593
5 sensors of the autopilot and their (so far) unsolvable problems
Life does not stand still and "Tesla" still fighting (Tesla Model X too, but without the help of the autopilot). What is wrong with the sensors of ADAS systems? And why in the coming years, nothing will not change dramatically?
Many, surprisingly, have approached their physical abilities. We can talk about it confidently, because the following systems are used not only on cars and have large markets outside the auto world. It's big money, billions in budgets for R&D and slow progress.
Now read more.
Types of sensors — like fingers on a hand, five:
What is important to know about the market in General?
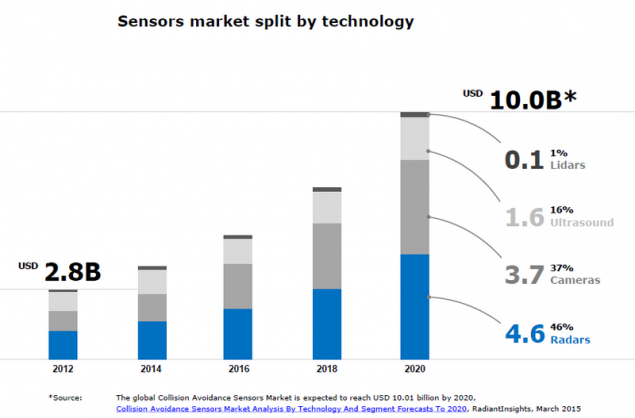
Estimates vary, but the procedure is the same. The balance is skewed in favour of cameras and radars, which two account for 85 percent of the market in money. Lidars remain a niche solution (only barring breakthroughs), and ultrasonic sensors can not go beyond its niche and breaks, again, not visible. Night vision systems are being lost even against lidars.
Now read more.
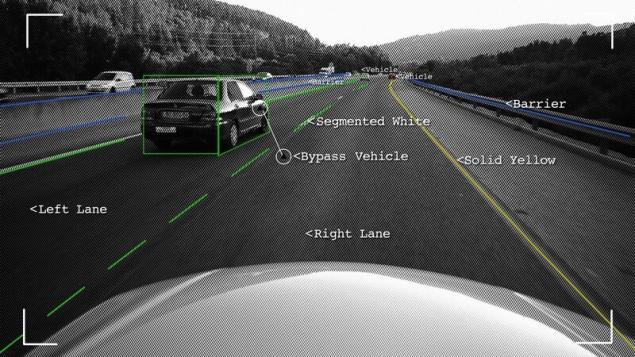
The CAMERAWorks like this: get the picture of the world in the visible range, treated (individual frames and sequence), recognized.
Pros:
Only a camera can detect road markings and signs. Cameras have good resolution in angle, so the camera's well "understands" the objects that move across the movement of the car (rolling road pedestrian). On the picture from the camera video possible classification of objects ("dog","child""adult""Bicycle""car""truck"). And, of course, the camera is available at a price — from several hundred dollars for the buyer. Cons:
Cameras have poor resolution in range, they struggle to understand the distance to the obstacle or speed of convergence (stereo camera partly solve the problem). There is no direct measurement of the speed of objects it can be understood by a series of frames, and still fuzzy the measurement is. Strongly influenced by weather and road conditions — the infamous "white van in the background of the bright sky" in the recent accident. Processing of data from cameras is the time delay is the greater, the more complex system cameras. Market trampled elephants from Intel and NVIDIA to Mobileye and Magna International. A lot of startups, the entry threshold low. The development of the technology rests on the speed and quality of processing, that is, processors and algorithms. Dramatically increase the speed of processing does not work, and breakthrough algorithms did not yet burst.
Conclusion:No cameras on the car is still not enough.

The RADARis radiated at very high frequency, listened back, and immediately recognized the distance to the obstacles, their speed and angles on them.
Pros:
On the radar is much less affected by weather conditions, does not affect the color of objects and lighting. Good resolution range and speed, available direct measurement of range and speed with good accuracy. Instant (1/20–1/50 second) data processing, which is especially important for high speeds. The ability to easily collect and analyze information in dynamics due to the small amount of information. For the same reason suitable for V2I/V2V Cons:
Not cheaper, and often more expensive cameras. More than 1000 dollars for a long-range radar. Poor resolution in angle (radar is difficult to understand the movement across). There is no direct possibility to classify the obstacle or to estimate its dimensions. A strong dependence of the range of viewing angle. If you Shine far and narrow beam, not seeing interference over the road and on the sides. Shine wide — get a small range. In the market of elephants, only with other names — Bosch Global, Delphi, Smartmicro. Startups almost no barrier of entry very high due to the high cost of equipment under the microwave. Processing methods have changed little over the past 50 years, investments in the development and organization of production of components (such as antenna-feeder tract) hundreds of millions of euros. Affordable and high-quality transceivers, without which there is not a mass solution, produced half a dozen companies all over the world. Radar gradually improved, but the development takes decades.
Conclusion:the Strengths of the radar is the weak side of the camera and Vice versa. No warning is also not necessary.
Not my idea, but Mr. Musk:
“...That said, I don't think you need LIDAR. I think you can do this all with passive optical and then with maybe one forward RADAR... if you are driving fast into rain or snow or dust. I think that completely solves it without the use of LIDAR. I'm not a big fan of LIDAR, I don't think it makes sense in this context.”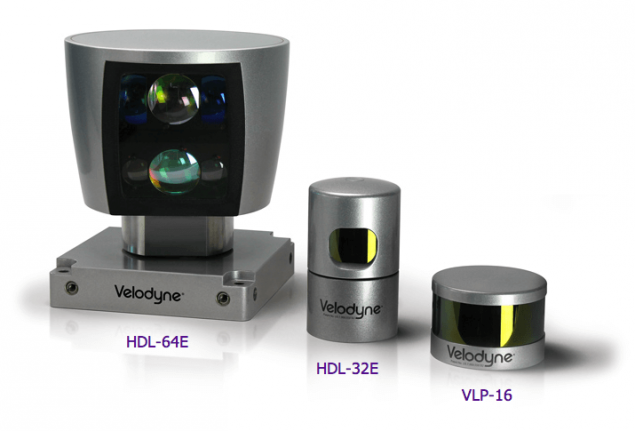
The LIDARLaser rangefinders: laser shone, looked, returned, given an array of points with distances to them.
Pros:
Vundervaflâ, sees everything in detail and with high accuracy. In addition to them so no one knows and never will. Cons:
Scanning lidars can see the same stretch of road only two or three times per second. High cost, no — COST lidar. More lidars fragile. In short, all the rest are cons In the market there are tough players — Velodyne LiDAR, Quanergy, Sick. All the decisions are relatively young, startups a few pieces, but relatively large. Do the major players in the Bosch level with a gain in automotive-direction in tens of billions in the market and will not be. To lower the cost of lidar and the abandonment of moving parts dramatically drop the possibility and necessity of lidar too. All need a solution for 250 bucks, but it doesn't seem to.
Simple and clear: the automotive market for lidar, a hundred times smaller than the market's radar or cameras, and those full of and other applications
Conclusion:up Until the revolution, the lidar will remain a niche solution. Good for prototyping, it does for a stock car. And for prototyping bad: sharpened by lidars logic not be adaptable to other sensors.

ULTRASOUND
The familiar Parktronic: radiated high frequency signal, wait until it comes back, and counted the time.
Pros:
Very cheap, a few hundreds of dollars for a system of several sensors can easily be combined. The technology was tested and clear, you can experiment even at home on the arduino. Cons:
The range is limited to units of meters. There is no way to understand the angle to the object or to directly measure the speed. Low confidence data. Us market reigns Chinese noname, clearing a long-trodden, those wishing to invest in new projects. Startups are few, but there is such Toposens who makes the coolest thing on the ultrasound, but something suddenly starts to make a radar too.
Conclusion:as soon As radars and lidars will learn to work closer distances, the ultrasound only for arduino and will remain. Joke:).

INFRARED CAMERAS
How it works: looked in the infrared range, has analyzed the image on the matrix.
Pros:
Clearly visible hot people and forest animals. Cons:
Expensive, couple of thousand of dollars just for a front camera and a Narrow field of use Limitations temperature of use. Conclusion:Even more niche story than lidars. Radar lidar throw them from the car market very soon, if not already.
And now — sweet. To summarize:
No sensor or sensor system can not be universal. If to speak about the role of the only low-end solutions is the camera. Secondly, the radar. Any system ADAS and especially since the autopilot will use the system from several sensors. This is called sensor fusion and will be used primarily to combine a camera and radar. I suspect they will end up. The more diverse information you want to collect, the more it costs (not so bad) and the more time it takes. The longer you process, the slower we have to go, that it was safe. Hence turtle riding most of the autopilots and the love of good weather. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: geektimes.ru/post/278534/
Many, surprisingly, have approached their physical abilities. We can talk about it confidently, because the following systems are used not only on cars and have large markets outside the auto world. It's big money, billions in budgets for R&D and slow progress.
Now read more.
Types of sensors — like fingers on a hand, five:
- camera
- radar,
- lidar,
- ultrasound,
- the infrared camera.
- passive (camera) and active (radar-lidar),
- in the visible range (camera) and not (everyone else, including the IR)
- frequency (ultrasound to the lidar).
What is important to know about the market in General?

Estimates vary, but the procedure is the same. The balance is skewed in favour of cameras and radars, which two account for 85 percent of the market in money. Lidars remain a niche solution (only barring breakthroughs), and ultrasonic sensors can not go beyond its niche and breaks, again, not visible. Night vision systems are being lost even against lidars.
Now read more.

The CAMERAWorks like this: get the picture of the world in the visible range, treated (individual frames and sequence), recognized.
Pros:
Only a camera can detect road markings and signs. Cameras have good resolution in angle, so the camera's well "understands" the objects that move across the movement of the car (rolling road pedestrian). On the picture from the camera video possible classification of objects ("dog","child""adult""Bicycle""car""truck"). And, of course, the camera is available at a price — from several hundred dollars for the buyer. Cons:
Cameras have poor resolution in range, they struggle to understand the distance to the obstacle or speed of convergence (stereo camera partly solve the problem). There is no direct measurement of the speed of objects it can be understood by a series of frames, and still fuzzy the measurement is. Strongly influenced by weather and road conditions — the infamous "white van in the background of the bright sky" in the recent accident. Processing of data from cameras is the time delay is the greater, the more complex system cameras. Market trampled elephants from Intel and NVIDIA to Mobileye and Magna International. A lot of startups, the entry threshold low. The development of the technology rests on the speed and quality of processing, that is, processors and algorithms. Dramatically increase the speed of processing does not work, and breakthrough algorithms did not yet burst.
Conclusion:No cameras on the car is still not enough.

The RADARis radiated at very high frequency, listened back, and immediately recognized the distance to the obstacles, their speed and angles on them.
Pros:
On the radar is much less affected by weather conditions, does not affect the color of objects and lighting. Good resolution range and speed, available direct measurement of range and speed with good accuracy. Instant (1/20–1/50 second) data processing, which is especially important for high speeds. The ability to easily collect and analyze information in dynamics due to the small amount of information. For the same reason suitable for V2I/V2V Cons:
Not cheaper, and often more expensive cameras. More than 1000 dollars for a long-range radar. Poor resolution in angle (radar is difficult to understand the movement across). There is no direct possibility to classify the obstacle or to estimate its dimensions. A strong dependence of the range of viewing angle. If you Shine far and narrow beam, not seeing interference over the road and on the sides. Shine wide — get a small range. In the market of elephants, only with other names — Bosch Global, Delphi, Smartmicro. Startups almost no barrier of entry very high due to the high cost of equipment under the microwave. Processing methods have changed little over the past 50 years, investments in the development and organization of production of components (such as antenna-feeder tract) hundreds of millions of euros. Affordable and high-quality transceivers, without which there is not a mass solution, produced half a dozen companies all over the world. Radar gradually improved, but the development takes decades.
Conclusion:the Strengths of the radar is the weak side of the camera and Vice versa. No warning is also not necessary.
Not my idea, but Mr. Musk:
“...That said, I don't think you need LIDAR. I think you can do this all with passive optical and then with maybe one forward RADAR... if you are driving fast into rain or snow or dust. I think that completely solves it without the use of LIDAR. I'm not a big fan of LIDAR, I don't think it makes sense in this context.”

The LIDARLaser rangefinders: laser shone, looked, returned, given an array of points with distances to them.
Pros:
Vundervaflâ, sees everything in detail and with high accuracy. In addition to them so no one knows and never will. Cons:
Scanning lidars can see the same stretch of road only two or three times per second. High cost, no — COST lidar. More lidars fragile. In short, all the rest are cons In the market there are tough players — Velodyne LiDAR, Quanergy, Sick. All the decisions are relatively young, startups a few pieces, but relatively large. Do the major players in the Bosch level with a gain in automotive-direction in tens of billions in the market and will not be. To lower the cost of lidar and the abandonment of moving parts dramatically drop the possibility and necessity of lidar too. All need a solution for 250 bucks, but it doesn't seem to.
Simple and clear: the automotive market for lidar, a hundred times smaller than the market's radar or cameras, and those full of and other applications
Conclusion:up Until the revolution, the lidar will remain a niche solution. Good for prototyping, it does for a stock car. And for prototyping bad: sharpened by lidars logic not be adaptable to other sensors.

ULTRASOUND
The familiar Parktronic: radiated high frequency signal, wait until it comes back, and counted the time.
Pros:
Very cheap, a few hundreds of dollars for a system of several sensors can easily be combined. The technology was tested and clear, you can experiment even at home on the arduino. Cons:
The range is limited to units of meters. There is no way to understand the angle to the object or to directly measure the speed. Low confidence data. Us market reigns Chinese noname, clearing a long-trodden, those wishing to invest in new projects. Startups are few, but there is such Toposens who makes the coolest thing on the ultrasound, but something suddenly starts to make a radar too.
Conclusion:as soon As radars and lidars will learn to work closer distances, the ultrasound only for arduino and will remain. Joke:).

INFRARED CAMERAS
How it works: looked in the infrared range, has analyzed the image on the matrix.
Pros:
Clearly visible hot people and forest animals. Cons:
Expensive, couple of thousand of dollars just for a front camera and a Narrow field of use Limitations temperature of use. Conclusion:Even more niche story than lidars. Radar lidar throw them from the car market very soon, if not already.
And now — sweet. To summarize:
No sensor or sensor system can not be universal. If to speak about the role of the only low-end solutions is the camera. Secondly, the radar. Any system ADAS and especially since the autopilot will use the system from several sensors. This is called sensor fusion and will be used primarily to combine a camera and radar. I suspect they will end up. The more diverse information you want to collect, the more it costs (not so bad) and the more time it takes. The longer you process, the slower we have to go, that it was safe. Hence turtle riding most of the autopilots and the love of good weather. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: geektimes.ru/post/278534/