515
Nanoparticles can be effective in treating broken bones
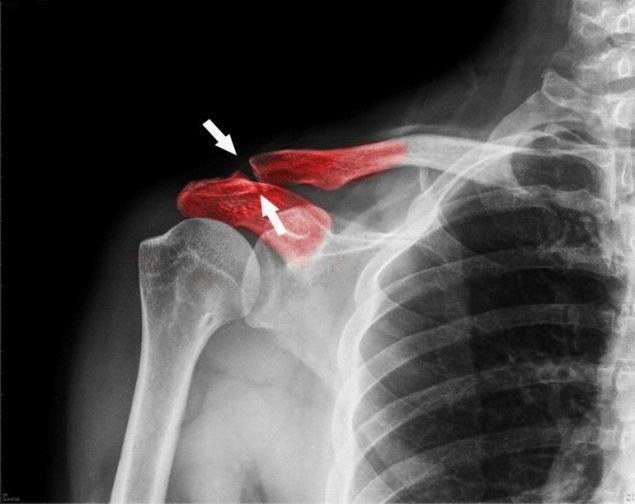
Fractures probably are not the most terrible injuries — in the world there are many diseases and injuries are terrible, but it's definitely one of the most painful tests, which are very common in people's lives. It is not surprising that science and medicine are trying to find and develop more effective ways not only to prevent but also more effectively treat their consequences.
One of the latest scientific advances relating to the treatment of fractures was proposed by the scientific staff of the British universities of Keele and Nottingham, who created the technique, lecheniia of bone fractures with the use of nanotechnology.
Unfortunately, the science is not yet able to make a real and multi-function nanites/nanobots that are common in works of fiction and movies, but scientists have mastered the methods of creating nanoparticles. And that nanoparticles are a key link in the new proposed method of treatment.
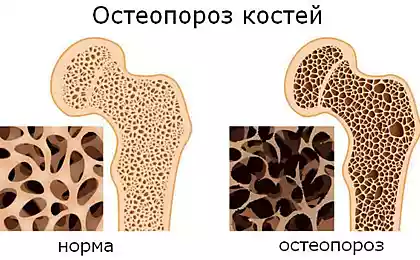
Fracture of the bone tissue often does not seem to be a daunting task for the treatment. It is enough to lock the two parts of the fracture what is bandage or a cast and wait a couple of months, while the fabric itself will not stick. However, the cases of fragmentation of the bones already look a much more complex task for physicians. The problem of treatment of such fractures may lie in the fact that some part of our Tala simply impossible to put a cast on. And it is in such cases often apply the method of osteoplasty or bone graft.
When osteoplasty is usually removed the affected area of bone (or bones in General) and replaced by new bone tissue, or the whole bone taken from a donor or from the recipient (the victim). After the transplant, the new bone, a person needs to undergo physical rehabilitation exercise, in which new bone or bone tissue survives, but the body triggers various biochemical processes, restoring nerve signals, releasing the right hormones, starting the process of cell regeneration and growth of tissue, which eventually leads to healing of the affected area of the skeleton.
And yet, a transplant of bone is an incredibly painful, invasive (surgical) procedure, so the doctors and scientists are looking for ways to find alternative methods of solving the issue associated with fractures and their treatment. One of these alternatives offers the use of magnetized nanoparticles.
Scientists from the universities of Keele and Nottingham believe that a protein coated nanoparticles can literally by magnets to send to the site of injury to those stimulated stem cells. This method not just will increase the effectiveness of a bone graft, but also provide an alternative method of treatment in cases when bone disorders and other pathologies allow to avoid a full transplant of bone.
But the most interesting part of the new method developed by scientists from the British universities is that it does not require surgery. Nanoparticles will be introduced into the body through the normal injection.
Source: hi-news.ru