502
15 facts about Ancient Rome, which are not told in history lessons

It turns out that Ancient Rome is not only philosophers, gladiators, and theaters. Romans left a lot of mysteries, and about some of their traditions we certainly would never tell at school in history class, and it's for the best.
The website have compiled for you 15 of the most unusual facts about the Romans.
1. The Romans drank the blood of gladiators

In Ancient Rome drank the blood of dead gladiators. It was considered that way in person, the life force. Several Roman authors describe how, after gladiatorial fighting had collected the blood of the dead Gladiator and sold it as a medicine. The Romans believed that the blood of a Gladiator could cure epilepsy.
2. The Romans died young

Although the average life expectancy in Ancient Rome was 25 years, many Romans lived to old age and could boast quite familiar to us by life expectancy. It is likely that establishment figures in 25 years affected frequent death of women during childbirth and high infant mortality. On average, Romans lived is not particularly smaller than ours.
3. The time dimension was rather conditional

Roman hour could last from 75 of our modern minute in summer and 44 in winter. The fact is that for the most part the Romans followed the sun. 12 daytime hours began with dawn, and after dusk was counted another 12 night. But as the duration of day in winter and summer were very different, and the length of each hour would change. So the Romans rather tolerant of delays and were not very punctual.
4. The color purple only for the rich

Among the Romans it was customary to greet strangers "dress for success", but rather, by its color. There were two options: all "natural" colors, either shades of brown-yellow and gray-black was the natural color of sheep wool, and therefore taken as a sign of humble, poor citizens; and all shades of red, purple, green, was created artificially, with the help of expensive dyes, privatissima from afar, and was considered a sign of wealth and aristocracy. It was considered particularly chic wearing purple clothes.
5. The unibrow was considered a sign of intelligence

In Rome among women were highly valued thick, heavy eyebrows. They were considered a sign of high intelligence, so the Roman ladies went to different lengths to increase the thickness and bushiness of her eyebrows. For example, used artificial eyebrows, made of goat hair. And glued them on the face with tree resin.
6. Dentistry was popular
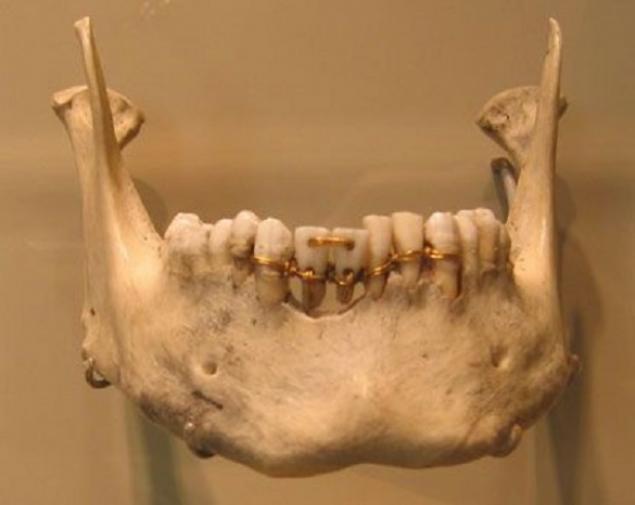
In Ancient Rome had their own dentists, and the Romans themselves really cared about the health of the teeth. Archaeologists have even discovered the female jaw with dentures. Scientists believe that such products of ancient dentists were intended not so much for the successful absorption of food, how much to demonstrate wealth, because you can afford to flash a mouth full of teeth could only very wealthy people.
7. The Romans disliked philosophers

In the Roman Empire were born such outstanding philosophers as Seneca and Marcus Aurelius. Nevertheless, many Romans were hostile towards philosophy. From the standpoint of the practical Romans, the study of philosophy with its concentration on the inner world of man makes people not adapted to the active life and the service of the state. Galen, physician to the Imperial court, noted that the Romans believed the philosophy is no more useful than drilling millet seeds.
8. Roman generals did not fight

In the art of military commanders often depicted fighting on the front lines with their soldiers. Usually, however, the Roman commanders did not participate in the battle. They held command positions and directed the actions of the army with his "bridge" to better navigate the ongoing. Only in exceptional circumstances, when the battle was almost lost, the captain was supposed to either kill herself or go looking for death at the hands of the enemy.
9. There was a tradition to drink the poison
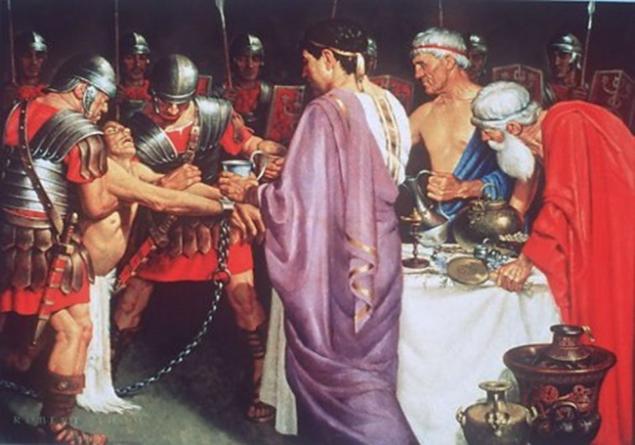

With the end of the first century ad, the Roman emperors started the tradition of daily use of small amount of every known poison in an attempt to obtain immunity. The mixture of poisons called Mithridates in honour of Mithridates the Great, king of Pontus, who first tried out this method.
10. Persecution of Christians
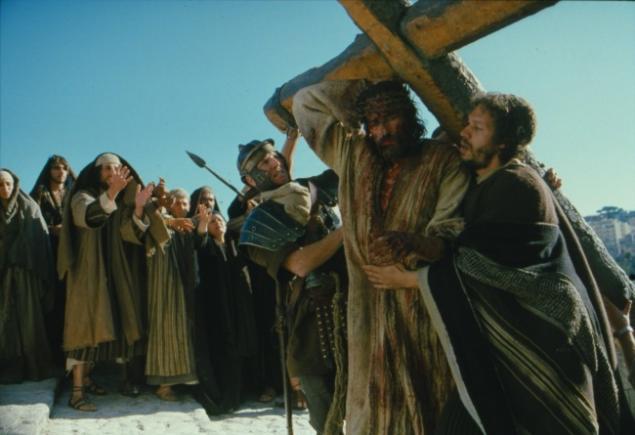

The Romans believed that they have good reason to persecute Christians. The Romans believed that their Empire is based on polytheism. The Christians argued that pagan gods evil demons, or even denied their existence. If the Romans allowed them to spread their beliefs, it angered their gods. However, the Roman pursuers gave the Christians a chance to recognize the traditional gods and thus to avoid martyrdom. But the believers could not accept such a deal.
11. At feasts was made to induce vomiting
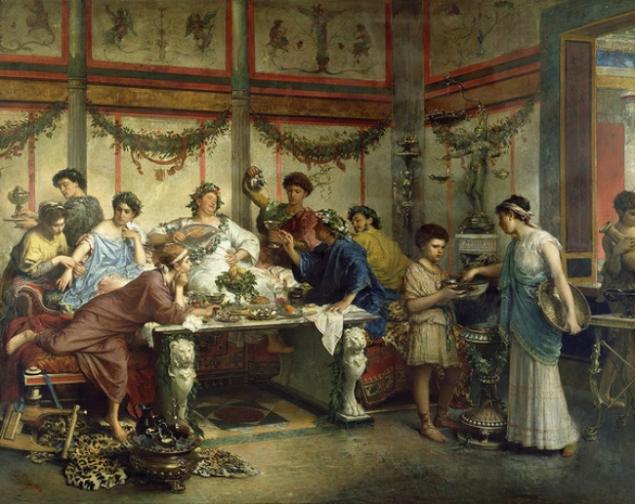

The Romans so loved excess in all things, even brought the tradition to induce vomiting during banquets. According to Seneca, the Romans at feasts eaten up until they just don't climb any more, and then summoned vomiting to clear the stomach and continue to eat.
12. Roman women dyed their hair
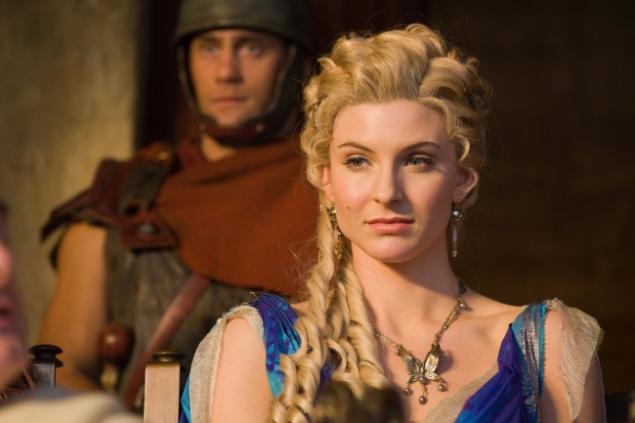

Roman women dyed their hair. Initially, dyed hair was considered a sign of women of easy virtue, but the third wife of Emperor Claudius, Messalina, introduced the fashion for wearing colored wigs, and later the color of the hair among the Roman nobility.
13. Horses were involved in politics

Intsitat was the favorite horse of Emperor Caligula. According to Suetonius, was a statue of Incitatus made of marble and ivory, he had purple robes and trappings of precious stones. Dion Cassius says that the horse ate oats mixed with gold flakes. Suetonius also wrote that Caligula planned to make Incitatus a Consul. Perhaps in this way the Emperor wanted to play a joke on to the Senate, showing that even the horse is able to perform the work of a Senator.
14. Not used soap
The Romans bathed every day, but soap is not used. Instead they rubbed themselves with the oils, and then scraped off together with mud with the help of special scrapers.
15. Use an unusual method of washing
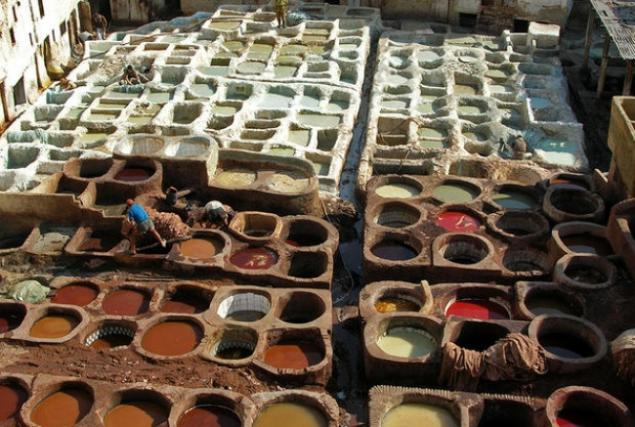

The Romans used human urine to wash the things. Workers filled the Chang clothes, and then poured her urine. Then one man climbed into a VAT and trampled on the garment to wash it.
Photo on preview Roberto Bompiani
See also
12 important archaeological findings that changed the history
7 iron evidence that we are not alone in this Universe
via www.adme.ru/zhizn-nauka/7-zheleznyh-dokazatelstv-chto-my-ne-odni-v-etoj-vselennoj-1443665/
Studies have shown that French fries are healthier cooked
10 household tricks that don't actually work