1235
Methods of detecting extrasolar planets
The news of the discovery of planets around other stars in our galaxy appears increasingly common, and many people may be interested in two questions: why, with all the development of astronomy, the discovery of the first confirmed exoplanet was only in 1991? And why, in fact, that the number of planets discovered exceeded one thousand - extrasolar planets similar to our own, among them a few pieces?
Despite the number of open exoplanets, the vast majority of them can not be seen even the best telescope exist at the moment. The reason is that the world is incredibly faint objects - light that they emit can be in the millions and billions of times less light coming from their stars. And if the planets have large sizes and are close to their stars (the so-called "hot Jupiters"), the radiation from them is still a thousand times smaller. But it is almost impossible to see from the fact that it takes an incredible angular resolution - on modern telescopes they just merge with its stars.
But somehow they are found? Indeed, there are several indirect methods that are capable of detecting extrasolar planets, most of them are based on the detection of the effect of the planet on its star.
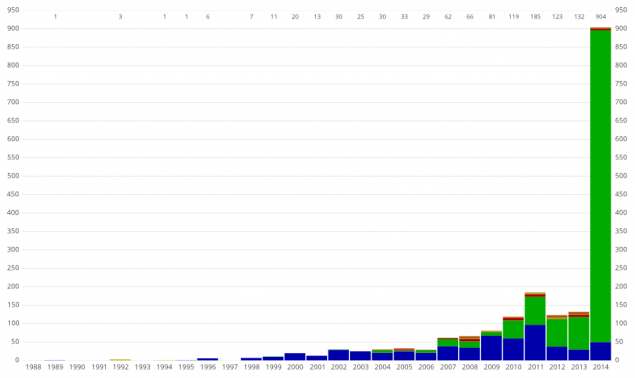
Schedule discovery of planets data (indicated by the ratio of open flowers on the methods of the planets). The jump in 2014 - the effect of processing Space Telescope "Kepler" (the green part - is the transit method, which he enjoyed).
Article the first confirmed exoplanet discovery was published in 1991, although a few are not confirmed at the time of discoveries have been made more three years earlier. Open it was the pulsar (a neutron star with a magnetic field), and there were reasons:
Radio work pulsars (the method of periodic pulsations)

The concept of a planetary system in the pulsar PSR B1257 + 12
The discovery of the pulsar itself is a very interesting story, but in this case we are interested in their observation. They have an extremely accurate frequency signal which slowly decreases due to the radiation associated with their rotation. Planets orbiting stars, and inevitably causes slight shifts its star, and this in turn - periodic changes in the frequency of the pulsar which can not be explained by any other reasons. This principle even directional antennas is not required - quite accurately record the frequency and strength of the signal from the neutron star. The radio signal travels through the atmosphere is good, and for such studies is sufficient ground telescopes.
Advantages: does not depend on the distance to the observer, rather simple equipment (by the standards of astronomy)
Disadvantages: can detect only those planets that are orbiting the parallel observation (or close to them); neutron stars in the total number of small, even less among them pulsars, so the total number of open stars of this method is low.
Doppler method

The absorption spectrum of hydrogen (the main part of the majority of stars)
The main way of studying the stars - a spectral analysis of its light by changing the type to a type of star, but has general parameters - such as the absorption band of hydrogen and helium, which are the majority in any star. These narrow black lines in the spectrum of radiation from the star does not depend on its properties, and are constant for the entire universe. And if they are displaced from their traditional positions - this means that the star is moving towards us (the shift to the violet region of the spectrum) or us (the shift into the red region of the spectrum).
If the star has a planetary system - it is in a place with a planet (s) revolves around a common center of gravity, and a planet (s) in such a way as though "swing" star. From here and limitations - too lungs of the planet do not affect the movement of their stars, and at large radii of treatment - and the effect of the rotation of a planet is drowning in the noise of the stars **.
* Advantages: does not depend on the distance to the observation, a sufficient condition is the ability to accumulate light for spectral analysis in a reasonable time.
Disadvantages: can detect only those planets that are orbiting the parallel observation (or close to them); It has a limit on the ratio of the mass of the star / planet mass **.
The transit method
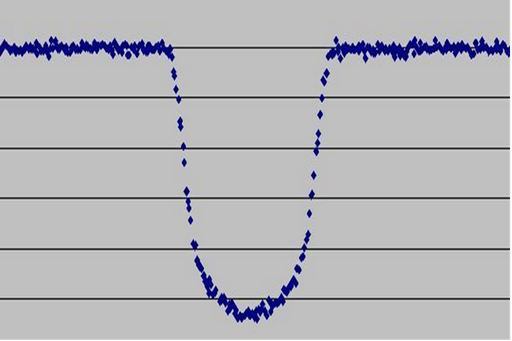
Change the luminosity of the star Kepler-6 from passing on its disk exoplanet Kepler-6 b (the telescope, "Kepler»)
Based on the fact that the planet rotates, it passes in front of its star partially closing it. The size of the planet is much smaller than its stars - for the Earth, the figure of about 10 000 for exoplanets can differ by an order in a big way (for planets the size of Jupiter) and downwards (large planets in white dwarfs).
At the moment he is the most "fruitful" by the number of planets discovered, mostly - by the Space Telescope "Kepler", which worked using this method.
Advantages: it depends on the apparent magnitude - for the brightest star has a large detection range; can detect a planet with a period of several years (in principle limited only by the period of observation - to confirm the discovery of the planet, it is necessary to fix the passage of the planet in a stellar disk at least twice).
Disadvantages: can detect planets that rotate parallel to the observer and tested on the stellar disk of its star (the angle is much smaller than the Doppler method); It has a limit on the ratio of the diameter of the star / planet's diameter **.
Astrometric technique
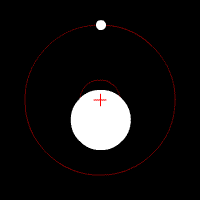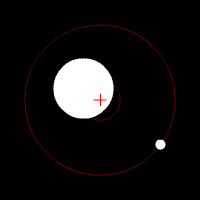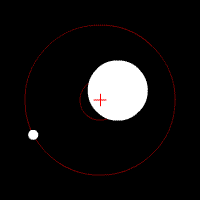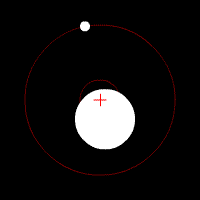
Influence of rotating planet on its star
Like the Doppler method is based on the movement of the stars under the influence of rotating it around the world. Exceeds the complexity of the previous ones, because we have to determine the minor displacement stars in the sky (the center of mass of a planetary system often is "inside" the star itself), even though the displacement of the Earth's rotation around the sun, used to measure the parallax of stars allow any precision only measure distance , the stars within our galaxy.
Advantages: can detect planets that are far away from their stars; along with direct observation can detect planets orbit of rotation perpendicular to the observer. ***
Disadvantages: can detect planets that are orbiting perpendicular observer (or close to them); Range is limited by the ability to detect the angular rotation of the star.
The method of gravitational microlensing
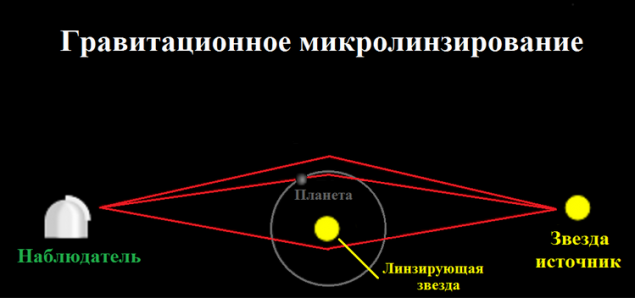
The method is based on the fact that the light is deflected by gravity, and if on the way between us and some other star will star with a planetary system, it will collect the light of a distant star like a huge lens. Initially this method was proposed to search for black holes - that can not be detected by direct observations, if a black hole falls of significant amounts of the substance, or if the black hole is at the last stage of evaporation (that black holes formed by the collapse of stars very long process - the account goes on tens of billions of years). Now, this method is mainly used to search for traces of dark matter, but also allows you to simultaneously open and the planet.
That this method was discovered the most distant currently known exoplanet - OGLE-2005-BLG-390L, where OGLE means "optical gravitational lensing experiment on».
Advantages: allows you to open the world at very faint stars down to the individual planets, found themselves far away from the star.
Disadvantages: as the transit method, requires precise alignment of the three bodies in a line - a distant star - a star with a planetary system - the Earth, and for this reason does not allow to open a significant number of planets.
Direct observation
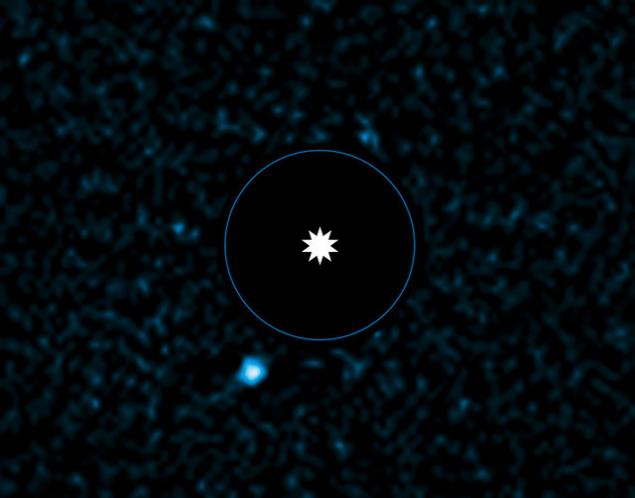

Direct Photo exoplanets HD95086 b, made with the help of ground-based telescope with adaptive optics VLT
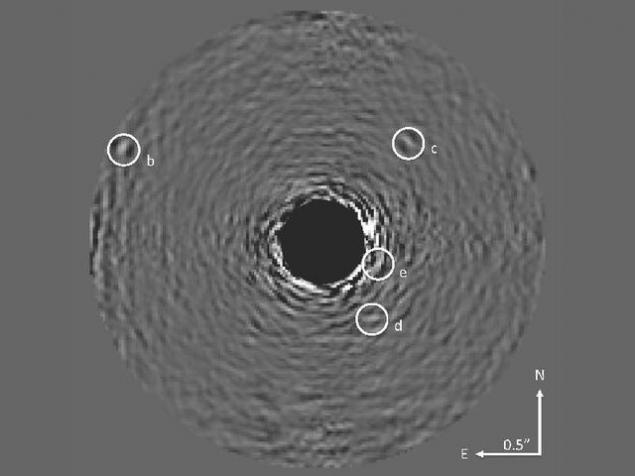
Photo planetary system HR 8799, made 5, 1 meter Hale telescope at Palomar obseravtorii, although it is not among the largest at the moment, but it allows a well to assess the problems that are associated with the direct study of the planets - they are barely visible in the background noise of the substance the filling star system noise and invested the Earth's atmosphere.
The method itself speaks for itself. To implement it in the focus of the telescope is placed a small disk obscures the star itself, thus becoming visible planets surrounding this star. If it turns out well enough to isolate the light coming from the planet itself, then attach to the knowledge of the light coming from the star itself (that which falls on the surface of the planet), you can judge the material that makes up this planet. Other methods allow us to judge the composition of the planet's only indirectly, by its density and have high accuracy of predictions.
Advantages of brilliance to determine the ratio of the albedo / area of the illuminated surface, on spectral analysis - composition of the atmosphere and the surface (the other methods do not allow to measure these parameters).
Disadvantages: Requires telescopes larger than the other methods (to observe the required telescope "sees" a star for several magnitudes less); for close to their planets luminaries limitation becomes resolution (which is solved by using spaced telescopes), ground-based telescopes to direct search for planets is even more of a problem than for space (partly solved by adaptive optics).
As can be seen from this description - no one method does not allow to detect any orbits of any planet (except for the method of direct observation, if you have a telescope, practically infinite size, of course). Each method complements the other, more than that - they are usually shared to determine such parameters that define a single method would not do. Say Transit and Doppler method allows to measure the area and mass of the planet, respectively, and these parameters - the density, and the force of gravity for this planet.

The list of potentially habitable planets from the University of Puerto Rico in the town of Arecibo (University of Puerto Rico at Arecibo)
At the moment we know nothing of the 31st planet is in the habitable zone, all of them have a mass close to the Earth, or more of it. This is only the imperfection of our technology - a heavy object can be seen from great distances than light. With the improvement of our technology will begin the discovery of planets similar to Earth in size, or less than in existing planetary systems around nearby stars, and who has not yet found its planets. In this heavy planet will not stop opening - a zone of detection will move on.
Now a lot of the largest telescopes used to search for extrasolar planets (along with other research, of course), because of the constant growth in the complexity of astronomical research today many telescopes are used together to provide the benefits of interference - these are the Keck Observatory in Hawaii, much more Telescope (VLT) Paranal Observatory in Chile and the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) in Arizona.
The first specialized for this purpose was the Space Telescope "Kepler" and gave his specialty fruit - three years of his work he has allowed to open more than a thousand planets, and its data continue to be used for the discovery of planets more than two years. Who can form a certain "break", when all the data will be processed by Kepler, and his successor - «Tess» will be launched only in 2017 and will not open a large number of exoplanets existing telescopes.
A significant breakthrough in this, and many other areas of astronomy with the planned launch of the Space Telescope "James Webb", scheduled for the end of 2018 year. It is not intended solely for the purposes of the search for extrasolar planets, and will be launched to replace the "Hubble" - but it will be enough opportunities for significant progress in the search for extrasolar planets in general, and planets like Earth in particular.
Future large telescopes - giant Magelanov Telescope (GMT), Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) and the European Extremely Large Telescope (E-ELT) will be commensurate with the possibilities, "James Webb" and E-ELT - almost all its surpass. The last two of the telescope will be built close to the VLT and the Keck Observatory, respectively, this is due to the favorable conditions for observations that are difficult to get in some other places. These telescopes will open a lot of new exoplanets, but more importantly - expand the bottom bracket of their discovery, which will find a much more Earth-like planets, and the planets much smaller than ours, until the discovery of extrasolar planets have moons.
* Assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of methods based on the total of the method, highly specialized telescopes can be "sharpened" under a certain method, and not be able to use some other methods do.
** Technical difficulties in this area is almost solved, and we ran into a "theoretical ceiling" of these methods - the problems associated with the fact that the stars are not static entities, they are a kind of "breathe", say our sun has pronounced 11 year cycle, and several periods of more and less than this, which have no such constancy. It is these fluctuations interfere with the measurements - at some point, the level of signal / noise ratio becomes so small that the effect of the rotation of the planet becomes impossible to isolate, with arbitrarily good telescope.
*** Parallel and perpendicular to the orbits of the planets are shown in the shortcomings due to the fact that they essentially limit the number of possible orbits, which can detect the planet to less than 50%. The advantage - due to the fact that the planet orbits perpendicular to the observer are capable of detecting only two methods of all.
For articles used photos wikipedia.org and subsection site JPL NASA , devoted to the subject. And list of potentially habitable planets from the University of Puerto Rico in the town of Arecibo.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/263018/
Despite the number of open exoplanets, the vast majority of them can not be seen even the best telescope exist at the moment. The reason is that the world is incredibly faint objects - light that they emit can be in the millions and billions of times less light coming from their stars. And if the planets have large sizes and are close to their stars (the so-called "hot Jupiters"), the radiation from them is still a thousand times smaller. But it is almost impossible to see from the fact that it takes an incredible angular resolution - on modern telescopes they just merge with its stars.
But somehow they are found? Indeed, there are several indirect methods that are capable of detecting extrasolar planets, most of them are based on the detection of the effect of the planet on its star.

Schedule discovery of planets data (indicated by the ratio of open flowers on the methods of the planets). The jump in 2014 - the effect of processing Space Telescope "Kepler" (the green part - is the transit method, which he enjoyed).
Article the first confirmed exoplanet discovery was published in 1991, although a few are not confirmed at the time of discoveries have been made more three years earlier. Open it was the pulsar (a neutron star with a magnetic field), and there were reasons:
Radio work pulsars (the method of periodic pulsations)

The concept of a planetary system in the pulsar PSR B1257 + 12
The discovery of the pulsar itself is a very interesting story, but in this case we are interested in their observation. They have an extremely accurate frequency signal which slowly decreases due to the radiation associated with their rotation. Planets orbiting stars, and inevitably causes slight shifts its star, and this in turn - periodic changes in the frequency of the pulsar which can not be explained by any other reasons. This principle even directional antennas is not required - quite accurately record the frequency and strength of the signal from the neutron star. The radio signal travels through the atmosphere is good, and for such studies is sufficient ground telescopes.
Advantages: does not depend on the distance to the observer, rather simple equipment (by the standards of astronomy)
Disadvantages: can detect only those planets that are orbiting the parallel observation (or close to them); neutron stars in the total number of small, even less among them pulsars, so the total number of open stars of this method is low.
Doppler method

The absorption spectrum of hydrogen (the main part of the majority of stars)
The main way of studying the stars - a spectral analysis of its light by changing the type to a type of star, but has general parameters - such as the absorption band of hydrogen and helium, which are the majority in any star. These narrow black lines in the spectrum of radiation from the star does not depend on its properties, and are constant for the entire universe. And if they are displaced from their traditional positions - this means that the star is moving towards us (the shift to the violet region of the spectrum) or us (the shift into the red region of the spectrum).
If the star has a planetary system - it is in a place with a planet (s) revolves around a common center of gravity, and a planet (s) in such a way as though "swing" star. From here and limitations - too lungs of the planet do not affect the movement of their stars, and at large radii of treatment - and the effect of the rotation of a planet is drowning in the noise of the stars **.
* Advantages: does not depend on the distance to the observation, a sufficient condition is the ability to accumulate light for spectral analysis in a reasonable time.
Disadvantages: can detect only those planets that are orbiting the parallel observation (or close to them); It has a limit on the ratio of the mass of the star / planet mass **.
The transit method

Change the luminosity of the star Kepler-6 from passing on its disk exoplanet Kepler-6 b (the telescope, "Kepler»)
Based on the fact that the planet rotates, it passes in front of its star partially closing it. The size of the planet is much smaller than its stars - for the Earth, the figure of about 10 000 for exoplanets can differ by an order in a big way (for planets the size of Jupiter) and downwards (large planets in white dwarfs).
At the moment he is the most "fruitful" by the number of planets discovered, mostly - by the Space Telescope "Kepler", which worked using this method.
Advantages: it depends on the apparent magnitude - for the brightest star has a large detection range; can detect a planet with a period of several years (in principle limited only by the period of observation - to confirm the discovery of the planet, it is necessary to fix the passage of the planet in a stellar disk at least twice).
Disadvantages: can detect planets that rotate parallel to the observer and tested on the stellar disk of its star (the angle is much smaller than the Doppler method); It has a limit on the ratio of the diameter of the star / planet's diameter **.
Astrometric technique

Influence of rotating planet on its star
Like the Doppler method is based on the movement of the stars under the influence of rotating it around the world. Exceeds the complexity of the previous ones, because we have to determine the minor displacement stars in the sky (the center of mass of a planetary system often is "inside" the star itself), even though the displacement of the Earth's rotation around the sun, used to measure the parallax of stars allow any precision only measure distance , the stars within our galaxy.
Advantages: can detect planets that are far away from their stars; along with direct observation can detect planets orbit of rotation perpendicular to the observer. ***
Disadvantages: can detect planets that are orbiting perpendicular observer (or close to them); Range is limited by the ability to detect the angular rotation of the star.
The method of gravitational microlensing

The method is based on the fact that the light is deflected by gravity, and if on the way between us and some other star will star with a planetary system, it will collect the light of a distant star like a huge lens. Initially this method was proposed to search for black holes - that can not be detected by direct observations, if a black hole falls of significant amounts of the substance, or if the black hole is at the last stage of evaporation (that black holes formed by the collapse of stars very long process - the account goes on tens of billions of years). Now, this method is mainly used to search for traces of dark matter, but also allows you to simultaneously open and the planet.
That this method was discovered the most distant currently known exoplanet - OGLE-2005-BLG-390L, where OGLE means "optical gravitational lensing experiment on».
Advantages: allows you to open the world at very faint stars down to the individual planets, found themselves far away from the star.
Disadvantages: as the transit method, requires precise alignment of the three bodies in a line - a distant star - a star with a planetary system - the Earth, and for this reason does not allow to open a significant number of planets.
Direct observation

Direct Photo exoplanets HD95086 b, made with the help of ground-based telescope with adaptive optics VLT

Photo planetary system HR 8799, made 5, 1 meter Hale telescope at Palomar obseravtorii, although it is not among the largest at the moment, but it allows a well to assess the problems that are associated with the direct study of the planets - they are barely visible in the background noise of the substance the filling star system noise and invested the Earth's atmosphere.
The method itself speaks for itself. To implement it in the focus of the telescope is placed a small disk obscures the star itself, thus becoming visible planets surrounding this star. If it turns out well enough to isolate the light coming from the planet itself, then attach to the knowledge of the light coming from the star itself (that which falls on the surface of the planet), you can judge the material that makes up this planet. Other methods allow us to judge the composition of the planet's only indirectly, by its density and have high accuracy of predictions.
Advantages of brilliance to determine the ratio of the albedo / area of the illuminated surface, on spectral analysis - composition of the atmosphere and the surface (the other methods do not allow to measure these parameters).
Disadvantages: Requires telescopes larger than the other methods (to observe the required telescope "sees" a star for several magnitudes less); for close to their planets luminaries limitation becomes resolution (which is solved by using spaced telescopes), ground-based telescopes to direct search for planets is even more of a problem than for space (partly solved by adaptive optics).
As can be seen from this description - no one method does not allow to detect any orbits of any planet (except for the method of direct observation, if you have a telescope, practically infinite size, of course). Each method complements the other, more than that - they are usually shared to determine such parameters that define a single method would not do. Say Transit and Doppler method allows to measure the area and mass of the planet, respectively, and these parameters - the density, and the force of gravity for this planet.

The list of potentially habitable planets from the University of Puerto Rico in the town of Arecibo (University of Puerto Rico at Arecibo)
At the moment we know nothing of the 31st planet is in the habitable zone, all of them have a mass close to the Earth, or more of it. This is only the imperfection of our technology - a heavy object can be seen from great distances than light. With the improvement of our technology will begin the discovery of planets similar to Earth in size, or less than in existing planetary systems around nearby stars, and who has not yet found its planets. In this heavy planet will not stop opening - a zone of detection will move on.
Now a lot of the largest telescopes used to search for extrasolar planets (along with other research, of course), because of the constant growth in the complexity of astronomical research today many telescopes are used together to provide the benefits of interference - these are the Keck Observatory in Hawaii, much more Telescope (VLT) Paranal Observatory in Chile and the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) in Arizona.
The first specialized for this purpose was the Space Telescope "Kepler" and gave his specialty fruit - three years of his work he has allowed to open more than a thousand planets, and its data continue to be used for the discovery of planets more than two years. Who can form a certain "break", when all the data will be processed by Kepler, and his successor - «Tess» will be launched only in 2017 and will not open a large number of exoplanets existing telescopes.
A significant breakthrough in this, and many other areas of astronomy with the planned launch of the Space Telescope "James Webb", scheduled for the end of 2018 year. It is not intended solely for the purposes of the search for extrasolar planets, and will be launched to replace the "Hubble" - but it will be enough opportunities for significant progress in the search for extrasolar planets in general, and planets like Earth in particular.
Future large telescopes - giant Magelanov Telescope (GMT), Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) and the European Extremely Large Telescope (E-ELT) will be commensurate with the possibilities, "James Webb" and E-ELT - almost all its surpass. The last two of the telescope will be built close to the VLT and the Keck Observatory, respectively, this is due to the favorable conditions for observations that are difficult to get in some other places. These telescopes will open a lot of new exoplanets, but more importantly - expand the bottom bracket of their discovery, which will find a much more Earth-like planets, and the planets much smaller than ours, until the discovery of extrasolar planets have moons.
* Assessment of the advantages and disadvantages of methods based on the total of the method, highly specialized telescopes can be "sharpened" under a certain method, and not be able to use some other methods do.
** Technical difficulties in this area is almost solved, and we ran into a "theoretical ceiling" of these methods - the problems associated with the fact that the stars are not static entities, they are a kind of "breathe", say our sun has pronounced 11 year cycle, and several periods of more and less than this, which have no such constancy. It is these fluctuations interfere with the measurements - at some point, the level of signal / noise ratio becomes so small that the effect of the rotation of the planet becomes impossible to isolate, with arbitrarily good telescope.
*** Parallel and perpendicular to the orbits of the planets are shown in the shortcomings due to the fact that they essentially limit the number of possible orbits, which can detect the planet to less than 50%. The advantage - due to the fact that the planet orbits perpendicular to the observer are capable of detecting only two methods of all.
For articles used photos wikipedia.org and subsection site JPL NASA , devoted to the subject. And list of potentially habitable planets from the University of Puerto Rico in the town of Arecibo.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/263018/
Delivery of furniture Kiev transportation of goods Kiev transport furniture Kiev
Physicists have put forward a new theory to explain the lack of observations of dark matter on Earth