1674
The First World
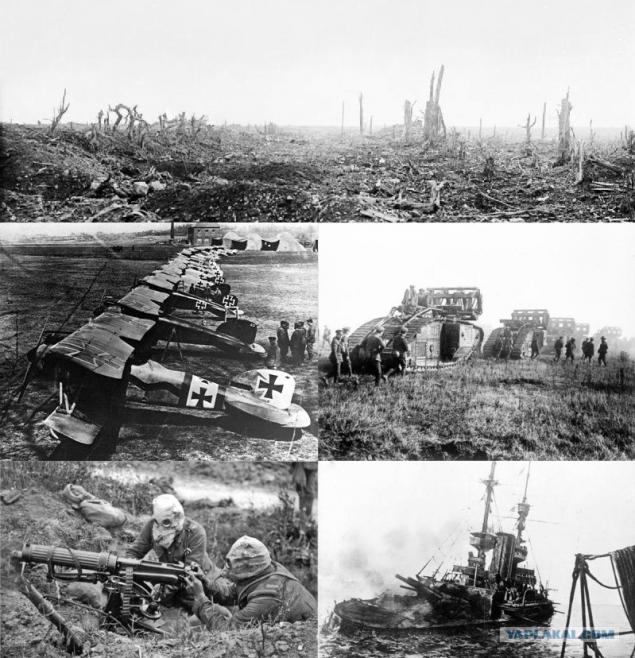
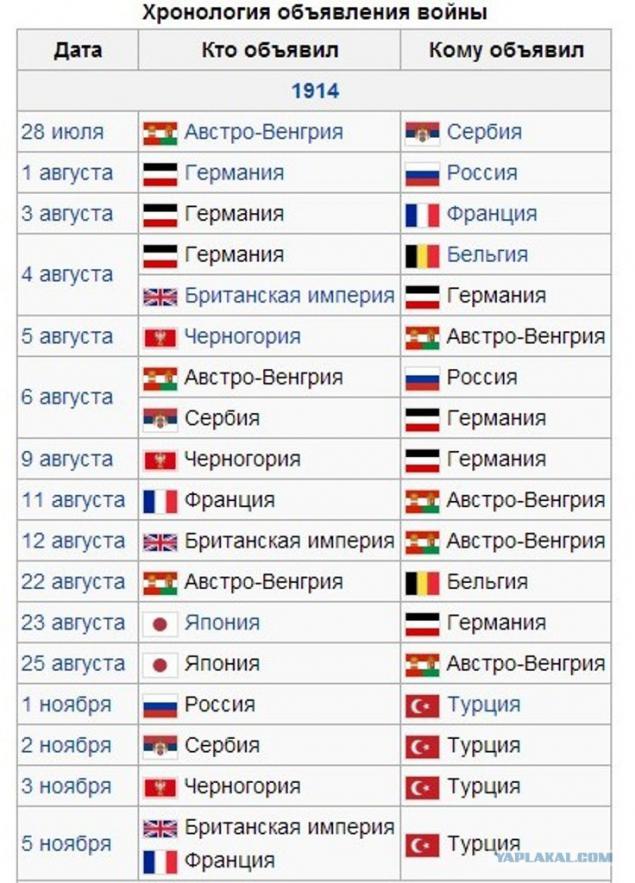
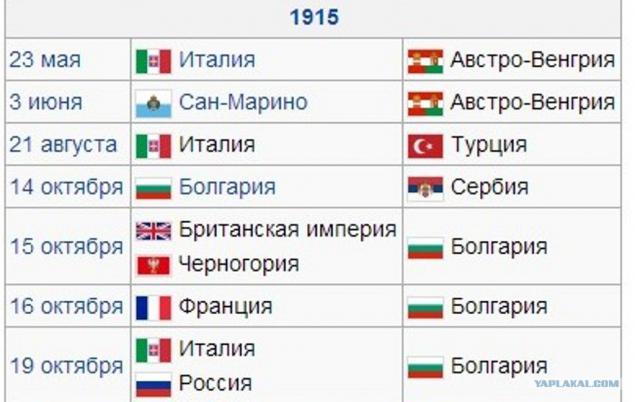
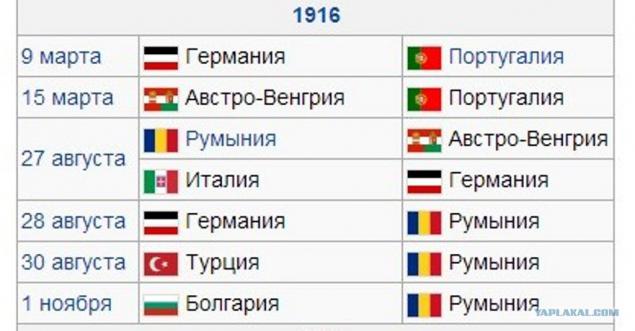
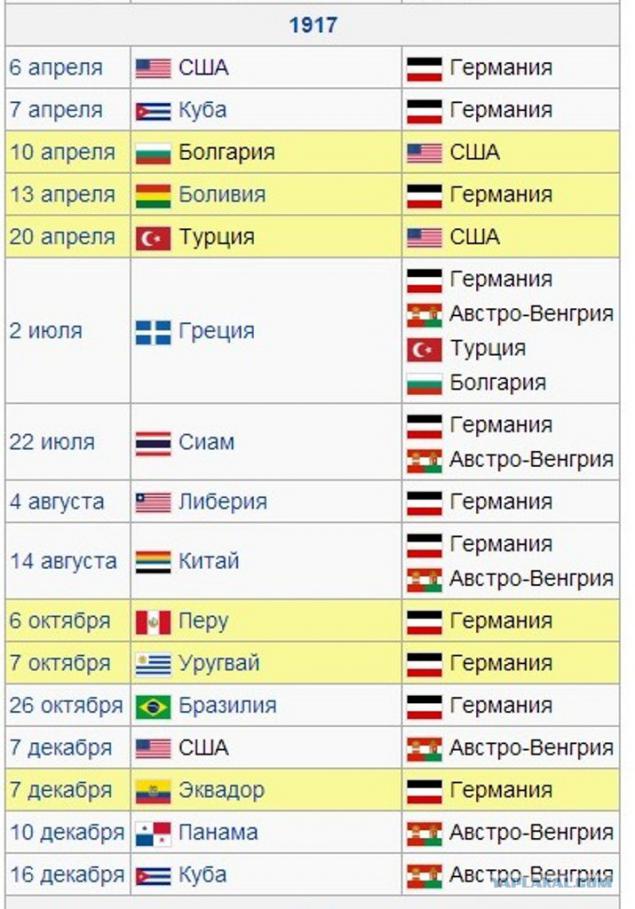
The First World War (28 July 1914 - 11 November 1918) - one of the most large-scale armed conflict in human history.
This title was confirmed in historiography only after the Second World War in 1939. In the interwar period to use the name "The Great War" (Eng. The Great War, fr. La Grande guerre), in the Russian Empire, it is also called the "Great War", "Great War", "Second World", "World", and also informally (and before the revolution, and after) - "German"; then in the Soviet Union - "imperialist war».
The reason for the war was the Sarajevo assassination June 28, 1914 the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand nineteen Serb terrorist, a student from Bosnia Gavrilo Princip, who was a member of a terrorist organization "Mlada Bosna", fought for the unification of all South Slavic peoples into a single state.
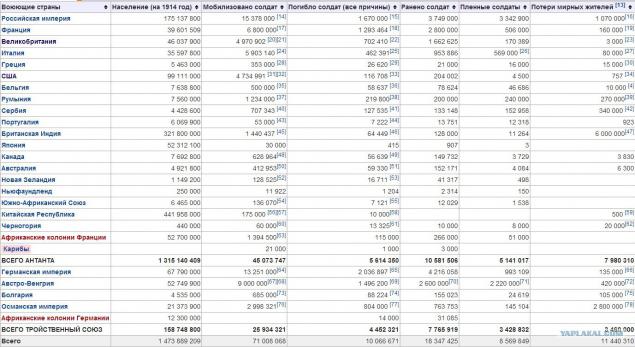
As a result of the war ceased to exist four empires: Russian, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman and German (although emerged instead of Imperial Germany Weimar Republic formally continued to be called the German Empire). Participating countries have lost more than 10 million people killed soldiers, about 12 million civilians killed, 55 million were wounded.

0111
00222
0033
0044
0055
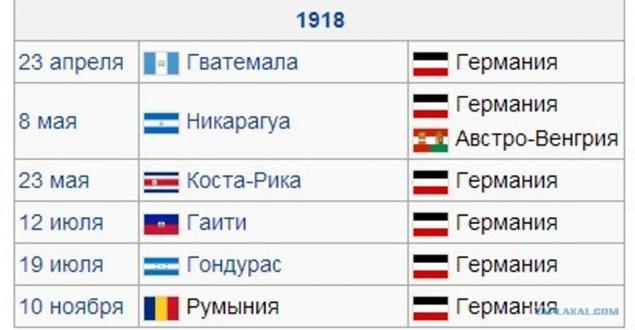
0066
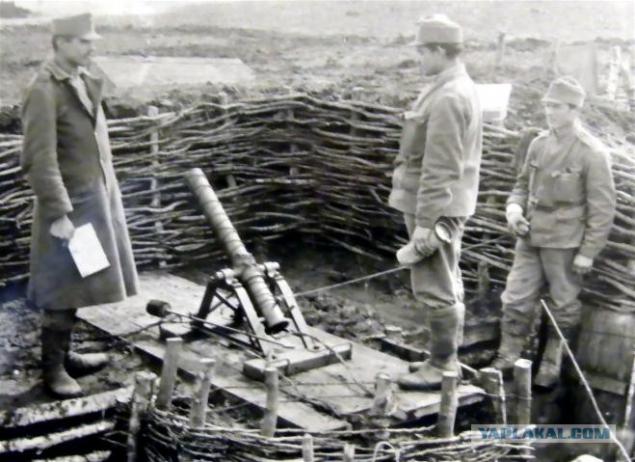
Austrian mortar calculation in the gun trench

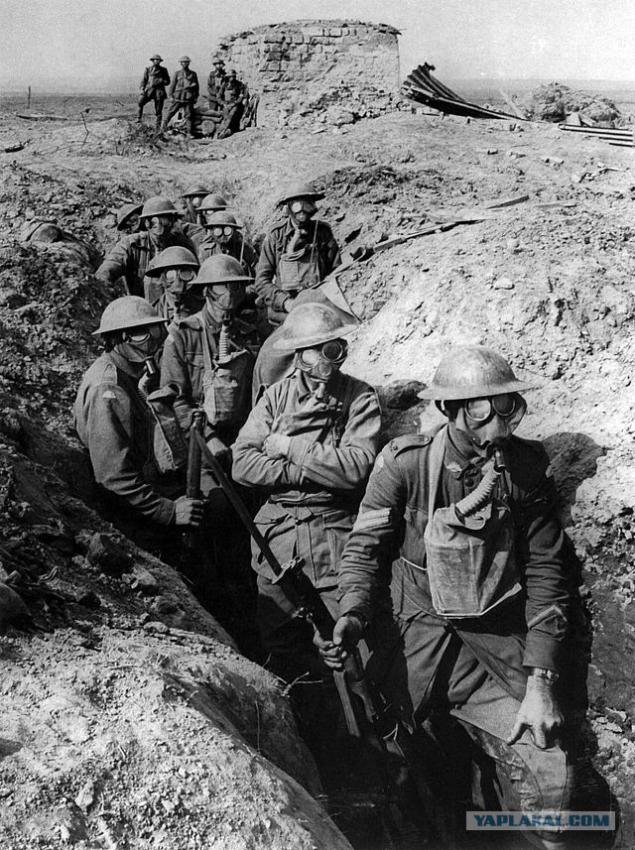
Australian soldiers in the trenches

Dogfight

Russian soldiers loyal oath, trying to stop their fellow soldiers

Russian 122mm howitzer fire leads to the German front. 1915

Belgian armored car «Sava». 1914

The advent of the British Infantry at the Battle of the Somme

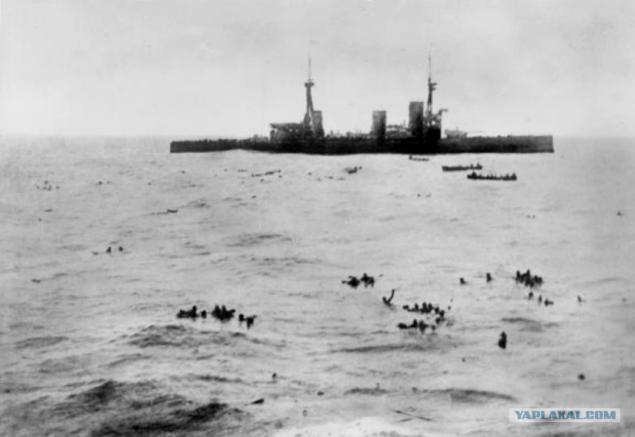
Rescues sailors with "Gneisenau". In the background, "Infleksibl»

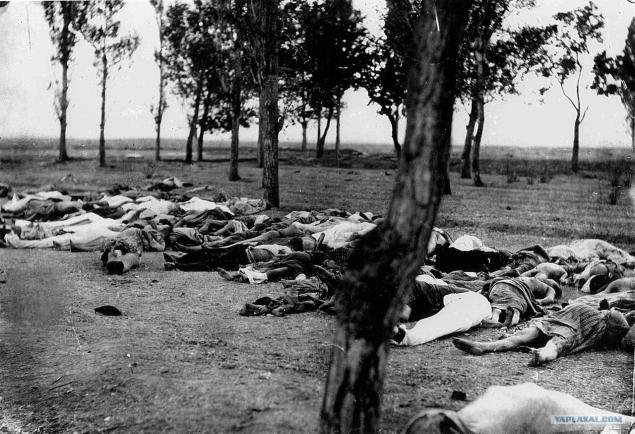
The remains of killed Armenians (Photo published in 1918 in the book of US Ambassador Henry Morgenthau)

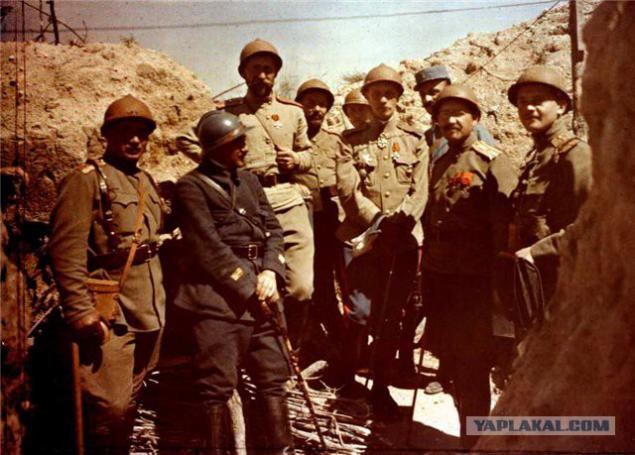
Russian Expeditionary Force in France. Summer 1916 Champagne. Head of the 1st Brigade General Lohvitsky with several Russian and French officers bypasses position

Trenches on the Western Front

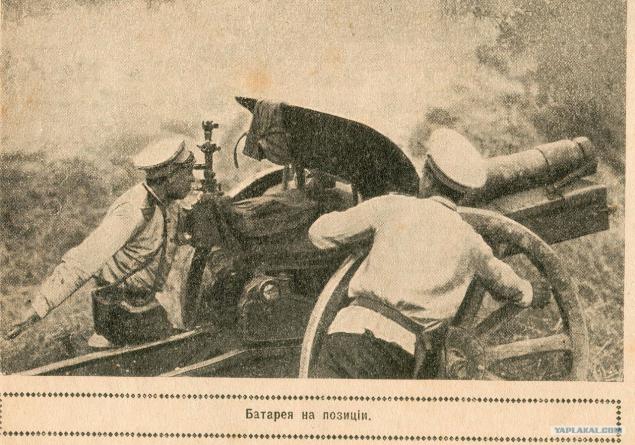
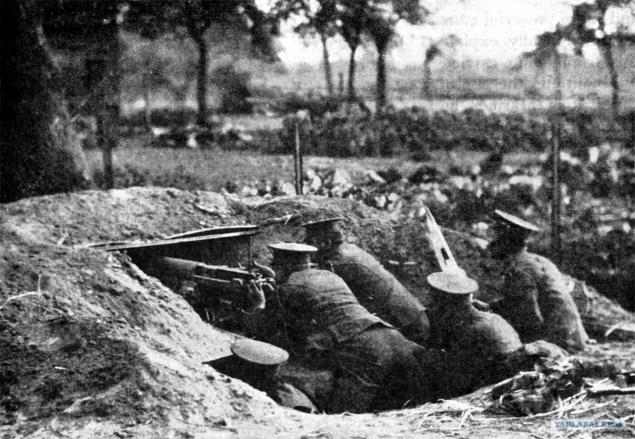
Masking machine gun positions. 1915

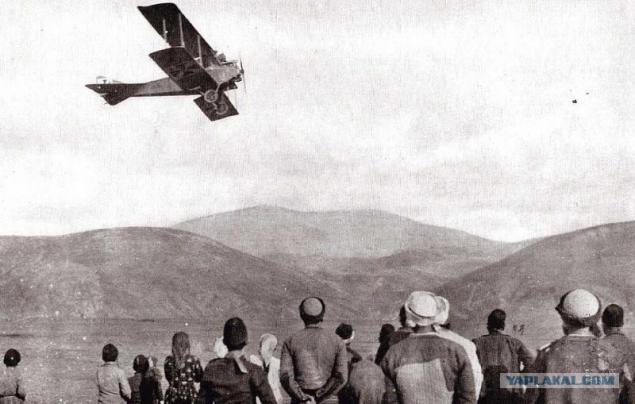
Balkans. Airplane watching a group of Serbs

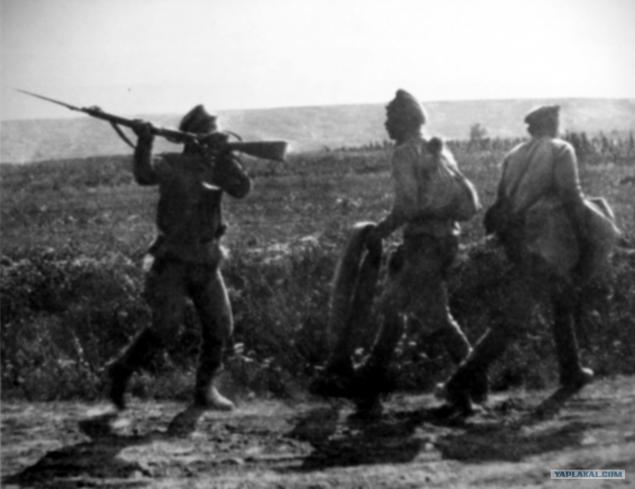
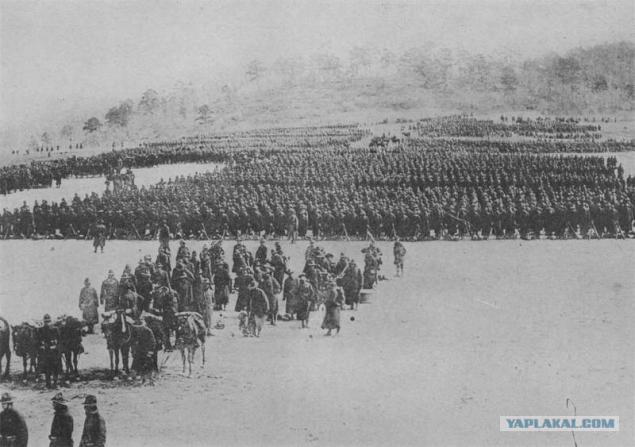
The brigade is ready to march

Armed armored train

The Brits are watching the coast of Belgium

10,000 Russian prisoners of war captured in Galicia

A column of German prisoners of war under the protection of Americans

Austrian prisoners of war captured in the Carpathians
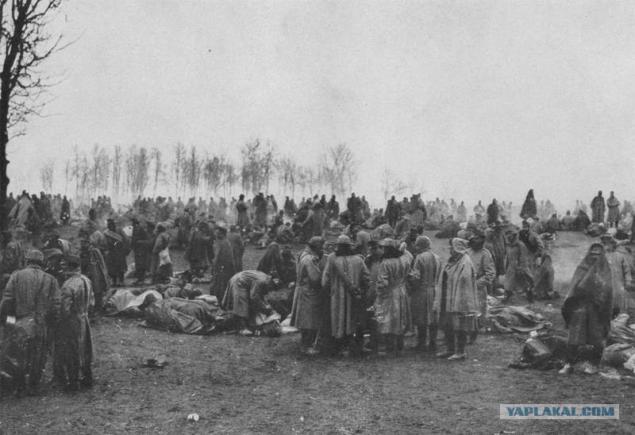

Turkish prisoners of war at Fort Shaibu

Canadian trenches on the Western Front
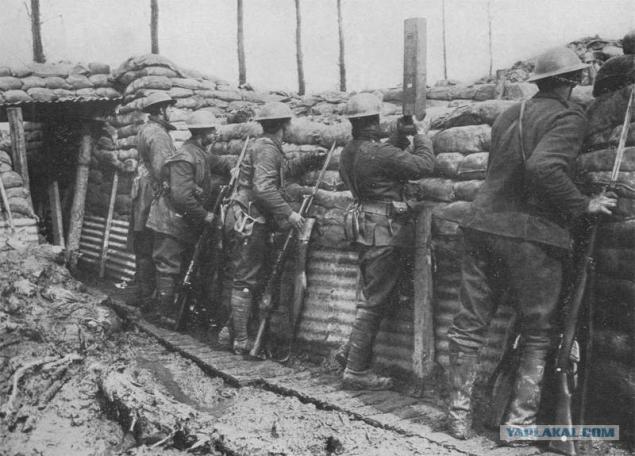

In anticipation of the German army

American Hospital in Fordham

Machine guns used against German aircraft in South Africa

Destroyed German machine-gun in the trenches

Destroyed German machine-gun in the trenches
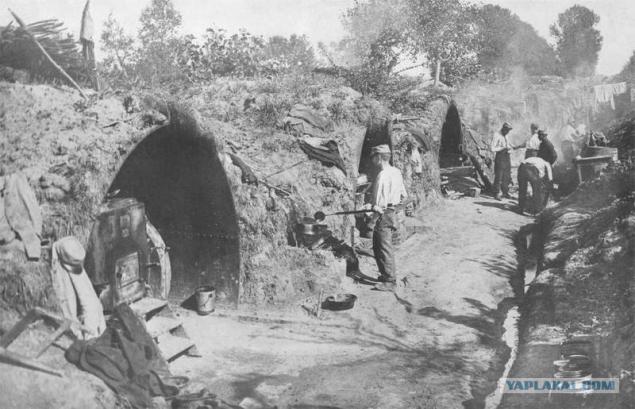

Battle of the Marne, the French troops

Attack of the Germans, Verdun

Captured by the Germans «Whippet».

In the battle of Cambrai 20.11-06.12.1917 British command first employed massive attack tanks (476 machines).
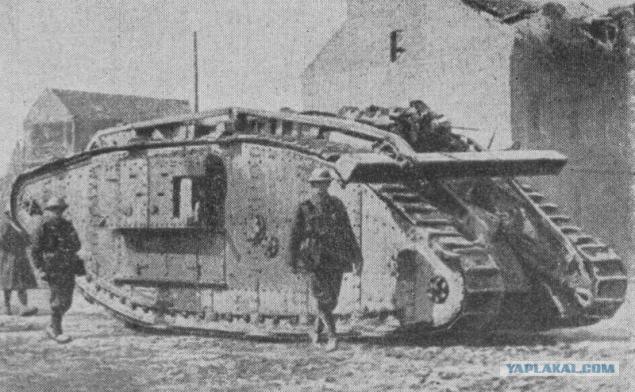
British tank

The cloud of poison gas on the battlefield

The cloud of poison gas on the battlefield
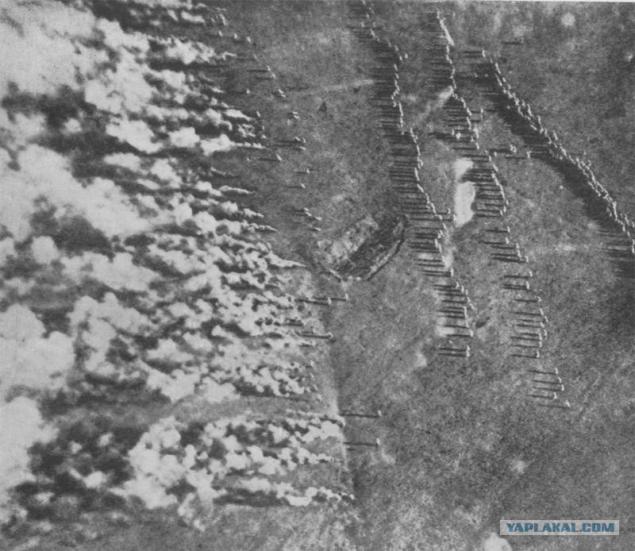

The outcome of the war
Six months later, Germany was forced to sign the Treaty of Versailles (June 28, 1919), compiled by the victor at the Paris Peace Conference, officially ended the First World War.
Peace treaties with
Germany (Treaty of Versailles)
Austria (Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye)
Bulgaria (Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine)
Hungary (Treaty of Trianon)
Turkey (Treaty of Sevres).
Results of the first World War began February and October revolutions in Russia and the November Revolution in Germany, the elimination of four empires: Russian, German, Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary, with the latter two were separated.
Germany ceased to be a monarchy, was trimmed geographically and economically weakened. Severe conditions for Germany Versailles Peace (reparations et al.) And moved its national humiliation engendered revanchist, which became one of the prerequisites Nazis came to power, started World War II.
Territorial changes
As a result of the war:
annexation
England - Tanzania and South West Africa, Iraq, Transjordan and Palestine, Togo and Cameroon, northeastern New Guinea and Nauru;
Belgium - Burundi, Rwanda, counties Eypena, Malmedy, joining territory Moresnet;
Greece - Western Thrace;
Denmark - North Schleswig;
Italy - South Tyrol and Istria;
Romania - Transylvania, Southern Dobruja, Bukovina, Bessarabia;
France - Alsace-Lorraine, Syria, Lebanon, the greater part of Cameroon and Togo;
Japan - German islands in the Pacific north of the equator (the Caroline, Marshall and Mariana);
occupation of France Saar;
joining Banat, Bačka and Baranja, Slovenia, Croatia and Slavonia, Montenegro to the Kingdom of Serbia, followed by the creation of Yugoslavia;
annexation of South West Africa to the South African Union.
proclaimed the independence of the Belarusian People's Republic, the Ukrainian People's Republic, Hungary, Danzig, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Estonia, Finland;
founded Austrian Republic;
German Empire de facto became a republic;
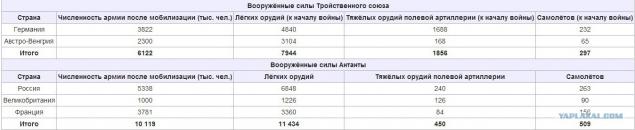
demilitarized Rhineland and the Straits. Population data, call and losses
This title was confirmed in historiography only after the Second World War in 1939. In the interwar period to use the name "The Great War" (Eng. The Great War, fr. La Grande guerre), in the Russian Empire, it is also called the "Great War", "Great War", "Second World", "World", and also informally (and before the revolution, and after) - "German"; then in the Soviet Union - "imperialist war».
The reason for the war was the Sarajevo assassination June 28, 1914 the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand nineteen Serb terrorist, a student from Bosnia Gavrilo Princip, who was a member of a terrorist organization "Mlada Bosna", fought for the unification of all South Slavic peoples into a single state.
As a result of the war ceased to exist four empires: Russian, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman and German (although emerged instead of Imperial Germany Weimar Republic formally continued to be called the German Empire). Participating countries have lost more than 10 million people killed soldiers, about 12 million civilians killed, 55 million were wounded.

0111

00222

0033

0044

0055

0066

Austrian mortar calculation in the gun trench

Australian soldiers in the trenches

Dogfight

Russian soldiers loyal oath, trying to stop their fellow soldiers

Russian 122mm howitzer fire leads to the German front. 1915

Belgian armored car «Sava». 1914

The advent of the British Infantry at the Battle of the Somme

Rescues sailors with "Gneisenau". In the background, "Infleksibl»

The remains of killed Armenians (Photo published in 1918 in the book of US Ambassador Henry Morgenthau)

Russian Expeditionary Force in France. Summer 1916 Champagne. Head of the 1st Brigade General Lohvitsky with several Russian and French officers bypasses position

Trenches on the Western Front

Masking machine gun positions. 1915

Balkans. Airplane watching a group of Serbs

The brigade is ready to march

Armed armored train

The Brits are watching the coast of Belgium

10,000 Russian prisoners of war captured in Galicia

A column of German prisoners of war under the protection of Americans

Austrian prisoners of war captured in the Carpathians

Turkish prisoners of war at Fort Shaibu

Canadian trenches on the Western Front

In anticipation of the German army

American Hospital in Fordham

Machine guns used against German aircraft in South Africa

Destroyed German machine-gun in the trenches

Destroyed German machine-gun in the trenches

Battle of the Marne, the French troops

Attack of the Germans, Verdun

Captured by the Germans «Whippet».

In the battle of Cambrai 20.11-06.12.1917 British command first employed massive attack tanks (476 machines).

British tank

The cloud of poison gas on the battlefield

The cloud of poison gas on the battlefield

The outcome of the war
Six months later, Germany was forced to sign the Treaty of Versailles (June 28, 1919), compiled by the victor at the Paris Peace Conference, officially ended the First World War.
Peace treaties with
Germany (Treaty of Versailles)
Austria (Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye)
Bulgaria (Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine)
Hungary (Treaty of Trianon)
Turkey (Treaty of Sevres).
Results of the first World War began February and October revolutions in Russia and the November Revolution in Germany, the elimination of four empires: Russian, German, Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary, with the latter two were separated.
Germany ceased to be a monarchy, was trimmed geographically and economically weakened. Severe conditions for Germany Versailles Peace (reparations et al.) And moved its national humiliation engendered revanchist, which became one of the prerequisites Nazis came to power, started World War II.
Territorial changes
As a result of the war:
annexation
England - Tanzania and South West Africa, Iraq, Transjordan and Palestine, Togo and Cameroon, northeastern New Guinea and Nauru;
Belgium - Burundi, Rwanda, counties Eypena, Malmedy, joining territory Moresnet;
Greece - Western Thrace;
Denmark - North Schleswig;
Italy - South Tyrol and Istria;
Romania - Transylvania, Southern Dobruja, Bukovina, Bessarabia;
France - Alsace-Lorraine, Syria, Lebanon, the greater part of Cameroon and Togo;
Japan - German islands in the Pacific north of the equator (the Caroline, Marshall and Mariana);
occupation of France Saar;
joining Banat, Bačka and Baranja, Slovenia, Croatia and Slavonia, Montenegro to the Kingdom of Serbia, followed by the creation of Yugoslavia;
annexation of South West Africa to the South African Union.
proclaimed the independence of the Belarusian People's Republic, the Ukrainian People's Republic, Hungary, Danzig, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Estonia, Finland;
founded Austrian Republic;
German Empire de facto became a republic;
demilitarized Rhineland and the Straits. Population data, call and losses
























