879
The birth, rise and death of the telegraph
Several decades ago, a telegram was a real event. The postman rang the doorbell, announcing the message transmitted envelope. But read the telegram could only head of the family. He was a few minutes looking for glasses, as he stood with this telegram, then he himself first, and then - read aloud a message. Telegram reported the death, birth, congratulations on holidays. Today it is easier to do - you can send a text message or a message on the social networks. That's just sometimes hard copy stored longer than we now live phones.
Let us remember how it all began and how the telegraph has become one of the best and fastest means of communication.

Telegram parents cosmonaut German Titov. Museum Titov
The first cell phones and telegraph lines
Europe
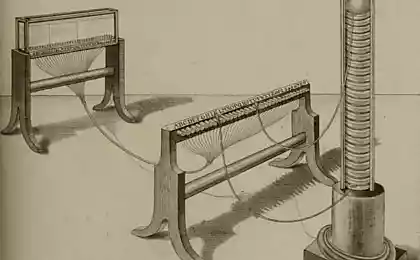
Swiss physicist Georges Louis Lessazh in 1774 brought one of the first working models of the electric telegraph. Information passed between the two rooms of his house, and each of the 26 letters of the alphabet corresponds to a separate wire.
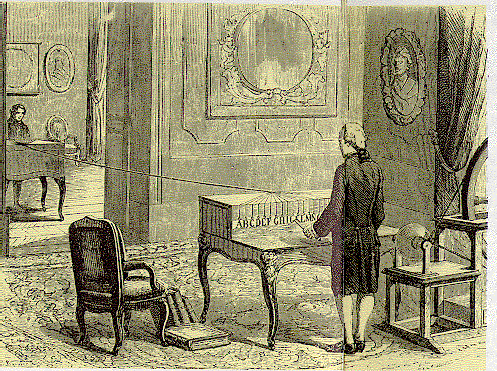
Another inventor, Lomon, use one wire to transmit information. This is an excerpt from an article published in Dublin in 1793 "Paris, October 16, 1787. In the evening I was at Monsieur Lomona, very witty and ingenious mechanics, which improved the cotton-spinning machine ... In power, he made a remarkable discovery. You write two or three words on the paper, he takes a sheet in the room and includes a car. Locked in a cylindrical housing, on top of which is the electrometer - a small cork ball, the wire is connected to the cylinder and electrometer in the other room, and my wife Lomona noticing corresponding ball movement, writes the words. It follows that the inventor formed the alphabet movements. Since the cable length does not affect the effect of the correspondence can be carried out at any distance within the city or outside it, or for the more worthy. As if this machine is used, this is a great invention. »
Telegraph Jean Louis Lessazha
February 22, 1804 Salva Francisco (Francisco Salvá) presented at the Academy of Sciences in Barcelona, the electric telegraph, based on the Volta battery. The system consisted of six small containers with water. The fluid omitted for two wires and, depending on their polarity change each tank showing on two signals due to hydrogen evolution.
More details, including the alphabet to decipher the signals, not extant.
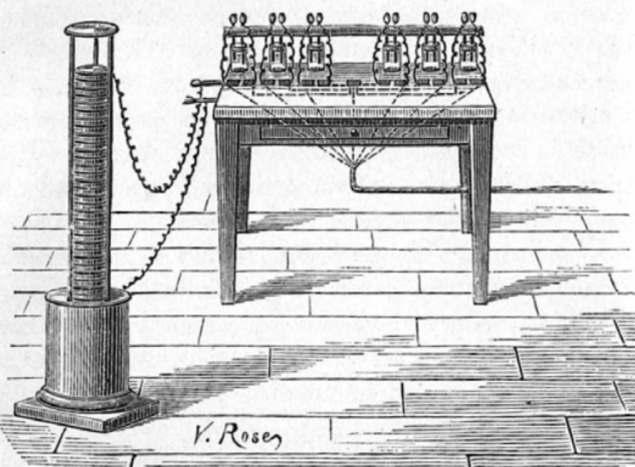
Telegraph Francisco Salva
After another five years, a member of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences Semmering (Sömmerring) on the orders of King Maximilian invents the telegraph, again using electrolysis and the voltaic pile. On the receiving side housed the aquarium, where the electrode corresponding to the desired letter, hydrogen bubbles were allocated. Twice less oxygen bubbles formed by the second letter - that is, at the same time two characters walked on wires
.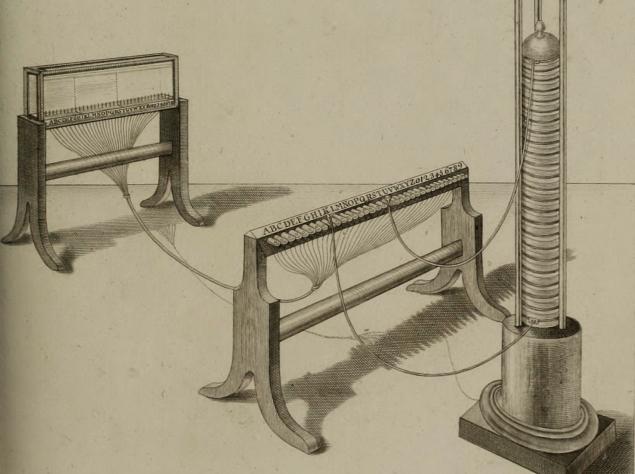
Telegraph Semmering
In 1820 the Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted sent to scientists available institutions and magazines brochure "Experiments on the operation of the electric conflict on a magnetic needle».
The lectures at the university, he showed the heating wire with electricity from the voltaic pile. On the table during the experiment lay mariner's compass, which cover over the wire passed. When the scientist closed electrical circuit, the compass needle deviate. According to legend, it is said one of those present in the audience. Another legend says that the scientist himself noticed this deviation. Oersted during their experiments found that when the distance from the wire to the arrow at least 3/4 inch deviation is 45 °, and when the distance is reduced in proportion to the angle. The amount of fluctuation changes depending on the power unit. Oersted check the effect on the wire of various materials, trying to escape the arrow wood, glass, resin, put in the water.
In a pamphlet in 1820 he wrote: "The main conclusion from these experiments is that the magnetic needle deviates from its equilibrium position under the influence of voltaicheskogo apparatus and that this effect is seen when the circuit is closed, and it does not appear when the circuit is open. It is because the circuit has remained open, were unsuccessful attempts of the same kind, made several years ago, famous physicists. »
Opening Hans Christian Oersted was the basis for the electromagnetic telegraph.
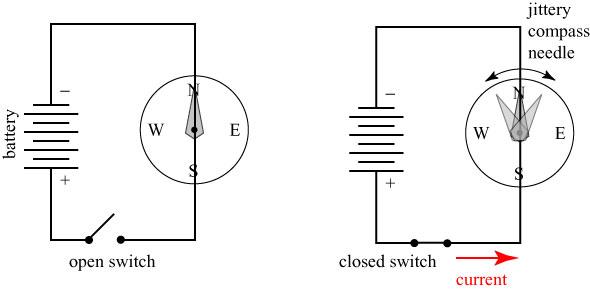
deviation of the magnetic needle under the influence of an electric current
Russian
In 1832, Paul Schilling, a Russian diplomat and historian, a member of World War II, gathered in St. Petersburg electromagnetic telegraph. The basis of the technology of the telegraph was the effect of the deviation of the magnetic needle in the interaction with the electromagnetic field of the electric wires. Background of the invention is extremely interesting: Schilling in the five years before that underwater mines exploded by an electric current passing through the wires with rubber isolation.
To transmit a letter clicked three or four keys simultaneously. On the receiving machine wires were connected to the electromagnet with a magnetic needle hanging over him, which turns on when the current went wire. At arrow rotated signal circle with a black and white on the other. Schilling developed a special code to the six arrows with warning mugs enough to transfer all the letters of the Russian alphabet. One minute eight wires can be sent ten marks.

Shestistrelochny multiplier telegraph Schilling
In 1841 he opened the first regular telegraph line connecting the Winter Palace with the General Staff. This happened after the inventor's death in 1837. But the work of Schilling continued Moritz von Jacobi, created in 1839 to several systems telegraphs, including writing.
In a writing telegraph Boris Jacobi electromagnet set in motion a pencil, leaving a record on a moving porcelain board. The unit worked on the line Winter Palace - Main Headquarters - Tsarskoye Selo. Entries difficult succumbed to decipher what the inventor was not happy.
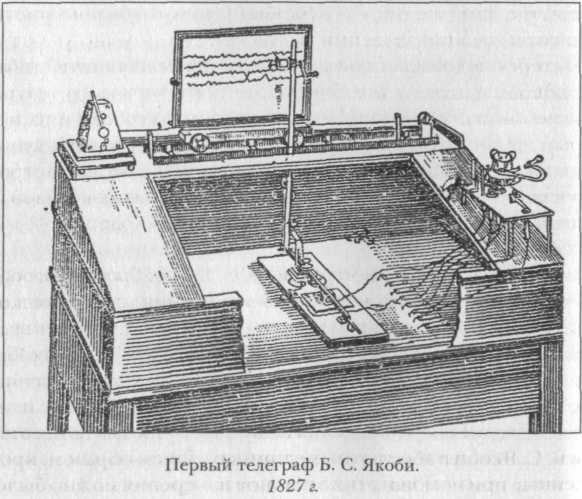
Jacobi made to the 1845 turnout synchronous machine with a horizontal dial, magnetic drive and keyboard, and by 1850 - the world's first direct-printing telegraphy. Only his government considered the work of the military secret, because of the project, few people knew.

Pointer telegraph BS Jacobi vertical dial
In 1844, Jacobi was invited for the construction of a telegraph line along the railway between Moscow and St. Petersburg. The inventor proposed to include in the line auxiliary battery that allows to broadcast is damaged insulation of underground cable. This device is then used for laying the cable on the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean.
Unfortunately, Jacobi is not added onto the line, ordering the construction of a network of telegraph lines in the end won the German company "Siemens & amp; Halske "

Pointer telegraph «Siemens & amp; Halske »
In 1852 in Moscow, founded the first telegraph station in the station building Peterurg-Moscow railway. Company "Central Telegraph" history started from October 1 this year. In 1869, the station moved to the Butcher Street.
By the end of 1855 Telegraph covered the cities of Central Russia and began to connect the country with Europe. In 1880 in Russia was used telegraphs of several types and teletypes.

Central Telegraph on Butcher Street, around 1900
US
American inventor Samuel Morse patented his version of the telegraph in 1840. Key or "hammer" make and break an electrical circuit, the receiver automatically recorded signals. The current pulses of a certain duration forced to oscillate electromagnetic pen reproduces the "point" and "dashes" on the tape. Perot was pushing or signals, or apply them in ink.

telegraph key, also known as "the hammer»
In 1843, Congress passed a bill, and the inventor has allocated a subsidy for the construction of the line between Washington and Baltimore 65 kilometers long.
The first attempt to lay underground cable with the invention of Ezra Cornell - special trenching plow - was unsuccessful. But in 1844 the line was opened, the wires were for telegraph poles. So insulation could save.
Former Postmaster General in the two cabinets of Presidents Amos Kendall immediately realized how the telegraph, with its highest speed transmission of information is useful, and attracted investors to the project. Morse began to sell the license for his invention, and in 1851 opened the fifty independent telegraph companies in the US.
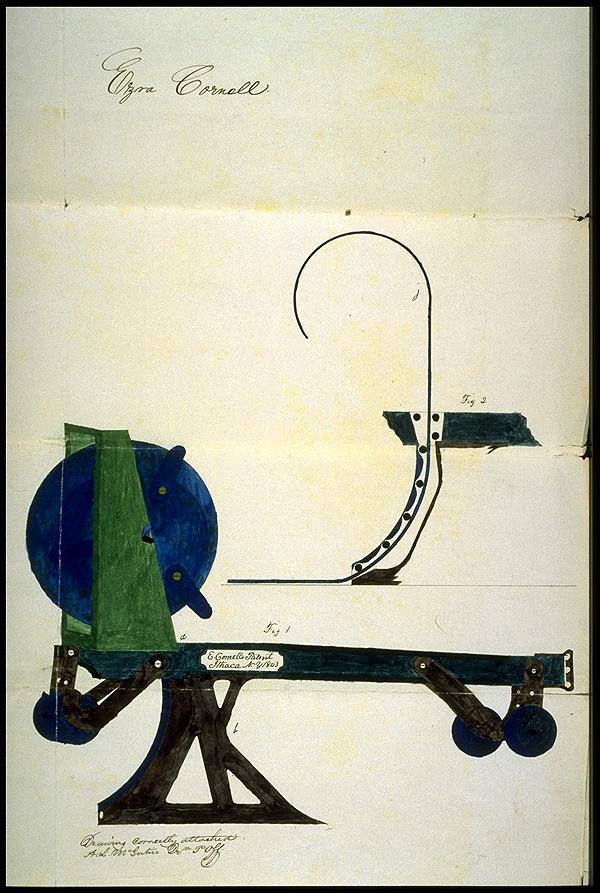
Illustration of patent Ezra Cornell to the plow for laying cables. Source
In 1846, by Royal Earl House patented printing telegraph, capable of transmitting and forty words per minute. Patent for this type of telegraph owned judge Samuel Selden, with whom Hiram Sibley, Sheriff of Monroe County, New York, founded the company «New York and Mississippi Valley Printing Telegraph Company» (NYMVPTC). Seven years later, the name was changed to "Western Union» -. «Western Union»
Instead of having to lay new telegraph lines, entrepreneurs began buying existing and combine them into one system. For three years the number of offices «Western Union» has increased to 4000, and the capital - from $ 220 thousand to 48 million
. Send a telegram to the US cost $ 20 in 1854 for reporting. Because of this, I am wishing it was not so much, and businessmen are willing to sell their companies Hiram Sibley. In 1854, the «Western Union» has bought the patent for the telegraph Morse.
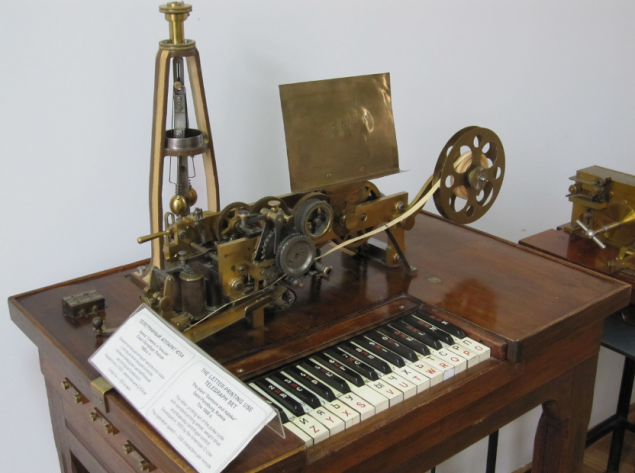

Printing Telegraph 1900, production of Siemens & amp; Halske, Saint Petersburg
In 1861, the «Western Union» for 112 days a single transcontinental line connected West and East coast of the USA. Before the appearance of this message line at such a distance walked for ten days - they carried the most courageous and desperate young men on horseback. And not all of the letters reached because of the constant attacks by bandits.

Laying transcontinental telegraph line. Pony Express service employee welcomes builders.
The link between the continents
underwater telegraph lines in Europe
By the middle of the XIX century the telegraph network connected most of the major cities in Europe and the United States - by land. But to send a telegram across the ocean was difficult. Letters continued to go by boat, the delivery was carried out for twenty days at best. In a world where international relations became more intensive, creating communication between the Old and the New World was a matter of time. The idea to build a telegraph wire at the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean expressed Samuel Morse, then it supported the British physicist Charles Whitson. But it rejected as unworkable. To help entrepreneurs and scholars came open in India gutta-percha, which Werner von Siemens proposed to be used for insulation.
One of the first submarine lines began to lay the English engineer John Brett between France and England. Military ship "Vigdeon" indicating the ship "Goliath" with the cable on board the path, marking it with buoys with flags. Cable plunged into the water every 15 minutes to it suspended load 10 kilograms of lead. Through the first telegram I went, but immediately after it stopped working relationship. French fisherman accidentally tore a piece of cable seine.
The first cable consists of two copper wires to two millimeters thick shell covered with gutta-percha. For the second attempt using four wires, each of which is protected gutta-percha coated six millimeters thick. All wire with five round tarred hemp and soaked fat cords tied in a cable entwined common tarred hemp cord. Top imposed another layer of hemp, and after ten cable wound iron galvanized wire with a diameter of seven millimeters. The first cable weighed 14 tons, and the second, improved, has 166 tons. Now the chance of nets cast into the sea could not prevent the communication between the two countries.
In November 1852 we established a direct telegraphic communication between London and Paris, and later joined England and Ireland, Germany, Holland and Belgium. Sweden joined Norway and Italy - with Sardinia and Corsica. In the years 1854-1855 the cable laid across the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
Transatlantic Cable The businessman Cyrus West Field, using the experience of companies lay submarine cables, assembled investments sufficient for the project of laying on the bottom of the Atlantic cable. In 1856, the ship "Agamemnon" and "Niagara" moved away from the coast of Ireland, each was carrying the coil cable weight in one and a half thousand tons. The cable is made of copper semiprovolochnogo rope with gutta-percha cover, which conductor obtyanuli tarred hemp and wound another 18 outside the cable cord of the iron wires 7 each. Cable length was four thousand kilometers.
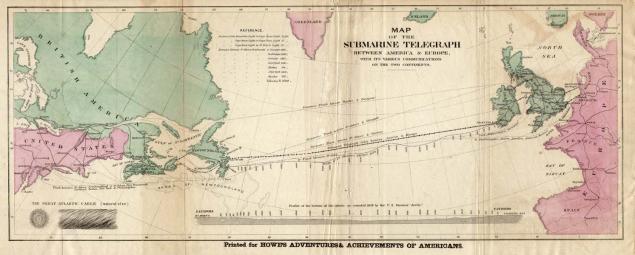
route for laying of the transatlantic link: Ireland - Newfoundland
A few days later the cable broke, and the project had to be postponed. After several months, a second attempt - again a failure. The third attempt took place in 1858, were able to lay the cable from Ireland to Newfoundland. August 16 that year, the British Queen Victoria congratulated US President James Buchanan to a successful project, but a few months later the connection was broken.
Cyrus Field and then did not give up. Eight years later, in 1864, he began laying the cable with improved insulation to help the British steamer "Great Eastern" with a displacement of 32,000 tons. The cable broke during installation. In 1866 the same ship made a second attempt - and then turned finally to provide a link between Europe and America. A cable previously found torn and affixed with a second fragment, so that it began to function.
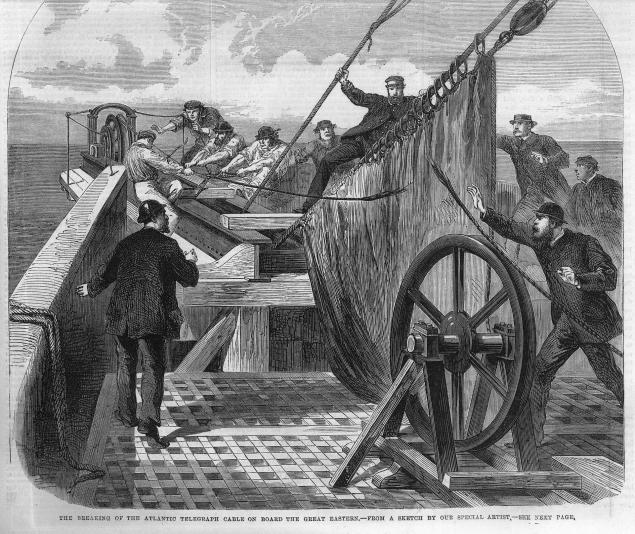

Scene cable break on the "Great Eastern". The Illustrated London News. Band 47. 1865.
Source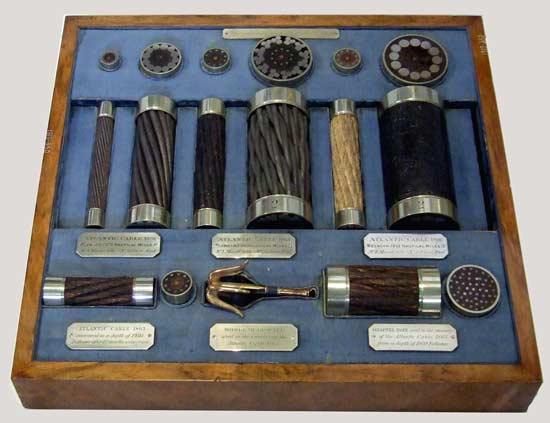
Samples cables that formed
transatlantic link from the USA to Europe via Alaska
American "Western Union" has decided to go the other way - through Alaska. In 1867, Russia sold Alaska to the United States for 7, 2 million dollars, and "Western Union" has received from the authorities the right to lay along the military line and mail routes, including the railway line.
cabling project through Alaska called the "Russian-American Telegraph". He envisioned a line from San Francisco, California to Moscow through Oregon, Washington area, Columbia, Alaska, the Bering Strait and Siberia, which made it possible to combine the US and Europe.
Although the project failed, he gave impetus to the development of the territories through which passed.
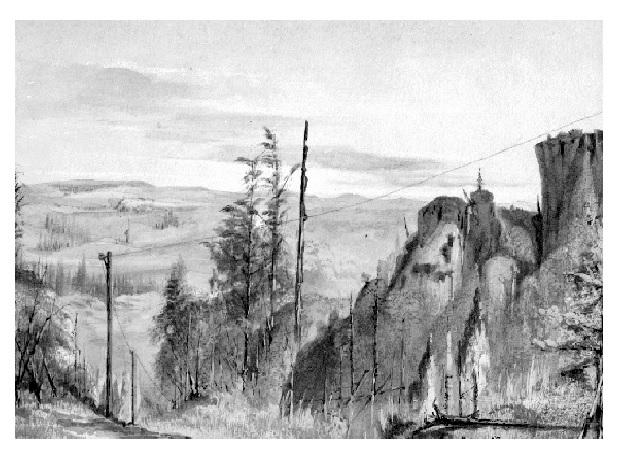

telegraph line in Alaska
main telegraph line in 1891
In 1870, a cable laid in India to establish a link between London and Bombay through Egypt and Malta. Below can be seen on the map the major telegraph line in 1891.
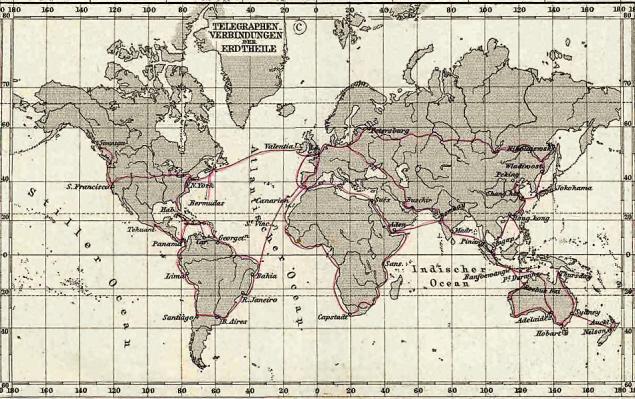
Public domain
Also congratulations and news
Remittances
The ability to instantly send messages over long distances has opened the way for new types of business. mail Money in Russia, according to the Great Soviet Encyclopedia forwarded 1781. In the XIX century there was modernized service - postal orders. By mail sent not the bills, and special coupons, which the recipient has brought to the post office to pick up the cash. And to invest money in the envelopes banned.
An extensive telegraph network in the United States allowed the «Western Union» start delivering in 1871 telegraph money orders. The service has proved so popular that within five years, the company held 37 190 transfers in the amount of 2, 6 million dollars at the average transfer amount $ 70. This is more than 56 million dollars in 2016 prices. That this service is now a core business for the company. In 2015, the «Western Union» has carried out 262 million money transfers between customers for a total of $ 82 billion.
In the Soviet Union money transfers are one of the essential services of public telegraph.

Blank wire transfer, USSR
Securities Market Quotes
In the middle of the XIX century began to emerge in the US stock market. Securities traded on the stock exchanges themselves. It would be much easier to get to know the current market price, sitting in a brokerage firm, and make buying and selling directly from it. This opportunity opened telegraph, bringing securities trading to real time.
Royal Earl House in 1846 patented a printing telegraph, which gave to the text output. It was the great-great-great-great-grandfather of today's printers. The first model was fragile, often synchronization between the sender and the receiver was broken. Print one letter needed several current pulses, and the system did not work over long distances. Улучшенная Дэвидом Хьюзом модель работала с помощью часовых механизмов — так достигалась синхронизация аппаратов. Эту модель использовали в России с 1865 года до начала Великой Отечественной войны.
Готовая печать телеграфных сообщений, без необходимости длительной расшифровки точек и тире, позволила создать тикерные аппараты для передачи биржевых котировок. В 1869 году Томас Эдисон представил такой аппарат, способный печатать один символ в секунду.
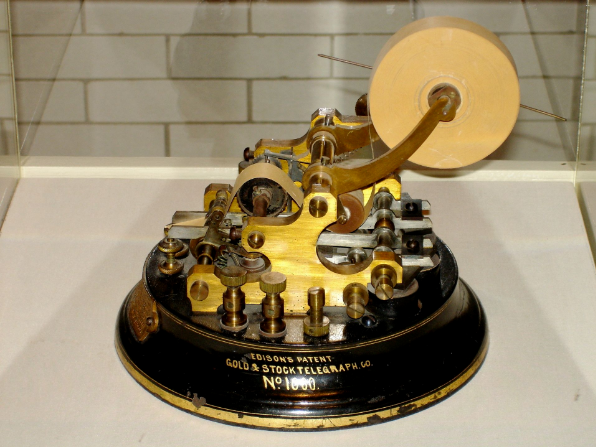

Тикерный аппарат Томаса Эдисона
Точное время
Сейчас наши смартфоны и компьютеры синхронизируют время с помощью радиосвязи. В 1930-е годы в США вы могли арендовать часы, которые синхронизировались с мастер-часами «Western Union», чтобы вы всегда могли точно знать, который час. В 1877 году на крыше штаб-квартиры компании в Нью-Йорке установили шар времени, по которому жители города могли сверять часы. За пять минут до полудня шар поднимали до самого верха шпиля, на высоту 96 метров над улицей. Десятиэтажное здание компании на тот момент было самым высоким в Нью-Йорке и США. За две минуты до полудня в Морскую обсерваторию США в Вашингтоне по телеграфу отправляли сигнал о статусе положительной готовности шара для спуска.
В полдень оператор из обсерватории активировал спусковой механизм и шар падал на семь метров вниз. После спуска шара сигнал отправляли в обсерваторию. Благодаря этой службе компания почти весь XX век была «Хранителем времени нации».

Часы с точным временем от Western Union
Возможность быстрой отправки сообщений открыла новые возможности для бизнеса. Крупные компании с развитой филиальной сетью благодаря телеграфной связи, а затем — телетайпу, стали работать как единое целое, передавая информацию в режиме реального времени.
Телетайп
Закодированный телеграфный сигнал было трудно читать и передавать без специальной подготовки, поэтому с самого начала учёные пытались изобрести более «дружелюбное» к пользователям устройство. Так было с пишущим телеграфом Бориса Якоби и аппаратом Вернера фон Сименса, и это стало причиной появления телетайпа.
В 1872 году французский изобретатель Жан Бодо разработал телеграфный аппарат, который позволял одновременно передавать два и более сообщений по одной линии. При этом аппарат передавал сообщения, используя буквы латинского алфавита, а после работы российских умельцев — и буквы русского алфавита. Устройства такого типа назвали стартстопными. Кроме этого Бодо создал телеграфный код Бодо, который передавали на перфорированных лентах. Первые аппараты Бодо стали использовать в 1877 году на линии Париж — Бордо. До конца XX века использовали двухкратные аппараты, способные передавать до 760 знаков в минуту. Дополнительно к аппарату Бодо сделал распределитель, дешифратор и печатающий механизм, что упрощало работу специалистов.
Два или шесть телеграфистов кодировали сообщения, стараясь не сбиться. Они использовали два пальца левой и три пальца правой руки, по очереди отправляя сигналы. Но самое интересное происходило с другой стороны — на бумажной ленте печатались буквы, а не код.
В 1901 году после создания клавиатуры для телеграфного аппарата код доработали, изменили порядок знаков и добавили дополнительные символы. 5-битная кодировка и использование буквенного и цифрового регистра остались.

Аппарат Бодо: клавиатура и распределитель
Изобретение Бодо и тикерный аппарат стали предшественниками телетайпа. Телетайп — это электромеханическая печатная машина для передачи текстовых сообщений.
В 1920-х годах была создана глобальная «Сеть Телекс», охват которой составил 600 тысяч абонентов в 100 странах мира. Отправленные через эту сеть документы имели юридическую силу. Сетью активно пользовались коммерческие компании, пока телетайп не был вытеснен факсом, а затем и интернетом.
Сейчас от популярности некогда распространенного устройства остались лишь бледные следы, например, традиционный префикс tty (от TeleTYpe) для обозначения текстовых терминалов в Unix. Некоторые ведомственные радиостанции до сих пор ведут вещание в режиме телетайпа, передавая информацию вроде сводок погоды.
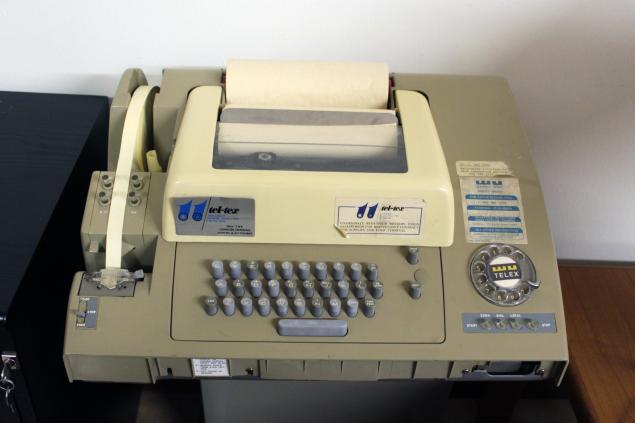

Телетайп, входивший в сеть Telex
Телеграф сегодня
Американская «Western Union» отправила последнюю телеграмму в 2006 году, полностью переключившись на трансфер денег. В 2004 году телеграф свернули в Нидерландах, а в 2013 году — в Индии. В некоторых странах, в частности в России, государственные службы работают до сих пор. Иногда телеграммы используют для отправки повесток в суд, для денежных переводов, даже для поздравлений. Во времена, когда передача информации перестала быть проблемой благодаря глубокому проникновению интернета и мобильной связи, простые письма или телеграммы становятся прихотью, позволяющей проникнуться атмосферой прошлого. Вот только сами телеграфные сети в основном демонтированы, поэтому сообщения передают по современным каналам связи.
Источник: geektimes.ru/post/278850/
Let us remember how it all began and how the telegraph has become one of the best and fastest means of communication.

Telegram parents cosmonaut German Titov. Museum Titov
The first cell phones and telegraph lines
Europe
Swiss physicist Georges Louis Lessazh in 1774 brought one of the first working models of the electric telegraph. Information passed between the two rooms of his house, and each of the 26 letters of the alphabet corresponds to a separate wire.
Another inventor, Lomon, use one wire to transmit information. This is an excerpt from an article published in Dublin in 1793 "Paris, October 16, 1787. In the evening I was at Monsieur Lomona, very witty and ingenious mechanics, which improved the cotton-spinning machine ... In power, he made a remarkable discovery. You write two or three words on the paper, he takes a sheet in the room and includes a car. Locked in a cylindrical housing, on top of which is the electrometer - a small cork ball, the wire is connected to the cylinder and electrometer in the other room, and my wife Lomona noticing corresponding ball movement, writes the words. It follows that the inventor formed the alphabet movements. Since the cable length does not affect the effect of the correspondence can be carried out at any distance within the city or outside it, or for the more worthy. As if this machine is used, this is a great invention. »

Telegraph Jean Louis Lessazha
February 22, 1804 Salva Francisco (Francisco Salvá) presented at the Academy of Sciences in Barcelona, the electric telegraph, based on the Volta battery. The system consisted of six small containers with water. The fluid omitted for two wires and, depending on their polarity change each tank showing on two signals due to hydrogen evolution.
More details, including the alphabet to decipher the signals, not extant.

Telegraph Francisco Salva
After another five years, a member of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences Semmering (Sömmerring) on the orders of King Maximilian invents the telegraph, again using electrolysis and the voltaic pile. On the receiving side housed the aquarium, where the electrode corresponding to the desired letter, hydrogen bubbles were allocated. Twice less oxygen bubbles formed by the second letter - that is, at the same time two characters walked on wires
.

Telegraph Semmering
In 1820 the Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted sent to scientists available institutions and magazines brochure "Experiments on the operation of the electric conflict on a magnetic needle».
The lectures at the university, he showed the heating wire with electricity from the voltaic pile. On the table during the experiment lay mariner's compass, which cover over the wire passed. When the scientist closed electrical circuit, the compass needle deviate. According to legend, it is said one of those present in the audience. Another legend says that the scientist himself noticed this deviation. Oersted during their experiments found that when the distance from the wire to the arrow at least 3/4 inch deviation is 45 °, and when the distance is reduced in proportion to the angle. The amount of fluctuation changes depending on the power unit. Oersted check the effect on the wire of various materials, trying to escape the arrow wood, glass, resin, put in the water.
In a pamphlet in 1820 he wrote: "The main conclusion from these experiments is that the magnetic needle deviates from its equilibrium position under the influence of voltaicheskogo apparatus and that this effect is seen when the circuit is closed, and it does not appear when the circuit is open. It is because the circuit has remained open, were unsuccessful attempts of the same kind, made several years ago, famous physicists. »
Opening Hans Christian Oersted was the basis for the electromagnetic telegraph.

deviation of the magnetic needle under the influence of an electric current
Russian
In 1832, Paul Schilling, a Russian diplomat and historian, a member of World War II, gathered in St. Petersburg electromagnetic telegraph. The basis of the technology of the telegraph was the effect of the deviation of the magnetic needle in the interaction with the electromagnetic field of the electric wires. Background of the invention is extremely interesting: Schilling in the five years before that underwater mines exploded by an electric current passing through the wires with rubber isolation.
To transmit a letter clicked three or four keys simultaneously. On the receiving machine wires were connected to the electromagnet with a magnetic needle hanging over him, which turns on when the current went wire. At arrow rotated signal circle with a black and white on the other. Schilling developed a special code to the six arrows with warning mugs enough to transfer all the letters of the Russian alphabet. One minute eight wires can be sent ten marks.

Shestistrelochny multiplier telegraph Schilling
In 1841 he opened the first regular telegraph line connecting the Winter Palace with the General Staff. This happened after the inventor's death in 1837. But the work of Schilling continued Moritz von Jacobi, created in 1839 to several systems telegraphs, including writing.
In a writing telegraph Boris Jacobi electromagnet set in motion a pencil, leaving a record on a moving porcelain board. The unit worked on the line Winter Palace - Main Headquarters - Tsarskoye Selo. Entries difficult succumbed to decipher what the inventor was not happy.

Jacobi made to the 1845 turnout synchronous machine with a horizontal dial, magnetic drive and keyboard, and by 1850 - the world's first direct-printing telegraphy. Only his government considered the work of the military secret, because of the project, few people knew.

Pointer telegraph BS Jacobi vertical dial
In 1844, Jacobi was invited for the construction of a telegraph line along the railway between Moscow and St. Petersburg. The inventor proposed to include in the line auxiliary battery that allows to broadcast is damaged insulation of underground cable. This device is then used for laying the cable on the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean.
Unfortunately, Jacobi is not added onto the line, ordering the construction of a network of telegraph lines in the end won the German company "Siemens & amp; Halske "

Pointer telegraph «Siemens & amp; Halske »
In 1852 in Moscow, founded the first telegraph station in the station building Peterurg-Moscow railway. Company "Central Telegraph" history started from October 1 this year. In 1869, the station moved to the Butcher Street.
By the end of 1855 Telegraph covered the cities of Central Russia and began to connect the country with Europe. In 1880 in Russia was used telegraphs of several types and teletypes.

Central Telegraph on Butcher Street, around 1900
US
American inventor Samuel Morse patented his version of the telegraph in 1840. Key or "hammer" make and break an electrical circuit, the receiver automatically recorded signals. The current pulses of a certain duration forced to oscillate electromagnetic pen reproduces the "point" and "dashes" on the tape. Perot was pushing or signals, or apply them in ink.

telegraph key, also known as "the hammer»
In 1843, Congress passed a bill, and the inventor has allocated a subsidy for the construction of the line between Washington and Baltimore 65 kilometers long.
The first attempt to lay underground cable with the invention of Ezra Cornell - special trenching plow - was unsuccessful. But in 1844 the line was opened, the wires were for telegraph poles. So insulation could save.
Former Postmaster General in the two cabinets of Presidents Amos Kendall immediately realized how the telegraph, with its highest speed transmission of information is useful, and attracted investors to the project. Morse began to sell the license for his invention, and in 1851 opened the fifty independent telegraph companies in the US.

Illustration of patent Ezra Cornell to the plow for laying cables. Source
In 1846, by Royal Earl House patented printing telegraph, capable of transmitting and forty words per minute. Patent for this type of telegraph owned judge Samuel Selden, with whom Hiram Sibley, Sheriff of Monroe County, New York, founded the company «New York and Mississippi Valley Printing Telegraph Company» (NYMVPTC). Seven years later, the name was changed to "Western Union» -. «Western Union»
Instead of having to lay new telegraph lines, entrepreneurs began buying existing and combine them into one system. For three years the number of offices «Western Union» has increased to 4000, and the capital - from $ 220 thousand to 48 million
. Send a telegram to the US cost $ 20 in 1854 for reporting. Because of this, I am wishing it was not so much, and businessmen are willing to sell their companies Hiram Sibley. In 1854, the «Western Union» has bought the patent for the telegraph Morse.

Printing Telegraph 1900, production of Siemens & amp; Halske, Saint Petersburg
In 1861, the «Western Union» for 112 days a single transcontinental line connected West and East coast of the USA. Before the appearance of this message line at such a distance walked for ten days - they carried the most courageous and desperate young men on horseback. And not all of the letters reached because of the constant attacks by bandits.

Laying transcontinental telegraph line. Pony Express service employee welcomes builders.
The link between the continents
underwater telegraph lines in Europe
By the middle of the XIX century the telegraph network connected most of the major cities in Europe and the United States - by land. But to send a telegram across the ocean was difficult. Letters continued to go by boat, the delivery was carried out for twenty days at best. In a world where international relations became more intensive, creating communication between the Old and the New World was a matter of time. The idea to build a telegraph wire at the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean expressed Samuel Morse, then it supported the British physicist Charles Whitson. But it rejected as unworkable. To help entrepreneurs and scholars came open in India gutta-percha, which Werner von Siemens proposed to be used for insulation.
One of the first submarine lines began to lay the English engineer John Brett between France and England. Military ship "Vigdeon" indicating the ship "Goliath" with the cable on board the path, marking it with buoys with flags. Cable plunged into the water every 15 minutes to it suspended load 10 kilograms of lead. Through the first telegram I went, but immediately after it stopped working relationship. French fisherman accidentally tore a piece of cable seine.
The first cable consists of two copper wires to two millimeters thick shell covered with gutta-percha. For the second attempt using four wires, each of which is protected gutta-percha coated six millimeters thick. All wire with five round tarred hemp and soaked fat cords tied in a cable entwined common tarred hemp cord. Top imposed another layer of hemp, and after ten cable wound iron galvanized wire with a diameter of seven millimeters. The first cable weighed 14 tons, and the second, improved, has 166 tons. Now the chance of nets cast into the sea could not prevent the communication between the two countries.
In November 1852 we established a direct telegraphic communication between London and Paris, and later joined England and Ireland, Germany, Holland and Belgium. Sweden joined Norway and Italy - with Sardinia and Corsica. In the years 1854-1855 the cable laid across the Mediterranean and the Black Sea.
Transatlantic Cable The businessman Cyrus West Field, using the experience of companies lay submarine cables, assembled investments sufficient for the project of laying on the bottom of the Atlantic cable. In 1856, the ship "Agamemnon" and "Niagara" moved away from the coast of Ireland, each was carrying the coil cable weight in one and a half thousand tons. The cable is made of copper semiprovolochnogo rope with gutta-percha cover, which conductor obtyanuli tarred hemp and wound another 18 outside the cable cord of the iron wires 7 each. Cable length was four thousand kilometers.

route for laying of the transatlantic link: Ireland - Newfoundland
A few days later the cable broke, and the project had to be postponed. After several months, a second attempt - again a failure. The third attempt took place in 1858, were able to lay the cable from Ireland to Newfoundland. August 16 that year, the British Queen Victoria congratulated US President James Buchanan to a successful project, but a few months later the connection was broken.
Cyrus Field and then did not give up. Eight years later, in 1864, he began laying the cable with improved insulation to help the British steamer "Great Eastern" with a displacement of 32,000 tons. The cable broke during installation. In 1866 the same ship made a second attempt - and then turned finally to provide a link between Europe and America. A cable previously found torn and affixed with a second fragment, so that it began to function.

Scene cable break on the "Great Eastern". The Illustrated London News. Band 47. 1865.
Source

Samples cables that formed
transatlantic link from the USA to Europe via Alaska
American "Western Union" has decided to go the other way - through Alaska. In 1867, Russia sold Alaska to the United States for 7, 2 million dollars, and "Western Union" has received from the authorities the right to lay along the military line and mail routes, including the railway line.
cabling project through Alaska called the "Russian-American Telegraph". He envisioned a line from San Francisco, California to Moscow through Oregon, Washington area, Columbia, Alaska, the Bering Strait and Siberia, which made it possible to combine the US and Europe.
Although the project failed, he gave impetus to the development of the territories through which passed.

telegraph line in Alaska
main telegraph line in 1891
In 1870, a cable laid in India to establish a link between London and Bombay through Egypt and Malta. Below can be seen on the map the major telegraph line in 1891.

Public domain
Also congratulations and news
Remittances
The ability to instantly send messages over long distances has opened the way for new types of business. mail Money in Russia, according to the Great Soviet Encyclopedia forwarded 1781. In the XIX century there was modernized service - postal orders. By mail sent not the bills, and special coupons, which the recipient has brought to the post office to pick up the cash. And to invest money in the envelopes banned.
An extensive telegraph network in the United States allowed the «Western Union» start delivering in 1871 telegraph money orders. The service has proved so popular that within five years, the company held 37 190 transfers in the amount of 2, 6 million dollars at the average transfer amount $ 70. This is more than 56 million dollars in 2016 prices. That this service is now a core business for the company. In 2015, the «Western Union» has carried out 262 million money transfers between customers for a total of $ 82 billion.
In the Soviet Union money transfers are one of the essential services of public telegraph.

Blank wire transfer, USSR
Securities Market Quotes
In the middle of the XIX century began to emerge in the US stock market. Securities traded on the stock exchanges themselves. It would be much easier to get to know the current market price, sitting in a brokerage firm, and make buying and selling directly from it. This opportunity opened telegraph, bringing securities trading to real time.
Royal Earl House in 1846 patented a printing telegraph, which gave to the text output. It was the great-great-great-great-grandfather of today's printers. The first model was fragile, often synchronization between the sender and the receiver was broken. Print one letter needed several current pulses, and the system did not work over long distances. Улучшенная Дэвидом Хьюзом модель работала с помощью часовых механизмов — так достигалась синхронизация аппаратов. Эту модель использовали в России с 1865 года до начала Великой Отечественной войны.
Готовая печать телеграфных сообщений, без необходимости длительной расшифровки точек и тире, позволила создать тикерные аппараты для передачи биржевых котировок. В 1869 году Томас Эдисон представил такой аппарат, способный печатать один символ в секунду.

Тикерный аппарат Томаса Эдисона
Точное время
Сейчас наши смартфоны и компьютеры синхронизируют время с помощью радиосвязи. В 1930-е годы в США вы могли арендовать часы, которые синхронизировались с мастер-часами «Western Union», чтобы вы всегда могли точно знать, который час. В 1877 году на крыше штаб-квартиры компании в Нью-Йорке установили шар времени, по которому жители города могли сверять часы. За пять минут до полудня шар поднимали до самого верха шпиля, на высоту 96 метров над улицей. Десятиэтажное здание компании на тот момент было самым высоким в Нью-Йорке и США. За две минуты до полудня в Морскую обсерваторию США в Вашингтоне по телеграфу отправляли сигнал о статусе положительной готовности шара для спуска.
В полдень оператор из обсерватории активировал спусковой механизм и шар падал на семь метров вниз. После спуска шара сигнал отправляли в обсерваторию. Благодаря этой службе компания почти весь XX век была «Хранителем времени нации».

Часы с точным временем от Western Union
Возможность быстрой отправки сообщений открыла новые возможности для бизнеса. Крупные компании с развитой филиальной сетью благодаря телеграфной связи, а затем — телетайпу, стали работать как единое целое, передавая информацию в режиме реального времени.
Телетайп
Закодированный телеграфный сигнал было трудно читать и передавать без специальной подготовки, поэтому с самого начала учёные пытались изобрести более «дружелюбное» к пользователям устройство. Так было с пишущим телеграфом Бориса Якоби и аппаратом Вернера фон Сименса, и это стало причиной появления телетайпа.
В 1872 году французский изобретатель Жан Бодо разработал телеграфный аппарат, который позволял одновременно передавать два и более сообщений по одной линии. При этом аппарат передавал сообщения, используя буквы латинского алфавита, а после работы российских умельцев — и буквы русского алфавита. Устройства такого типа назвали стартстопными. Кроме этого Бодо создал телеграфный код Бодо, который передавали на перфорированных лентах. Первые аппараты Бодо стали использовать в 1877 году на линии Париж — Бордо. До конца XX века использовали двухкратные аппараты, способные передавать до 760 знаков в минуту. Дополнительно к аппарату Бодо сделал распределитель, дешифратор и печатающий механизм, что упрощало работу специалистов.
Два или шесть телеграфистов кодировали сообщения, стараясь не сбиться. Они использовали два пальца левой и три пальца правой руки, по очереди отправляя сигналы. Но самое интересное происходило с другой стороны — на бумажной ленте печатались буквы, а не код.
В 1901 году после создания клавиатуры для телеграфного аппарата код доработали, изменили порядок знаков и добавили дополнительные символы. 5-битная кодировка и использование буквенного и цифрового регистра остались.

Аппарат Бодо: клавиатура и распределитель
Изобретение Бодо и тикерный аппарат стали предшественниками телетайпа. Телетайп — это электромеханическая печатная машина для передачи текстовых сообщений.
В 1920-х годах была создана глобальная «Сеть Телекс», охват которой составил 600 тысяч абонентов в 100 странах мира. Отправленные через эту сеть документы имели юридическую силу. Сетью активно пользовались коммерческие компании, пока телетайп не был вытеснен факсом, а затем и интернетом.
Сейчас от популярности некогда распространенного устройства остались лишь бледные следы, например, традиционный префикс tty (от TeleTYpe) для обозначения текстовых терминалов в Unix. Некоторые ведомственные радиостанции до сих пор ведут вещание в режиме телетайпа, передавая информацию вроде сводок погоды.

Телетайп, входивший в сеть Telex
Телеграф сегодня
Американская «Western Union» отправила последнюю телеграмму в 2006 году, полностью переключившись на трансфер денег. В 2004 году телеграф свернули в Нидерландах, а в 2013 году — в Индии. В некоторых странах, в частности в России, государственные службы работают до сих пор. Иногда телеграммы используют для отправки повесток в суд, для денежных переводов, даже для поздравлений. Во времена, когда передача информации перестала быть проблемой благодаря глубокому проникновению интернета и мобильной связи, простые письма или телеграммы становятся прихотью, позволяющей проникнуться атмосферой прошлого. Вот только сами телеграфные сети в основном демонтированы, поэтому сообщения передают по современным каналам связи.
Источник: geektimes.ru/post/278850/