1553
"Venera-7": the first soft landing on Venus with the subsequent transfer of data to Earth
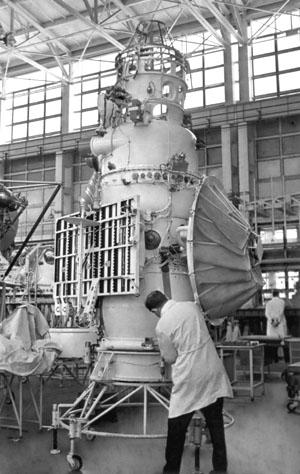
August 17, 1970 at 8 o'clock 38 minutes Moscow time from the Baikonur cosmodrome launched automatic research space station "Venera-7". In December of the same year, the lander got on the planet's surface and transmit data back to Earth. It was the first landing of working spacecraft on another planet.
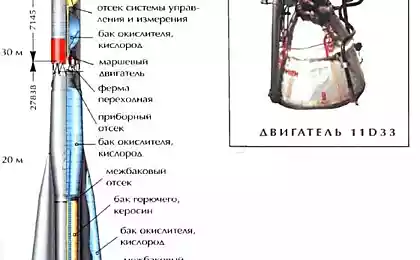
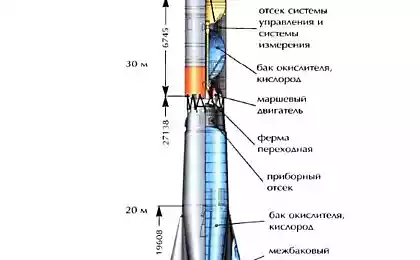
Triggers devices "Venus" that preceded the successful landing, allowed scientists to construct the apparatus in view of the data on temperature, pressure, wind speed and other characteristics of the planet. Housing "Venus-7" is made of titanium, the housing lander added thermal insulation of glass wool and fiberglass, and overload protection in contact with the ground cushioning device installed.
The first attempt to explore Venus by Soviet scientists was the unit "Sputnik 7" in 1961. The station has remained in Earth orbit. The second attempt was more successful: a few days later on sent to the planet, "Venus 1" - she passed away a hundred thousand kilometers from the planet. "Venera 1" equipped with magnetometer, radiation sensors, and the dome was placed Soviet pennant. Communication with the station lost a week after launch.
The next few starts have led to accidents, failure to start, faults in the earth's orbit, while in 1965 did not run "Venus 2" with scientific instruments and TV system on board. February 27, 1966 Station has flown by at a distance of twenty-four thousand kilometers from Venus.

Venus 1 i>
"Venus 3", which was launched four days after the previous station, the first station that has reached the surface of another planet. But she could not transmit data after landing. The lander - the scope and ninety centimeters in diameter - placed metal globe of the Earth with a pendant with a picture of the coat of arms of the Soviet Union in.
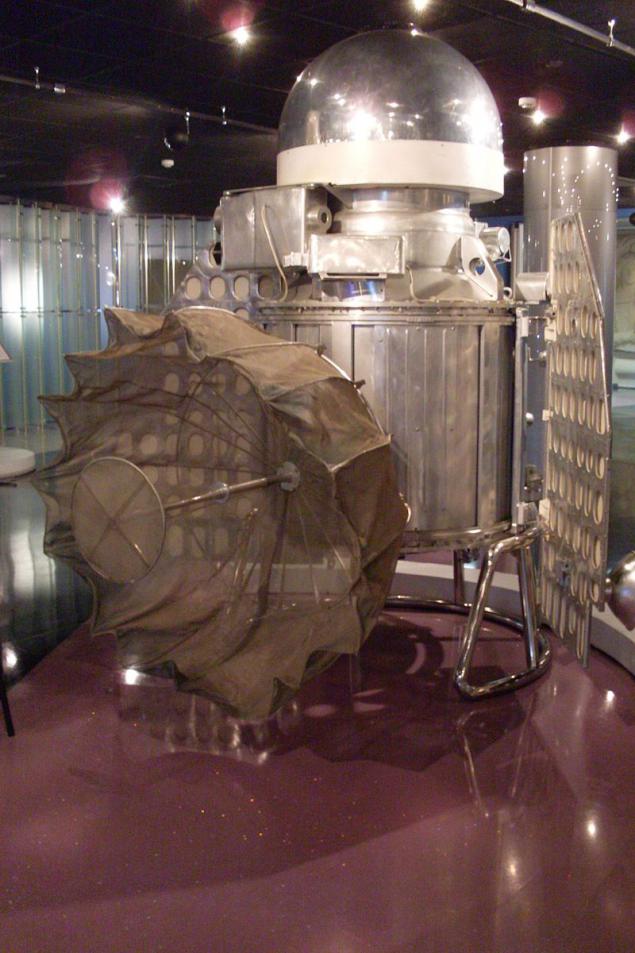
"4 Venus" in 1967 was crushed by the atmosphere, but managed to pass the information on pressure, temperature and composition of the planet's atmosphere. "5 Venus" was also crushed, but the station along with the "6 Venus" was able to convey a lot of pressure and temperature measurement.
29,317,406
The lander "Venus 4» i>
"7 Venus" was built in order to put the lander on the surface of the planet. It was built so that it could withstand the pressure is six times larger than the previous two phones. The station was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome August 17, 1970. Housing lander built from titanium - with the expectation that it will withstand pressures of up to one hundred and eighty atmospheres. Thermal insulation made from the lower hemisphere fiberglass, top - glass wool. Depreciation device must be reduced congestion in contact with the surface. Apparatus equipped with a parachute corrugated conical area of 2, 8 square meters. The parachute produced four layers steklonitrona. To provide power station established lead-zinc battery that fifteen days before approaching the planet was charged by solar panels.
Lander transmit data to Earth for fifty-three minutes, of which about twenty minutes - long after both appeared on the surface of Venus. From the measurements, scientists have calculated the pressure - 90 ± 15 atmospheres and temperature - 475 ± 20 ° C.
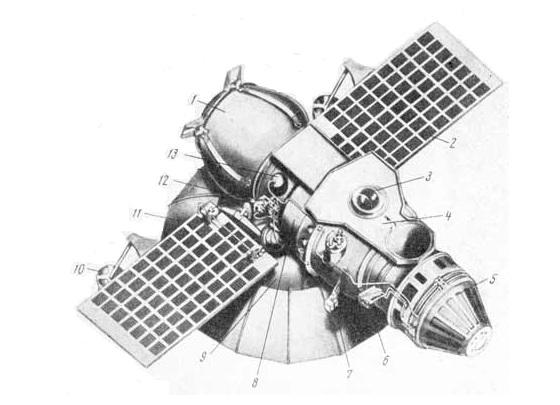
1 - lander;
2 - solar panels;
3 - sensor astroorientation;
4 - a protective cover;
5 - corrective propulsion system;
6 - collectors with pneumatic control nozzles;
7 - counter space particles;
8 - orbital compartment;
9 - radiator-cooler;
10 - malonapravlennaya antenna;
11 - beam antenna;
12 - the block of pneumatic automation;
13 - cylinder of compressed nitrogen i>
A few years later, in 1975, "Venera-9, 10 'were able to transfer images from the surface of Venus - first black and white panoramic images from the surface of another Planet .

Source: geektimes.ru/post/259620/
A team of scientists from the United States and Europe hold a year in isolation to study the characteristics of life on Mars
NASA released photos of the Martian surface with traces of water flows