655
The asymmetry in the structure of the human body
The importance of the concept of "asymmetry" was realized at the end of XX century due to its importance in science in General and biology in particular. The data of the various Sciences suggests that the ideas of symmetry and its violations acquire features of the principle, i.e. the fundamental theoretical ideas needed to explain a variety of phenomena. This principle is becoming increasingly important in scientific knowledge.
Definition of symmetry (compliance, proportionality, harmony, homogeneity) and asymmetry (disparity, disproportion, heterogeneity, disproportion), based on enumeration of object properties, there are other definitions that emphasize not only the essential properties, but the relationship between them.
Strictly speaking, the "symmetry is a category, indicating the existence and formation of identical moments in certain conditions and in certain relations between different and opposing States of the phenomena of the world, asymmetry is the category that refers to the existence and formation in certain conditions and relations of differences and opposites within unity, identity, wholeness of the phenomena of the world."
As you know, people on the external structure is a mirror symmetrical right-left object of nature. However, on closer examination it appears that the axial symmetry of the human body is largely conditional — the left half of the face is not similar to the right, right hand on left, left foot on the right, etc.
If the asymmetry of the face gives each of us individual uniqueness and charm, the different hand, usually does not cause any trouble, the asymmetry in the zone of the lower extremities in the conditions of bipedalism is of paramount importance. In this literature review consider the common structural and functional discrepancies in biokinematic chain spine-pelvis-lower limb, which include a functional inequality of the length of the support limbs, reduced pollutes and twisted pelvis.
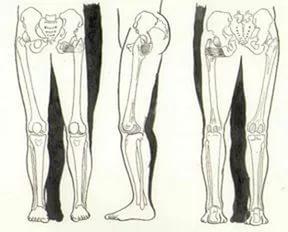
The functional difference of length of lower extremities Inequality of leg length, in contrast to the common perception, is a widespread phenomenon. The vast majority of people can easily verify this, we need only to consider carefully our own image in the mirror and pay attention to their clothes and shoes. Functional difference of length of lower extremities, not giving it, as a rule, no value, daily facing many professions, far from medicine.
First and foremost is the cutters and the tailors manufacture the clothing or customized ready industrial designs "on the figure." The cutters are well aware of the fact that when removing the eleventh measurements (skirt length) is removed on the side from Tapia to the desired length of the skirt — and twelfth measurements (pants length) is removed on the side from the waist to the heel of the absolute values of these measurements to the left and right have the same customer is rarely equal to each other. Industrial garments are manufactured to perfectly symmetrical patterns with the use of computers, and if the garment requires fitting to 'fit', therefore the figure is not symmetrical.
Cobblers, changing worn out soles and heels, face different degree of wear of the left and right Shoe in one pair of shoes. Monitoring of A. F. Brandt, footwear, sewn "two strictly symmetrical pads, sits tighter on one than on the other foot". People lost in an unfamiliar area and moving forward, describes a circle, returning to the starting point. This is the manifestation of the functional difference of length of lower extremities.
The first physician to call attention to the prevalence of inequality of length of the lower limbs, was a German physician Eva Braun. An important observation made in 1926 and later received his artistic development. So, Rush W. A. and Sleiner ON when x-ray measurement of leg length, 1000 demobilized from the army soldiers found the same length as the foot in 23% of cases, the remaining 77% of the surveyed observed asymmetry, the difference in leg length was in the range of 0.6–0.7 cm, According to P. J. R. Nichols, when examining 72 healthy subjects, 7% of them difference leg length exceeded 1.3 cm W. M. Pearson et al. x-ray examination of 1446 schoolchildren aged 5 to 17 years found that in 80% of patients the difference in leg length was not less than 0,16 cm, and 3.4% from 1.3 cm or more. The author of the examination of 142 students aged 7 to 14 different pet foot length was detected in 93 (65,5%) children, with shortening of the right leg in 41 (44%) left 52 (56%). The largest functional difference of length of lower extremities (FRANK) ranged from 2.4 to 30 mm.
Here we should clarify what the author understands under FRANK.
The functional difference of length of lower extremities is the presence of a difference in leg length, leading to the oblique setting of pelvic ring, regardless of the causes of this difference. The functional difference of length of lower extremities should be distinguished from "true" or anatomical differences, as FRANK is a broader concept. It must be emphasized that FRANK can meet at the same and at different anatomical leg length. For example, the presence of FRANK in the absence of anatomical difference observed in adductor or abductor contractures of hip, unilateral reduction of the height of the arch of the foot, paresis of the muscles of the limbs, etc. on the other hand, the presence of anatomical differences, which, within certain limits, can be compensated for the functional mechanisms of elongation are short and (or) shortening of the long legs. Failing full payment of the anatomical difference of the functional mechanisms of the missing value leads to the oblique installation of the pelvic ring and is FRANK.
Let us consider the functional mechanisms of redress inequality of length of the supporting limbs. Zachow S. D. identifies the following types of compensation:
The second compensatory adaptation of musculoskeletal system by shortening the legs is an equinus foot position. The degree of equinus is in direct dependence on extent of shortening and is in the range of 110-180°. When walking on foot back avenirovna her Department is not involved in the loading, anterior and descended like a continuation of the tibia, and this is achieved by a functional lengthening of the limb. The body weight of the patient by relying completely falls on bones forefoot. In these circumstances, the pelvis is approaching the horizontal position. This type of compensation is possible with the shortening of 6 cm.
If shortening of more than 6 cm compensation is accomplished by combining tilting of the pelvis and equinus of the foot. When such a combination is not enough, patients seeking to equalize the length of the legs, artificially shorten the long limb. This is achieved by active closure of hip and knee joints of long leg in flexion.
If shortening of more than 12 cm, the patient is not able to compensate for the difference in leg length. A short leg may not participate in the load. Movement is possible only in the orthopedic device with dual track or on crutches.
On the trailing installation of a basin when the inequality of the length of the lower limbs attention of many authors, which leads to the conclusion that it is always in the presence of FRANK occurs oblique setting of pelvic ring relative to the bearing and the upper half of the body, and the larger the value of FRANC, the greater the tilt of the pelvis. So, Hull L. I. and Tardieu found that the person with the growth of 167 cm, the pelvis tilt 10° is observed in the shortening of the leg by 3.5 cm, tilt is 20° with a shortening of 6.8 cm, 30° — the difference in leg length equal to 10 cm.
It should be noted that the probability of the presence FRANK increases with age. Thus, according to Klein, K. K. was among a group of primary school pupils feet of different lengths were detected in 75%, and among a group of high school students, 92%. The unadjusted difference tends to increase with age. It is interesting to note that adjusted in childhood the difference in the length of the legs decreases with age [48,62].
According Redler I., in 7 out of 11 children aged from 1,5 to 15 years difference in the length of the legs equal to 1.3–1.9 cm, disappeared after wearing special shoes lining the length of the legs. within 3-7 months. Further 3-year study conducted by Klein KK, Redler I., and C. L. Lowman among students in elementary, middle and high schools, confirmed the need for corrective equalization of leg length in childhood and adolescence by a temporary rise of the compensatory heel short legs. Stimulated by such a correction mechanism, which provides the accelerated growth short legs and the alignment length of the two legs of the children and young people, remains, according to the authors, unknown. A comprehensive answer to this question is contained in the works of A. T. Brusco and 8.P. Omelchuk. Protsenko V. N. (Something that accelerates the bone growth is more stimulated by foot — it is just a healthy physiological response of the body. I ask to pay attention to how cleverly functional shortening we have changed the anatomical and, consequently, piled correction methods).
It should be noted another important pattern — that most authors who have studied the disparity of the length of the support limb, note the development of lateral curvatures of the spine directed towards short leg and causing compensatory scoliosis. According to W. W. Pearson the upper half of the body compensates for the different lengths of the legs mainly due to the curvatures of the spine without reduction of asymmetry.
A detailed consideration of the impact of FRANK and other asymmetries of the structure biokinematic chain pelvis — lower limb on the formation of scoliotic deformities of the spine is beyond the scope of this literature review due to the significant amount of information regarding this topic.
Reduced polutes Reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis — a much more rare phenomenon than the presence FRANK. Thus, according to Lowman C. L. at 20-30% of all observed orthopedic bolnichnyi reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis and this bone anomaly was found both separately and together with the short leg usually on the same side. The patient with a reduced vertical size of the pelvis and a short leg on the same side of the pelvis is tilted in the direction of shortening in a standing position and in sitting position, accompanied by the same symptoms in both of these positions. With a reduced polutes as well as the presence of FRANK, the upper half of the body responds education compensatory scoliosis.
Reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis is much more common than FRANK overlooked as a cause of spinal curvature. Patients with reduced poluchasa sitting, leaning downward. Often they prefer to sit with his legs than is achieved by lifting the reduced half of the pelvis.
A reduction of one half of the pelvis is important in obstetrics, which explains the great interest of the obstetricians and gynaecologists to consider bone abnormalities. In the literature on the diagnosis of this anomaly is called kosorinova, compostainer, deformed pelvis or twisting of half of the pelvis. Despite the different terms, they essentially represent the same deformation of the pelvic ring — the reduction of one half, or reduced pautas. Chain diagnosis reduce one half of the pelvis in 1927 J. Koerner proposed to measure a lateral conjugate — distance between the front upper and rear upper spines of the Ilium of one side. Normal lateral conjugate of 14.5 cm or more, reduce its size less than 13.5 cm, according to the author, indicates a decrease in the corresponding half of the pelvis.
Important side conjugates in the diagnosis of reduced poluchasa was subsequently confirmed by several researchers. Kalganova R. I. on the basis of his own research mark irregular shape of the rhombus of Michaelis in the presence of colouring and deformed pelvis. It should be noted an interesting fact — in the literature in obstetrics, some authors pay attention to the combination of colouring pelvis with scoliotic deformations of the vertebral column. So, P. N. Demidkin and A. I. Shnirelman, considering the anomalies of the pelvis when pathological changes in other parts of the skeleton, noted that women suffering from scoliosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine is much more common semi-asymmetric shape of the pelvic ring. In scoliosis of the thoracic spine changes the shape of the pelvis are much rarer than in the scoliotic deformation of the lumbar spine.
It must be emphasized that the methods of diagnosis of reduce one half of the pelvic ring, proposed and adopted by obstetricians in obstetric practice, is unacceptable for use in orthopedics because they do not allow to determine the amount of reduction of vertical size of one half of the pelvis, which are important for the formation of scoliotic deformities of the spine, mentioned above, and other goals and objectives — define the mode of delivery and labor management plan.
In orthopedics if you suspect the presence of reduced poluchasa the patient is examined in sitting position on a hard, flat surface back to the doctor. Foot patient should rely on the floor or stand so that the patient could freely push the fingers of the hands between the thighs and the front edge of the seat. In this position, the patient sits leaning on both buttock bones the sciatic. During the inspection special attention is paid on the mutual position of the posterior superior iliac spines, the crests of the iliac bones, scoliosis and shoulder girdle tilting. If these bony landmarks are located on one side of the pelvis lower than on the opposite, there is a compensatory scoliosis and tilting of the shoulder girdle, which, according to Bourdillon v. F., indicates the presence of reduced poluchasa.
However, the survey results can be distorted if the left and right halves of the pelvis rotated about the front transverse axis of the sacrum. In detail such a pathological setting of pelvic ring, twisting of the pelvis is explored in the next section. In order to avoid misdiagnosis reduced poluchasa required to perform additional palpation examination — thumbs doctor fixes the posterior superior iliac spine, and putting his palms crests of the iliac bones, index finger determines the position of the front upper iliac spines. When one side of the front upper, rear upper iliac axis and the crest of the Ilium located lower than the opposite, it indicates the presence of reduced poluchasa. The above-described diagnostic method has a significant drawback — it is not possible to quantify the value of reducing one half of the pelvis and, consequently, to make accurate orthopedic correction.
Twisted pelvis For understanding the mechanism of twisting of the pelvis describe the features of the sacroiliac joints, which are of primary importance for the functioning of the pelvic ring as part of the musculoskeletal system of man.
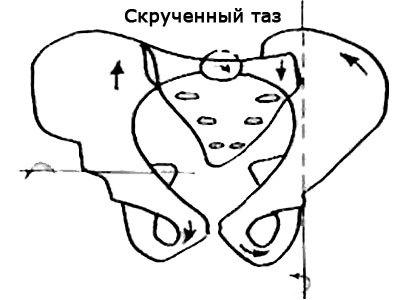
Anatomically the sacral wedge inserted between the iliac wings and narrowed in the caudal and doralina directions. The dorsal constriction is noticeable only in the upper part of the sacrum at the level of the SI-SII. Discongruence articular surface on the Ilium already long, and the sacrum is shorter and wider. About the middle of the iliac surface is a large tubercle, corresponding to the fossa of the sacrum at the level of SII.
Particularly important, but until now controversial is the question of mobility in the sacroiliac joints. The sacroiliac joint, despite their anatomical diversity — a true joint, with articular cartilage, synovial membrane and the articular capsule. The peculiarity of this joint is not only in the anatomical peculiarity of the articular surfaces, but in the powerful ligaments, which strengthens the joint capsule and significantly reduces the mobility of the joint. There are no muscles that specifically would lead to the movement of the joint. From the clinical point of view desirable at the minimum possible movement. However, from a biological perspective, it is difficult to imagine a true joint without function.
The most significant movement in the sacroiliac joint, according to most authors, is rotation about the front transverse axis of the sacrum in the form of the sternocleidomastoid movement of nutation. The axis of motion passes through the said protuberance at the level of SII. This movement is familiar to gynecologists in the generic act. Weisl H. found that the true conjugate as a result of nutation of the sacrum changes its length of 5.6 mm. These data were confirmed Colachis, S. C. et al. Mennell J. proved the nutation of the sacrum in the x-ray study of the pelvis in different positions with the use of lead markers, strengthens the skin over the respective offset points.
According Duckworth J. W. A., with nutation of sacrum ventral is the divergence of the pubic bones at the symphysis, in dorsal nutation — their approach. Nutation may precede movement of the spine up and the top down while walking. It is, in the opinion of the author, and unilaterally in moving back both sacroiliac joints. On the side of the supporting leg, the pelvis bends under the load of the spine with respect to the fixed here of the Ilium forward and downward, i.e., the pelvic bone is relatively shifted backward. This (moving back) mechanism may be the cause of sacroiliac displacement or more corresponds to the twisting of the pelvis.
Priority in the discovery and further detailed study of the twisting of the pelvis belongs to A. Cramer. Clinical data the following twisted pelvis: posterior superior iliac spine is located on one side lower than the other. The same data gives paravertebral probing the posterior edge of the Ilium.
Ventral, however, created the opposite situation: on the side of the low back upper spine front upper spine is higher than on the opposite side, and Vice versa.
As well as front iliac spine located ventral divisions of the crests of the iliac bones. At first glance the impression is that one Ilium is rotated relative to the other around the front transverse axis. For palpation in this study it does not matter whether there was a relative rotation, for example, left Ilium ago associated setback of the sacrum or with a relative rotation of the right Ilium forward, which means the same thing, accompanying the displacement of the sacrum forward.
A. Cramer sees the primary process in asymmetric nutation and rotation of the sacrum relative to both halves of the pelvis. If you test one Ilium rotated posteriorly clearly, the sacrum tilts forward and down (ventrocaudal); on the other hand, it is respectively shifted upwards and backwards (dorsomedial) relative to the Ilium. Thus, there is a kind of breeding with a relative rotation of the sides of the pelvis on the side of the slope of the sacrum in the direction ventrocaudal half of the pelvis is rotated outward about its longitudinal axis, on the opposite side it rotates relative to the front axis passing through the acetabulum. In the symphysis occurs only relative breeding with the asymmetric position of the pubic bones.
It should be noted the fact that, in details describing the mechanism of twisting of the pelvis, A. Cramer does not indicate the root cause of the asymmetric nutation of the sacrum, because the sacroiliac joints, as mentioned above, have strong ligaments and lack of muscles specifically resulting in the joints in motion. Hence, the reason of asymmetric nutation need to look at the nearby large joints with powerful muscle support. It is primarily the hip joints.
It is appropriate to recall the widespread asymmetry of the human skeleton — functional difference in the length of the lower extremities. In fact, the movement is in a vertical position in the limbs of different length, creates the torque transmitted through vertline basin on the structure of the pelvic ring, which may be the root cause of asymmetric nutation of the sacrum, leading to twisting of the pelvis. In this context, the twisting of the pelvis can be considered as compensatory-adaptive mechanism of musculoskeletal system, aims to compensate for the functional difference of length of lower extremities in the conditions of bipedal locomotion.
However, twisting of the pelvis leads to static violations, as in this situation, the lumbar spine is located at an angle to the axis of the sacrum, which serves as a kind of Foundation for all the overlying parts of the spine. This inevitably leads to a compensatory scoliosis, at least in the lumbar spinal column, to maintain equilibrium of the body in an upright position.
K. Levit et al. indicate that the twisting of the pelvis persists orthopedic correction and requires special treatment by the method of performing manual therapy techniques.
In this connection it should be emphasized that ignoring the presence of a twisted pelvis makes a significant error in the measurement of the functional difference of length of lower extremities until about diagnosis. published
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: healthy-back.livejournal.com/239909.html
Definition of symmetry (compliance, proportionality, harmony, homogeneity) and asymmetry (disparity, disproportion, heterogeneity, disproportion), based on enumeration of object properties, there are other definitions that emphasize not only the essential properties, but the relationship between them.

Strictly speaking, the "symmetry is a category, indicating the existence and formation of identical moments in certain conditions and in certain relations between different and opposing States of the phenomena of the world, asymmetry is the category that refers to the existence and formation in certain conditions and relations of differences and opposites within unity, identity, wholeness of the phenomena of the world."
As you know, people on the external structure is a mirror symmetrical right-left object of nature. However, on closer examination it appears that the axial symmetry of the human body is largely conditional — the left half of the face is not similar to the right, right hand on left, left foot on the right, etc.
If the asymmetry of the face gives each of us individual uniqueness and charm, the different hand, usually does not cause any trouble, the asymmetry in the zone of the lower extremities in the conditions of bipedalism is of paramount importance. In this literature review consider the common structural and functional discrepancies in biokinematic chain spine-pelvis-lower limb, which include a functional inequality of the length of the support limbs, reduced pollutes and twisted pelvis.
The functional difference of length of lower extremities Inequality of leg length, in contrast to the common perception, is a widespread phenomenon. The vast majority of people can easily verify this, we need only to consider carefully our own image in the mirror and pay attention to their clothes and shoes. Functional difference of length of lower extremities, not giving it, as a rule, no value, daily facing many professions, far from medicine.
First and foremost is the cutters and the tailors manufacture the clothing or customized ready industrial designs "on the figure." The cutters are well aware of the fact that when removing the eleventh measurements (skirt length) is removed on the side from Tapia to the desired length of the skirt — and twelfth measurements (pants length) is removed on the side from the waist to the heel of the absolute values of these measurements to the left and right have the same customer is rarely equal to each other. Industrial garments are manufactured to perfectly symmetrical patterns with the use of computers, and if the garment requires fitting to 'fit', therefore the figure is not symmetrical.
Cobblers, changing worn out soles and heels, face different degree of wear of the left and right Shoe in one pair of shoes. Monitoring of A. F. Brandt, footwear, sewn "two strictly symmetrical pads, sits tighter on one than on the other foot". People lost in an unfamiliar area and moving forward, describes a circle, returning to the starting point. This is the manifestation of the functional difference of length of lower extremities.
The first physician to call attention to the prevalence of inequality of length of the lower limbs, was a German physician Eva Braun. An important observation made in 1926 and later received his artistic development. So, Rush W. A. and Sleiner ON when x-ray measurement of leg length, 1000 demobilized from the army soldiers found the same length as the foot in 23% of cases, the remaining 77% of the surveyed observed asymmetry, the difference in leg length was in the range of 0.6–0.7 cm, According to P. J. R. Nichols, when examining 72 healthy subjects, 7% of them difference leg length exceeded 1.3 cm W. M. Pearson et al. x-ray examination of 1446 schoolchildren aged 5 to 17 years found that in 80% of patients the difference in leg length was not less than 0,16 cm, and 3.4% from 1.3 cm or more. The author of the examination of 142 students aged 7 to 14 different pet foot length was detected in 93 (65,5%) children, with shortening of the right leg in 41 (44%) left 52 (56%). The largest functional difference of length of lower extremities (FRANK) ranged from 2.4 to 30 mm.
Here we should clarify what the author understands under FRANK.
The functional difference of length of lower extremities is the presence of a difference in leg length, leading to the oblique setting of pelvic ring, regardless of the causes of this difference. The functional difference of length of lower extremities should be distinguished from "true" or anatomical differences, as FRANK is a broader concept. It must be emphasized that FRANK can meet at the same and at different anatomical leg length. For example, the presence of FRANK in the absence of anatomical difference observed in adductor or abductor contractures of hip, unilateral reduction of the height of the arch of the foot, paresis of the muscles of the limbs, etc. on the other hand, the presence of anatomical differences, which, within certain limits, can be compensated for the functional mechanisms of elongation are short and (or) shortening of the long legs. Failing full payment of the anatomical difference of the functional mechanisms of the missing value leads to the oblique installation of the pelvic ring and is FRANK.
Let us consider the functional mechanisms of redress inequality of length of the supporting limbs. Zachow S. D. identifies the following types of compensation:
- the tilt of the pelvis in the direction of the short legs,
- equinus foot
- bending over long legs in knee and hip joints, as well as
- the combination of these types of compensation.
The second compensatory adaptation of musculoskeletal system by shortening the legs is an equinus foot position. The degree of equinus is in direct dependence on extent of shortening and is in the range of 110-180°. When walking on foot back avenirovna her Department is not involved in the loading, anterior and descended like a continuation of the tibia, and this is achieved by a functional lengthening of the limb. The body weight of the patient by relying completely falls on bones forefoot. In these circumstances, the pelvis is approaching the horizontal position. This type of compensation is possible with the shortening of 6 cm.
If shortening of more than 6 cm compensation is accomplished by combining tilting of the pelvis and equinus of the foot. When such a combination is not enough, patients seeking to equalize the length of the legs, artificially shorten the long limb. This is achieved by active closure of hip and knee joints of long leg in flexion.
If shortening of more than 12 cm, the patient is not able to compensate for the difference in leg length. A short leg may not participate in the load. Movement is possible only in the orthopedic device with dual track or on crutches.
On the trailing installation of a basin when the inequality of the length of the lower limbs attention of many authors, which leads to the conclusion that it is always in the presence of FRANK occurs oblique setting of pelvic ring relative to the bearing and the upper half of the body, and the larger the value of FRANC, the greater the tilt of the pelvis. So, Hull L. I. and Tardieu found that the person with the growth of 167 cm, the pelvis tilt 10° is observed in the shortening of the leg by 3.5 cm, tilt is 20° with a shortening of 6.8 cm, 30° — the difference in leg length equal to 10 cm.
It should be noted that the probability of the presence FRANK increases with age. Thus, according to Klein, K. K. was among a group of primary school pupils feet of different lengths were detected in 75%, and among a group of high school students, 92%. The unadjusted difference tends to increase with age. It is interesting to note that adjusted in childhood the difference in the length of the legs decreases with age [48,62].
According Redler I., in 7 out of 11 children aged from 1,5 to 15 years difference in the length of the legs equal to 1.3–1.9 cm, disappeared after wearing special shoes lining the length of the legs. within 3-7 months. Further 3-year study conducted by Klein KK, Redler I., and C. L. Lowman among students in elementary, middle and high schools, confirmed the need for corrective equalization of leg length in childhood and adolescence by a temporary rise of the compensatory heel short legs. Stimulated by such a correction mechanism, which provides the accelerated growth short legs and the alignment length of the two legs of the children and young people, remains, according to the authors, unknown. A comprehensive answer to this question is contained in the works of A. T. Brusco and 8.P. Omelchuk. Protsenko V. N. (Something that accelerates the bone growth is more stimulated by foot — it is just a healthy physiological response of the body. I ask to pay attention to how cleverly functional shortening we have changed the anatomical and, consequently, piled correction methods).
It should be noted another important pattern — that most authors who have studied the disparity of the length of the support limb, note the development of lateral curvatures of the spine directed towards short leg and causing compensatory scoliosis. According to W. W. Pearson the upper half of the body compensates for the different lengths of the legs mainly due to the curvatures of the spine without reduction of asymmetry.
A detailed consideration of the impact of FRANK and other asymmetries of the structure biokinematic chain pelvis — lower limb on the formation of scoliotic deformities of the spine is beyond the scope of this literature review due to the significant amount of information regarding this topic.
Reduced polutes Reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis — a much more rare phenomenon than the presence FRANK. Thus, according to Lowman C. L. at 20-30% of all observed orthopedic bolnichnyi reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis and this bone anomaly was found both separately and together with the short leg usually on the same side. The patient with a reduced vertical size of the pelvis and a short leg on the same side of the pelvis is tilted in the direction of shortening in a standing position and in sitting position, accompanied by the same symptoms in both of these positions. With a reduced polutes as well as the presence of FRANK, the upper half of the body responds education compensatory scoliosis.

Reduced the vertical size of one half of the pelvis is much more common than FRANK overlooked as a cause of spinal curvature. Patients with reduced poluchasa sitting, leaning downward. Often they prefer to sit with his legs than is achieved by lifting the reduced half of the pelvis.
A reduction of one half of the pelvis is important in obstetrics, which explains the great interest of the obstetricians and gynaecologists to consider bone abnormalities. In the literature on the diagnosis of this anomaly is called kosorinova, compostainer, deformed pelvis or twisting of half of the pelvis. Despite the different terms, they essentially represent the same deformation of the pelvic ring — the reduction of one half, or reduced pautas. Chain diagnosis reduce one half of the pelvis in 1927 J. Koerner proposed to measure a lateral conjugate — distance between the front upper and rear upper spines of the Ilium of one side. Normal lateral conjugate of 14.5 cm or more, reduce its size less than 13.5 cm, according to the author, indicates a decrease in the corresponding half of the pelvis.
Important side conjugates in the diagnosis of reduced poluchasa was subsequently confirmed by several researchers. Kalganova R. I. on the basis of his own research mark irregular shape of the rhombus of Michaelis in the presence of colouring and deformed pelvis. It should be noted an interesting fact — in the literature in obstetrics, some authors pay attention to the combination of colouring pelvis with scoliotic deformations of the vertebral column. So, P. N. Demidkin and A. I. Shnirelman, considering the anomalies of the pelvis when pathological changes in other parts of the skeleton, noted that women suffering from scoliosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine is much more common semi-asymmetric shape of the pelvic ring. In scoliosis of the thoracic spine changes the shape of the pelvis are much rarer than in the scoliotic deformation of the lumbar spine.
It must be emphasized that the methods of diagnosis of reduce one half of the pelvic ring, proposed and adopted by obstetricians in obstetric practice, is unacceptable for use in orthopedics because they do not allow to determine the amount of reduction of vertical size of one half of the pelvis, which are important for the formation of scoliotic deformities of the spine, mentioned above, and other goals and objectives — define the mode of delivery and labor management plan.
In orthopedics if you suspect the presence of reduced poluchasa the patient is examined in sitting position on a hard, flat surface back to the doctor. Foot patient should rely on the floor or stand so that the patient could freely push the fingers of the hands between the thighs and the front edge of the seat. In this position, the patient sits leaning on both buttock bones the sciatic. During the inspection special attention is paid on the mutual position of the posterior superior iliac spines, the crests of the iliac bones, scoliosis and shoulder girdle tilting. If these bony landmarks are located on one side of the pelvis lower than on the opposite, there is a compensatory scoliosis and tilting of the shoulder girdle, which, according to Bourdillon v. F., indicates the presence of reduced poluchasa.
However, the survey results can be distorted if the left and right halves of the pelvis rotated about the front transverse axis of the sacrum. In detail such a pathological setting of pelvic ring, twisting of the pelvis is explored in the next section. In order to avoid misdiagnosis reduced poluchasa required to perform additional palpation examination — thumbs doctor fixes the posterior superior iliac spine, and putting his palms crests of the iliac bones, index finger determines the position of the front upper iliac spines. When one side of the front upper, rear upper iliac axis and the crest of the Ilium located lower than the opposite, it indicates the presence of reduced poluchasa. The above-described diagnostic method has a significant drawback — it is not possible to quantify the value of reducing one half of the pelvis and, consequently, to make accurate orthopedic correction.
Twisted pelvis For understanding the mechanism of twisting of the pelvis describe the features of the sacroiliac joints, which are of primary importance for the functioning of the pelvic ring as part of the musculoskeletal system of man.

Anatomically the sacral wedge inserted between the iliac wings and narrowed in the caudal and doralina directions. The dorsal constriction is noticeable only in the upper part of the sacrum at the level of the SI-SII. Discongruence articular surface on the Ilium already long, and the sacrum is shorter and wider. About the middle of the iliac surface is a large tubercle, corresponding to the fossa of the sacrum at the level of SII.
Particularly important, but until now controversial is the question of mobility in the sacroiliac joints. The sacroiliac joint, despite their anatomical diversity — a true joint, with articular cartilage, synovial membrane and the articular capsule. The peculiarity of this joint is not only in the anatomical peculiarity of the articular surfaces, but in the powerful ligaments, which strengthens the joint capsule and significantly reduces the mobility of the joint. There are no muscles that specifically would lead to the movement of the joint. From the clinical point of view desirable at the minimum possible movement. However, from a biological perspective, it is difficult to imagine a true joint without function.
The most significant movement in the sacroiliac joint, according to most authors, is rotation about the front transverse axis of the sacrum in the form of the sternocleidomastoid movement of nutation. The axis of motion passes through the said protuberance at the level of SII. This movement is familiar to gynecologists in the generic act. Weisl H. found that the true conjugate as a result of nutation of the sacrum changes its length of 5.6 mm. These data were confirmed Colachis, S. C. et al. Mennell J. proved the nutation of the sacrum in the x-ray study of the pelvis in different positions with the use of lead markers, strengthens the skin over the respective offset points.
According Duckworth J. W. A., with nutation of sacrum ventral is the divergence of the pubic bones at the symphysis, in dorsal nutation — their approach. Nutation may precede movement of the spine up and the top down while walking. It is, in the opinion of the author, and unilaterally in moving back both sacroiliac joints. On the side of the supporting leg, the pelvis bends under the load of the spine with respect to the fixed here of the Ilium forward and downward, i.e., the pelvic bone is relatively shifted backward. This (moving back) mechanism may be the cause of sacroiliac displacement or more corresponds to the twisting of the pelvis.
Priority in the discovery and further detailed study of the twisting of the pelvis belongs to A. Cramer. Clinical data the following twisted pelvis: posterior superior iliac spine is located on one side lower than the other. The same data gives paravertebral probing the posterior edge of the Ilium.
Ventral, however, created the opposite situation: on the side of the low back upper spine front upper spine is higher than on the opposite side, and Vice versa.
As well as front iliac spine located ventral divisions of the crests of the iliac bones. At first glance the impression is that one Ilium is rotated relative to the other around the front transverse axis. For palpation in this study it does not matter whether there was a relative rotation, for example, left Ilium ago associated setback of the sacrum or with a relative rotation of the right Ilium forward, which means the same thing, accompanying the displacement of the sacrum forward.
A. Cramer sees the primary process in asymmetric nutation and rotation of the sacrum relative to both halves of the pelvis. If you test one Ilium rotated posteriorly clearly, the sacrum tilts forward and down (ventrocaudal); on the other hand, it is respectively shifted upwards and backwards (dorsomedial) relative to the Ilium. Thus, there is a kind of breeding with a relative rotation of the sides of the pelvis on the side of the slope of the sacrum in the direction ventrocaudal half of the pelvis is rotated outward about its longitudinal axis, on the opposite side it rotates relative to the front axis passing through the acetabulum. In the symphysis occurs only relative breeding with the asymmetric position of the pubic bones.
It should be noted the fact that, in details describing the mechanism of twisting of the pelvis, A. Cramer does not indicate the root cause of the asymmetric nutation of the sacrum, because the sacroiliac joints, as mentioned above, have strong ligaments and lack of muscles specifically resulting in the joints in motion. Hence, the reason of asymmetric nutation need to look at the nearby large joints with powerful muscle support. It is primarily the hip joints.
It is appropriate to recall the widespread asymmetry of the human skeleton — functional difference in the length of the lower extremities. In fact, the movement is in a vertical position in the limbs of different length, creates the torque transmitted through vertline basin on the structure of the pelvic ring, which may be the root cause of asymmetric nutation of the sacrum, leading to twisting of the pelvis. In this context, the twisting of the pelvis can be considered as compensatory-adaptive mechanism of musculoskeletal system, aims to compensate for the functional difference of length of lower extremities in the conditions of bipedal locomotion.
However, twisting of the pelvis leads to static violations, as in this situation, the lumbar spine is located at an angle to the axis of the sacrum, which serves as a kind of Foundation for all the overlying parts of the spine. This inevitably leads to a compensatory scoliosis, at least in the lumbar spinal column, to maintain equilibrium of the body in an upright position.
K. Levit et al. indicate that the twisting of the pelvis persists orthopedic correction and requires special treatment by the method of performing manual therapy techniques.
In this connection it should be emphasized that ignoring the presence of a twisted pelvis makes a significant error in the measurement of the functional difference of length of lower extremities until about diagnosis. published
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: healthy-back.livejournal.com/239909.html
This natural remedy is useful in diseases of the joints, rheumatism and skin diseases
To grow from seed large onion possible!