715
USEFUL info: knee injury— traditional methods of treatment
The knee joint allows only flexion and extension the tibia, but also has such abilities as a rotation, i.e. torsion.
The knee joint consists of three bones:
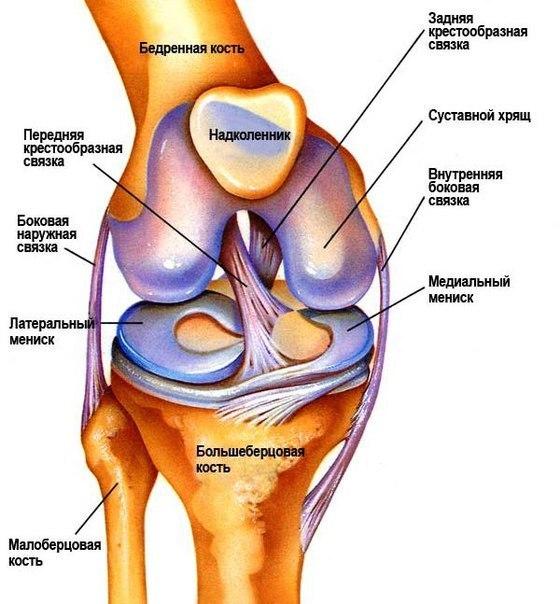
The main structures stabilizing the knee joint are:
Each of the ligaments has a multidirectional course of the fibres and performs a complex function at different angles of flexion in the knee joint when the different beams of the same ligaments strengthen the knee joint.
In the knee joint may flexion and extension, but when flexed at an angle of 90 degrees the knee joint is also possible to rotate the leg and foot inwards and outwards (due mostly to mobile meniscus).
When you fully straighten the knee (leg straight) knee joint is the most fixed.
Thus, the knee joint is quite complicated, and in trauma of the knee joint required the examination of the lower limbs doctor traumatologist-orthopedist to identify clinical signs of damage to the intraarticular structures in the future -to clarify the diagnosis can help radiographs of the knee joint, magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
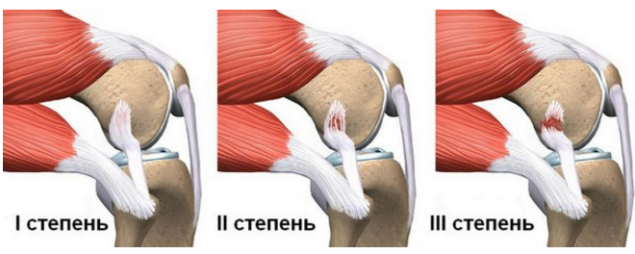
Due to the impact of external factors (friction, pressure), as well as direct trauma to the joint can occur partial or complete rupture of the ligaments. Damage to individual collagen fibers bundles, generally reversible: having high ability to regenerate, ligaments can repair themselves. A common symptom tear any ligaments – swelling and swelling in the knee area, often a significant increase in volume. As a rule, the swelling increases and becomes larger in size after 2-3 hours after injury.
The most common injuries of the knee:
A meniscus tear
The meniscus of the knee the cartilage is a Crescent-shaped strip that performs shock absorption and load distribution, as well as sensitive function that provides a sense of knee joint position in space and, together with ligaments, muscles and tendons stabilizing function.
Damage to the meniscus, the gap arises from different mechanisms. The primary mechanism is twisting the hip inwards or outwards with respect to the fixed tibia.
A meniscus can be torn in different directions along or across.
The meniscus may delaminate. If the gap is small, mechanically stable and the severed part does not move in the joint, there is a feeling of pain and permanent swelling of the knee joint.
Tear of the meniscus throughout cause mechanical instability. The meniscus begins to shift when moving the joint and can jam the knee joint. In this case, the leg ceases to straighten the knee joint. This condition is called blockade of the knee joint and requires urgent surgical treatment.
Rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament
The ACL rupture is a common sports injury, requiring surgery, and is often accompanied by damage to other structures of the knee joint. Together with the cruciate ligament damaged meniscus, lateral ligaments, and even cartilage surface.
The anterior cruciate ligament functions as the stabilizer, forcing the knee joint during the movement of the shift relative to the physiological axis of rotation, its strength corresponds to 200 kg at the gap. According to statistics women have a cruciate ligament is damaged 4 times more often than men.
In the event of damage to the PCB is a violation of the physiological axis of rotation in the joint, which causes damage to cartilage and menisci. In addition to the mechanical stabilization of the cruciate ligament also serves as a sensitive organ, providing transfer (sense of movement) and proprioception (sense of position of the knee in space).
Damage to the PCB are more common in athletes in those sports where you need a twisting motion in the knee, and sudden acceleration (sports, ski, football, trampoline).
The main complaintfor patients with ACL rupture is instability of the knee joint, that is, there is a feeling of "divergence" of the bones relative to each other in the knee joint — podvigina. This sensation often occurs at an awkward movement or during acceleration.
Rupture of lateral ligament
Ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the knee joint occur when indirect mechanism of injury — excessive deviation of the tibia inwards or outwards, with a torn lateral ligament, opposite side of the deviation.
When rupture of the lateral ligament of the note, the excess deviation of the tibia in the direction opposite to the damaged ligament. For example, if there is suspicion of rupture of the internal lateral ligament, the doctor with one hand captures the outer surface of the knee joint of the patient, and the second rejects the tibia outwards.
The opportunity to reject the tibia outward much more than on the healthy leg indicates ruptured internal lateral ligament. Leg of the patient in the study needs to be straightened in the knee joint.
Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament
Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)is one of the most severe injuries of the knee joint. To damage the posterior cruciate ligament is quite difficult, most often this happens as a result of car accident (a blow to the front part of the leg by a car bumper) and high speed sports (during a fall on an obstacle in Alpine skiing and snowboarding, team sports in a collision with another player.) In this regard, the PCL tear is rarely isolated and is accompanied by damage to anterior cruciate, outer and inner lateral ligaments.
There are always damaged in dislocation of the tibia, as it is the main stabilising structure of the knee joint.
Posterior cruciate ligament consists of two powerful beams at rupture of one of the beams ligament can heal on their own, the patient is assigned to conservative treatment including wearing a special brace-knee brace for two months from the date of injury.
In the complete rupture of PCL occur gross violations of the biomechanics of the knee. Any flexion of the knee joint is offset from the tibia posteriorly. Instead when bending to perform a rotation in the knee joint, the slipping of the tibia and its displacement ago. As a result, when walking is the front part of the tibia and back part of the condyles of the femur, the rest of load is not involved. While the load on the cartilage increases thousands of times, and the knee joint is completely destroyed in 5 years.
In addition, the displacement of the tibia increases the load back in patellofemoral the joint, the cartilage under the kneecap wears out quickly also, there is a crunch and pain in the knee joint.
Diagnosis of injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament begins with an external examination, is often determined by the retraction of the leg back, a number of patients may spontaneously perform the displacement of the tibia.
Fracture of the condyle of the tibia bone
One of the most severe damage in the knee joint is a fracture in the joint area (cartilage-covered) surfaces. The result of damage to the formation of irregularities and steps on the surface of the cartilage, which can be corrected only surgically.
Almost all intra-articular fractures even with slight displacement necessary to operate, to prevent joint destruction as a result of development of posttraumatic osteoarthritis.
The most frequent damage to the bones in the knee joint are fractures of the kneecap (patella), as well as fractures of the condyles of the tibia.
In fractures of the patella most frequent is the transverse fracture which can be caused by a direct blow or excessive contraction of the quadriceps muscle.
Your reaction to trauma:
1. Rest – immediately after injury is necessary to limit to the minimum of movement to reduce pain and swelling, prevent further damage and pave the way for an earlier recovery.
2. Cold – applying cold compresses, ice packs and other methods of cryotherapy in the first days after a break up leads to a narrowing of the blood vessels, which reduces edema and hemorrhage in the tissue.
3. Elastic bandaging, dressings, bandages – create pressure on the region of the knee, prevent the formation of edema, stabilize the knee joint, limit abnormal movement.
4. Giving the leg elevation position – with the help of available items (e.g., pillows) or special medical equipment leg is raised above heart level. This hampered the inflow of large amounts of blood in the location of the injury reduces the swelling of tissues.
In order to unload the joint, while gaps of 1 degree apply tight bandages on the affected area. They can be performed using elastic bandages or tapes special adhesive tapes, resembling a band-aid. In the first days after injury, treatment Supplement ice packsthat are applied to the damaged area. The cold will reduce swelling of tissues and relieve the pain.
Applying ice packs on their own, remember thatthe burden of cold exposure should not exceed 15 minutes. During the first 24 hours you can use a cold compress 3 – 4 times.
It is very important to completely eliminate heat treatments, which are so like to recommend to our grandmothers. Treatment warming ointments can only be performed after 3-5 days after injury.
For the treatment of pain used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in pill or injections. Fighting with pain is made using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorolac, diclofenac, ibuprofen), which the doctor prescribes as in the form of tablets for oral administration, and in the form of analgesic creams, ointments, lotions: "Indovazin", "Dolobene", "Lioton", "Troxevasin".
Topically applied different warming ointment: "I experienced an unexpected side effect", "Indovazin", "Lioton", "Larkspur", "We", "Vibrators".
5. Warm – start applying warming compresses, ointments, heating pads on the area of the knee only a few days after a torn ligament after the cessation of bleeding from small vessels. Such procedures bring relief of pain for the patient.
6. Physiotherapy – applied applications of paraffin wax.
7. The complex of physical exercises – you need to perform regular rehabilitation to restore muscle strength and mobility in the joint.
8. Massage – is carried out either by a specialist, either in the form of self-massage to relieve pain and swelling.
Traditional methods of treatment is able to reduce the size of the swelling and reduce pain, but you must remember that they are used only in conjunction with a course of basic therapy prescribed by a doctor:
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: moyaspina.ru/bolezni/razryv-kolennyh-svyazok-chastichnyy-ili-polnyy
The knee joint consists of three bones:
- tibial,
- femoral,
- the patella.

The main structures stabilizing the knee joint are:
- the outer and inner collateral ligament,
- anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
Each of the ligaments has a multidirectional course of the fibres and performs a complex function at different angles of flexion in the knee joint when the different beams of the same ligaments strengthen the knee joint.
In the knee joint may flexion and extension, but when flexed at an angle of 90 degrees the knee joint is also possible to rotate the leg and foot inwards and outwards (due mostly to mobile meniscus).
When you fully straighten the knee (leg straight) knee joint is the most fixed.
Thus, the knee joint is quite complicated, and in trauma of the knee joint required the examination of the lower limbs doctor traumatologist-orthopedist to identify clinical signs of damage to the intraarticular structures in the future -to clarify the diagnosis can help radiographs of the knee joint, magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
Due to the impact of external factors (friction, pressure), as well as direct trauma to the joint can occur partial or complete rupture of the ligaments. Damage to individual collagen fibers bundles, generally reversible: having high ability to regenerate, ligaments can repair themselves. A common symptom tear any ligaments – swelling and swelling in the knee area, often a significant increase in volume. As a rule, the swelling increases and becomes larger in size after 2-3 hours after injury.

The most common injuries of the knee:
A meniscus tear
The meniscus of the knee the cartilage is a Crescent-shaped strip that performs shock absorption and load distribution, as well as sensitive function that provides a sense of knee joint position in space and, together with ligaments, muscles and tendons stabilizing function.
Damage to the meniscus, the gap arises from different mechanisms. The primary mechanism is twisting the hip inwards or outwards with respect to the fixed tibia.
A meniscus can be torn in different directions along or across.
The meniscus may delaminate. If the gap is small, mechanically stable and the severed part does not move in the joint, there is a feeling of pain and permanent swelling of the knee joint.
Tear of the meniscus throughout cause mechanical instability. The meniscus begins to shift when moving the joint and can jam the knee joint. In this case, the leg ceases to straighten the knee joint. This condition is called blockade of the knee joint and requires urgent surgical treatment.
Rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament
The ACL rupture is a common sports injury, requiring surgery, and is often accompanied by damage to other structures of the knee joint. Together with the cruciate ligament damaged meniscus, lateral ligaments, and even cartilage surface.
The anterior cruciate ligament functions as the stabilizer, forcing the knee joint during the movement of the shift relative to the physiological axis of rotation, its strength corresponds to 200 kg at the gap. According to statistics women have a cruciate ligament is damaged 4 times more often than men.
In the event of damage to the PCB is a violation of the physiological axis of rotation in the joint, which causes damage to cartilage and menisci. In addition to the mechanical stabilization of the cruciate ligament also serves as a sensitive organ, providing transfer (sense of movement) and proprioception (sense of position of the knee in space).
Damage to the PCB are more common in athletes in those sports where you need a twisting motion in the knee, and sudden acceleration (sports, ski, football, trampoline).
The main complaintfor patients with ACL rupture is instability of the knee joint, that is, there is a feeling of "divergence" of the bones relative to each other in the knee joint — podvigina. This sensation often occurs at an awkward movement or during acceleration.
Rupture of lateral ligament
Ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the knee joint occur when indirect mechanism of injury — excessive deviation of the tibia inwards or outwards, with a torn lateral ligament, opposite side of the deviation.
When rupture of the lateral ligament of the note, the excess deviation of the tibia in the direction opposite to the damaged ligament. For example, if there is suspicion of rupture of the internal lateral ligament, the doctor with one hand captures the outer surface of the knee joint of the patient, and the second rejects the tibia outwards.
The opportunity to reject the tibia outward much more than on the healthy leg indicates ruptured internal lateral ligament. Leg of the patient in the study needs to be straightened in the knee joint.
Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament
Rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)is one of the most severe injuries of the knee joint. To damage the posterior cruciate ligament is quite difficult, most often this happens as a result of car accident (a blow to the front part of the leg by a car bumper) and high speed sports (during a fall on an obstacle in Alpine skiing and snowboarding, team sports in a collision with another player.) In this regard, the PCL tear is rarely isolated and is accompanied by damage to anterior cruciate, outer and inner lateral ligaments.
There are always damaged in dislocation of the tibia, as it is the main stabilising structure of the knee joint.
Posterior cruciate ligament consists of two powerful beams at rupture of one of the beams ligament can heal on their own, the patient is assigned to conservative treatment including wearing a special brace-knee brace for two months from the date of injury.
In the complete rupture of PCL occur gross violations of the biomechanics of the knee. Any flexion of the knee joint is offset from the tibia posteriorly. Instead when bending to perform a rotation in the knee joint, the slipping of the tibia and its displacement ago. As a result, when walking is the front part of the tibia and back part of the condyles of the femur, the rest of load is not involved. While the load on the cartilage increases thousands of times, and the knee joint is completely destroyed in 5 years.
In addition, the displacement of the tibia increases the load back in patellofemoral the joint, the cartilage under the kneecap wears out quickly also, there is a crunch and pain in the knee joint.
Diagnosis of injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament begins with an external examination, is often determined by the retraction of the leg back, a number of patients may spontaneously perform the displacement of the tibia.
Fracture of the condyle of the tibia bone
One of the most severe damage in the knee joint is a fracture in the joint area (cartilage-covered) surfaces. The result of damage to the formation of irregularities and steps on the surface of the cartilage, which can be corrected only surgically.
Almost all intra-articular fractures even with slight displacement necessary to operate, to prevent joint destruction as a result of development of posttraumatic osteoarthritis.
The most frequent damage to the bones in the knee joint are fractures of the kneecap (patella), as well as fractures of the condyles of the tibia.
In fractures of the patella most frequent is the transverse fracture which can be caused by a direct blow or excessive contraction of the quadriceps muscle.
Your reaction to trauma:
1. Rest – immediately after injury is necessary to limit to the minimum of movement to reduce pain and swelling, prevent further damage and pave the way for an earlier recovery.
2. Cold – applying cold compresses, ice packs and other methods of cryotherapy in the first days after a break up leads to a narrowing of the blood vessels, which reduces edema and hemorrhage in the tissue.
3. Elastic bandaging, dressings, bandages – create pressure on the region of the knee, prevent the formation of edema, stabilize the knee joint, limit abnormal movement.
4. Giving the leg elevation position – with the help of available items (e.g., pillows) or special medical equipment leg is raised above heart level. This hampered the inflow of large amounts of blood in the location of the injury reduces the swelling of tissues.
In order to unload the joint, while gaps of 1 degree apply tight bandages on the affected area. They can be performed using elastic bandages or tapes special adhesive tapes, resembling a band-aid. In the first days after injury, treatment Supplement ice packsthat are applied to the damaged area. The cold will reduce swelling of tissues and relieve the pain.
Applying ice packs on their own, remember thatthe burden of cold exposure should not exceed 15 minutes. During the first 24 hours you can use a cold compress 3 – 4 times.
It is very important to completely eliminate heat treatments, which are so like to recommend to our grandmothers. Treatment warming ointments can only be performed after 3-5 days after injury.
For the treatment of pain used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in pill or injections. Fighting with pain is made using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ketorolac, diclofenac, ibuprofen), which the doctor prescribes as in the form of tablets for oral administration, and in the form of analgesic creams, ointments, lotions: "Indovazin", "Dolobene", "Lioton", "Troxevasin".
Topically applied different warming ointment: "I experienced an unexpected side effect", "Indovazin", "Lioton", "Larkspur", "We", "Vibrators".
5. Warm – start applying warming compresses, ointments, heating pads on the area of the knee only a few days after a torn ligament after the cessation of bleeding from small vessels. Such procedures bring relief of pain for the patient.
6. Physiotherapy – applied applications of paraffin wax.
7. The complex of physical exercises – you need to perform regular rehabilitation to restore muscle strength and mobility in the joint.
8. Massage – is carried out either by a specialist, either in the form of self-massage to relieve pain and swelling.
Traditional methods of treatment is able to reduce the size of the swelling and reduce pain, but you must remember that they are used only in conjunction with a course of basic therapy prescribed by a doctor:
- Application of potato: to grate raw potatoes (1 unit), applied to the affected knee, and the top to place a thin cloth. After 15 minutes, rinse.
- Well eliminates swelling a mixture of white clay and concoctions. Grind the dry herb concoctions, take 1 scoop of raw materials and 1 teaspoon of clay diluted with warm water to a pulp. The tool is applied to the knee, leave under cover for half an hour.
- Grind aloe leaf and the leaf of Kalanchoe. Mix well and use as a compress to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Grate the horseradish root (1 kg), pour 4 l of water, boil 3 minutes. In the cooled broth add 500 g of honey, leave in the fridge for a day. Further, the means to drain and ingest 1 teaspoon 3 times/day. This recipe will help to quickly restore tissue damaged ligaments.
- Not less effective in this case is the healing salve of comfrey, which removes the swelling and pain reliever and helps to dissolve the hematoma.
- If you manage to find the pharmacy the fat of the Viper, you can RUB the affected knee this tool twice a day and it will regenerate several times faster than normal.
- Grate the knee vodka tincture of propolis.
- Overnight fixed knee leaves of fresh sage.
- Applying a mixture of onion pulp and sugar to the dislocation at 6 hours in the form of a gauze compress.published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: moyaspina.ru/bolezni/razryv-kolennyh-svyazok-chastichnyy-ili-polnyy
Connection to Sky — qigong for getting rid of diseases and prolonging life
SUPER effective recipes masks for dry hair