921
NASA released video report on the tests "flying saucer" for landing on Mars
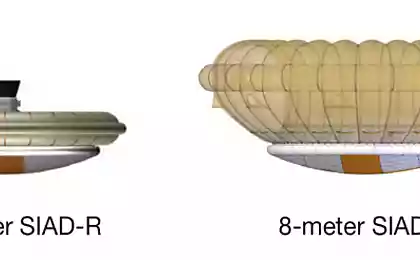
On June 29 Hawaii tested new aerodynamic braking system, which NASA plans to use to put on Mars heavier vehicles with greater precision than now. Inhibit any spacecraft rarefied atmosphere of Mars is much more difficult than on a dense atmosphere. Scientists have developed an inflatable "skirt", called Low Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) , which greatly increases the aerodynamic drag of the lander. LDSD operates at speeds from 4 to 2 speed of sound when the brake housing is already inefficient and parachute to disclose early. To test LDSD and supersonic parachute test lander with a helium balloon rose to a height of 36 km, and then use a rocket engine dispersed to fourfold speed of sound and scored another 20 km upstream. The density of air at this altitude corresponds approximately to the layers of the atmosphere of Mars, which will operate the brake device on a real machine.
During the tests, inflatable brake LDSD worked well, but there were problems with the parachute. However, it is not surprising - a giant parachute diameter of 33, 5 meters should be disclosed at a rate of about two and a half the speed of sound. Moreover, its weight is only about 100 kg. Despite the fact that when you create it used heavy-duty Kevlar fibers during the opening parachute torn in several places and confused. According to scientists, the reason for this - very strong chaotic turbulence arising under braking at this speed. The data obtained in the course of this, only partially successful experiment will help to increase the chances of overall success during the following tests, scheduled for 2015.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/232835/
During the tests, inflatable brake LDSD worked well, but there were problems with the parachute. However, it is not surprising - a giant parachute diameter of 33, 5 meters should be disclosed at a rate of about two and a half the speed of sound. Moreover, its weight is only about 100 kg. Despite the fact that when you create it used heavy-duty Kevlar fibers during the opening parachute torn in several places and confused. According to scientists, the reason for this - very strong chaotic turbulence arising under braking at this speed. The data obtained in the course of this, only partially successful experiment will help to increase the chances of overall success during the following tests, scheduled for 2015.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/232835/