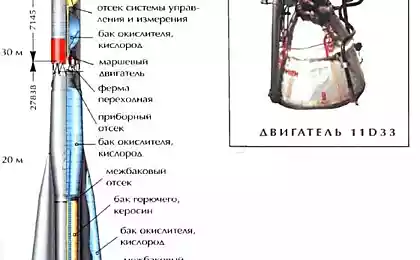
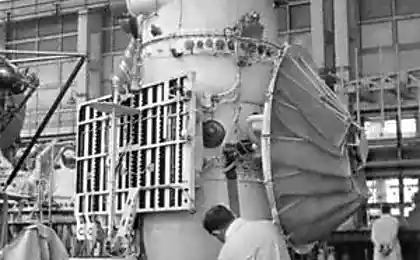
973
Venus, for what it is (22 photos)
Continuing the theme about Mars!
Venus - the Earth's nearest neighbor, the second order of the planet of the solar system, its average distance from the Sun 108, 2 million kilometers. The size and mass of Venus and Earth is also very close: the radius of Venus 6051 km (6378 km from the Earth), the mass of Venus is 0, 815 Earth masses, the average density of 5240 kg / m, the acceleration of gravity at the equator, 8, 76 m / s, is 0, 89 earth. After the Sun and the Moon, Venus is the brightest luminary in Earth's sky: its magnitude at maximum is 4, 45m, and under favorable conditions, you can even watch the shadow of the objects created by the light of Venus. It makes one revolution around the Sun in an orbit of 225 Earth days.
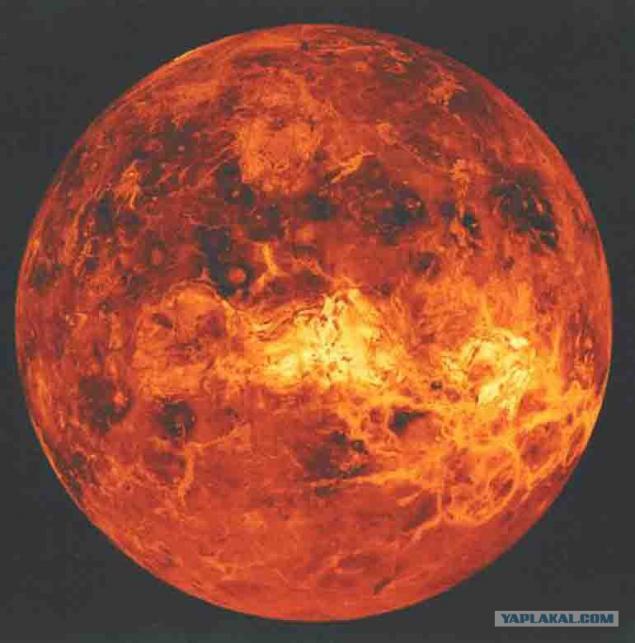

2
Temperature of the atmosphere of the planet Venus, the surface (at a level corresponding to the radius of 6052 km) 735 K, pressure of 9 MPa, the density of the gas is 60 times greater than the earth's atmosphere. The atmosphere of Venus up to 50 km from the surface is maintained close to adiabatic and 50 km above the temperature gradient is reduced by about half. Daily temperature fluctuations at the surface 1 K, and at a height of 50 to 80 km reach 15-20 C. The temperature of the upper boundary of the cloud layer in the polar zone of 5-10 K higher than at the equator, which is apparently connected with the change the height of the clouds . The high temperature of the atmosphere at the surface is due to the influence of the greenhouse effect: according to direct measurements, a significant part of the solar radiation (3 - 4%) reaches the surface and heats it, and a strong opacity for their own infrared radiation of the dense atmosphere of carbon dioxide with an admixture of water vapor prevents the cooling of the surface. < br />

3
The first research unit, the directional ground to another planet, was the Soviet automatic station "Venera-1", launched on 12 February 1961. Three months later, she went to a distance of 100 thousand kilometers from Venus and entered the orbit of the satellite of the sun. The main objectives of "Venera-1" is to check the output methods of space objects in interplanetary highway, checking and management of super-range radio station, conducting research in the physical space.
In December 1962 the US probe "Mariner-2" flying at a distance of 35 thousand kilometers from Venus, carrying a radiometer centimeter range, a magnetometer and a number of instruments for the study of charged particles in cosmic dust. The magnetic field is not detected; According to the radiometer, it was concluded that the radio emission is generated in the lower atmosphere of Venus, but not in the ionosphere, as previously allowed.
In 1965, to the "most beautiful of the stars of heaven," so named Venus Homer has gone "Venera-2", which carried out the so-called flight research. Works reliably instruments for measuring cosmic rays, magnetic fields, streams of charged particles and micrometeorites, radio transmitters and the whole system of transmission of the results of scientific observations. Spread wings solar fueled appliances and electricity equipment.
The main technical problem faced by designers of the interplanetary station, was to ensure its operation during the descent in the atmosphere of Venus under tremendous heat and pressure, as well as in the period of aerodynamic braking.
4. The surface of the planet resembles a stone desert

And then came a new stage in 1965 "Venera-3" for the first time reached the planet's surface, and the 1967 "Venera-4" for the first time carried out a smooth descent in its atmosphere and held direct physico-chemical studies. The first in the history of humanity interplanetary radio communication session lasted 93 minutes. They were measured as a function of the height of the density, pressure and temperature of the atmosphere, carried out a chemical analysis of the composition of the atmosphere. The lander was designed for pressures up to 20 atmospheres, and data transmission stopped before landing on a hard surface of Venus. It has been found that carbon dioxide is the major component of the atmosphere (no less than 95%), the following limits on the content of other components, uniquely establish the existence of high pressures and temperatures in the atmosphere. At the transit unit measured hydrogen corona of Venus, carried out observations of charged particles and micrometeorites.
A day after the landing, "Venus-4" past the planet at a distance of 4000 km flown "Mariner-5", by which the passage of the radio signal was investigated through the atmosphere and ionosphere (radio sounding) and measured hydrogen corona. According to the radio occultation were obtained depending on the temperature and pressure of the height in the range 90- 35 km and ionospheric electron density.
5. The surface is relatively young, her virtually no craters
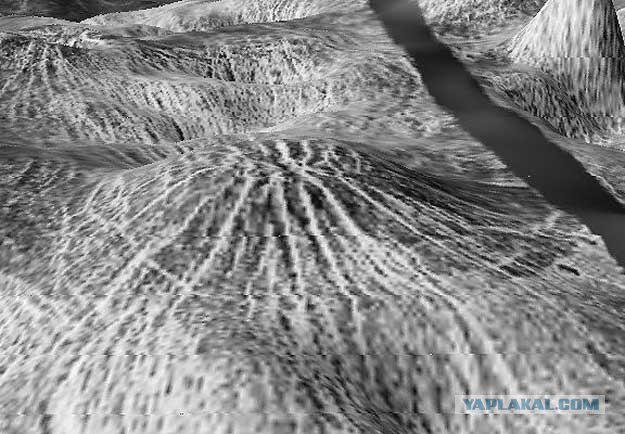

The existence of a less dense than Earth, hydrogen corona of Venus was found in the measurements of the spacecraft "Venera-4" and "5-Mariner." For the upper regions of Venus is characterized by a number of features defined by photochemistry CO2 c possible participation in the complex reactions of water and halogen, in terms of atomic and molecular interactions and interactions with the solar wind. The main purpose of the launch in 1969 of two stations "Venus-5" and "Venus-6" - an increase in penetration into the atmosphere of Venus, vovyshenie precision measurements of the chemical composition of atmospheric parameters and their respective heights. Housing lander was somewhat strengthen, allowing to measure-cloud atmosphere at lower altitudes (up to 19 km above the surface of the planet).
6.

Lander new design was created and joined the "Venera-7", which reached the planet's environs in December 1970. Its equipment to take measurements not only during the descent of the entire thickness of the atmosphere, but for 23 minutes on the surface of the planet. Conditions seemed unusually harsh: Pressure reaches 90 atmospheres and temperatures - up to 500 ° C; in cloud cover, enveloping the planet, a lot of carbon dioxide and low oxygen. The data on the nature of the rocks of the surface layer of Venus.
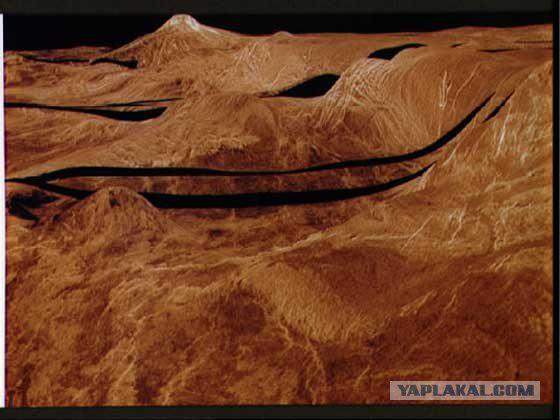

With lander "Venera-8" in 1972 it was conducted multidisciplinary studies of the atmosphere and surface of Venus. Further measurements of atmospheric pressure, temperature and density were measured illuminance and the vertical structure of the aerosol medium, including the cloud layer determined wind speed at various altitudes in the atmosphere from the Doppler frequency shift of a radio transmitter carried gamma spectroscopy of surface species. Photometric measurements showed that the cloud layer extends to an altitude of about 40 km, estimated its optical thickness and transparency; illuminance on the surface of the dayside of Venus was enough to capture the image the landing site. First obtained altitude wind speed profile, which is characterized by an increase in speed from 0 to 5 m / sec at the surface of up to 100 m / sec at the cloud top. According to the content of natural radioactive elements (uranium, thorium, potassium) surface rocks on Venus are intermediate between basalt and granite.
8. Clouds consisting of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide ...
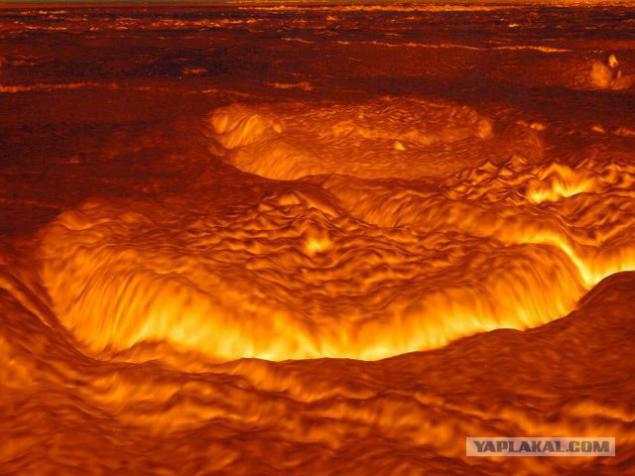
In February 1974, at a distance of 6000 km from Venus passed the US probe "Mariner-10", which were installed a television camera, ultraviolet spectrometer and an infrared radiometer. These television images of the cloud layer was used to study the dynamics of the atmosphere. Using ultraviolet spectrometer obnaruzhenyi The amount of helium in the atmosphere.
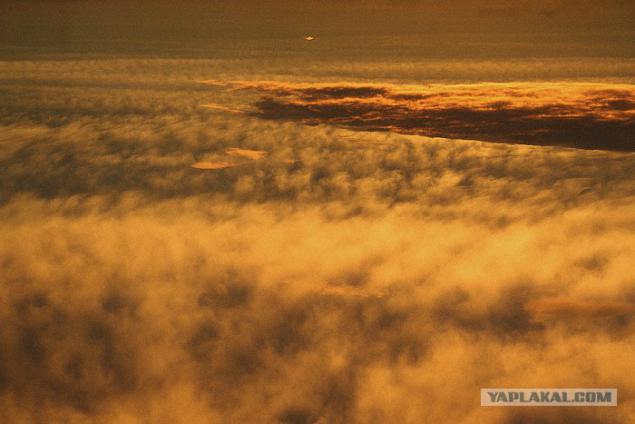

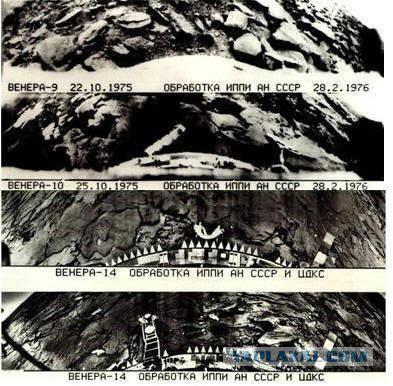
Stations of a new generation of "Venera-9" and "Venera-10", reached the planet in October 1975, became the first artificial satellite of Venus, and their landers made a soft landing on the sunlit side of the planet. For the first time were handed over panoramic television images from another planet, measured on landers density, pressure, temperature of the atmosphere, the amount of water vapor held nephelometric measure cloud particles, measuring the brightness in different parts of the spectrum. For measurements of soil characteristics in addition to the gamma-ray spectrometer was used plotnometr radiation. Satellites have provided television pictures of the cloud layer, the temperature distribution of the upper boundary of the clouds, the spectra of the night glow of the planet, to conduct studies of the hydrogen corona, multiple radio sounding atmosphere and ionosphere, the measurement of magnetic fields and plasma circumplanetary. At the stations, the second generation of information by landers indulged in the orbiter then relayed to Earth. This led to a significant increase in the amount of information received.
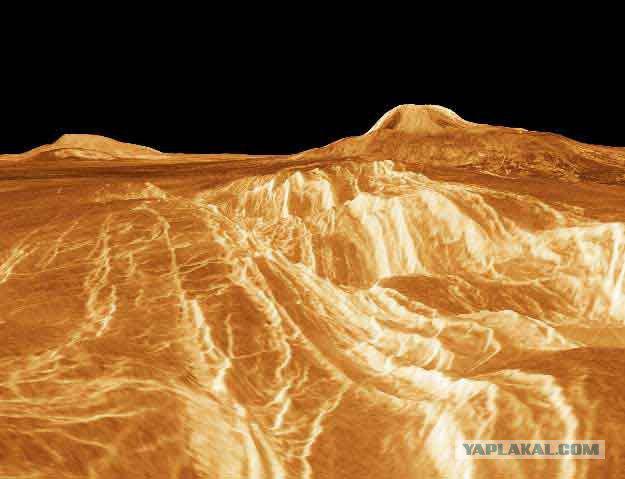
10. Hill. By the way, the colors on the surface of the brown-orange ...
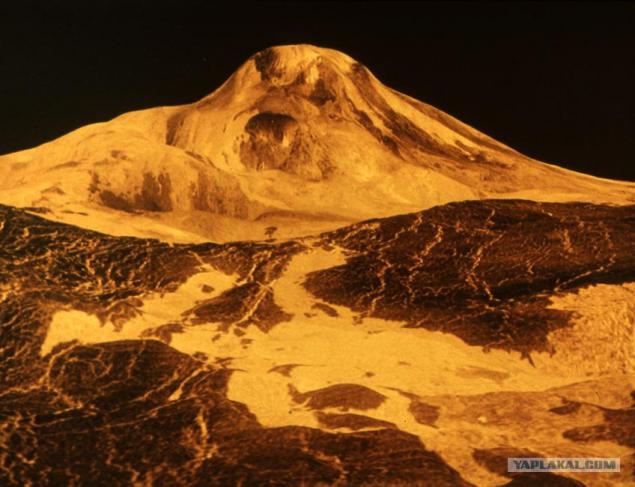

On the panoramas visible rock outcrops along with eroded material; disintegrated stones may result from shifts in the crust and serve as a confirmation of tectonic activity on Venus. In general, the surface of Venus - a hot dry stony desert.
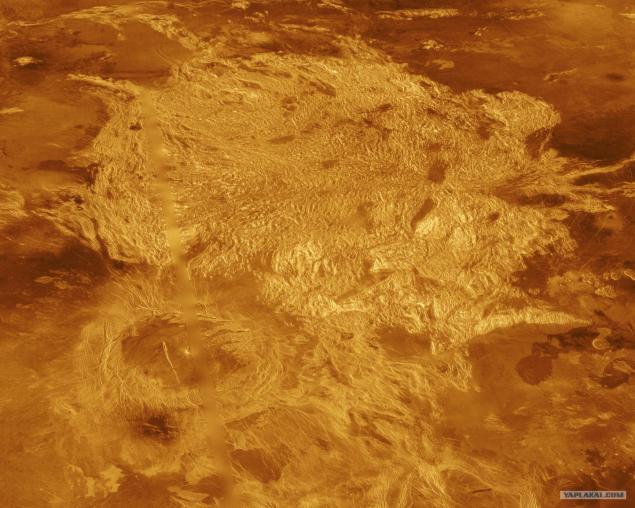
In 1978, for interplanetary highway passed and reached the intended target two messenger - "Venera-11" and "Venera-12", whose main task was a detailed study of the chemical composition of the lower atmosphere by mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, optical and X-ray spectroscopy . We measured the amount of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, water vapor, sulfur, argon, neon and identified isotopic ratios of argon, neon, oxygen, carbon, and found chlorine and sulfur in the cloud particles obtained detailed data on the absorption of solar radiation at different heights the atmosphere required to study its thermal regime.
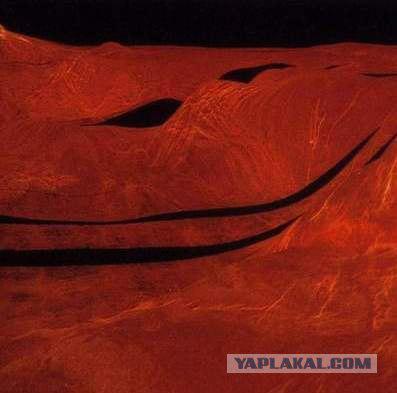
Special receivers were registered pulses of electromagnetic radiation, indicating the existence of electrical charges in the atmosphere similar to Earth's lightning. In the span devices were installed ultraviolet spectrometers to study the composition of the upper atmosphere.
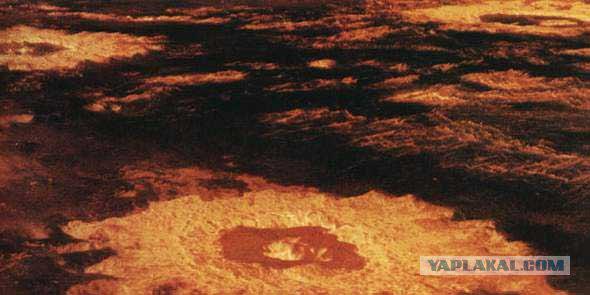
The main component of the atmosphere of Venus - carbon dioxide (96% by volume) and nitrogen (4%), carbon monoxide uglerodadvuokis sulfur, oxygen, practically no water vapor content, apparently kolebletsyaot 0, 1 - 0, 4% by cloud layers 15 -30% above them. Ground-based spectroscopic studies also found the molecule HCl.

16

17
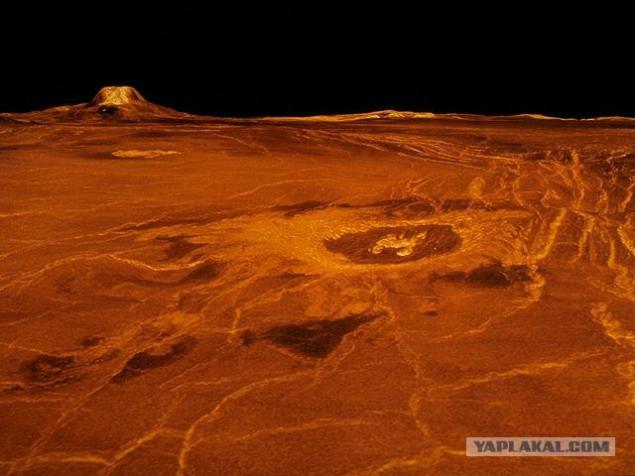
18

19 20
Photography made near one of the poles.

21
22
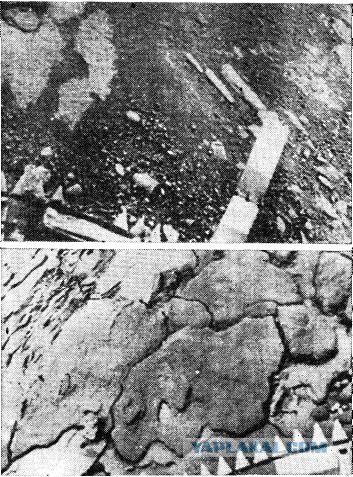
Source:
Venus - the Earth's nearest neighbor, the second order of the planet of the solar system, its average distance from the Sun 108, 2 million kilometers. The size and mass of Venus and Earth is also very close: the radius of Venus 6051 km (6378 km from the Earth), the mass of Venus is 0, 815 Earth masses, the average density of 5240 kg / m, the acceleration of gravity at the equator, 8, 76 m / s, is 0, 89 earth. After the Sun and the Moon, Venus is the brightest luminary in Earth's sky: its magnitude at maximum is 4, 45m, and under favorable conditions, you can even watch the shadow of the objects created by the light of Venus. It makes one revolution around the Sun in an orbit of 225 Earth days.

2
Temperature of the atmosphere of the planet Venus, the surface (at a level corresponding to the radius of 6052 km) 735 K, pressure of 9 MPa, the density of the gas is 60 times greater than the earth's atmosphere. The atmosphere of Venus up to 50 km from the surface is maintained close to adiabatic and 50 km above the temperature gradient is reduced by about half. Daily temperature fluctuations at the surface 1 K, and at a height of 50 to 80 km reach 15-20 C. The temperature of the upper boundary of the cloud layer in the polar zone of 5-10 K higher than at the equator, which is apparently connected with the change the height of the clouds . The high temperature of the atmosphere at the surface is due to the influence of the greenhouse effect: according to direct measurements, a significant part of the solar radiation (3 - 4%) reaches the surface and heats it, and a strong opacity for their own infrared radiation of the dense atmosphere of carbon dioxide with an admixture of water vapor prevents the cooling of the surface. < br />

3
The first research unit, the directional ground to another planet, was the Soviet automatic station "Venera-1", launched on 12 February 1961. Three months later, she went to a distance of 100 thousand kilometers from Venus and entered the orbit of the satellite of the sun. The main objectives of "Venera-1" is to check the output methods of space objects in interplanetary highway, checking and management of super-range radio station, conducting research in the physical space.

In December 1962 the US probe "Mariner-2" flying at a distance of 35 thousand kilometers from Venus, carrying a radiometer centimeter range, a magnetometer and a number of instruments for the study of charged particles in cosmic dust. The magnetic field is not detected; According to the radiometer, it was concluded that the radio emission is generated in the lower atmosphere of Venus, but not in the ionosphere, as previously allowed.
In 1965, to the "most beautiful of the stars of heaven," so named Venus Homer has gone "Venera-2", which carried out the so-called flight research. Works reliably instruments for measuring cosmic rays, magnetic fields, streams of charged particles and micrometeorites, radio transmitters and the whole system of transmission of the results of scientific observations. Spread wings solar fueled appliances and electricity equipment.
The main technical problem faced by designers of the interplanetary station, was to ensure its operation during the descent in the atmosphere of Venus under tremendous heat and pressure, as well as in the period of aerodynamic braking.
4. The surface of the planet resembles a stone desert

And then came a new stage in 1965 "Venera-3" for the first time reached the planet's surface, and the 1967 "Venera-4" for the first time carried out a smooth descent in its atmosphere and held direct physico-chemical studies. The first in the history of humanity interplanetary radio communication session lasted 93 minutes. They were measured as a function of the height of the density, pressure and temperature of the atmosphere, carried out a chemical analysis of the composition of the atmosphere. The lander was designed for pressures up to 20 atmospheres, and data transmission stopped before landing on a hard surface of Venus. It has been found that carbon dioxide is the major component of the atmosphere (no less than 95%), the following limits on the content of other components, uniquely establish the existence of high pressures and temperatures in the atmosphere. At the transit unit measured hydrogen corona of Venus, carried out observations of charged particles and micrometeorites.
A day after the landing, "Venus-4" past the planet at a distance of 4000 km flown "Mariner-5", by which the passage of the radio signal was investigated through the atmosphere and ionosphere (radio sounding) and measured hydrogen corona. According to the radio occultation were obtained depending on the temperature and pressure of the height in the range 90- 35 km and ionospheric electron density.
5. The surface is relatively young, her virtually no craters

The existence of a less dense than Earth, hydrogen corona of Venus was found in the measurements of the spacecraft "Venera-4" and "5-Mariner." For the upper regions of Venus is characterized by a number of features defined by photochemistry CO2 c possible participation in the complex reactions of water and halogen, in terms of atomic and molecular interactions and interactions with the solar wind. The main purpose of the launch in 1969 of two stations "Venus-5" and "Venus-6" - an increase in penetration into the atmosphere of Venus, vovyshenie precision measurements of the chemical composition of atmospheric parameters and their respective heights. Housing lander was somewhat strengthen, allowing to measure-cloud atmosphere at lower altitudes (up to 19 km above the surface of the planet).
6.

Lander new design was created and joined the "Venera-7", which reached the planet's environs in December 1970. Its equipment to take measurements not only during the descent of the entire thickness of the atmosphere, but for 23 minutes on the surface of the planet. Conditions seemed unusually harsh: Pressure reaches 90 atmospheres and temperatures - up to 500 ° C; in cloud cover, enveloping the planet, a lot of carbon dioxide and low oxygen. The data on the nature of the rocks of the surface layer of Venus.

With lander "Venera-8" in 1972 it was conducted multidisciplinary studies of the atmosphere and surface of Venus. Further measurements of atmospheric pressure, temperature and density were measured illuminance and the vertical structure of the aerosol medium, including the cloud layer determined wind speed at various altitudes in the atmosphere from the Doppler frequency shift of a radio transmitter carried gamma spectroscopy of surface species. Photometric measurements showed that the cloud layer extends to an altitude of about 40 km, estimated its optical thickness and transparency; illuminance on the surface of the dayside of Venus was enough to capture the image the landing site. First obtained altitude wind speed profile, which is characterized by an increase in speed from 0 to 5 m / sec at the surface of up to 100 m / sec at the cloud top. According to the content of natural radioactive elements (uranium, thorium, potassium) surface rocks on Venus are intermediate between basalt and granite.
8. Clouds consisting of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide ...

In February 1974, at a distance of 6000 km from Venus passed the US probe "Mariner-10", which were installed a television camera, ultraviolet spectrometer and an infrared radiometer. These television images of the cloud layer was used to study the dynamics of the atmosphere. Using ultraviolet spectrometer obnaruzhenyi The amount of helium in the atmosphere.

Stations of a new generation of "Venera-9" and "Venera-10", reached the planet in October 1975, became the first artificial satellite of Venus, and their landers made a soft landing on the sunlit side of the planet. For the first time were handed over panoramic television images from another planet, measured on landers density, pressure, temperature of the atmosphere, the amount of water vapor held nephelometric measure cloud particles, measuring the brightness in different parts of the spectrum. For measurements of soil characteristics in addition to the gamma-ray spectrometer was used plotnometr radiation. Satellites have provided television pictures of the cloud layer, the temperature distribution of the upper boundary of the clouds, the spectra of the night glow of the planet, to conduct studies of the hydrogen corona, multiple radio sounding atmosphere and ionosphere, the measurement of magnetic fields and plasma circumplanetary. At the stations, the second generation of information by landers indulged in the orbiter then relayed to Earth. This led to a significant increase in the amount of information received.
10. Hill. By the way, the colors on the surface of the brown-orange ...

On the panoramas visible rock outcrops along with eroded material; disintegrated stones may result from shifts in the crust and serve as a confirmation of tectonic activity on Venus. In general, the surface of Venus - a hot dry stony desert.

In 1978, for interplanetary highway passed and reached the intended target two messenger - "Venera-11" and "Venera-12", whose main task was a detailed study of the chemical composition of the lower atmosphere by mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, optical and X-ray spectroscopy . We measured the amount of nitrogen, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, water vapor, sulfur, argon, neon and identified isotopic ratios of argon, neon, oxygen, carbon, and found chlorine and sulfur in the cloud particles obtained detailed data on the absorption of solar radiation at different heights the atmosphere required to study its thermal regime.

Special receivers were registered pulses of electromagnetic radiation, indicating the existence of electrical charges in the atmosphere similar to Earth's lightning. In the span devices were installed ultraviolet spectrometers to study the composition of the upper atmosphere.

The main component of the atmosphere of Venus - carbon dioxide (96% by volume) and nitrogen (4%), carbon monoxide uglerodadvuokis sulfur, oxygen, practically no water vapor content, apparently kolebletsyaot 0, 1 - 0, 4% by cloud layers 15 -30% above them. Ground-based spectroscopic studies also found the molecule HCl.

16

17

18

19 20
Photography made near one of the poles.

21

22

Source: