568
10 little-known facts about Ancient Rome that may shock
For many centuries Ancient Rome ruled the world. Incredibly influential, the Roman Empire United the world — as it does neither one state before and after it. In General, however, we are aware of the facts of life of the members of the upper class and rulers, while interesting nuances of everyday life of other Roman remains obscure. And sometimes they can even shock.
The website offers readers a selection of amazing facts about Ancient Rome.
Parasites were a common problem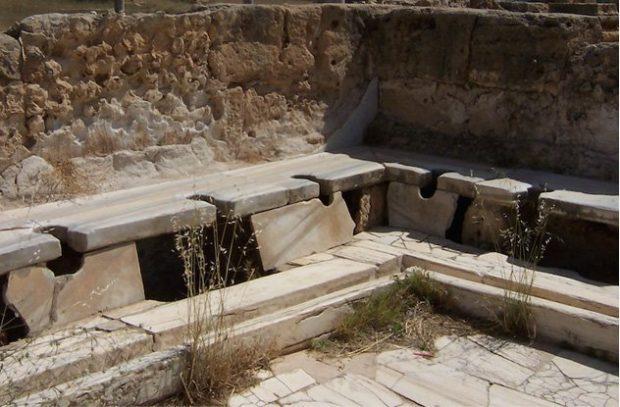
Photo source: Publy.gerim could boast of an impressive health system in comparison with other civilizations, but her job was more than just to deliver people from unpleasant smell. Examining the 2000-year-old feces found in several historical places, scientists have found that problems with parasites in the Roman period was even worse than in earlier times, which are not considered as hygienic as the Bronze or Iron age.
While most Romans had access to clean food and drink water in their bathroom was a favorable environment for parasitic infestation. The water was always warm and rarely updated — which enabled her to become the perfect breeding ground for parasites of all types. Along with the use of human feces as fertilizer, it led to massive disease outbreaks.
Most Romans ate like animals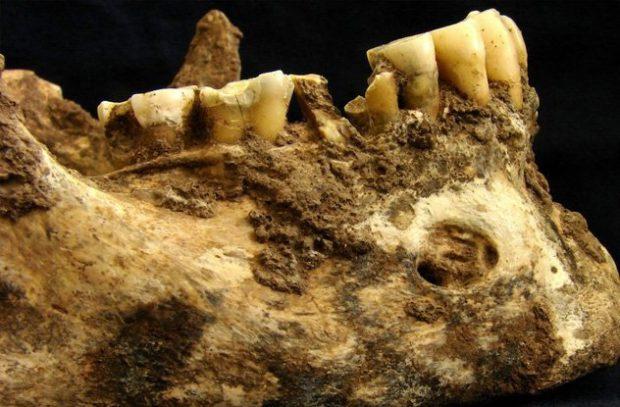
Ancient Rome is known for his incredible gluttony, however the celebrations with exotic delicacies were available only to upper class. The rest of the population of Rome was sitting on a forced diet, eating mostly cereals such as wheat, his wheat was the cheapest and was treated as food for cattle — it means that most people literally ate like animals.
Despite a life near the sea, representatives of the lower classes in Rome rarely ate fish and had only a cereals. This diet leads to various health problems, including anemia and diseases of the oral cavity. The majority of urban residents are well fed, but the further away people lived, the poorer was their food.
Air pollution in Ancient Rome
As a result of tests of glaciers in Greenland, climate scientists found that the level of methane in the atmosphere began to increase even in ancient times. Methane was at its natural level before 100 BC, and then rose and remained at a high level up to 1600. This peak release of methane corresponds in time to the heyday of the Roman Empire.
During this period was recorded methane emissions of about 31 million tons per year, only 5 million less than the current level of emissions throughout the United States. In order to feed the whole Empire, would require a huge amount of livestock — cattle and sheep and goats. This, as well as the growth of the population of the Roman Empire in the West and the Chinese Empire in the East, contributed to air pollution.
Roman wrestling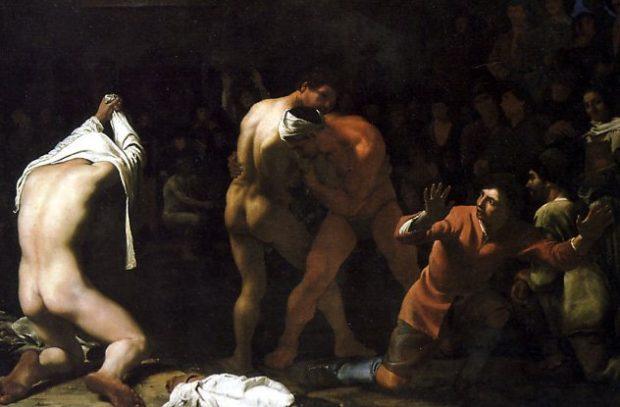
Wrestling as entertainment is prevalent in many countries, and this tradition came to us from ancient Roman competitions. The papyrus, dated to 267 BC, found in the Egyptian city of Occuring, represents the first documented fact of bribery in sport: the wrestler was willing to pay for winning the duel of about 3,800 drachmas — this amount was enough to buy a donkey. This amount is relatively small, but the competition on the Nile was spectacular, so I doubt that other wrestlers had the opportunity to sign such an agreement does not arise.
Bribery was widespread among Roman athletes, but the punishment was cruel. They say that the statue of Zeus at Olympia was built at the expense of penalties from bribes. The Greek philosopher philostratus, once spoke about the status of athletics, declaring that the coaches "did not correlate with the reputation of athletes, but have become their advisers on buying and selling to get a profit."
Show bestiaries in the Coliseum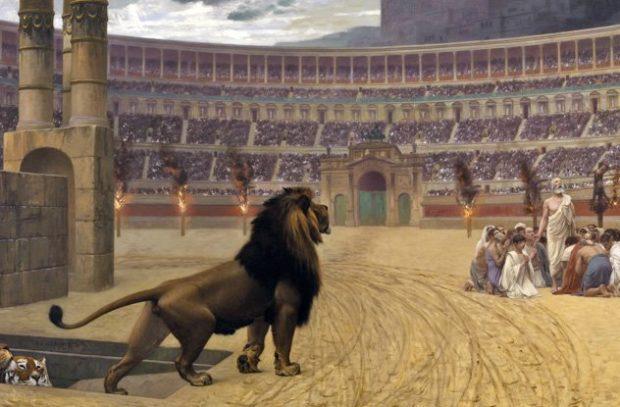
Roman gladiatorial combat dated to 247 BC, when two brothers decided to celebrate the inheritance from their father the battle between the slaves. Over the years the game improved and became more perverse and cruel, to satisfy the desires of the fastidious Romans.
Gladiator fights started with the famous Caligula and became famous thanks to the bestiary Carpophorus — they were designed to demonstrate the cruelty of man and the world. Bestiaries were supposed to train animals for show — for example, to train the eagles to eat the entrails of the vanquished Gladiator. Carpophorus was the most famous bestiary of his time. He not only trained their beasts to kill the poor devils in the Colosseum the most sophisticated ways, but also fought with them myself. A most shocking event, which I learned from animal Carpophorus was raped prisoners of the gladiators — the audience of the Coliseum it caused shock and awe.
Energy drinks Gladiator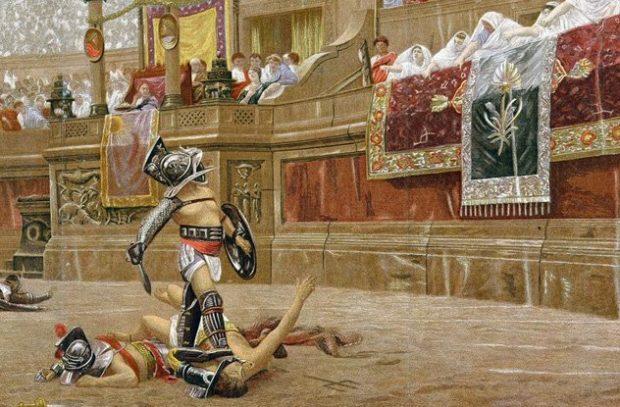
Energy is widely distributed among modern athletes because of their ability to increase endurance. These drinks are popular among fitness enthusiasts. But this is not the invention of the modern world. Energy drinks gladiators existed for centuries before the advent of Gatorade.
In gladiatorial drink contained the extract of ash, which is rich in calcium, stimulating the strengthening of bones. In the remains of gladiators indeed found elevated levels of calcium, so this idea is not so far-fetched. What was the ancient energy drink taste like? Given that the drink was just ash and water, he had to be incredibly bitter, but vinegar could give it a more pleasant taste.
Ancient texts for the study of Latin
Most inhabitants of the Roman Empire spoke Greek and its dialects, but if someone wanted to learn Latin, he turned to the colloquia. These books not only taught the Greeks the Latin language, but also talked about many situations and how the most profitable of them out.
From the original manuscripts reached us only two, dated to the second and sixth centuries. Some of them described situations narrate about the first visit to the public baths, about what to do if late to school, and how to deal with a drinking a close relative. These texts were widely distributed and available equally to rich and poor. It is believed that these situations were described for the role-playing of educational games, where students were able to feel the material and speech.
The Roman tavern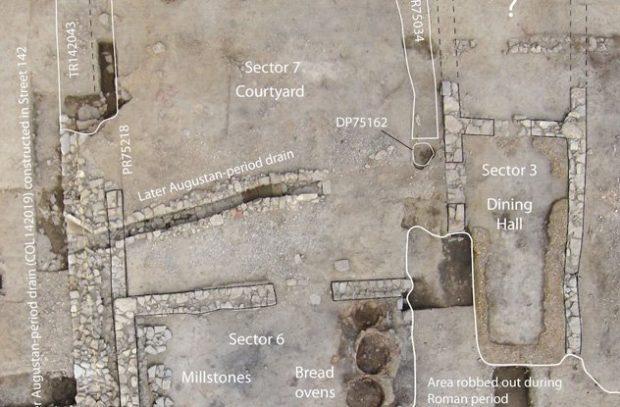
In Lattara, historical place of France, has survived two thousand years of the tavern in the days of the Roman Empire, in which were found the bones of animals and the pins used by the visitors. This place probably was popular among the local population in the 175 — 75 BC during the capture region of the Roman armies. Besides drinks, the tavern was a great choice of dishes — including cakes, fish and sheep and veal.
On one end of the room were three large ovens, on the other — millstones to make flour. In the service area there was a fireplace and soft chairs that were created in the tavern a cozy and comfortable atmosphere — that's what we would like to see bars today.
Infanticide
Us wildly to hear about it, but in Ancient Rome, infanticide was quite common. Before the advent of effective contraception, the woman can, if desired, to get rid of your child. Boys were valued higher than girls, but archaeological research suggests that the number of killed children of both sexes about the same.
In ancient Roman texts even mention of the practice of infanticide, which suggests that the life of newborns is not particularly valued in Roman society. At birth the infant has not yet been considered. The child could wear the title only to achieve certain stages of development — ability to speak, the appearance of the teeth and ability to eat solid foods.
How to build Rome
In 2014, archaeologists began excavating the supposed Temple of Fortune, the first temple, built by the Romans. Since the temple was built in the seventh century, the geographical landscape since that time much has changed. According to the description, the temple was built on the river Tiber, but he was found thirty meters from her and was several feet below the groundwater level. Although archaeologists expect other surprises the ancient Romans put a lot of effort to build a perfect city.
The builders had to level the hills to fill in marshy areas, even change the direction of the city's waterways with a further spread of the buildings. They understood that for the construction of the city and its further development they will need to make changes to the natural landscape to meet their needs. Such sophistication and engineering talent amazes us to this day — as a result of these difficult works was the city that became the center of the Western world, proved that all the efforts of the Romans were not in vain.
Humanity still admires the Roman Empire as the ideal of not only an ancient civilization, but civilization as a whole — its government, residents and workers were progressive and ahead of its time. Modern people can learn from the ancient Romans — with the exception of cruelty and violence.
via www.publy.ru/post/23867
The website offers readers a selection of amazing facts about Ancient Rome.
Parasites were a common problem

Photo source: Publy.gerim could boast of an impressive health system in comparison with other civilizations, but her job was more than just to deliver people from unpleasant smell. Examining the 2000-year-old feces found in several historical places, scientists have found that problems with parasites in the Roman period was even worse than in earlier times, which are not considered as hygienic as the Bronze or Iron age.
While most Romans had access to clean food and drink water in their bathroom was a favorable environment for parasitic infestation. The water was always warm and rarely updated — which enabled her to become the perfect breeding ground for parasites of all types. Along with the use of human feces as fertilizer, it led to massive disease outbreaks.
Most Romans ate like animals

Ancient Rome is known for his incredible gluttony, however the celebrations with exotic delicacies were available only to upper class. The rest of the population of Rome was sitting on a forced diet, eating mostly cereals such as wheat, his wheat was the cheapest and was treated as food for cattle — it means that most people literally ate like animals.
Despite a life near the sea, representatives of the lower classes in Rome rarely ate fish and had only a cereals. This diet leads to various health problems, including anemia and diseases of the oral cavity. The majority of urban residents are well fed, but the further away people lived, the poorer was their food.
Air pollution in Ancient Rome

As a result of tests of glaciers in Greenland, climate scientists found that the level of methane in the atmosphere began to increase even in ancient times. Methane was at its natural level before 100 BC, and then rose and remained at a high level up to 1600. This peak release of methane corresponds in time to the heyday of the Roman Empire.
During this period was recorded methane emissions of about 31 million tons per year, only 5 million less than the current level of emissions throughout the United States. In order to feed the whole Empire, would require a huge amount of livestock — cattle and sheep and goats. This, as well as the growth of the population of the Roman Empire in the West and the Chinese Empire in the East, contributed to air pollution.
Roman wrestling

Wrestling as entertainment is prevalent in many countries, and this tradition came to us from ancient Roman competitions. The papyrus, dated to 267 BC, found in the Egyptian city of Occuring, represents the first documented fact of bribery in sport: the wrestler was willing to pay for winning the duel of about 3,800 drachmas — this amount was enough to buy a donkey. This amount is relatively small, but the competition on the Nile was spectacular, so I doubt that other wrestlers had the opportunity to sign such an agreement does not arise.
Bribery was widespread among Roman athletes, but the punishment was cruel. They say that the statue of Zeus at Olympia was built at the expense of penalties from bribes. The Greek philosopher philostratus, once spoke about the status of athletics, declaring that the coaches "did not correlate with the reputation of athletes, but have become their advisers on buying and selling to get a profit."
Show bestiaries in the Coliseum

Roman gladiatorial combat dated to 247 BC, when two brothers decided to celebrate the inheritance from their father the battle between the slaves. Over the years the game improved and became more perverse and cruel, to satisfy the desires of the fastidious Romans.
Gladiator fights started with the famous Caligula and became famous thanks to the bestiary Carpophorus — they were designed to demonstrate the cruelty of man and the world. Bestiaries were supposed to train animals for show — for example, to train the eagles to eat the entrails of the vanquished Gladiator. Carpophorus was the most famous bestiary of his time. He not only trained their beasts to kill the poor devils in the Colosseum the most sophisticated ways, but also fought with them myself. A most shocking event, which I learned from animal Carpophorus was raped prisoners of the gladiators — the audience of the Coliseum it caused shock and awe.
Energy drinks Gladiator

Energy is widely distributed among modern athletes because of their ability to increase endurance. These drinks are popular among fitness enthusiasts. But this is not the invention of the modern world. Energy drinks gladiators existed for centuries before the advent of Gatorade.
In gladiatorial drink contained the extract of ash, which is rich in calcium, stimulating the strengthening of bones. In the remains of gladiators indeed found elevated levels of calcium, so this idea is not so far-fetched. What was the ancient energy drink taste like? Given that the drink was just ash and water, he had to be incredibly bitter, but vinegar could give it a more pleasant taste.
Ancient texts for the study of Latin

Most inhabitants of the Roman Empire spoke Greek and its dialects, but if someone wanted to learn Latin, he turned to the colloquia. These books not only taught the Greeks the Latin language, but also talked about many situations and how the most profitable of them out.
From the original manuscripts reached us only two, dated to the second and sixth centuries. Some of them described situations narrate about the first visit to the public baths, about what to do if late to school, and how to deal with a drinking a close relative. These texts were widely distributed and available equally to rich and poor. It is believed that these situations were described for the role-playing of educational games, where students were able to feel the material and speech.
The Roman tavern

In Lattara, historical place of France, has survived two thousand years of the tavern in the days of the Roman Empire, in which were found the bones of animals and the pins used by the visitors. This place probably was popular among the local population in the 175 — 75 BC during the capture region of the Roman armies. Besides drinks, the tavern was a great choice of dishes — including cakes, fish and sheep and veal.
On one end of the room were three large ovens, on the other — millstones to make flour. In the service area there was a fireplace and soft chairs that were created in the tavern a cozy and comfortable atmosphere — that's what we would like to see bars today.
Infanticide

Us wildly to hear about it, but in Ancient Rome, infanticide was quite common. Before the advent of effective contraception, the woman can, if desired, to get rid of your child. Boys were valued higher than girls, but archaeological research suggests that the number of killed children of both sexes about the same.
In ancient Roman texts even mention of the practice of infanticide, which suggests that the life of newborns is not particularly valued in Roman society. At birth the infant has not yet been considered. The child could wear the title only to achieve certain stages of development — ability to speak, the appearance of the teeth and ability to eat solid foods.
How to build Rome

In 2014, archaeologists began excavating the supposed Temple of Fortune, the first temple, built by the Romans. Since the temple was built in the seventh century, the geographical landscape since that time much has changed. According to the description, the temple was built on the river Tiber, but he was found thirty meters from her and was several feet below the groundwater level. Although archaeologists expect other surprises the ancient Romans put a lot of effort to build a perfect city.
The builders had to level the hills to fill in marshy areas, even change the direction of the city's waterways with a further spread of the buildings. They understood that for the construction of the city and its further development they will need to make changes to the natural landscape to meet their needs. Such sophistication and engineering talent amazes us to this day — as a result of these difficult works was the city that became the center of the Western world, proved that all the efforts of the Romans were not in vain.
Humanity still admires the Roman Empire as the ideal of not only an ancient civilization, but civilization as a whole — its government, residents and workers were progressive and ahead of its time. Modern people can learn from the ancient Romans — with the exception of cruelty and violence.
via www.publy.ru/post/23867
20 hilarious cards that are worth to share with your friends!
What would Odessa an operating system. Fantastically funny!























