and 70-80% of polysaccharides, which identified D - and L-galactose, 3,6-anhydrogalactose, pentoses, D-glucuronic and pyruvic acid.
The molecules of agar are formed by agaroses (galactosyl as a frame) and agaropectin. Agarose is a non-ionic polysaccharide without alkanolamide sulfate and gel-forming part. Agaropectin is a complex of polysaccharides with alkanolamides and pyruvic acid group.
Action: detoxifying, anti-inflammatory, sorbtsionnoe, helatiruyushchey, soothing, nourishing, moisturizing
Masks with agar relieve swelling, improve the complexion. In the agar well to make the mask Express care.

Mask to improve the complexion and hydration (agar+xanthan)
Composition (for 50 ml):
- water 55, 3%-27, 65 ml
- agar-agar - 0, 5x1, 25 ml
- chitosan - 0, 5% -0, 25 g-1, 25ml
- xanthan 0, 2% -0, 1 C - speech. head
- oil:
- apricot-4% -2 ml
- Mak-4%-2 ml
- jojoba oil-5%- 2, 5 ml
- cocoa - 2% -1 g
- Shi-2% -1 g
- mango 2%-1 g
- glycerin 3%-1, 5 ml
- EXT. honey - 5% -2, 5 ml
- EXT. cloudberry 5% -2, 5 ml
- EXT. green tea-3% -1, 5 ml
- EXT. blueberries-3% -1, 5 gr-2x1, 25ml
- powder lemon 2%- 1 g
- peptides silk 3%- 1, 5 ml 30 drops
- opticen + 1% 0,5 ml
- EM: geranium 2, lavender 2, carrot 2, roses. tree 2. ("moisture locking")

Preparation:
1. The aqueous phase is divided into 2 parts. In a large pour the agar-agar and put in a water bath. To introduce the xanthan gum, solid oil, then the liquid and leave to cool, stirring occasionally.
How to color your hair without chemicals: only natural productsFenugreek for rapid growth and volume of hair
2. To prepare the active phase on chitosane and slightly warm in a water bath (just put in the water where basking agar with the oils, but the fire not include). With a minute to hold and pour into agar jelly. The idea is that both phases should be possible to match the temp-re.
3. Add the essential oil.published
Source: /users/15106
How to cook vegetable terrine
The drink of youth and health: strengthen the kidneys, purify the blood