568
With the knee injury exercises are effective not less than surgery
The knee is the joint most frequently traumatized athletes; annually, the emergency Department dealing with over $ 2.5 million sports injuries. Tear of the meniscus is at 35 percent of people older than 50 years.
Number of ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament is important for stabilizing the knee joint is from 100 000 to 200 000 cases annually. Injuries of the knee treated a lot of doctors, from surgeons to therapists, physiotherapists and rehabilitation specialists.
The knee joint can suffer from acute or traumatic injuries; in addition, due to excessive load, the meniscus can begin degenerative changes. How you will treat those injuries will impact your ability to return to normal activities and chances to degenerative arthritis in the future.
A recent randomized controlled trial demonstrated the effectiveness of using a structured exercise program during rehabilitation of the knee either prior to surgery or, in many cases, instead of surgery.
To restore the joint to the full, it is important to understand how it works, and what key factors need to be evaluated in order to determine which option is best suited for a particular situation.
Anatomy of the knee and the meniscus
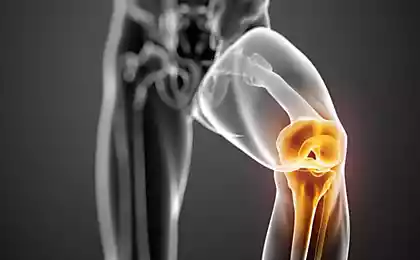
Three bones articulate at the knee, forming a joint, which is the largest and most complex in the body. Although the knee is a hinge joint, it should not only to bend and be flexible to walk, but also sustainable, so you can stand still.
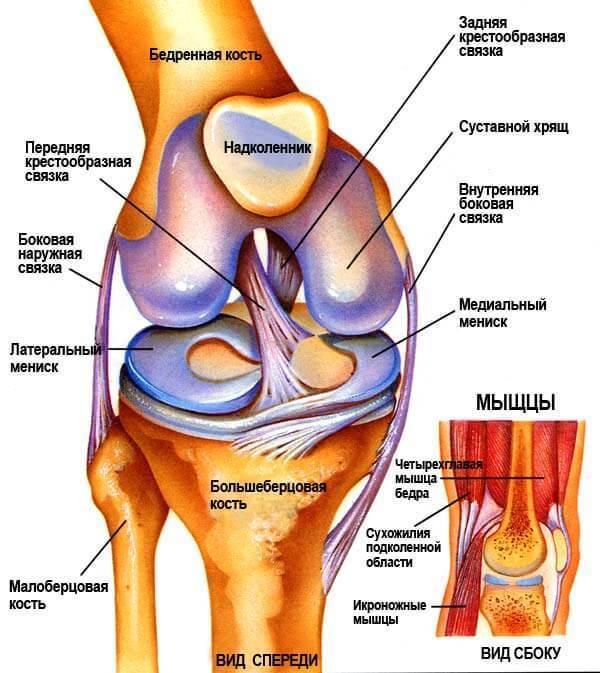
Between the thigh bone (femur) and the Shin bone (tibia) are two wedge-shaped cartilage pads. Rigid and elastic, they, like a pillow, do not give these bones to RUB against each other. These pads called meniscus.
To the outer edges of the menisci have a blood supply, which decreases rapidly as you move toward the center of the cartilage located directly between two major bones. There are many types of meniscus tears, including trauma and degenerative changes over time.
The number of operations to restore the meniscus is increasing every year. Recent data from the American journal of sports medicine showed that during 2005-2011 the restoration of the meniscus increased by 100 percent.
In addition, the study showed that pain experienced by the patient initially may not be connected with the meniscus.
The researchers found that patients report less pain, although the gap is still not healed after surgery. The lack of recovery was confirmed by subsequent arthroscopy. And to reduce pain and improve function helped immobilization and physical therapy.
Studies show that the effect of exercise is comparable with the result of the operation
Two studies showed the effectiveness of using a structured programme of physiotherapy to eliminate the need for surgical intervention or to improve the results if the therapy is used before surgery.
In the first study within five years of participants with minimal loss of function in the observation period. Study participants had an injury of the anterior cruciate ligament, the Researchers found that the results of those who underwent surgery and those who received restorative treatment, were almost identical.
In another study published in 2016, for two years, he conducted participant observation with a torn meniscus of the knee joint. Again, the researchers found that exercise and rehabilitation treatment for patients of middle age with damage to the knee was as effective as surgical treatment of the meniscus, which is an outpatient procedure.
Researchers have estimated that every year 2 million people around the world are doing arthroscopic surgery. But in the literature review, scientists have not identified the advantages for the patient, which prompted the researchers from Denmark and Norway to carry out this two-year observation.
While scientists have identified 140 patients with a torn meniscus, most of which were not osteoarthritic changes in the knee joint. Half of the patients received an intensive 12-week exercise program while the other half had arthroscopic surgery and rehabilitation program in the home.
Between these two groups was found clinical differences regarding their ability to do daily chores, participate in sports activities, as well as regarding the intensity of pain. From the group, which received only the exercise, thirteen participants decided on arthroscopic surgery, but had not noted any additional benefits.
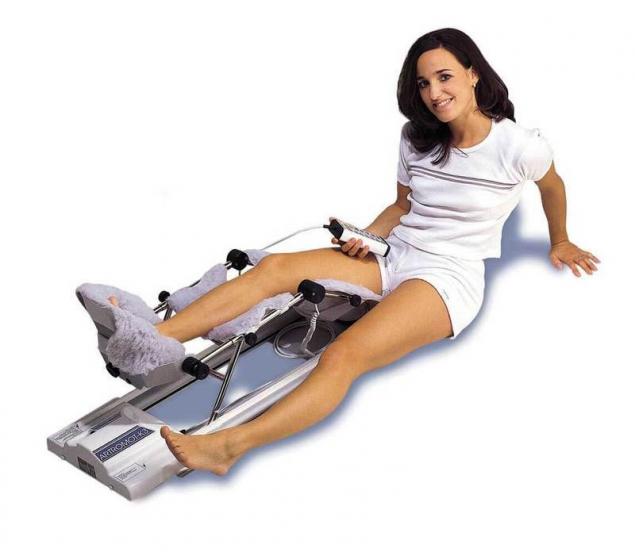

Additional benefits of exercise compared to surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is considered a procedure with low risk. The most serious side effects are deep vein thrombosis, infection and pulmonary embolism, which occur only in 0.4 percent of cases.
But no matter how low a risk level, the operation increases the costs of medical care and insurance and, obviously, does not guarantee good results. On the other hand, an intensive rehabilitation program effectively increases the strength of the large muscles that support the knee joint.
In the latest study, the researchers checked the condition of the quadriceps (thigh) participants at baseline, three months and 12 months.
They found that the results of people who completed rehabilitation, similar to the results of those who had done arthroscopic surgery and, in addition, they have increased the strength of this muscle.
In "Science Daily" quoting the authors:
"Controlled exercise-therapy showed a positive effect compared to surgery, strengthen the muscle power of the hip, at least in the short term.
Our results should encourage physicians and patients of middle age characterized by degenerative changes of the meniscus without radiographic signs of osteoarthritis to consider the use of controlled structured exercise therapy as a treatment option".
The increase in force was observed during the first 12 months of the study but not assessed during the remaining time of the study. Increasing the strength of the knee joint can effectively reduce the possibility of further injury and improve ability to do daily activities.
For such patients surgery is placebo as effective as arthroscopic and
The placebo effect occurs when you think that you are getting treatment, but the medications that you take, have no physiological effect. To Management on control of products and medicines USA (FDA) approved the drug, it is necessary to prove that it is effective fake drug or a placebo. And for the approval of medical devices or surgical procedures for the treatment, such proof is not required.
In 2002, a study published in the journal "journal of medicine New England", proved that the results of people who underwent arthroscopic surgery about osteoarthritis were no better than results that you would expect from a placebo.
In another study, conducted among 146 patients with meniscus tear without osteoarthritis, the researchers found that a surgical procedure placebo gave the same results as those who actually did the surgery on the meniscus. The study participants were followed for 12 months and found no significant differences between the groups.
A study proving the placebo effect of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis was conducted in 2002. Unfortunately, to date this information has not changed, the annual number of arthroscopy, the cost of which for insurance companies and private individuals is more than $ 3 billion a year — a procedure that yields the same results as physical therapy and rehabilitation.
Before deciding on the surgery, think about these important factors
If you think about how to do the surgery for her injuries, we note several factors that could improve or reduce the likelihood of a successful outcome.
1. Functional changes
Despite the fact that MRI may be visible changes in the meniscus, if you don't feel pain or functional changes in gait, surgery is likely not necessary. To evaluate how a knee injury affects strength and stability, sports medicine physicians apply the "duck step". Sit down and walk like a duck. If you can't do because of knee pain or weakness, consider a program of rehabilitation to improve the strength of the joint and reduce pain.
2. Weight
Your weight is an important factor in determining the potential success of surgical intervention. So, studies have found significant changes in the curvature of the knee joint during the first three months after injury in connection with the increase in body weight. Found that those who underwent surgery, the knee joint was more flattened than those who underwent rehabilitation without surgical intervention, when their body mass index was higher.
3. The size and location of the gap
Reduction of blood flow to the meniscus in the center of the knee increases the likelihood that surgical intervention will not remove the problem or will not help. The size of rupture, whether in the centre of the meniscus, or along the outer edges, where better blood flow – affects the decision about surgery.
The restoration of the meniscus has a higher probability of success in young patients with gaps on the periphery near the attachment of the capsules horizontal or longitudinal. Even in these cases, success depends on exercise and rehabilitation in the postoperative period, including the wearing of special supporting devices.
Before surgery is seriously think about ozone therapy
Earlier, I interviewed Dr. Robert Rowen about ozone therapy in various diseases. He is one of the leading ozonoterapie in the United States, which successfully treats many patients with this alternative to surgery. If the ozone treatment does not help, from him no harm, and you can always do the surgery, but if we fail the operation, this may cause irreversible damage.
Another option is treatment with infrared laser (K-Laser). This is a relatively new type of treatment that accelerates wound healing by increasing tissue oxygenation and gives the opportunity to injured cells to absorb photons of light. This is a special type of laser has a positive effect on the muscles, ligaments and even bones, so it can be used to accelerate the healing of damage from injuries, but also with such chronic problems as arthritis of the knee joint.published
Author: Dr. Joseph Mercola
The materials are for informational purposes. Remember, self-life-threatening, for advice regarding the use of any medicines and methods of treatment, contact your doctor.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: russian.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2016/12/16/%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BC%D0%B0-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BE%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F.aspx
Number of ruptures of the anterior cruciate ligament is important for stabilizing the knee joint is from 100 000 to 200 000 cases annually. Injuries of the knee treated a lot of doctors, from surgeons to therapists, physiotherapists and rehabilitation specialists.

The knee joint can suffer from acute or traumatic injuries; in addition, due to excessive load, the meniscus can begin degenerative changes. How you will treat those injuries will impact your ability to return to normal activities and chances to degenerative arthritis in the future.
A recent randomized controlled trial demonstrated the effectiveness of using a structured exercise program during rehabilitation of the knee either prior to surgery or, in many cases, instead of surgery.
To restore the joint to the full, it is important to understand how it works, and what key factors need to be evaluated in order to determine which option is best suited for a particular situation.
Anatomy of the knee and the meniscus
Three bones articulate at the knee, forming a joint, which is the largest and most complex in the body. Although the knee is a hinge joint, it should not only to bend and be flexible to walk, but also sustainable, so you can stand still.
Between the thigh bone (femur) and the Shin bone (tibia) are two wedge-shaped cartilage pads. Rigid and elastic, they, like a pillow, do not give these bones to RUB against each other. These pads called meniscus.
To the outer edges of the menisci have a blood supply, which decreases rapidly as you move toward the center of the cartilage located directly between two major bones. There are many types of meniscus tears, including trauma and degenerative changes over time.

The number of operations to restore the meniscus is increasing every year. Recent data from the American journal of sports medicine showed that during 2005-2011 the restoration of the meniscus increased by 100 percent.
In addition, the study showed that pain experienced by the patient initially may not be connected with the meniscus.
The researchers found that patients report less pain, although the gap is still not healed after surgery. The lack of recovery was confirmed by subsequent arthroscopy. And to reduce pain and improve function helped immobilization and physical therapy.
Studies show that the effect of exercise is comparable with the result of the operation
Two studies showed the effectiveness of using a structured programme of physiotherapy to eliminate the need for surgical intervention or to improve the results if the therapy is used before surgery.
In the first study within five years of participants with minimal loss of function in the observation period. Study participants had an injury of the anterior cruciate ligament, the Researchers found that the results of those who underwent surgery and those who received restorative treatment, were almost identical.
In another study published in 2016, for two years, he conducted participant observation with a torn meniscus of the knee joint. Again, the researchers found that exercise and rehabilitation treatment for patients of middle age with damage to the knee was as effective as surgical treatment of the meniscus, which is an outpatient procedure.
Researchers have estimated that every year 2 million people around the world are doing arthroscopic surgery. But in the literature review, scientists have not identified the advantages for the patient, which prompted the researchers from Denmark and Norway to carry out this two-year observation.
While scientists have identified 140 patients with a torn meniscus, most of which were not osteoarthritic changes in the knee joint. Half of the patients received an intensive 12-week exercise program while the other half had arthroscopic surgery and rehabilitation program in the home.
Between these two groups was found clinical differences regarding their ability to do daily chores, participate in sports activities, as well as regarding the intensity of pain. From the group, which received only the exercise, thirteen participants decided on arthroscopic surgery, but had not noted any additional benefits.

Additional benefits of exercise compared to surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is considered a procedure with low risk. The most serious side effects are deep vein thrombosis, infection and pulmonary embolism, which occur only in 0.4 percent of cases.
But no matter how low a risk level, the operation increases the costs of medical care and insurance and, obviously, does not guarantee good results. On the other hand, an intensive rehabilitation program effectively increases the strength of the large muscles that support the knee joint.
In the latest study, the researchers checked the condition of the quadriceps (thigh) participants at baseline, three months and 12 months.
They found that the results of people who completed rehabilitation, similar to the results of those who had done arthroscopic surgery and, in addition, they have increased the strength of this muscle.
In "Science Daily" quoting the authors:
"Controlled exercise-therapy showed a positive effect compared to surgery, strengthen the muscle power of the hip, at least in the short term.
Our results should encourage physicians and patients of middle age characterized by degenerative changes of the meniscus without radiographic signs of osteoarthritis to consider the use of controlled structured exercise therapy as a treatment option".
The increase in force was observed during the first 12 months of the study but not assessed during the remaining time of the study. Increasing the strength of the knee joint can effectively reduce the possibility of further injury and improve ability to do daily activities.
For such patients surgery is placebo as effective as arthroscopic and
The placebo effect occurs when you think that you are getting treatment, but the medications that you take, have no physiological effect. To Management on control of products and medicines USA (FDA) approved the drug, it is necessary to prove that it is effective fake drug or a placebo. And for the approval of medical devices or surgical procedures for the treatment, such proof is not required.
In 2002, a study published in the journal "journal of medicine New England", proved that the results of people who underwent arthroscopic surgery about osteoarthritis were no better than results that you would expect from a placebo.
In another study, conducted among 146 patients with meniscus tear without osteoarthritis, the researchers found that a surgical procedure placebo gave the same results as those who actually did the surgery on the meniscus. The study participants were followed for 12 months and found no significant differences between the groups.
A study proving the placebo effect of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis was conducted in 2002. Unfortunately, to date this information has not changed, the annual number of arthroscopy, the cost of which for insurance companies and private individuals is more than $ 3 billion a year — a procedure that yields the same results as physical therapy and rehabilitation.
Before deciding on the surgery, think about these important factors
If you think about how to do the surgery for her injuries, we note several factors that could improve or reduce the likelihood of a successful outcome.
1. Functional changes
Despite the fact that MRI may be visible changes in the meniscus, if you don't feel pain or functional changes in gait, surgery is likely not necessary. To evaluate how a knee injury affects strength and stability, sports medicine physicians apply the "duck step". Sit down and walk like a duck. If you can't do because of knee pain or weakness, consider a program of rehabilitation to improve the strength of the joint and reduce pain.
2. Weight
Your weight is an important factor in determining the potential success of surgical intervention. So, studies have found significant changes in the curvature of the knee joint during the first three months after injury in connection with the increase in body weight. Found that those who underwent surgery, the knee joint was more flattened than those who underwent rehabilitation without surgical intervention, when their body mass index was higher.
3. The size and location of the gap
Reduction of blood flow to the meniscus in the center of the knee increases the likelihood that surgical intervention will not remove the problem or will not help. The size of rupture, whether in the centre of the meniscus, or along the outer edges, where better blood flow – affects the decision about surgery.
The restoration of the meniscus has a higher probability of success in young patients with gaps on the periphery near the attachment of the capsules horizontal or longitudinal. Even in these cases, success depends on exercise and rehabilitation in the postoperative period, including the wearing of special supporting devices.
Before surgery is seriously think about ozone therapy
Earlier, I interviewed Dr. Robert Rowen about ozone therapy in various diseases. He is one of the leading ozonoterapie in the United States, which successfully treats many patients with this alternative to surgery. If the ozone treatment does not help, from him no harm, and you can always do the surgery, but if we fail the operation, this may cause irreversible damage.
Another option is treatment with infrared laser (K-Laser). This is a relatively new type of treatment that accelerates wound healing by increasing tissue oxygenation and gives the opportunity to injured cells to absorb photons of light. This is a special type of laser has a positive effect on the muscles, ligaments and even bones, so it can be used to accelerate the healing of damage from injuries, but also with such chronic problems as arthritis of the knee joint.published
Author: Dr. Joseph Mercola
The materials are for informational purposes. Remember, self-life-threatening, for advice regarding the use of any medicines and methods of treatment, contact your doctor.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: russian.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2016/12/16/%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B2%D0%BC%D0%B0-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B0-%D0%BE%D0%BF%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D1%8F.aspx
Any symptom is something you do not want to see, hear or notice.
You're not worth that to worry about you...