729
TMJ: How changes in one organ causes a cascade of reactions throughout the body
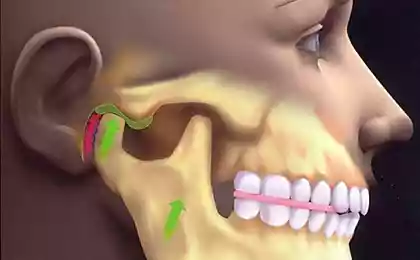
TMJ — temporomandibular joint - is the articulation point of the head of mandible and temporal bone of the skull. Between the heads and articular cavities of the temporal bones in the norm should be located the articular disc.
The articular disc has an oval shape and is held by ligaments on the articular head of the mandible in all movements in the TMJ joint, creating a damping of the opening and closing of the mouth.
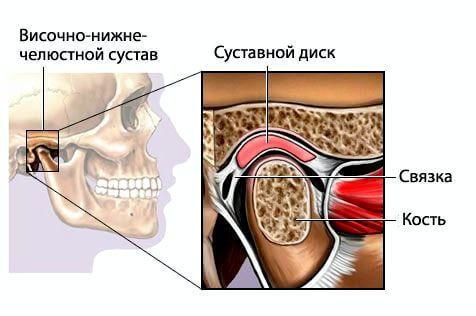
Dysfunction TMJ. Anatomy
How is a dislocated joint?
If you experience problems at the level of the teeth or bones of the skull, the lower jaw can vary its position in the temporomandibular joint, to turn around or distantsirovaniya (slide back) within the joint capsule. In this interarticular disc exposed to the pressure head of the mandible, and may be displaced forward within the joint, which leads to dislocation of the TMJ disc.
This dislocation can occur each time the opening and closing of the mouth, thus becoming chronic.
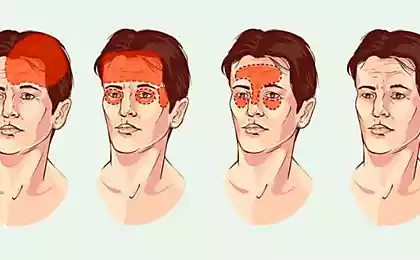
The first symptoms of a dislocated TMJ is the onset of clicking, cracking or discomfort around the ear in the joint.
The head of the mandible on one side or both is pushed into the glenoid cavity, starting to squeeze bilaminar the area of the joint, is rich in vessels and nerves, which is already protected by velinovska anterior disc. There is a pain.
What happens if you don't treat dislocation of the TMJ?
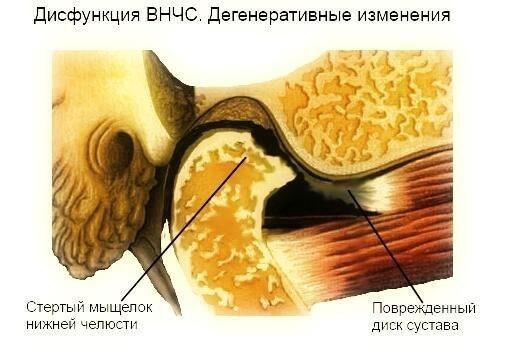
Every time You eat, talk, TMJ joint is in motion. The same thing happens when swallowing. That is, approximately every 60 seconds.
Thus, You see that this is one of the most moving and the most involved joints in the body. When the intra-articular disc dysfunction again and again subjected to luxation during movement of the joint.
The disc, if the joint doesn't heal in time, begins to deform, fragmented, erased. Ligament that holds the disc, can be broken and thinned. Next is the process of destruction of the articular surface of the head lower jaw, which will move without depreciation and damage. The clicks in this case are replaced by an unpleasant sensation of crunching "broken glass" in the joint when opening the mouth.
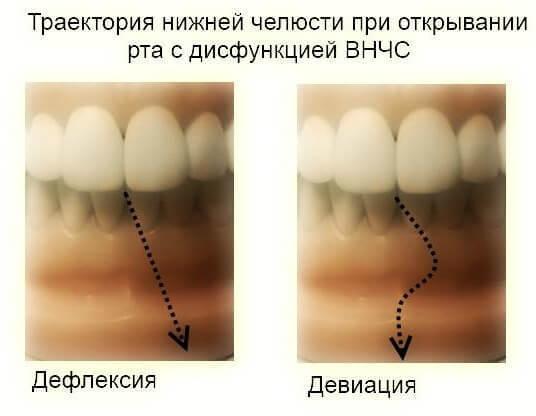
Symptoms
Thus, You see that this is one of the most moving and the most involved joints in the body. When the dysfunction, pain, clicking, intra-articular disc again and again subjected to dislocation during movement of the joint.
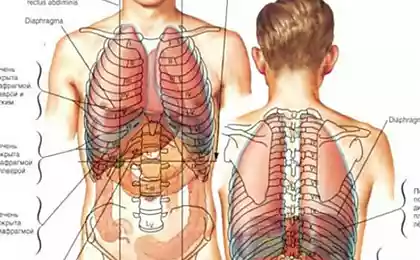
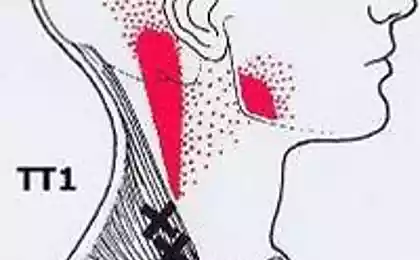
Compensatory response to injury in the joint will be the voltage of masticatory muscles to tight to fix the joint, in an attempt to limit its movement. Appear the symptom of muscle hyperconservative muscles on one or both sides. When the TMJ ceases to function normally, it affects all aspects of Your daily life and becomes a constant source of pain and discomfort. After the hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles become tense and the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the trapezius, which causes discomfort in the neck, shoulders, and gradually, throughout the spine. Externally, begins to develop scoliosis of the spine.
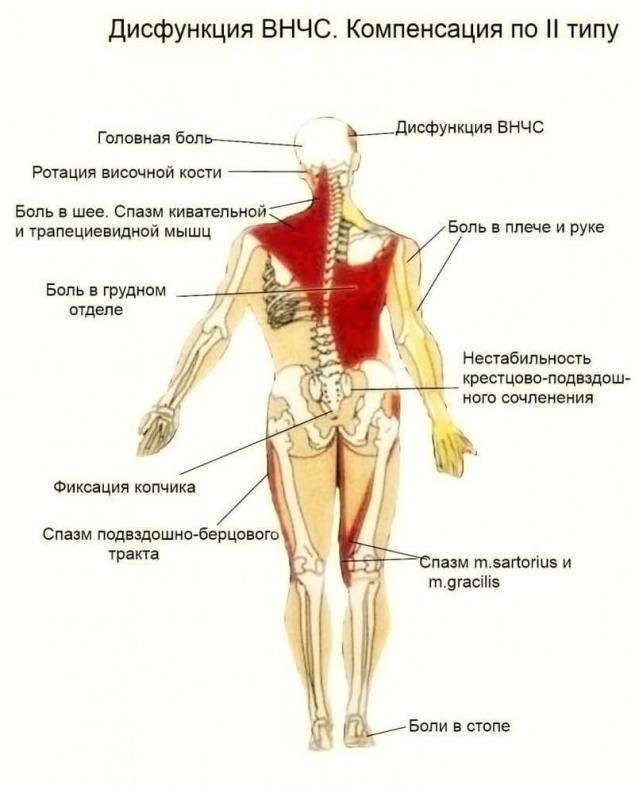
No need to endure the pain caused by TMJ disorder, seeing it as inevitable. Dysfunction can occur under the influence of various forces which cause overloading of the temporomandibular joint. It is necessary to consider the nature of these forces to understand the cause of dysfunction.
The main causes of TMJ disorder
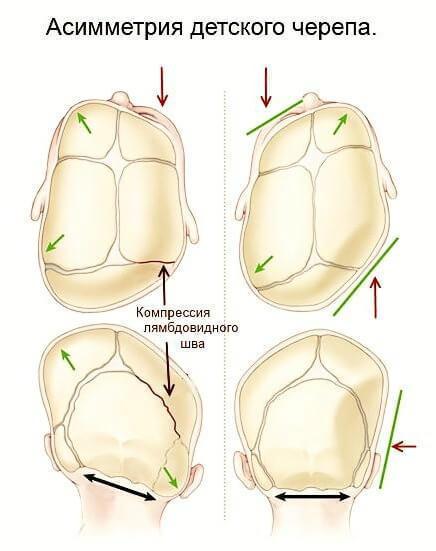
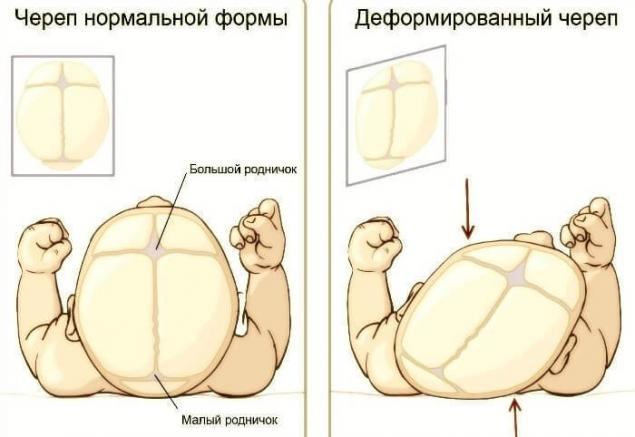
1. Birth trauma
The flexibility and plasticity of a baby's skull is required for the physiological passage of the head through the birth canal. The skull of the child is subjected to strong pressure and distortion, which normally is self-correcting in the first weeks of life. However, in many cases, the distortion imposed on the skull at birth are not corrected spontaneously with time.
Changing the shape and symmetry of the structures of the skull, which are visible to the naked eye and the extent of which can be measured, can adversely affect the adaptive abilities of the organism and the General health of the child. During the deformation of the bones of the skull are pressed into with any party or parties and lose the completeness of mobility. The violation of rhythmic movements of the skull bones entails membranous and fascial tension in the head and body. Vertebral scoliosis in children, often develops as a consequence of the cranial (skull) scoliosis arising at birth.
Also for compression of the skull, the child may experience the following diseases and symptoms:
With age, the body compensates for the distortion of the skull bones, began to develop malocclusion, mismatched upper and lower jaw, scoliosis, forward head posture and mouth breathing. All these factors provoke the development of TMJ disorder. But the body tries to compensate and adapt to the existing birth trauma, however, any push from the outside, will break down this payment.
Cranial injury received during life, blows, falls, problems with posture, loss of teeth, incorrect orthodontic treatment, errors in dental prosthetics, it will all be a triggering factor of violation of compensation and development of TMJ dysfunction.
2. The skull injury received before or after 12 years
Cranial damage is usually the primary etiological factor that underlies various pathologies of the bite. It is the trauma that even a "minor" at first glance, could lead to the displacement of the skull bones, especially within the squamosal sutures. While on the radiographic images, we do not see any signs of fractures or damage to bone structures. However, it happened.
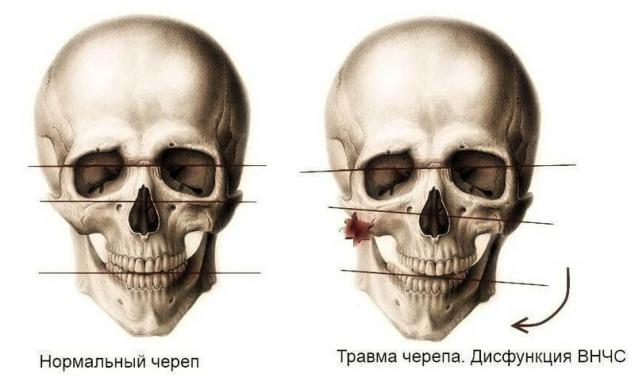
As a result, the upper jaw is normally located horizontally relative to the base of the skull, will get distortion in three-dimensional space of the skull.
Compliance with the occlusal plane of the upper and lower jaws will be broken. The first to react muscle. Compensatory will be increased tonus of the masticatory muscles, in an attempt to close new bite during the act of eating, swallowing, talking. Excessive interdigitation on the low side of the upper jaw will create a heavy contact, leading in consequence to periodontal problems, recession, pain the teeth on this side. In contact with such patients in the dental clinic, they unsuccessfully begin to heal possible cause the teeth one after the other, but the pain persisted..
In the end, the mismatched upper and lower jaw, and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, the problem appeared in the oral cavity (attrition or lack of teeth) will certainly lead to TMJ disorder.
However, cranial pathology can also occur under the influence related postural problems of the spine and pelvis that affect posture and muscle tone of the entire skeleton, being often primary factors in the development of the compensatory cranial dysfunction without injuries to the skull.
Scoliosis of the spine
However, cranial pathology can also occur under the influence related postural problems of the spine and pelvis that affect posture and muscle tone of the entire skeleton, being often primary factors in the development of the compensatory cranial dysfunctions.
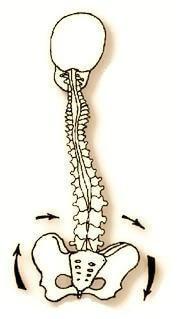
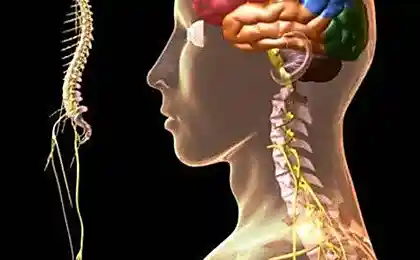
In human body everything is interconnected. Changes in one body will cause a cascade of reactions throughout the body, including muscular-skeletal
Most practitioners do not look at the TMJ joint, and pay attention to the pain arising in different parts of the body due to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Ascending postural causes dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is often associated with pelvic instability or instability of the sacroiliac joint. system — posture. Thus, the postural instability of the body extends upwards, causing changes in the functioning of the TMJ — temporo-mandibular joint. In addition, interactions at the level of the teeth also affect the TMJ.
When the treatment of a patient's body associated with TMJ dysfunction and malocclusion, it is important to look at the whole system.
The pelvis is important for a balanced stable position of the spine.
Inside the spine is the Dura mater, which also lines the cranial cavity from the inside, and is a single, non-stretchable high-density structure. It is extremely important for the formation of the relationship between the skull and the spine. The Dura is especially in places of attachment to bone structures, but we are particularly interested in the sacrum and the occipital bone in the area where the main seam. Thus, it is possible to trace the close relationship of the occipital bone and sacrum, which normally should have synchronized movement. Stretched in an unnatural way as a result of scoliosis or pelvic pathology Dura mater, will directly lead to malfunction as the occipital bone and the sacrum. Dysfunction in the pelvis rises up quickly, causing neck pain, thoracic, lower back, and finally affecting the function of the temporomandibular joint.
There is also an upward type of dysfunction, in which the issues in the lower floors of the body to cause dysfunction of the overlying departments. Now imagine that you have a foot injury or spasm in the region of the sacroiliac joint on one side.What would a body do? It will move the main load on the healthy side (leg, or the side without pain and spasms).
The spine and the whole postural system of the body will adapt to the new center of gravity with body distortion. Misalignment of the body arise by means of the muscles which will contract or relax in "chess" order, under the command of the Central nervous system. HER team will be aimed at maintaining body balance, because otherwise people will simply fall on its side. This mechanism will also affect the head, which is to maintain the balance tilts in the opposite direction. Now consider the skull.
Intracranial pressure will automatically increase on the low side of the slope and long-term this position of the head, the skull will tend to equalize this pressure. Central nervous system once again will command the muscles of the Antero-lateral surface of the neck, chewing the group. They will be reduced resulting reduction in a way that the middle and front areas of the skull to expand in the opposite direction, balancing the thereby intracranial pressure. Also using muscle implemented other mechanisms to maintain balance and postural balance of the body.
There are 3 powerful areas responsible for body balance:
4. Malocclusion
The malocclusion can often be caused by:
If the existing lock on the upper jaw, the developing dentition can be much crowding, due to constriction of the maxillary bones, and the teeth simply do not fit in the tooth row, and will begin to erupt smoothly and not outside the arc.
When the location of the upper jaw in retroposition, i.e. slightly posterior to its rightful place, there is a narrowing of the airway space of the nasopharynx. Subsequently the lower jaw also goes backwards, aiming to clamp his teeth forced occlusion. This situation upper and lower jaw in turn restricts movement in other bones that are responsible for breathing through the nose( vomer, ethmoid bone). Block of bones in turn causes a disruption at the tissue level. Squeezed the mucous membrane begins to swell, developing a venous stasis, accumulation of lymphoid tissue, there is a looseness of the mucosa of the nasopharynx. With this comes a pretty serious violation of nasal breathing.
In children with such a problem begins to dominate the mouth breathing. In adults there appears the sleep apnea syndrome and snoring. The body's attempt to release the upper respiratory tract leads to a forward position of the head relative to the body. In the mucosa of the nasopharynx and oropharynx grows the lymphoid tissue — increase of tonsils, nasal polyps, which further narrows the lumen of the respiratory tract. Also increases the reactivity of the mucosa to allergens, first to local, in the form of pollinozov, Allergy to dust, then intense becomes the common kreativnosti of the body, there is a reaction to food, drug Allergy.
5. The consequences of prosthesis or orthodontic treatment
Any discrepancies and problems, our body is trying to solve and to adapt to them. This process is constantly going on, for example, even for the regulation of temperature inside the body, in severe frosts in the environment. Moreover, the adaptation process is activated when violations of the mutual arrangement of the skull bones.
The body quickly adapts and changes primarily affect the bite. Any dental work does not take into account possible global problem, and addressed in isolation only on the tooth will inevitably break the adaptation. Change the height of the teeth, occlusion, number of teeth affects the whole body.
When tilting of the upper jaw, the side with the greatest load will give pain.
It may be neuritis of the trigeminal nerve maxillary branch, periodontal pockets this way, an increased dental abrasion, the appearance of wedge-shaped defects and gum recessions. All this is happening because of change of a vector load per tooth, or total overload (due to any resulting pathology of the mutual arrangement of the bones, possible trauma) and the body gets
After the upper jaw should be lower, trying to find the occlusion and to close the teeth each time when swallowing, eating, talking. Any pivot, tilt, retroposition the upper jaw, will be accompanied by a turn, tilt and retroposition lower jaw. But, as we know from the anatomy of the lower jaw, the heads of which are strictly accordingly to the articular cavities of the temporal bones, the deviation of its position would harm the TMJ. Very quickly comes the dysfunction of the joint. Head being out of place, displace the articular disc and lead to its dislocation.
The General syntax of the treatment of TMJ dysfunction. Cranio-mandibular disorders.
When the TMJ ceases to function normally, it affects all aspects of Your daily life and becomes a constant source of pain and discomfort.
After the hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles become tense and the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the trapezius, which causes discomfort in the neck, shoulders, and gradually, throughout the spine.
Externally, begins to develop scoliosis of the spine. Also, you may experience increasing facial asymmetry.published
See also:
Dr. Hamer: what we call disease is not a pointless ordeal
It's a simple remedy get rid of nail fungus
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: asgardmed.ru/content/lechenie-disfunkciy-visochno-nizhnechelyustnogo-sustava-vnchs
The articular disc has an oval shape and is held by ligaments on the articular head of the mandible in all movements in the TMJ joint, creating a damping of the opening and closing of the mouth.

Dysfunction TMJ. Anatomy
How is a dislocated joint?
If you experience problems at the level of the teeth or bones of the skull, the lower jaw can vary its position in the temporomandibular joint, to turn around or distantsirovaniya (slide back) within the joint capsule. In this interarticular disc exposed to the pressure head of the mandible, and may be displaced forward within the joint, which leads to dislocation of the TMJ disc.
This dislocation can occur each time the opening and closing of the mouth, thus becoming chronic.
The first symptoms of a dislocated TMJ is the onset of clicking, cracking or discomfort around the ear in the joint.
The head of the mandible on one side or both is pushed into the glenoid cavity, starting to squeeze bilaminar the area of the joint, is rich in vessels and nerves, which is already protected by velinovska anterior disc. There is a pain.
What happens if you don't treat dislocation of the TMJ?

Every time You eat, talk, TMJ joint is in motion. The same thing happens when swallowing. That is, approximately every 60 seconds.
Thus, You see that this is one of the most moving and the most involved joints in the body. When the intra-articular disc dysfunction again and again subjected to luxation during movement of the joint.
The disc, if the joint doesn't heal in time, begins to deform, fragmented, erased. Ligament that holds the disc, can be broken and thinned. Next is the process of destruction of the articular surface of the head lower jaw, which will move without depreciation and damage. The clicks in this case are replaced by an unpleasant sensation of crunching "broken glass" in the joint when opening the mouth.

Symptoms
Thus, You see that this is one of the most moving and the most involved joints in the body. When the dysfunction, pain, clicking, intra-articular disc again and again subjected to dislocation during movement of the joint.
Compensatory response to injury in the joint will be the voltage of masticatory muscles to tight to fix the joint, in an attempt to limit its movement. Appear the symptom of muscle hyperconservative muscles on one or both sides. When the TMJ ceases to function normally, it affects all aspects of Your daily life and becomes a constant source of pain and discomfort. After the hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles become tense and the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the trapezius, which causes discomfort in the neck, shoulders, and gradually, throughout the spine. Externally, begins to develop scoliosis of the spine.

No need to endure the pain caused by TMJ disorder, seeing it as inevitable. Dysfunction can occur under the influence of various forces which cause overloading of the temporomandibular joint. It is necessary to consider the nature of these forces to understand the cause of dysfunction.
The main causes of TMJ disorder
- Birth trauma
- The skull injury received before or after 12 years
- Malocclusion
- Scoliosis of the spine
- The lack of chewing teeth
- Wrong orthodontic treatment or prosthetic
- The pathogenesis of the development of TMJ dysfunction

1. Birth trauma
The flexibility and plasticity of a baby's skull is required for the physiological passage of the head through the birth canal. The skull of the child is subjected to strong pressure and distortion, which normally is self-correcting in the first weeks of life. However, in many cases, the distortion imposed on the skull at birth are not corrected spontaneously with time.
Changing the shape and symmetry of the structures of the skull, which are visible to the naked eye and the extent of which can be measured, can adversely affect the adaptive abilities of the organism and the General health of the child. During the deformation of the bones of the skull are pressed into with any party or parties and lose the completeness of mobility. The violation of rhythmic movements of the skull bones entails membranous and fascial tension in the head and body. Vertebral scoliosis in children, often develops as a consequence of the cranial (skull) scoliosis arising at birth.

Also for compression of the skull, the child may experience the following diseases and symptoms:
- Torticollis with spasm of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, because of possible compression of the jugular holes – accessory nerve
- Muscular hypertonicity – the tendency to extension, irritability (the child early begins to walk) – the tension of the Dura mater
- Colic, digestive disorders, frequent regurgitation – compression of jugular hole – Vagus nerve
- Restless sleep – increased intracranial pressure, compression of the occipital bone
- Underdevelopment – a violation of CSF dynamics, compression of the skull.
- Hormonal disorders – compression and tension of the fascia in the area of the pituitary gland
- Violation of sucking and swallowing – Gothic or overly flattened palate, stenosis of the nasopharynx and the violation of nasal breathing, compression on the nerves responsible for swallowing.
- Decreased sense of smell – unit of the ethmoid bone, and compression of the olfactory nerves
- Frequent colds, due to edema of the mucosa of the nasopharynx and oropharynx at the unit opener
- Allergic rhinitis – block of the vomer, the ethmoid bone
- Enlarged tonsils, enlarged – unit opener, upper jaw, venous stasis in the mucosa of the nasopharynx, a cluster of lymphoid tissue, mucosa of allergic readiness
- Myoclonia, convulsive twitching of the muscles
- Respiratory problems – compression of the occipital, vagus nerve, twisting of the Dura mater
- Mouth breathing due to narrowing of the nasopharynx
- Ophthalmic disorders – strabismus, nystagmus when rotation of the sphenoid bone and narrowing verhnelenskoe gap (compression of the Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducent nerves)
- Speech disorder, and many other types of dysfunction.
With age, the body compensates for the distortion of the skull bones, began to develop malocclusion, mismatched upper and lower jaw, scoliosis, forward head posture and mouth breathing. All these factors provoke the development of TMJ disorder. But the body tries to compensate and adapt to the existing birth trauma, however, any push from the outside, will break down this payment.
Cranial injury received during life, blows, falls, problems with posture, loss of teeth, incorrect orthodontic treatment, errors in dental prosthetics, it will all be a triggering factor of violation of compensation and development of TMJ dysfunction.
2. The skull injury received before or after 12 years
Cranial damage is usually the primary etiological factor that underlies various pathologies of the bite. It is the trauma that even a "minor" at first glance, could lead to the displacement of the skull bones, especially within the squamosal sutures. While on the radiographic images, we do not see any signs of fractures or damage to bone structures. However, it happened.

As a result, the upper jaw is normally located horizontally relative to the base of the skull, will get distortion in three-dimensional space of the skull.
Compliance with the occlusal plane of the upper and lower jaws will be broken. The first to react muscle. Compensatory will be increased tonus of the masticatory muscles, in an attempt to close new bite during the act of eating, swallowing, talking. Excessive interdigitation on the low side of the upper jaw will create a heavy contact, leading in consequence to periodontal problems, recession, pain the teeth on this side. In contact with such patients in the dental clinic, they unsuccessfully begin to heal possible cause the teeth one after the other, but the pain persisted..
In the end, the mismatched upper and lower jaw, and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles, the problem appeared in the oral cavity (attrition or lack of teeth) will certainly lead to TMJ disorder.
However, cranial pathology can also occur under the influence related postural problems of the spine and pelvis that affect posture and muscle tone of the entire skeleton, being often primary factors in the development of the compensatory cranial dysfunction without injuries to the skull.
Scoliosis of the spine
However, cranial pathology can also occur under the influence related postural problems of the spine and pelvis that affect posture and muscle tone of the entire skeleton, being often primary factors in the development of the compensatory cranial dysfunctions.

In human body everything is interconnected. Changes in one body will cause a cascade of reactions throughout the body, including muscular-skeletal
Most practitioners do not look at the TMJ joint, and pay attention to the pain arising in different parts of the body due to dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Ascending postural causes dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is often associated with pelvic instability or instability of the sacroiliac joint. system — posture. Thus, the postural instability of the body extends upwards, causing changes in the functioning of the TMJ — temporo-mandibular joint. In addition, interactions at the level of the teeth also affect the TMJ.
When the treatment of a patient's body associated with TMJ dysfunction and malocclusion, it is important to look at the whole system.
The pelvis is important for a balanced stable position of the spine.
Inside the spine is the Dura mater, which also lines the cranial cavity from the inside, and is a single, non-stretchable high-density structure. It is extremely important for the formation of the relationship between the skull and the spine. The Dura is especially in places of attachment to bone structures, but we are particularly interested in the sacrum and the occipital bone in the area where the main seam. Thus, it is possible to trace the close relationship of the occipital bone and sacrum, which normally should have synchronized movement. Stretched in an unnatural way as a result of scoliosis or pelvic pathology Dura mater, will directly lead to malfunction as the occipital bone and the sacrum. Dysfunction in the pelvis rises up quickly, causing neck pain, thoracic, lower back, and finally affecting the function of the temporomandibular joint.
There is also an upward type of dysfunction, in which the issues in the lower floors of the body to cause dysfunction of the overlying departments. Now imagine that you have a foot injury or spasm in the region of the sacroiliac joint on one side.What would a body do? It will move the main load on the healthy side (leg, or the side without pain and spasms).
The spine and the whole postural system of the body will adapt to the new center of gravity with body distortion. Misalignment of the body arise by means of the muscles which will contract or relax in "chess" order, under the command of the Central nervous system. HER team will be aimed at maintaining body balance, because otherwise people will simply fall on its side. This mechanism will also affect the head, which is to maintain the balance tilts in the opposite direction. Now consider the skull.
Intracranial pressure will automatically increase on the low side of the slope and long-term this position of the head, the skull will tend to equalize this pressure. Central nervous system once again will command the muscles of the Antero-lateral surface of the neck, chewing the group. They will be reduced resulting reduction in a way that the middle and front areas of the skull to expand in the opposite direction, balancing the thereby intracranial pressure. Also using muscle implemented other mechanisms to maintain balance and postural balance of the body.
There are 3 powerful areas responsible for body balance:
- 1 — Eyes
- 2 — the Vestibular system
- 3 — Foot
4. Malocclusion
The malocclusion can often be caused by:
- A violation of the mutual arrangement of the upper and lower jaw, the resulting trauma.
- Wrong orthodontic treatment or prosthetic
- The lack of chewing teeth
If the existing lock on the upper jaw, the developing dentition can be much crowding, due to constriction of the maxillary bones, and the teeth simply do not fit in the tooth row, and will begin to erupt smoothly and not outside the arc.
When the location of the upper jaw in retroposition, i.e. slightly posterior to its rightful place, there is a narrowing of the airway space of the nasopharynx. Subsequently the lower jaw also goes backwards, aiming to clamp his teeth forced occlusion. This situation upper and lower jaw in turn restricts movement in other bones that are responsible for breathing through the nose( vomer, ethmoid bone). Block of bones in turn causes a disruption at the tissue level. Squeezed the mucous membrane begins to swell, developing a venous stasis, accumulation of lymphoid tissue, there is a looseness of the mucosa of the nasopharynx. With this comes a pretty serious violation of nasal breathing.
In children with such a problem begins to dominate the mouth breathing. In adults there appears the sleep apnea syndrome and snoring. The body's attempt to release the upper respiratory tract leads to a forward position of the head relative to the body. In the mucosa of the nasopharynx and oropharynx grows the lymphoid tissue — increase of tonsils, nasal polyps, which further narrows the lumen of the respiratory tract. Also increases the reactivity of the mucosa to allergens, first to local, in the form of pollinozov, Allergy to dust, then intense becomes the common kreativnosti of the body, there is a reaction to food, drug Allergy.
5. The consequences of prosthesis or orthodontic treatment
Any discrepancies and problems, our body is trying to solve and to adapt to them. This process is constantly going on, for example, even for the regulation of temperature inside the body, in severe frosts in the environment. Moreover, the adaptation process is activated when violations of the mutual arrangement of the skull bones.
The body quickly adapts and changes primarily affect the bite. Any dental work does not take into account possible global problem, and addressed in isolation only on the tooth will inevitably break the adaptation. Change the height of the teeth, occlusion, number of teeth affects the whole body.
When tilting of the upper jaw, the side with the greatest load will give pain.
It may be neuritis of the trigeminal nerve maxillary branch, periodontal pockets this way, an increased dental abrasion, the appearance of wedge-shaped defects and gum recessions. All this is happening because of change of a vector load per tooth, or total overload (due to any resulting pathology of the mutual arrangement of the bones, possible trauma) and the body gets
After the upper jaw should be lower, trying to find the occlusion and to close the teeth each time when swallowing, eating, talking. Any pivot, tilt, retroposition the upper jaw, will be accompanied by a turn, tilt and retroposition lower jaw. But, as we know from the anatomy of the lower jaw, the heads of which are strictly accordingly to the articular cavities of the temporal bones, the deviation of its position would harm the TMJ. Very quickly comes the dysfunction of the joint. Head being out of place, displace the articular disc and lead to its dislocation.

The General syntax of the treatment of TMJ dysfunction. Cranio-mandibular disorders.
- Stabilization of the TMJ with the manufacture of individual artoteka – splint therapy (neuromuscular, decompression, NTI-deprogrammer, etc.)
- Correction of cranial disorders in 3 planes – Roll, Pitch, Yaw.
- Neuro-muscular balance and postural system.
- Observation in dynamics. Asymptomatic period must be at least 4 months
- Completion of treatment on dentoalveolar level to develop a new occlusal relationship (prosthetics, orthodontics)
When the TMJ ceases to function normally, it affects all aspects of Your daily life and becomes a constant source of pain and discomfort.
After the hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles become tense and the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the trapezius, which causes discomfort in the neck, shoulders, and gradually, throughout the spine.
Externally, begins to develop scoliosis of the spine. Also, you may experience increasing facial asymmetry.published
See also:
Dr. Hamer: what we call disease is not a pointless ordeal
It's a simple remedy get rid of nail fungus
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: asgardmed.ru/content/lechenie-disfunkciy-visochno-nizhnechelyustnogo-sustava-vnchs