485
Human shield the planet
Mangroves are constantly teetering on the brink, and in a literal sense: their house is a narrow coastal strip of the tropics, the meeting place of water and land. Here there is debilitating heat, and in the swampy mud under his feet dissolved a huge amount of salt that can kill any other plant for a matter of hours. Despite the marginal position, any mangrove forest is a complex ecosystem of great importance for the nature of the region. Under the dense canopy of branches the birds nest on submerged roots live molluscs and snakes in the muddy waters crocodiles stalk their prey. Mangroves are feeding grounds for fish, tree crabs, monkeys, deer and even kangaroo. Fans of nectar – bats and bees – will also find something here to eat.
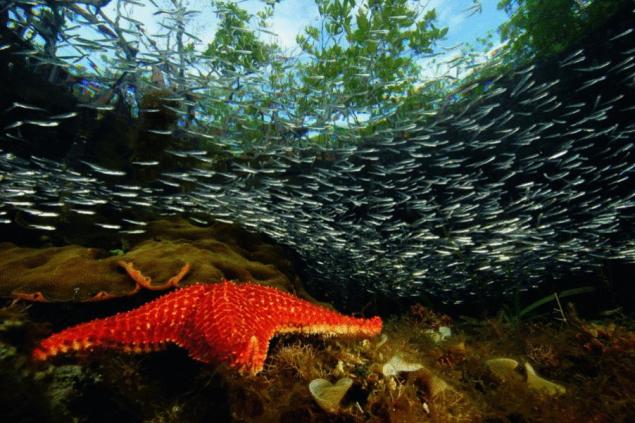

Mangrove flora is a rather relative term: there are about seventy species of plants from dozens of families, among which are palm, hibiscus, Holly, plyumbago, acanthus, Myrtle, and representatives of legumes. Their height is various: you can meet a low creeping shrub, and marching trees, reaching a height of sixty meters.
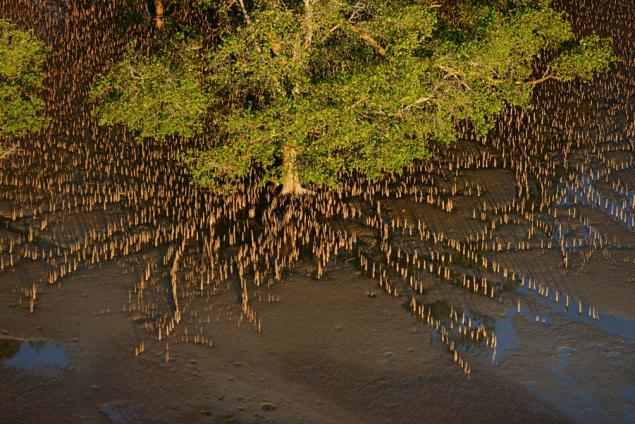

Our planet's mangrove forests are distributed mainly in South-East Asia – the region is traditionally considered to be their homeland. Now, however, the mangroves located in different parts of the globe. Usually they are located not more than thirty degrees from the equator, but there are a few especially stable species which could adapt to moderate climate. One species of mangrove grows at all far from the tropical sun in New Zealand. From mangrove forests is a very important quality: wherever they grow, they are always perfectly adapted to the local conditions. Each representative has a very complex mangrove root system and the unique ability to filtering, allowing it to exist in a supersaturated salt soil. Without this system, the mangroves would be difficult to survive in the narrow tidal zone. Many plants have breathing roots-pneumatophores that allow oxygen. Other roots are called "stilted" and used as a prop in a soft-sediment tidal sediment. A strong root system keeps the sediment carried by the river, and the trunks and branches of trees do not allow waves to erode the coast.
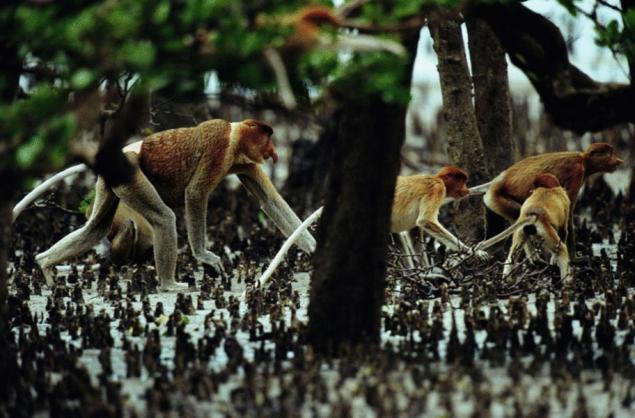

Mangrove forests are unique in their value function – soil formation. The aborigines of Northern Australia, even identify some species of mangrove with his mythical ancestor named Giavera. Ancient legend has it that he wandered through the viscous sludge, and the song awakened the earth to life.
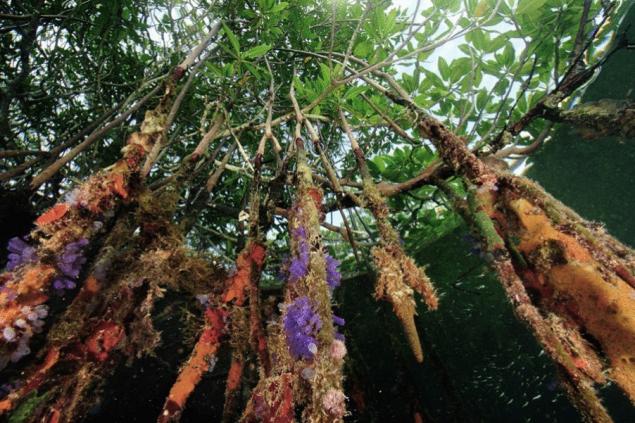

Unfortunately, despite its strategic importance for nature mangrove forests everywhere are under threat of destruction. The salt flats, ponds for the cultivation of shellfish, fish and shrimp, the construction of houses, roads, ports, hotels and farms – the onslaught of civilization are not able to withstand even those accustomed to the hard conditions of plants like mangroves. Forests are cut down or killed by indirect factors – emissions of chemicals and industrial oils, excessive accumulation of ground deposits and salt balance disruptions.
Source: /users/147

Mangrove flora is a rather relative term: there are about seventy species of plants from dozens of families, among which are palm, hibiscus, Holly, plyumbago, acanthus, Myrtle, and representatives of legumes. Their height is various: you can meet a low creeping shrub, and marching trees, reaching a height of sixty meters.

Our planet's mangrove forests are distributed mainly in South-East Asia – the region is traditionally considered to be their homeland. Now, however, the mangroves located in different parts of the globe. Usually they are located not more than thirty degrees from the equator, but there are a few especially stable species which could adapt to moderate climate. One species of mangrove grows at all far from the tropical sun in New Zealand. From mangrove forests is a very important quality: wherever they grow, they are always perfectly adapted to the local conditions. Each representative has a very complex mangrove root system and the unique ability to filtering, allowing it to exist in a supersaturated salt soil. Without this system, the mangroves would be difficult to survive in the narrow tidal zone. Many plants have breathing roots-pneumatophores that allow oxygen. Other roots are called "stilted" and used as a prop in a soft-sediment tidal sediment. A strong root system keeps the sediment carried by the river, and the trunks and branches of trees do not allow waves to erode the coast.

Mangrove forests are unique in their value function – soil formation. The aborigines of Northern Australia, even identify some species of mangrove with his mythical ancestor named Giavera. Ancient legend has it that he wandered through the viscous sludge, and the song awakened the earth to life.

Unfortunately, despite its strategic importance for nature mangrove forests everywhere are under threat of destruction. The salt flats, ponds for the cultivation of shellfish, fish and shrimp, the construction of houses, roads, ports, hotels and farms – the onslaught of civilization are not able to withstand even those accustomed to the hard conditions of plants like mangroves. Forests are cut down or killed by indirect factors – emissions of chemicals and industrial oils, excessive accumulation of ground deposits and salt balance disruptions.
Source: /users/147