3295
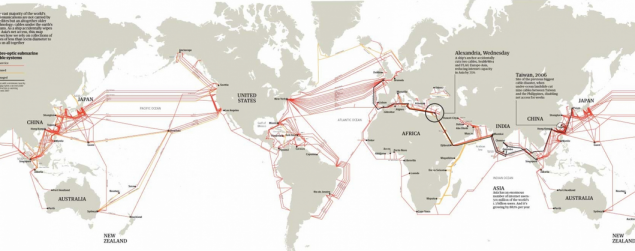
Transoceanic submarine communications cables
Again hi Habr.
Yesterday I was published material concerning gaskets Google's own fiber optic cable connection on the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, which will connect the data centers of the company in Oregon US, Japan. It would seem that this is a huge project worth $ 300 million. And length of 10 000 km. However, if you dig a little deeper it becomes clear that this project is outstanding because it will make one giant media for personal use. The whole planet is already tightly enmeshed communication cables and underwater they are much more than it seems at first glance. Intrigued by this theme, I prepared the general educational material for curiosity.
The origins of intercontinental communication. H4> The practice of laying a cable across the ocean dates back to the XIX century. As сообщает Wikipedia , the first attempts to connect the two continents wired communications were undertaken in 1847. Successfully bind the United Kingdom and the United States Transatlantic telegraph cable was only by August 5, 1858, but in September, the connection was lost. It is assumed that the cause was a violation of waterproofing the cable and its subsequent corrosion and breakage. A stable relationship between the Old and the New World was established only in 1866. In 1870, the cable was laid in India, which allowed to directly link to London and Bombay. These projects involved some of the best minds and industrialists of the time: William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin great), Charles Wheatstone, Siemens brothers. As can be seen, almost 150 years ago, people were actively engaged in the creation of over thousands of kilometers of lines. And on this progress, of course, did not stop. However, telephone service with America was established only in 1956, and the work lasted almost 10 years. More about laying the first transatlantic telegraph and telephone cables can be found in the book by Arthur C. Clarke «Voice over ocean» .
Device Cable h4> great interest is the raw device cable that will run at a depth of 5-8 km, inclusive.
Yesterday I was published material concerning gaskets Google's own fiber optic cable connection on the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, which will connect the data centers of the company in Oregon US, Japan. It would seem that this is a huge project worth $ 300 million. And length of 10 000 km. However, if you dig a little deeper it becomes clear that this project is outstanding because it will make one giant media for personal use. The whole planet is already tightly enmeshed communication cables and underwater they are much more than it seems at first glance. Intrigued by this theme, I prepared the general educational material for curiosity.

The origins of intercontinental communication. H4> The practice of laying a cable across the ocean dates back to the XIX century. As сообщает Wikipedia , the first attempts to connect the two continents wired communications were undertaken in 1847. Successfully bind the United Kingdom and the United States Transatlantic telegraph cable was only by August 5, 1858, but in September, the connection was lost. It is assumed that the cause was a violation of waterproofing the cable and its subsequent corrosion and breakage. A stable relationship between the Old and the New World was established only in 1866. In 1870, the cable was laid in India, which allowed to directly link to London and Bombay. These projects involved some of the best minds and industrialists of the time: William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin great), Charles Wheatstone, Siemens brothers. As can be seen, almost 150 years ago, people were actively engaged in the creation of over thousands of kilometers of lines. And on this progress, of course, did not stop. However, telephone service with America was established only in 1956, and the work lasted almost 10 years. More about laying the first transatlantic telegraph and telephone cables can be found in the book by Arthur C. Clarke «Voice over ocean» .
Device Cable h4> great interest is the raw device cable that will run at a depth of 5-8 km, inclusive.
It is understood that a deep-water cable must have the following number of basic characteristics:
- Durability
- Must be waterproof (suddenly!)
- Maintain the enormous pressure of the water masses over a
- has sufficient strength for laying and operation
- Materials cable must be chosen so that when the mechanical changes (extension cord during operation / stacking, for example) does not change its performance
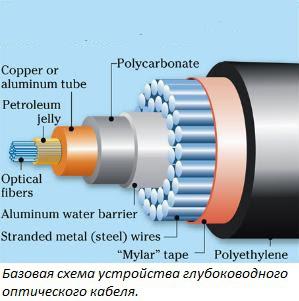
The working part of the cable under consideration by more cases than especially from conventional optics is no different. The whole essence of deep-sea cables lies in the protection of the working part of this and maximize its lifetime, as shown in the schematic drawing on the right. Let us analyze the order of appointment of all structural elements.
PE - a traditional external insulation layer of the cable. This material is an excellent choice for direct contact with the water, as it has the following properties:
Resistance to water, does not react with the alkali at any concentration from a solution of neutral, acidic and basic salts, organic and inorganic acids, even with concentrated sulfuric acid. I>
Oceans contains virtually all the elements of the periodic table, and the water is a universal solvent. The use of such a common chemical. industrial material such as polyethylene is logical and justifiable, because in the first place it was necessary to exclude engineers cable and reaction water, thus avoiding its destruction under the influence of the environment. Polyethylene was used as an insulating material in the course of laying the first intercontinental telephone lines in the mid XX century.
However, due to its porous structure of polyethylene can not provide complete waterproofing cable, so we move to the next layer.
Mylar - a synthetic material based on the полиэтилентерефталата. Has the following properties:
has no odor, taste. Transparent, non-reactive, high barrier properties (including to many corrosive environments), resistant to tearing (10 times stronger than PE), abrasion, impact. Mylar (or the USSR Lavsan) is widely used in industry, packaging, textile, aerospace industry. From it even sew tents. However, the use of this material is restricted to multilayer films due to shrinkage during heat sealing. I>
After a layer of Mylar film can meet the reinforcement of cable different power, depending on the actual characteristics of the product and its purpose. Mainly used strong steel braided cable to give sufficient stiffness and strength, as well as to counter the aggressive mechanical influences from outside. According to some, wandering in the network cable coming from the EMR can lure sharks that gnaw through cables. Just at great depths cable just laid on the bottom, without digging trenches and can catch fishing boats with their gear. To protect against such influences cable and reinforced steel braid. Used in the reinforcement steel wire pre-galvanized. Amplification of the cable can occur in several layers. The main task of the manufacturer in the course of this operation is the uniformity of effort during the winding steel wire. When you double-wrap reinforcement occurs in different directions. When not maintaining the balance in the course of this operation, the cable may spontaneously curl up into a spiral, forming a loop.
As a result of these measures the mass of linear kilometer can reach several tons. "Why does not light and durable aluminum?" - Asked by many. The problem is that the air is stable aluminum oxide film, but in contact with seawater active metal may enter into an intense chemical reaction with the displacement of the hydrogen ions that have a detrimental effect on the part of the cable for which everything was started - fiber. Therefore, use steel.
Aluminium water barrier , or alumopolyethylene layer is used as another layer of waterproofing and cable shielding. Alumopolyethylene is a combination of aluminum foil and a polyethylene film interconnected by adhesive. Bonding can be as one-sided and double-sided. Across the design alumopolyethylene looks almost imperceptible. The film thickness can vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, but, for example, one of the producers on the territory of the Russian Federation the thickness of the final product is 0.15-0.2 mm in unilateral sizing.
A layer of polycarbonate is again used for reinforcement. Lightweight, durable and resistant to pressure and shock, the material is widely used in everyday products, such as in bicycle and motorcycle helmets, also used as a material in the manufacture of lenses, CDs and lighting products, sheet option is used in the construction of both transparent material. Has high коэффициентом thermal expansion i>. Applying it was found in the production of cables.
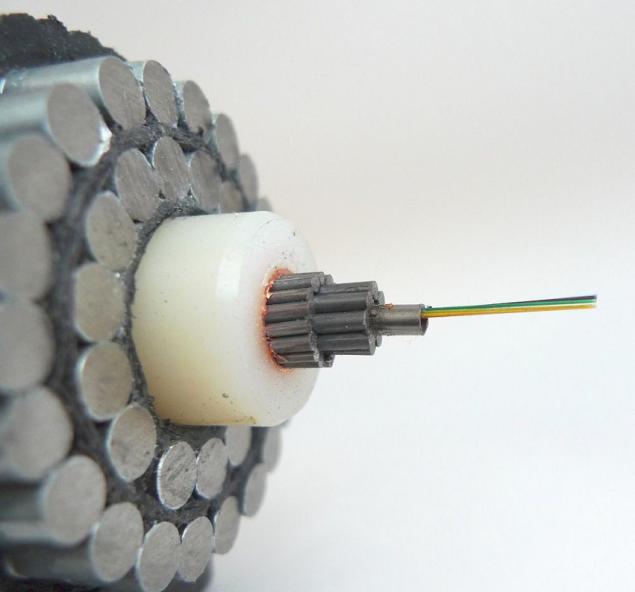
Copper or aluminum tube is part of the core of the cable and is used for its screening. Directly in this design stacked copper tubes with optical fiber inside. Depending on the design of the cable, the tubes can be several and they can be interwoven in different ways. Below are four examples of organizing core of the cable:
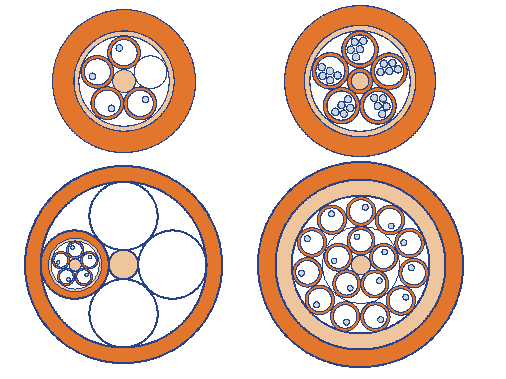
Laying fiber to copper tubes which are filled with thixotropic gel hydrophobic and metallic structural elements are used for the remote supply of intermediate regenerators - devices that provide shape recovery of the optical pulse that propagates along the fiber undergoes distortion.
In terms of get something like this:
Manufacturing cable h4> especially the production of optical deepwater cable is that most of it is located near the port, as close to the sea shore. One of the main reasons for this placement is that the linear kilometers of cable can reach masses of several tons, and for the reduction of the required count of splices in the process of laying the cable manufacturer to strive to do as long as possible. Normal now long for such a cable is considered 4 km, which could result in about 15 tons of weight. As can be understood from the above, the transport of such a deep-water bay OK not the easiest logistical task for land transport. Conventional cable storage timber drums do not stand as previously described for the transport of mass and OK on land, for example, have to lay out the entire length of the building "eight" on the twin railway platforms to prevent damage to the optical fiber inside the structure.
Cabling h4> It would seem that having such a powerful-looking product can ship it on ships and drop into the sea. The reality is somewhat different. Routing the cable - it is a long and laborious process. The route should be, of course, cost-effective and safe as the use of different methods of cable protection increases the cost of the project and increases the payback time. In the case of cable routing between the different countries, you must obtain permission to use the coastal waters of a country, you must obtain all necessary permits and licenses to conduct cable laying works. After conducted geological exploration, assessment of seismic activity in the region, volcanism, the probability of submarine landslides and other natural disasters in the region will work and, subsequently, to lay cable. Similarly important are predictions of meteorologists, that timeline works were not ripped off. During the geological survey of the route is taken into account a wide range of parameters: depth, bottom topology, soil density, the presence of foreign objects, such as boulders, or wrecks. Just estimated possible deviation from the original route, ie the possible extension of the cable and increase the cost and duration of the work. Only after all the necessary preparatory work cable can be loaded onto ships and start laying.

Actually, the process of laying out SIFCO becomes very clear.
Laying fiber optic cable on sea / ocean bottom extends continuously from point A to point B. The cable is laid in the bay on ships and transported to the place of the descent to the bottom. These bays look like this:
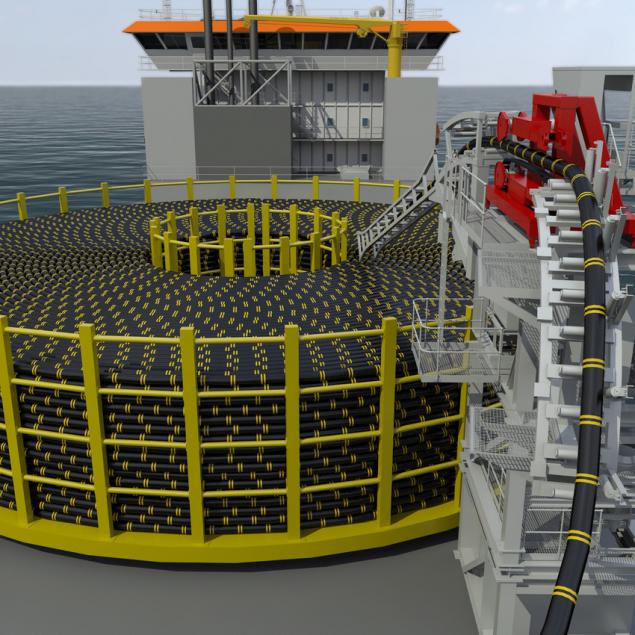

If you think that it is too small, then pay attention to this photo:
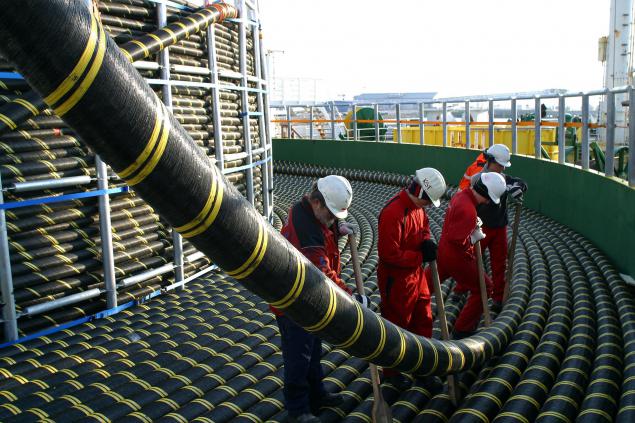

After the release of the ship at sea remains solely the technical side of the process. Command handlers using special machines unwind the cable at a certain rate and maintaining the necessary tension of the cable due to the motion of the ship is moving at a pre-created route.
Looks the part so:
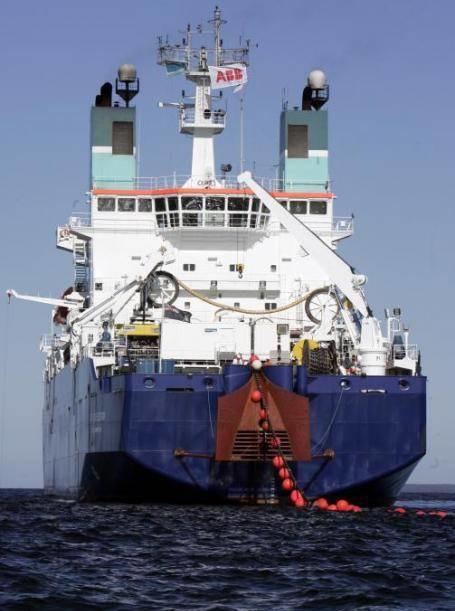

If any problems, breakage, or damage to the cable provided special anchors that allow you to raise it to the surface and repair the problem area line.
And, finally, thanks to all that we can with the comfort and high-speed internet to watch photos and videos with the seals around the world.
In comments to the article about the project Google user Lux_In_Tenebris provided list of interesting literature on this topic , maybe someone will come in handy.
Just by YoMan provide a link to a video of the ship-of cable «Tyco Resolute», thank you.
Dear readers. Article is extremely comprehensive. If you have something to say on this subject, complement or correct - I will be only too happy. Reported in the PM, or comment. I> h6>
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/228415/