583
5 mental mistakes which take you from making the right decisions
The researchers and economists for a long time believed that people always make logical, well-thought-out decisions. However, over the past decade, scientists had discovered a wide range of mental errors that undermined our reputation myshleniya.Vremya from the time we are able to make the right decisions, but in most cases we do a strange, irrational choices, based on their emotions. < Website published an article describing the five most common mental mistakes that keep us constantly make decisions.
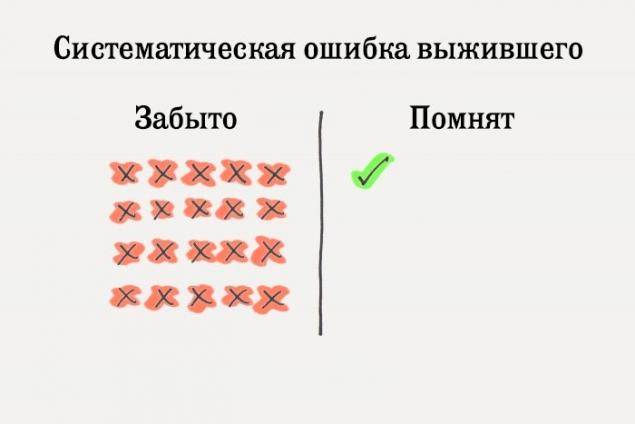
1. Systematic error vyzhivshegoSegodnya virtually all popular online media are filled with survivorship bias (Eng. Survivorship bias). Titles like "8 things that successful people do every day," "the best advice ever received Richard Branson" or "How LeBron James trains in the off-season" - a survivorship bias in action
. survivor Systematic errors related to our tendency to focus on the winners in any particular field and to learn from them, completely forgetting the losers, who used the same strategy.
There are thousands of athletes who train just as LeBron James, but they could not get in the NBA. The problem is that no one has heard about the thousands of athletes who failed to reach the top. We only hear about people who have "survived". We mistakenly overestimate the strategy, tactics and tips one "survivor", ignoring the fact that they do not work for most people.
Another example: "Richard Branson, Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg dropped out of school and become billionaires! You do not need a school to succeed. Entrepreneurs just need to stop wasting time to study and get to work. »
For every Branson, Gates and Zuckerberg hopes for thousands of other entrepreneurs who have failed, we got into debt and left with an incomplete education. Survivorship bias say that we do not know how this or that strategy will manifest itself concretely in this case.
Since the winners often remembered, but the losers generally forgotten, it becomes very difficult to determine whether the lead to the success of one or the other strategy or not.
2. Fear of losing poteryamiStrah (Eng. Loss aversion) refers to our tendency to strongly avoid losses on the way to the acquisition of profits. Studies show that if someone will give you $ 10, you will experience a small increase in satisfaction. But if you lose $ 10, you will experience a significantly higher loss of satisfaction. Yes, the opposite reaction, but they are equal in magnitude.
Our tendency to avoid losses of forces us to make stupid decisions and change their behavior only in order to preserve the things that we already have. We strive to protect the things that we have, and this can lead to the fact that we will be too overestimate them, compared with other options.
For example, if you buy a new pair of shoes, it will bring you a little pleasure gain. If you have never been able to wear these shoes and decided to sell them after a few months, then this step is likely to be extremely painful for you. You never wore them, but for some reason you can not part with them. Fear of loss.
Likewise, you may feel a little bit of joy, when on the way to all traffic lights will illuminate for you the green light, but if the driver of the car in front of you act too late and you miss the opportunity to slip on the green light, then you cover feelings of anger. The pain of losing the possibility of much more than a pleasure, emerged first.
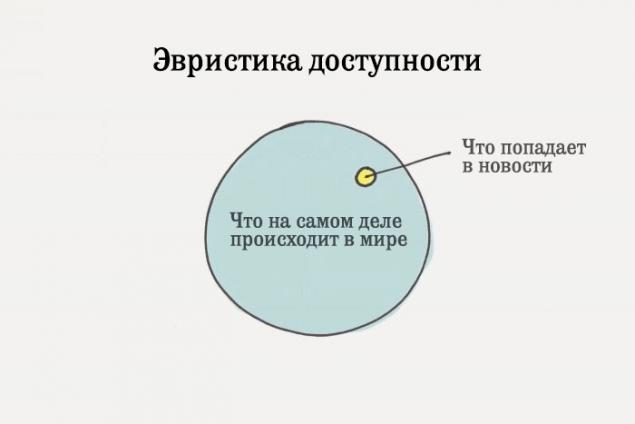
3. Heuristics dostupnostiEvristika availability (English availability heuristic.) - This is a very common mistake that our brain does, suggesting that the examples, readily come to mind are the most important things, or prevailing
. The study, conducted by Steven Pinker of Harvard University, showed that we are living in the least cruel time in the history of mankind. Today a lot more people in the world than ever. The number of murders, rapes, and sdomogatelstv cases of child abuse has been steadily declining.
Many people are surprised when they hear these statistics. Some people still refuse to believe in them. If we live in the most peaceful time in history, then why in the world there are so many wars right now? Why is every day we hear news that somewhere someone was killed or raped? Why is it so often happens terrorist acts and destruction?
Welcome to the availability heuristic.
The answer lies in the fact that we live in a world where each event immediately becomes common knowledge. Information about any accident or a crime is widely available than ever before. Go online and you will find much information about recent events, as would hardly fit in the same issue of the newspaper a hundred years ago.
The total percentage of hazardous events is reduced, however, the likelihood that you will hear about them, increases. And as the information on these events is always available, our brain thinks that they occur with greater frequency than it actually is.
We overestimate the impact of what we remember, and underestimate the prevalence of events, which we have not heard anything.
4. binding effect (anchor) Not far from my house there is a fast food restaurant, where they sell delicious burgers with cheese. The menu stated in large letters: "FOR ONE BURGER can select up to 6 kinds of cheese»
. My first thought: this is absurd. Who wants to order a burger with six kinds of cheese?
The second thought: What are the six types of cheese, I would choose
? I have not thought about what genius are the owners of cafes, as long as learned about the effect of binding (or anchor;. English anchoring). You see, ordering a burger here, I usually chose any one kind of cheese. But after I read the menu "FOR ONE BURGER can select up to six types of cheese," my brain is attached to the fact that you can order more cheese than usual.
Most people will not order the six kinds of cheese, but this binding is sufficient to move from one piece to two or three, thus increasing the cost of a burger on a couple of bucks.
This effect is often used in the commercial field. For example, businesses have discovered that if you set a limit, for example, "12 pieces of goods in the hands of" the people will buy two times more than usual.
But perhaps the most common area where applicable binding effect, is pricing. If you see the clock in the store price tag of $ 500, you will find them too expensive for their budget. However, if, going to the store, you first see the clock for $ 5,000, and then - for 500, the price of the past will seem quite reasonable. Most premium products play a very important role: they allow goods midrange seem cheaper than it really is
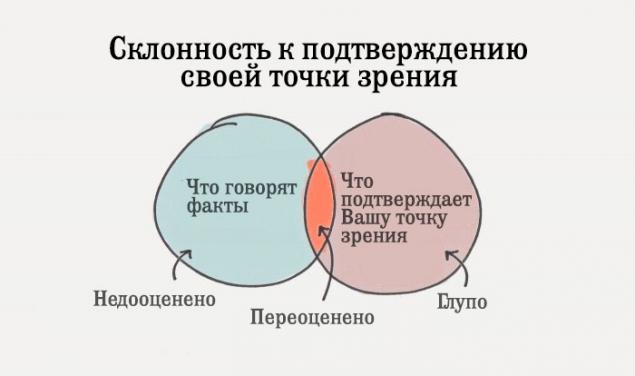
5.. Tendency to validate his point zreniyaSklonnost to validate their point of view (Eng confirmation bias.) - It is the tendency to seek or to give priority to information that confirms our beliefs, and at the same time ignore or devalue what they contradict
. For example, people, and believes that climate change - this is a serious problem, so he seeks and reads only books and articles on the conservation of the environment, climate and renewable energy. As a result, people, and continues to confirm and reinforce their current beliefs.
In turn, Person B does not believe that climate change is a serious problem, therefore, seeks and reads only those materials that climate change is called a myth. As a result, Person B continues to confirm and reinforce their current beliefs.
Change your point of view is not as easy as it seems. The more you believe in something, the more you ignore and filter the entire opposite information.
Another example. If you have just purchased a Honda Accord, considering it to be the best car on the market, then, of course, you will read only the articles that praise this machine. Meanwhile, if you are in any magazine run into information that the vehicle has been selected, for example, Chevrolet Impala, you reject it, considering an error or find some other excuse.
Most people do not want new information, they tend to validate what is already known.
* * *
< After reading this article you have a question: how to make the brain does not make these mistakes
? For a start do not think of them as a sign that your brain does not work properly. Treat them as evidence that the labels used by the brain, not always carry with them a favor. There are many areas of everyday life, where the mental processes, mentioned above, are incredibly useful, so you should not get rid of them.
The problem is that our brains perform well as those functions that we ultimately use them in situations where they manifest themselves negative. In such cases, self-awareness is one of the best solutions to the problem.
Author James Clear, translation Muz4in.net
via factroom.ru
1. Systematic error vyzhivshegoSegodnya virtually all popular online media are filled with survivorship bias (Eng. Survivorship bias). Titles like "8 things that successful people do every day," "the best advice ever received Richard Branson" or "How LeBron James trains in the off-season" - a survivorship bias in action
. survivor Systematic errors related to our tendency to focus on the winners in any particular field and to learn from them, completely forgetting the losers, who used the same strategy.
There are thousands of athletes who train just as LeBron James, but they could not get in the NBA. The problem is that no one has heard about the thousands of athletes who failed to reach the top. We only hear about people who have "survived". We mistakenly overestimate the strategy, tactics and tips one "survivor", ignoring the fact that they do not work for most people.
Another example: "Richard Branson, Bill Gates and Mark Zuckerberg dropped out of school and become billionaires! You do not need a school to succeed. Entrepreneurs just need to stop wasting time to study and get to work. »
For every Branson, Gates and Zuckerberg hopes for thousands of other entrepreneurs who have failed, we got into debt and left with an incomplete education. Survivorship bias say that we do not know how this or that strategy will manifest itself concretely in this case.
Since the winners often remembered, but the losers generally forgotten, it becomes very difficult to determine whether the lead to the success of one or the other strategy or not.

2. Fear of losing poteryamiStrah (Eng. Loss aversion) refers to our tendency to strongly avoid losses on the way to the acquisition of profits. Studies show that if someone will give you $ 10, you will experience a small increase in satisfaction. But if you lose $ 10, you will experience a significantly higher loss of satisfaction. Yes, the opposite reaction, but they are equal in magnitude.
Our tendency to avoid losses of forces us to make stupid decisions and change their behavior only in order to preserve the things that we already have. We strive to protect the things that we have, and this can lead to the fact that we will be too overestimate them, compared with other options.
For example, if you buy a new pair of shoes, it will bring you a little pleasure gain. If you have never been able to wear these shoes and decided to sell them after a few months, then this step is likely to be extremely painful for you. You never wore them, but for some reason you can not part with them. Fear of loss.
Likewise, you may feel a little bit of joy, when on the way to all traffic lights will illuminate for you the green light, but if the driver of the car in front of you act too late and you miss the opportunity to slip on the green light, then you cover feelings of anger. The pain of losing the possibility of much more than a pleasure, emerged first.
3. Heuristics dostupnostiEvristika availability (English availability heuristic.) - This is a very common mistake that our brain does, suggesting that the examples, readily come to mind are the most important things, or prevailing
. The study, conducted by Steven Pinker of Harvard University, showed that we are living in the least cruel time in the history of mankind. Today a lot more people in the world than ever. The number of murders, rapes, and sdomogatelstv cases of child abuse has been steadily declining.
Many people are surprised when they hear these statistics. Some people still refuse to believe in them. If we live in the most peaceful time in history, then why in the world there are so many wars right now? Why is every day we hear news that somewhere someone was killed or raped? Why is it so often happens terrorist acts and destruction?
Welcome to the availability heuristic.
The answer lies in the fact that we live in a world where each event immediately becomes common knowledge. Information about any accident or a crime is widely available than ever before. Go online and you will find much information about recent events, as would hardly fit in the same issue of the newspaper a hundred years ago.
The total percentage of hazardous events is reduced, however, the likelihood that you will hear about them, increases. And as the information on these events is always available, our brain thinks that they occur with greater frequency than it actually is.
We overestimate the impact of what we remember, and underestimate the prevalence of events, which we have not heard anything.

4. binding effect (anchor) Not far from my house there is a fast food restaurant, where they sell delicious burgers with cheese. The menu stated in large letters: "FOR ONE BURGER can select up to 6 kinds of cheese»
. My first thought: this is absurd. Who wants to order a burger with six kinds of cheese?
The second thought: What are the six types of cheese, I would choose
? I have not thought about what genius are the owners of cafes, as long as learned about the effect of binding (or anchor;. English anchoring). You see, ordering a burger here, I usually chose any one kind of cheese. But after I read the menu "FOR ONE BURGER can select up to six types of cheese," my brain is attached to the fact that you can order more cheese than usual.
Most people will not order the six kinds of cheese, but this binding is sufficient to move from one piece to two or three, thus increasing the cost of a burger on a couple of bucks.
This effect is often used in the commercial field. For example, businesses have discovered that if you set a limit, for example, "12 pieces of goods in the hands of" the people will buy two times more than usual.
But perhaps the most common area where applicable binding effect, is pricing. If you see the clock in the store price tag of $ 500, you will find them too expensive for their budget. However, if, going to the store, you first see the clock for $ 5,000, and then - for 500, the price of the past will seem quite reasonable. Most premium products play a very important role: they allow goods midrange seem cheaper than it really is
5.. Tendency to validate his point zreniyaSklonnost to validate their point of view (Eng confirmation bias.) - It is the tendency to seek or to give priority to information that confirms our beliefs, and at the same time ignore or devalue what they contradict
. For example, people, and believes that climate change - this is a serious problem, so he seeks and reads only books and articles on the conservation of the environment, climate and renewable energy. As a result, people, and continues to confirm and reinforce their current beliefs.
In turn, Person B does not believe that climate change is a serious problem, therefore, seeks and reads only those materials that climate change is called a myth. As a result, Person B continues to confirm and reinforce their current beliefs.
Change your point of view is not as easy as it seems. The more you believe in something, the more you ignore and filter the entire opposite information.
Another example. If you have just purchased a Honda Accord, considering it to be the best car on the market, then, of course, you will read only the articles that praise this machine. Meanwhile, if you are in any magazine run into information that the vehicle has been selected, for example, Chevrolet Impala, you reject it, considering an error or find some other excuse.
Most people do not want new information, they tend to validate what is already known.

* * *
< After reading this article you have a question: how to make the brain does not make these mistakes
? For a start do not think of them as a sign that your brain does not work properly. Treat them as evidence that the labels used by the brain, not always carry with them a favor. There are many areas of everyday life, where the mental processes, mentioned above, are incredibly useful, so you should not get rid of them.
The problem is that our brains perform well as those functions that we ultimately use them in situations where they manifest themselves negative. In such cases, self-awareness is one of the best solutions to the problem.
Author James Clear, translation Muz4in.net
via factroom.ru