604
How to deal with the heat loss of the house
The outer walls of the buildings historically were made of red burnt clinker bricks. The heating was furnace, and one or two of heating per day is enough to maintain normal building temperatures. This is due to the fact that clinker has a high heat capacity, is heated and then over long time slowly releases heat into the environment.

In thermal calculations in most regions of Russia the thickness of external brick walls of plain red solid bricks you need to take 2.5 brick (64cm). However, during the time from this rule for various reasons, has repeatedly backed off
1. In the postwar period of recovery of the economy, with a deficit of building materials and housing, it was decided to build wall thickness 2.5 brick, and the thickness of 2 bricks. This allowed us to build 5 houses instead of 4 and was intended as a temporary measure. However, it increases the heat loss through external walls by 15%. Unfortunately, the "temporary measure" remained for a long time.
2. In the sixties of the last century was the invention of low cement white silicate brick. Sand-lime brick, along with the red brick has many positive properties, but the masonry of sand-lime brick has a higher teploproject than the walls of red brick.
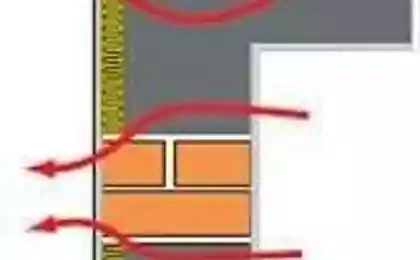
For the purpose of using a silicate brick in construction, the masonry walls with a thickness of 2 brick outer facing layer in 0.5 bricks laid from a white silicate brick. Due to this heat loss through external walls is increased by 4%.
3. At installation of heating devices are sill niche depth of 0,5 brick. Niche is made by reducing the thickness of the outer wall. At this point, the thickness of the outer wall is 380 mm 510 mm. instead of the usual Additional heat loss through external walls is increased by 2%.
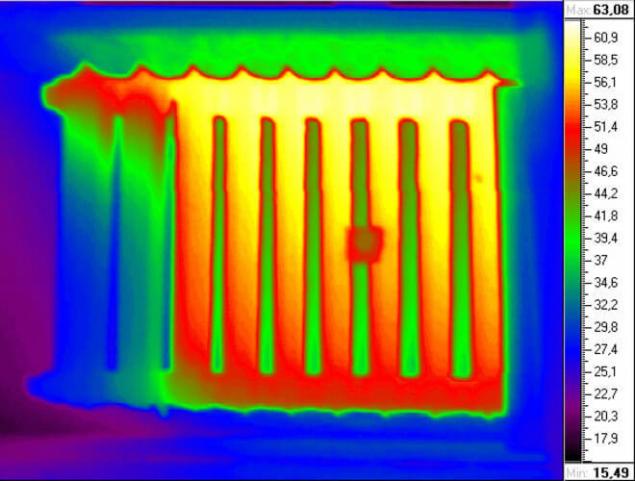
4. A lot of heat energy is lost because of the location of heating appliances directly on the outer wall of the building. The warm air behind the radiator becomes stagnant and there is formed a temperature comparable to the temperature of the coolant in the heating system. The temperature difference between outdoor and indoor air within the area of the outer wall of the heating device 2 times higher in comparison with other sections of the wall.
Additional heat losses at the outer walls for another 10% higher.
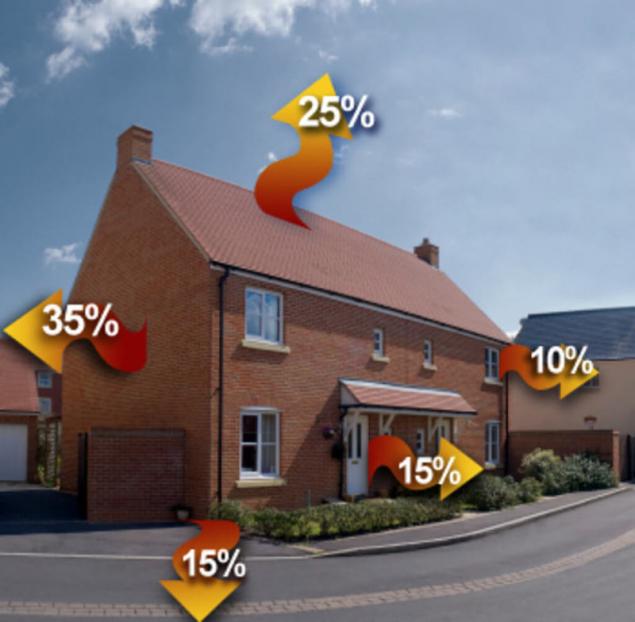

When the total heat loss through the exterior walls to heat the ambient air of the street goes: 15% + 4% + 2% + 10% = 31% heat energy! Not less heat loss occurs through ventilation buildings. Ventilation in most cases, as such, no, there is a system of ducts through which warm air extending to the premises of the oxygen is expelled. This process is not regulated, as no duct louvered shutters. In the cold season warm air out of the buildings "with a whistle"! Thermal energy losses in this case are enormous.
Loss through ventilation cannot be counted, as the houses are constructed so that they cannot be applied ventilation and air recuperation. Life volumes in existing buildings are so small and fragmented that in residential premises to establish an effective air movement and mixing is impossible.
In order to approximately estimate the magnitude of financial losses from this situation, we assume that we have in Russia, 1 billion square meters of low-quality housing. For heating which during the season is spent 80 kg of conditional fuel per 1 sqm
At heating of buildings, we assume that through walls and other structures, ventilation, etc. is lost, wasted 31% of thermal energy.
At a cost in 2016 of 1 ton of standard coal, equal to 17 830 RUB, we lose annually wasted:
1 000 000 000 x 80 x 0.31 = 24.8 billion kg of conditional fuel, or 24.8 million tonnes of equivalent fuel. The money it would be: 24 800 000 17 830 x = 443.4 th bn RUB!
But this is only a rough estimate. Actually unnecessary loss of thermal energy in buildings much larger and require clarification. Based on the foregoing we can draw the following conclusions and proposals:
Source: estp-blog.ru/rubrics/rid-30175/

In thermal calculations in most regions of Russia the thickness of external brick walls of plain red solid bricks you need to take 2.5 brick (64cm). However, during the time from this rule for various reasons, has repeatedly backed off
1. In the postwar period of recovery of the economy, with a deficit of building materials and housing, it was decided to build wall thickness 2.5 brick, and the thickness of 2 bricks. This allowed us to build 5 houses instead of 4 and was intended as a temporary measure. However, it increases the heat loss through external walls by 15%. Unfortunately, the "temporary measure" remained for a long time.
2. In the sixties of the last century was the invention of low cement white silicate brick. Sand-lime brick, along with the red brick has many positive properties, but the masonry of sand-lime brick has a higher teploproject than the walls of red brick.
For the purpose of using a silicate brick in construction, the masonry walls with a thickness of 2 brick outer facing layer in 0.5 bricks laid from a white silicate brick. Due to this heat loss through external walls is increased by 4%.
3. At installation of heating devices are sill niche depth of 0,5 brick. Niche is made by reducing the thickness of the outer wall. At this point, the thickness of the outer wall is 380 mm 510 mm. instead of the usual Additional heat loss through external walls is increased by 2%.
4. A lot of heat energy is lost because of the location of heating appliances directly on the outer wall of the building. The warm air behind the radiator becomes stagnant and there is formed a temperature comparable to the temperature of the coolant in the heating system. The temperature difference between outdoor and indoor air within the area of the outer wall of the heating device 2 times higher in comparison with other sections of the wall.
Additional heat losses at the outer walls for another 10% higher.

When the total heat loss through the exterior walls to heat the ambient air of the street goes: 15% + 4% + 2% + 10% = 31% heat energy! Not less heat loss occurs through ventilation buildings. Ventilation in most cases, as such, no, there is a system of ducts through which warm air extending to the premises of the oxygen is expelled. This process is not regulated, as no duct louvered shutters. In the cold season warm air out of the buildings "with a whistle"! Thermal energy losses in this case are enormous.
Loss through ventilation cannot be counted, as the houses are constructed so that they cannot be applied ventilation and air recuperation. Life volumes in existing buildings are so small and fragmented that in residential premises to establish an effective air movement and mixing is impossible.
In order to approximately estimate the magnitude of financial losses from this situation, we assume that we have in Russia, 1 billion square meters of low-quality housing. For heating which during the season is spent 80 kg of conditional fuel per 1 sqm
At heating of buildings, we assume that through walls and other structures, ventilation, etc. is lost, wasted 31% of thermal energy.
At a cost in 2016 of 1 ton of standard coal, equal to 17 830 RUB, we lose annually wasted:
1 000 000 000 x 80 x 0.31 = 24.8 billion kg of conditional fuel, or 24.8 million tonnes of equivalent fuel. The money it would be: 24 800 000 17 830 x = 443.4 th bn RUB!
But this is only a rough estimate. Actually unnecessary loss of thermal energy in buildings much larger and require clarification. Based on the foregoing we can draw the following conclusions and proposals:
- Thermal energy losses in buildings high and over their reduction of the need to work tirelessly.
- To increase the capital buildings and the increase in heat capacity be commonly used in the walls of red baked brick, proven over many years of operation.
- The construction of the buildings necessary to conduct taking into account technical indicators on energy and material consumption per 1 sq. m of total area.
- In buildings it is necessary to limit the device of balconies and loggias, as they are the window shade and lower lighting. The use of balconies and loggias should be linked with the climate and environment of the area.
- Houses heaters with exterior walls should be moved closer to the middle of the buildings.
- To increase the light through the high Windows and increase the living space, the ceiling height should be not less than 3 m.
- For buildings with low technical indicators on energy consumption and material consumption per 1 sq. m total area needed to develop a model of the ventilation system and recuperation. published
Source: estp-blog.ru/rubrics/rid-30175/
Smoothes wrinkles: cosmetic use of viburnum
Ivan formanek: Recovery and regeneration. My path to health