145
Bioengineers move closer to creating poppy-free opioid painkillers
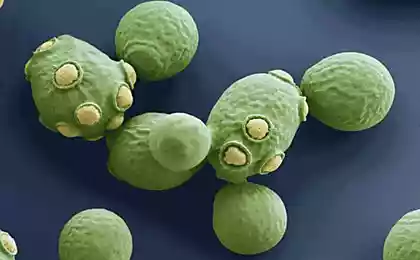
Stanford bioengineers have cracked and reprogrammed the DNA of yeast, which will allow to reproduce the biochemical processes of creating drugs based on opium without poppy.
Professor Christina Smolke said: We are now very close to replication of the entire opioid production process in a way that eliminates the need to grow poppy and allows us to produce the necessary drugs.
Opioid molecules are complex three-dimensional objects. In nature, they are located inside the poppy. Since yeast cells do not have such complex structures and tissues, biotechnologies have decided to recreate the poppy equivalent as the “chemical neighborhood” inside bioengineered yeast cells.
According to the developers, it takes several more years to refine the latest steps in the laboratory and expand the process to produce large batches of bioengineered opioids that are pharmacologically identical to today’s drugs, the path of which begins in the field and ends in factories.
“This will allow us to create a reliable supply of essential medicines in a way that does not depend on good or bad yields. We will have more sustainable, cost-effective and safe methods of producing essential drugs.”
Source: nauka24news.ru/
Professor Christina Smolke said: We are now very close to replication of the entire opioid production process in a way that eliminates the need to grow poppy and allows us to produce the necessary drugs.
Opioid molecules are complex three-dimensional objects. In nature, they are located inside the poppy. Since yeast cells do not have such complex structures and tissues, biotechnologies have decided to recreate the poppy equivalent as the “chemical neighborhood” inside bioengineered yeast cells.
According to the developers, it takes several more years to refine the latest steps in the laboratory and expand the process to produce large batches of bioengineered opioids that are pharmacologically identical to today’s drugs, the path of which begins in the field and ends in factories.
“This will allow us to create a reliable supply of essential medicines in a way that does not depend on good or bad yields. We will have more sustainable, cost-effective and safe methods of producing essential drugs.”
Source: nauka24news.ru/
Eco-design as a direction in the interior of modern cities
10 examples of preserving humanity in the face of danger