1454
Tobacco smoke, mercury and other drug
These medical practices and beliefs (whether ancient or recent enough) in the eyes of the man of the 21st century look ridiculous or even wild. Although the ancient Egyptians sincerely believed that the brain cools the blood, and for the intellect and the mind meets the heart, even the Hippocrates gave strange diagnoses, such as wandering through the body the uterus. So, how our ancestors treated?
hence
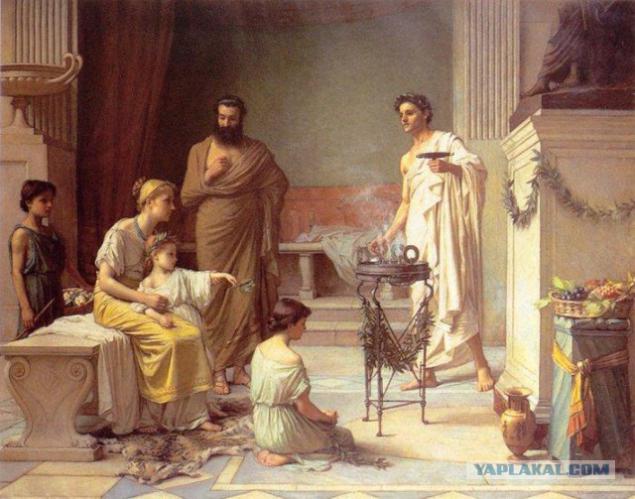

1. Mercury procedures
According to legend, the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang rested in the tomb, surrounded by rivers of liquid mercury. With its help he craved immortality, and from her, and died, and did not live up to 40 years.
Mercury was used as an antiseptic and to treat skin sores, and add in salt solutions and cosmetics. Syphilis is treated by it though. Side effects of mercury treatments one: a slow death.

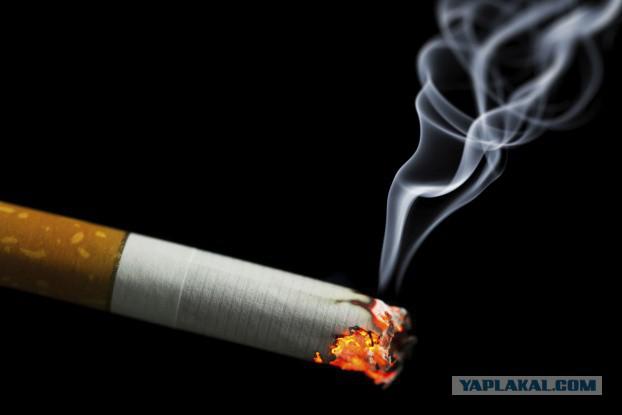
2. Enema of smoke
The kit resuscitator in 17-18 century included spicy tobacco enema, for which we developed an innovative device for those standards: rubber rectal tube and a couple of furs. Doctors believe that tobacco smoke can warm up almost dead body and breath. First, such an enema reanimated drowned, and then it became a fashionable way of treatment from everything: the common cold, headache, hernia, typhoid and cholera. By 1811, scientists discovered the toxic effects of nicotine on the heart, and that enema out of use.

3. Rotating chairs
Swivel chair became the personification of the humane treatment of mental patients in the 19th century. Shackling chain content in a dark room, ice shower, laxatives, insulin coma or frontal lobotomy special effect is not allowed. Now patients elegantly seated in a chair and whirled up until the poor fellow did not lose consciousness. Considers that such a roundabout can shake the brain and relieve of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.

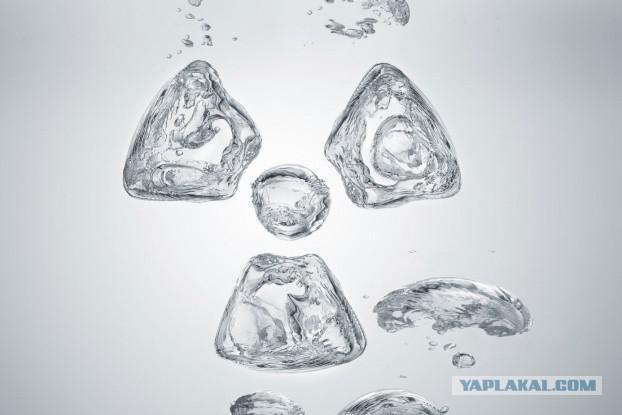
4. Radioactive water
In the early 1900s, was considered insanely popular radioactive water, treated mental illness and prevents aging. She even used to treat diarrhea and malaria. Radium added not only in water but also in the candy, contraceptives, suppositories and toothpaste. Spa-goers began visiting radio broadcast resorts. Today we know that radiation exposure is fatal, and although the body is able to filter out 80% of the toxins of radium, the remaining 20% accumulates in the bones, blood and tissues.
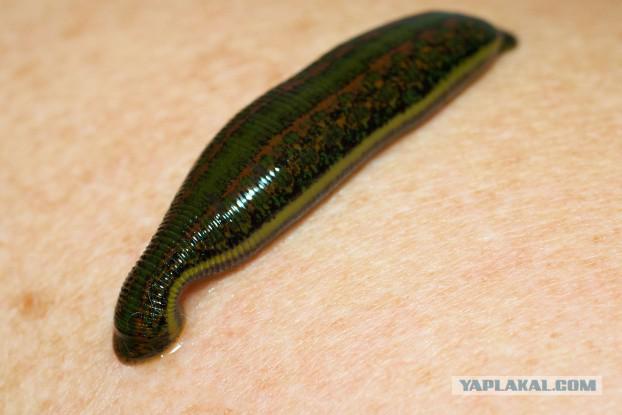
6. leeches and bloodletting
Long ago, went to the hairdresser, not only for britёm and hair, but also for the extraction of a tooth, fixing a broken arm or bloodletting. Initially, his practice as a way to drive away evil spirits from the body, and then as though treatment of bleeding from the nose, even pneumonia. The then humoral medicine believes that the body should be a balance of four fluids: phlegm, yellow and black bile and blood, and bleeding was the main method of preserving this balance. Then, to this end have already begun to use leeches and not lancets, which expose the vein. Leech therapy is used today only approach to these procedures has become more scientific.

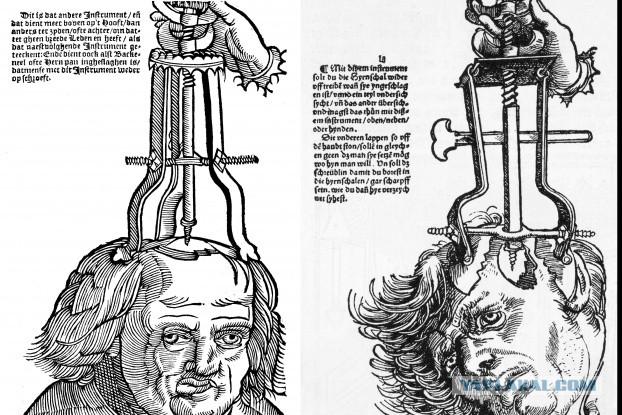
8. Craniotomy
Drill hole in the skull of the patient (without any anesthesia) in ancient times was considered an effective treatment. Trepanation - one of the oldest surgical procedures known in the Mesolithic. To her constantly resorted medical pioneers such as Hippocrates in ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Galen. Ancient medicine was based largely on the mystical and ritual nature of the operation, believing that with the help of her evil spirit is produced as a source of mental illness. Socially trepanation tried to cure migraines and seizures. Although it sounds barbaric, but many patients still survived the procedure. In the 21st century, too, there is trepanation, but surgical intervention in traumatic brain injuries.
9. Cannibalism
Today, modern medicine often uses one body to heal another body: blood transfusion and organ transplantation. But our ancient ancestors existed whole direction "cadaveric medicine." Headache? Ancient Egyptians prescribed powdered mummy. Sore muscles? Rub these places human fat. Epilepsy? The Romans believed that the blood of gladiators will orally, that is inside. Human organs, fat, bone, blood, and mummified remains were considered magical and were used in healing until the 18th century.
Also:
hence

1. Mercury procedures
According to legend, the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang rested in the tomb, surrounded by rivers of liquid mercury. With its help he craved immortality, and from her, and died, and did not live up to 40 years.
Mercury was used as an antiseptic and to treat skin sores, and add in salt solutions and cosmetics. Syphilis is treated by it though. Side effects of mercury treatments one: a slow death.

2. Enema of smoke
The kit resuscitator in 17-18 century included spicy tobacco enema, for which we developed an innovative device for those standards: rubber rectal tube and a couple of furs. Doctors believe that tobacco smoke can warm up almost dead body and breath. First, such an enema reanimated drowned, and then it became a fashionable way of treatment from everything: the common cold, headache, hernia, typhoid and cholera. By 1811, scientists discovered the toxic effects of nicotine on the heart, and that enema out of use.

3. Rotating chairs
Swivel chair became the personification of the humane treatment of mental patients in the 19th century. Shackling chain content in a dark room, ice shower, laxatives, insulin coma or frontal lobotomy special effect is not allowed. Now patients elegantly seated in a chair and whirled up until the poor fellow did not lose consciousness. Considers that such a roundabout can shake the brain and relieve of schizophrenia and other mental disorders.

4. Radioactive water
In the early 1900s, was considered insanely popular radioactive water, treated mental illness and prevents aging. She even used to treat diarrhea and malaria. Radium added not only in water but also in the candy, contraceptives, suppositories and toothpaste. Spa-goers began visiting radio broadcast resorts. Today we know that radiation exposure is fatal, and although the body is able to filter out 80% of the toxins of radium, the remaining 20% accumulates in the bones, blood and tissues.

6. leeches and bloodletting
Long ago, went to the hairdresser, not only for britёm and hair, but also for the extraction of a tooth, fixing a broken arm or bloodletting. Initially, his practice as a way to drive away evil spirits from the body, and then as though treatment of bleeding from the nose, even pneumonia. The then humoral medicine believes that the body should be a balance of four fluids: phlegm, yellow and black bile and blood, and bleeding was the main method of preserving this balance. Then, to this end have already begun to use leeches and not lancets, which expose the vein. Leech therapy is used today only approach to these procedures has become more scientific.

8. Craniotomy
Drill hole in the skull of the patient (without any anesthesia) in ancient times was considered an effective treatment. Trepanation - one of the oldest surgical procedures known in the Mesolithic. To her constantly resorted medical pioneers such as Hippocrates in ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Galen. Ancient medicine was based largely on the mystical and ritual nature of the operation, believing that with the help of her evil spirit is produced as a source of mental illness. Socially trepanation tried to cure migraines and seizures. Although it sounds barbaric, but many patients still survived the procedure. In the 21st century, too, there is trepanation, but surgical intervention in traumatic brain injuries.

9. Cannibalism
Today, modern medicine often uses one body to heal another body: blood transfusion and organ transplantation. But our ancient ancestors existed whole direction "cadaveric medicine." Headache? Ancient Egyptians prescribed powdered mummy. Sore muscles? Rub these places human fat. Epilepsy? The Romans believed that the blood of gladiators will orally, that is inside. Human organs, fat, bone, blood, and mummified remains were considered magical and were used in healing until the 18th century.
Also: