2127
Copy / Paste in the Soviet
Many of us remember the wonderful electronic toys, "Well, wait a minute!", Which in the 1980s were almost every Soviet family. Despite this, few people know that these toys were pirated copied and adapted to Soviet realities such samples developed by Nintendo. In the Soviet Union able and loved to copy foreign equipment, often not caring about copyright.

Like the Nintendo into a "electronics»
Let's start with the most toys, "Well, wait a minute!". In order to trace the history of their appearance in the Soviet Union, you must first pay a visit to Japan. It was there the developer of games for Nintendo's Gumpeyu Yokoi once had the idea to create such a decision.
According to the legend, Yokoi once rode the train and saw one of his companion amused himself that pressed the keys of the calculator. It was then that the idea to create a miniature electronic game that has as functional watches, which can take anywhere. Such an idea like leadership Nintendo, and a game called Game & Watch began producing in 1980. There are several types of Game & Watch, but each of them is allowed to play only one game, which was caused by the use of a segmented LCD display.
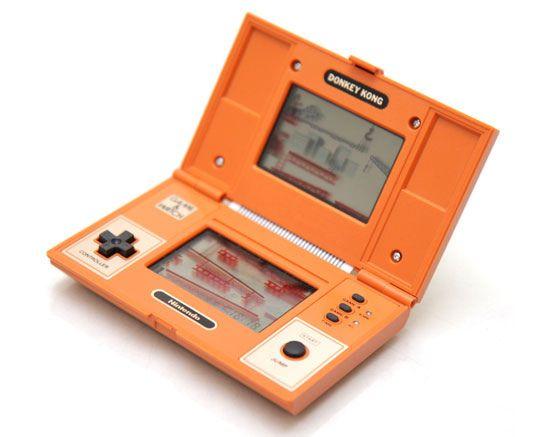

The novelty soon came to the attention of representatives of the Soviet government - it was decided to release their own game of this type. Without further ado, the Ministry of Electronics Industry of the USSR decided to purchase several copies of the Japanese game and give the plant "Electronics" for a comprehensive study. Thus, the method of reverse engineering and was born a Soviet version of the Game & Watch, entitled "Well, wait a minute!».

The game was created on the domestic element base, in particular, are used KB1013VK1-2 processor and LCD display or IZHM2-71-01 IZHM13-71. The release of the game has been launched in 1984 at the "diffusing" in Orel. Soon after, she became very popular throughout the Soviet Union. The cost of "Well, wait!" Amounted to 23 rubles.
"Agate" - Soviet Apple II
Computer Apple II, first released in 1977, made a small company one of the leaders in the PC market, and its founders - multimillionaires. Total production for the period was released about six million of such computers.
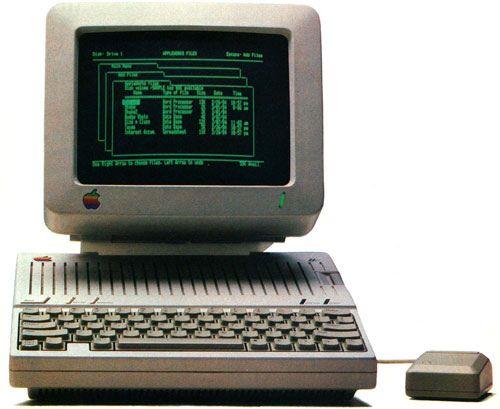

Meanwhile, despite the Iron Curtain in the Soviet Union very soon we met with this decision, and the country's leadership decided that this computer will not be superfluous, and for the Soviet people. So, in the early 1980s in the Institute of computing complex was "developed" own personal computer "Agat", the basis of which were taken architecture and software Apple II.
We must pay tribute to the engineers NIIVK, since the device is not an exact copy of your computer from Apple. This was primarily due to the use of domestic components. It has its own design and revised software. The computer was placed in a red plastic case, and as the monitor is widely used model produced small TV "Silelis" and "Yunost-404." Series production began in 1984 and lasted until 1993

"Agat" was positioned as a training computer, equipped with a magnetic disk drive and was completed two gaming consoles. However, computer users get the OS Apple DOS 3.3 and interpreter Basic, and also some other software. Because of the architectural features of "Agat" I was not able to execute programs created for the original Apple II. It is noteworthy that the USSR put one copy of a computer at the exhibition CeBIT, despite its origin was a pirate.
Spectrum in the domestic incarnation
In the 1980s, around the world enjoyed great popularity home computers, which we were told not long ago. One of the most popular models has been ZX Spectrum, manufactured by the British company Sinclair.

It is this computer and has become the latest victim of the Soviet "pirates-in-law." At the end of 1980 on the shelves of stores in different cities of the USSR came home computer "byte", which is now a sort of legend. Computing power is provided or the Soviet KR1858VM1 processor or as the Soviet T34VM1 is a complete clone of ZiLOG Z80, installed in the original ZX Spectrum.

Like other examples of Western art cloned, "Byte" has some differences from the original. In particular, it has been installed on the four-channel audio synthesizer chip domestic and four-way joystick on the keyboard. Dimensions "Byte" significantly exceed those of the ZX Spectrum. Moreover, one of the modifications produced in the system unit with the floppy disk drive. Despite this, the device software was completely identical to the one that was installed on the ZX Spectrum.
It must be said that the computer was very popular in the Soviet Union, despite the high cost - 950 rubles. Its production was curtailed only in 1996. During this time, the Brest plant BPO SVT has released about 65 thousand computers.
Almost Hasselblad
Not without copying foreign models and photographic edition. One of these representatives is a single-lens medium format camera "Salute", with the creation of which was based on the camera Hasselblad 1600F, which was produced in 1948.

Outwardly, the two cameras though are somewhat different, but still very similar. The internal structure of cells and is almost identical. "Salute" (as Hasselblad 1600F) made modular to him alone joins the lens and viewfinder and the cassette tape. The camera is equipped with a curtain focal plane shutter with corrugated shutters made of stainless steel. Exposure range is from 1/2 to 1/1000, and the earlier versions - from 1/2 to 1/1500 with.

An important difference is the use of their own in the mount, which possess many other cameras Kiev factory "Arsenal". The overall quality of the device is at a fairly high level. It is noteworthy that the company Hasselblad discontinued the model 1600F in 1953, while in the USSR "Salute" in various modifications produced until 1980, and the model of the "Kiev-88", has undergone minor changes - to the present day.
Honest conditioners "BK»
Despite the adoption of the norm stealing foreign technology, in the Soviet Union it is still something to be produced and licensed. The most striking example is the RAC "BC" that mass-produced in a factory in Baku. In the 1970s, the Soviet Union bought the equipment and issue a license for the production of household air conditioners technology company Hitachi. Soon it was mass production of home air conditioners, which have become widely installed in various state institutions.

Baku factory had a large production capacity - up to half a million units a year. In this part of the production, about 120 thousand. Per year for export. The main buyer of air conditioners "TC" was Cuba, which acquired all of the time about 700 thousand. Units. However, among the buyers it was not only Soviet bloc country, but also quite capitalist Australia. It is worth noting that the quality of the plant's products is quite consistent with international standards. This is evidenced by the fact that the factory, which produced compressors for air conditioners, has been calculated at 1 million units a year and a half of the products are manufactured for Toshiba.
By the way, air-conditioners, "BC" can still be seen in various cities of the former Soviet Union. However, many of them still keep working.
Source: www.omgadget.ru

Like the Nintendo into a "electronics»
Let's start with the most toys, "Well, wait a minute!". In order to trace the history of their appearance in the Soviet Union, you must first pay a visit to Japan. It was there the developer of games for Nintendo's Gumpeyu Yokoi once had the idea to create such a decision.
According to the legend, Yokoi once rode the train and saw one of his companion amused himself that pressed the keys of the calculator. It was then that the idea to create a miniature electronic game that has as functional watches, which can take anywhere. Such an idea like leadership Nintendo, and a game called Game & Watch began producing in 1980. There are several types of Game & Watch, but each of them is allowed to play only one game, which was caused by the use of a segmented LCD display.

The novelty soon came to the attention of representatives of the Soviet government - it was decided to release their own game of this type. Without further ado, the Ministry of Electronics Industry of the USSR decided to purchase several copies of the Japanese game and give the plant "Electronics" for a comprehensive study. Thus, the method of reverse engineering and was born a Soviet version of the Game & Watch, entitled "Well, wait a minute!».

The game was created on the domestic element base, in particular, are used KB1013VK1-2 processor and LCD display or IZHM2-71-01 IZHM13-71. The release of the game has been launched in 1984 at the "diffusing" in Orel. Soon after, she became very popular throughout the Soviet Union. The cost of "Well, wait!" Amounted to 23 rubles.
"Agate" - Soviet Apple II
Computer Apple II, first released in 1977, made a small company one of the leaders in the PC market, and its founders - multimillionaires. Total production for the period was released about six million of such computers.

Meanwhile, despite the Iron Curtain in the Soviet Union very soon we met with this decision, and the country's leadership decided that this computer will not be superfluous, and for the Soviet people. So, in the early 1980s in the Institute of computing complex was "developed" own personal computer "Agat", the basis of which were taken architecture and software Apple II.
We must pay tribute to the engineers NIIVK, since the device is not an exact copy of your computer from Apple. This was primarily due to the use of domestic components. It has its own design and revised software. The computer was placed in a red plastic case, and as the monitor is widely used model produced small TV "Silelis" and "Yunost-404." Series production began in 1984 and lasted until 1993

"Agat" was positioned as a training computer, equipped with a magnetic disk drive and was completed two gaming consoles. However, computer users get the OS Apple DOS 3.3 and interpreter Basic, and also some other software. Because of the architectural features of "Agat" I was not able to execute programs created for the original Apple II. It is noteworthy that the USSR put one copy of a computer at the exhibition CeBIT, despite its origin was a pirate.
Spectrum in the domestic incarnation
In the 1980s, around the world enjoyed great popularity home computers, which we were told not long ago. One of the most popular models has been ZX Spectrum, manufactured by the British company Sinclair.

It is this computer and has become the latest victim of the Soviet "pirates-in-law." At the end of 1980 on the shelves of stores in different cities of the USSR came home computer "byte", which is now a sort of legend. Computing power is provided or the Soviet KR1858VM1 processor or as the Soviet T34VM1 is a complete clone of ZiLOG Z80, installed in the original ZX Spectrum.

Like other examples of Western art cloned, "Byte" has some differences from the original. In particular, it has been installed on the four-channel audio synthesizer chip domestic and four-way joystick on the keyboard. Dimensions "Byte" significantly exceed those of the ZX Spectrum. Moreover, one of the modifications produced in the system unit with the floppy disk drive. Despite this, the device software was completely identical to the one that was installed on the ZX Spectrum.
It must be said that the computer was very popular in the Soviet Union, despite the high cost - 950 rubles. Its production was curtailed only in 1996. During this time, the Brest plant BPO SVT has released about 65 thousand computers.
Almost Hasselblad
Not without copying foreign models and photographic edition. One of these representatives is a single-lens medium format camera "Salute", with the creation of which was based on the camera Hasselblad 1600F, which was produced in 1948.

Outwardly, the two cameras though are somewhat different, but still very similar. The internal structure of cells and is almost identical. "Salute" (as Hasselblad 1600F) made modular to him alone joins the lens and viewfinder and the cassette tape. The camera is equipped with a curtain focal plane shutter with corrugated shutters made of stainless steel. Exposure range is from 1/2 to 1/1000, and the earlier versions - from 1/2 to 1/1500 with.

An important difference is the use of their own in the mount, which possess many other cameras Kiev factory "Arsenal". The overall quality of the device is at a fairly high level. It is noteworthy that the company Hasselblad discontinued the model 1600F in 1953, while in the USSR "Salute" in various modifications produced until 1980, and the model of the "Kiev-88", has undergone minor changes - to the present day.
Honest conditioners "BK»
Despite the adoption of the norm stealing foreign technology, in the Soviet Union it is still something to be produced and licensed. The most striking example is the RAC "BC" that mass-produced in a factory in Baku. In the 1970s, the Soviet Union bought the equipment and issue a license for the production of household air conditioners technology company Hitachi. Soon it was mass production of home air conditioners, which have become widely installed in various state institutions.

Baku factory had a large production capacity - up to half a million units a year. In this part of the production, about 120 thousand. Per year for export. The main buyer of air conditioners "TC" was Cuba, which acquired all of the time about 700 thousand. Units. However, among the buyers it was not only Soviet bloc country, but also quite capitalist Australia. It is worth noting that the quality of the plant's products is quite consistent with international standards. This is evidenced by the fact that the factory, which produced compressors for air conditioners, has been calculated at 1 million units a year and a half of the products are manufactured for Toshiba.
By the way, air-conditioners, "BC" can still be seen in various cities of the former Soviet Union. However, many of them still keep working.
Source: www.omgadget.ru