939
Helicopter Museum in Torzhok
Helicopter Museum 344th Center for operational use and retraining of pilots of Army Aviation, located in the town of Torzhok in the Tver region, was established in the early 1990s. Despite the fact that several years ago the museum was officially enrolled in the list of museums in the Tver region, get to it still is not easy because of the location of the museum in the grounds of a military airfield ...
The museum contains samples of all helicopters ever absorbed in the 344th Center. And given the special status of the military unit (the 344th and Center BP PLC is preparing highly qualified crews of helicopters), it's safe to say that it's almost the entire fleet of military and naval helicopters, produced in the USSR.
36 photos via 4,044,415 and bigpicture
1) The exposition of the museum opens Mi-1 (Hare - according to NATO classification). This multi-purpose Soviet helicopter Mil developed in the late 1940s. Originally designated as GM-1 (helicopter Mil 1). First flew in 1948 and became the first Soviet serial helicopter.
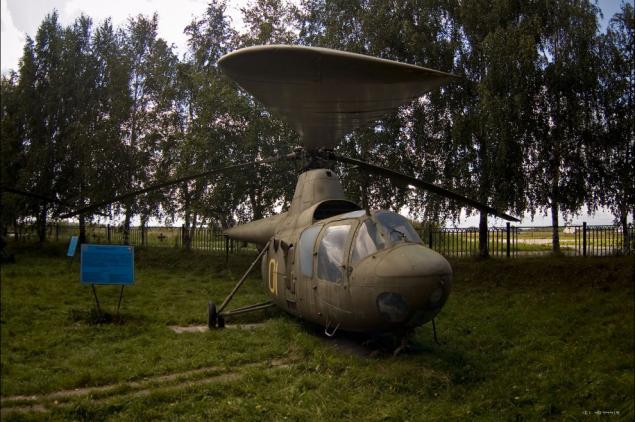

2) In addition to the basic version, designed for the pilot and three passengers were released and the other versions and modifications - health with lateral detachable gondolas, postal with hanging containers, ferry with additional fuel tanks, agricultural spraying and dusting, with floats, military training and others.
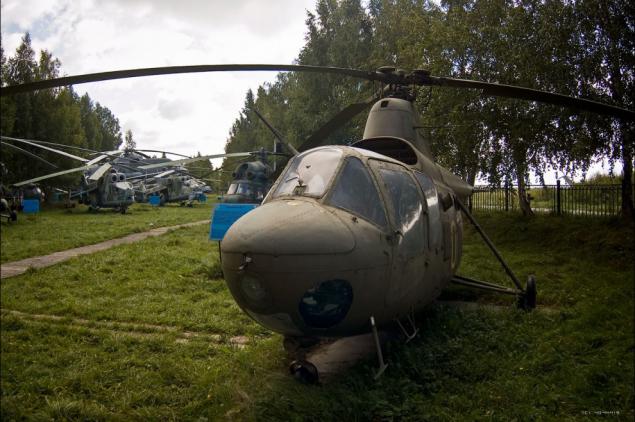

3) One of these helicopters, made in a version of "luxury", the President of Finland enjoyed. Two further equipped with Mi-1T used as a base for Arctic icebreakers.

4) Attack of the Mi-1 began to build in 1958 on the basis of the modification of the Mi-1mu. On each side of the machine secured 2 cassettes 12 rockets. Some modifications were equipped with machine guns, 100 kg bombs, anti-tank missiles "Phalanx" and "Baby". Also offers the option to install large-aviapulemetov in the side pods. An attempt was made to use the Mi-1 as an anti-submarine helicopter, but its engine was not enough to carry the search and bomb equipment.

5) Military Mi-1B actively used in China in police operations. Egypt and Syria used the Mi-1 in the conflict with Israel. The helicopter was also used in the civil war in North Yemen, Iraq to crush Kurdish revolts in Cuba to eliminate armed opposition. Today, this car can be found only rarely as an exhibit in a museum or a monument.
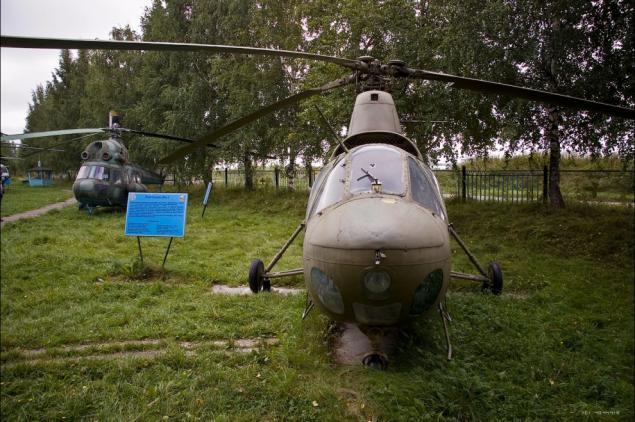

6) The crew - 1 persons + 3 passengers. Cruising speed - 145 km / h. Radius - 360 km. The ceiling - 1220 m.

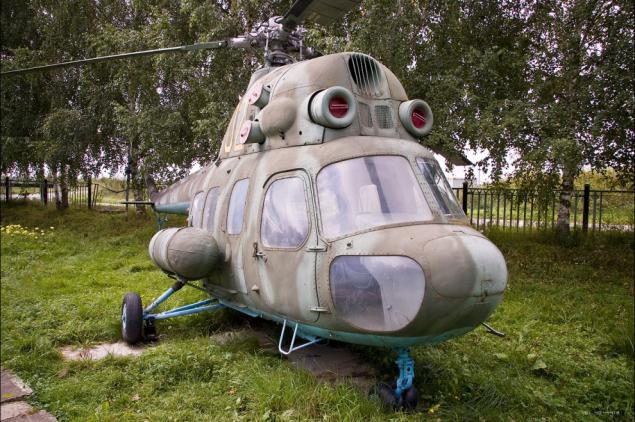
7) Mi-2 (Hoplite - according to NATO classification) - Soviet multi-purpose helicopter, which is used in military and civil aviation since the 1960's. Even today, the Mi-2 is actively taking part in tenders in competition with the new helicopters. It is simple to operate, nepriholivaya and reliable machine, which for many helicopter was the first training. It is believed that if you can manage Mi-2, so you can pick up any helicopter in the air. His crew - 10 people + 1 passengers. Speed - 194 km / h. Flight range - 580 km. The ceiling - 4000 m.

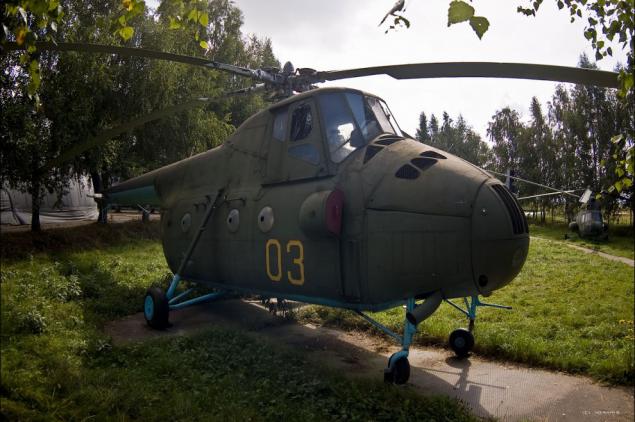
8) Mi-4 (Hound - according to NATO classification) - another Soviet multipurpose helicopter. Widely used for civilian traffic in the national economy and in the armed forces until the appearance of the Mi-8.

9) The crew of the Mi-4 consisted of 3 people. Mi-4 transport up to 16 passengers, a car or a cannon, could be equipped with floats.

10) Cruising speed - 140 km / h. Flight range - 465 km. The ceiling - 1200 m.

11) Mi-8 (Hip - according to NATO classification) - a multi-purpose helicopter, developed in the early 1960s. Is the most popular twin-engined helicopter in the world, and is also included in the list of the most popular helicopters in the history of aviation. Widely used for the moment to perform a variety of civilian and military tasks.
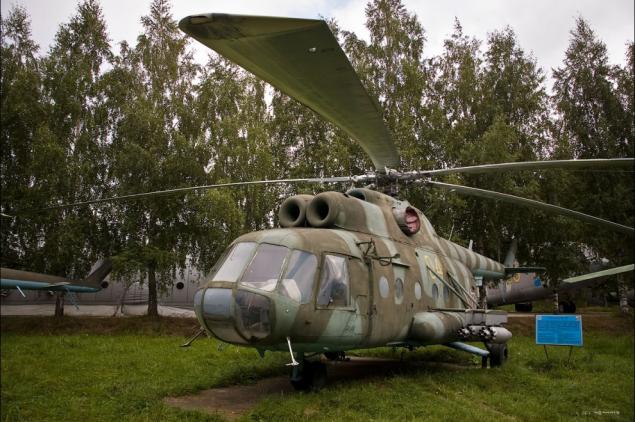

12) The history of the Mi-8 has a huge variety of modifications and upgrades. This variety of options for passenger helicopters, transport, agricultural, anti, mine layers, with night-vision equipment, flying workshop, refueling-tanker towing trawl, sea life, headquarters, command post, an artillery spotter helicopter remote surveillance systems, radio-chemical reconnaissance, air hospital, the helicopter radio-electronic countermeasures jammer, transport and assault, etc.

13) Mi-24 (Hind - according to NATO classification) is presented at the Museum 3 machines. This Soviet military transport helicopter, production of which began in 1971. It has a lot of modifications, was exported to many countries. Actively used in many armed conflicts and wars. Its unofficial name - "Crocodile".

14) Mi-24 first modification (Mi-24A) had a "rectangular" glazing. Designated pilot and radio operator-arrow located next to, not in tandem.
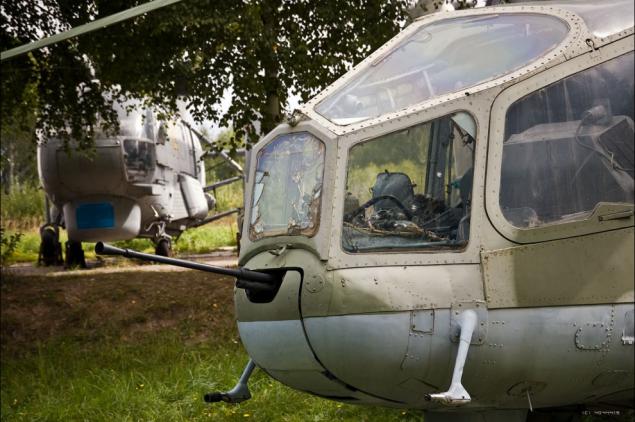

15) The nose Mi-24A was mounted mobile machine-gun installation FCC-1 with the gun A-12.7 (ammo - 900 rounds). Pole - units of unguided rockets and anti-tank missiles 4 "Falanga-M."

16) Such cars have been built about 250 units.

17) Mi-24V (export version - Mi-35) - the most mass modification of the helicopter. Cabs were arranged in tandem is already isolated.
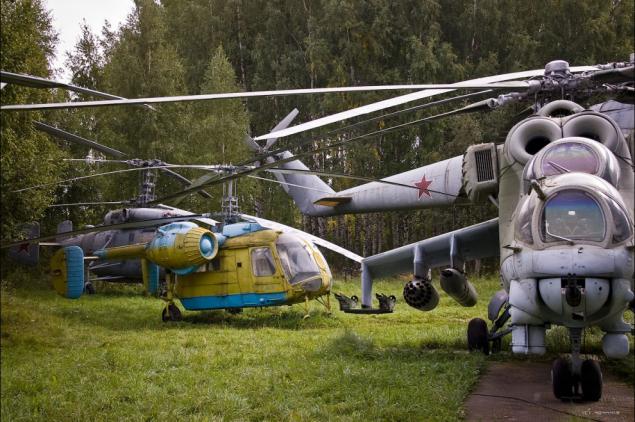

18) Instead of nizkoskorostrelnogo A-12.7 machine gun was installed chetyrehstvolny Yakushev-Borzov, a new missile and bomb weapons, new guidance systems and engines.

19) Like the Mi-8, Mi-24 helicopter of the history of their time to participate in the operation of a large number of armed conflicts in many parts of the world.
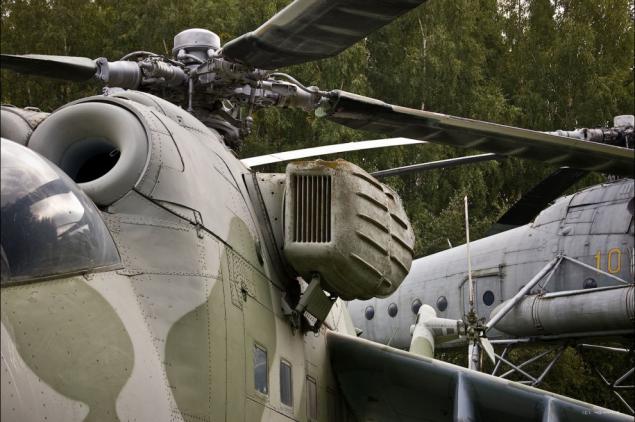

20) In addition to the basic functions of combat transport helicopter, were also options: minesweeper, anti-tank, reconnaissance and correction, sea (draft), night, patrol and rescue, reconnaissance, and other high-rise.

21) The crew of the Mi-24 - 3 person + 8 paratroopers.

22) Mi-10 (Harke - according to NATO classification) - a military transport helicopter "flying crane", created on the basis of the Mi-6. His civil modification to perform construction and installation works - Mi-10K.
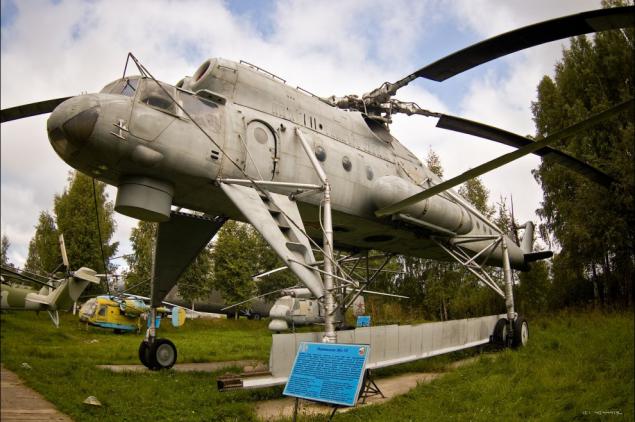

23) The crew was 5 people. The main objective of the design was the ability to carry cruise and ballistic missiles. Cargo can be transported on the outside of the platform or by means of hydraulic grips.
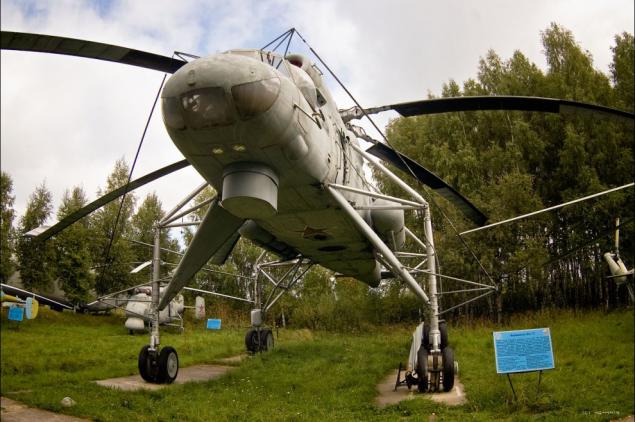

24) In view of the fact that these helicopters were released in limited edition, would lead them to live even in the museums - a rarity.
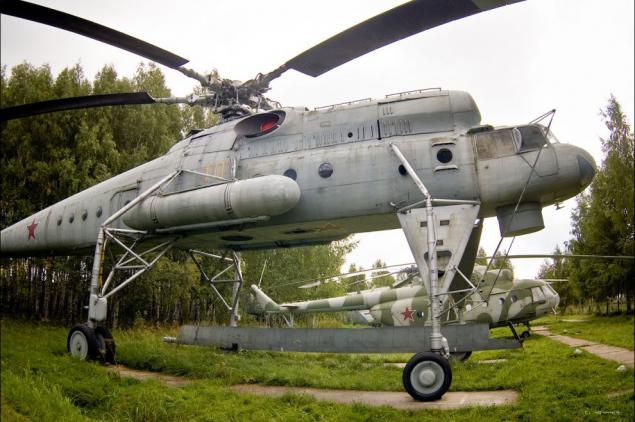

25) Mi-18 - one of the experimental versions of the Mi-8. It features a stretched fuselage (technical requirements demand more capacity), removing the side fuel tanks, enhanced rigidity and strength of the fuselage.
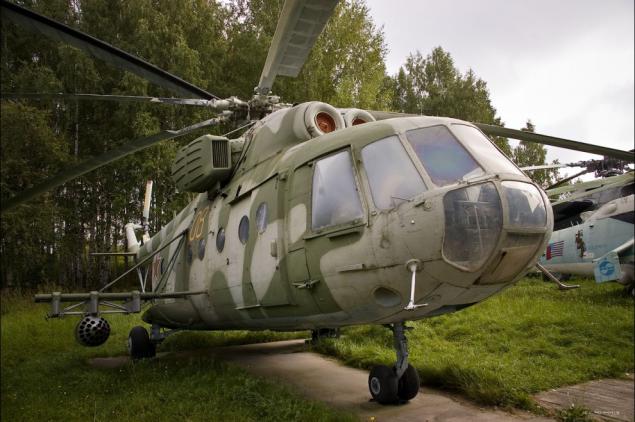

26) Since the rate of the Mi-18 was supposed to increase to 270 km / h, was the installation of low-retractable landing gear. The tail rotor moved from right to left, set the screen-exhaust suppression devices IR engines. Number of side doors increased to two.

27) In connection with a number of different factors, the Soviet Air Force refused to finance further rarabotku Mi-18, determined to manage the existing fleet of Mi-8.

28) Two samples of the Mi-18 were as visual aids in the training centers (one right here, Torzhok). Spent on the Mi-18, the new design elements and equipment were subsequently introduced in other production Mi-8.

29) The third car of the Mi-24 at the Museum of PPI-344 and PLC - unique. In 1992, the female crew (pilot - G.Rastorgueva navigator - L.Polyanskaya) on a specially prepared Mi-24B realized flight Torzhok - Miami (USA), dedicated to the 500th anniversary of the discovery of America and the 50th anniversary of the Lend-Lease.
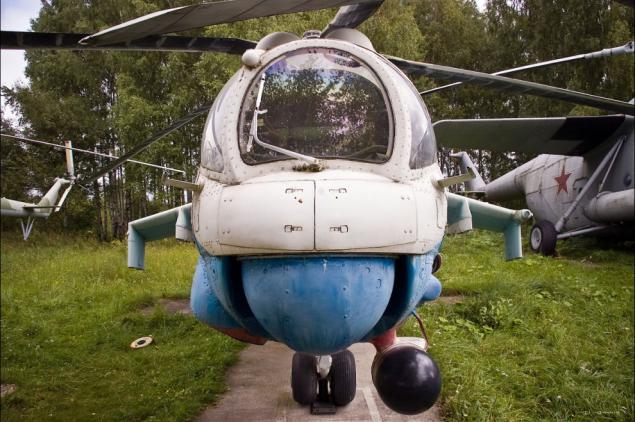

30) After this exciting trip the car was handed over to the museum.

31) Mi-6 (Hook - according to NATO classification) - a heavy military transport helicopter. it was built in 1964 as a series of major military and civil versions.

32) The crew of the helicopter were 5 people. Speed - 300 km / h. Payload - 12 tons.
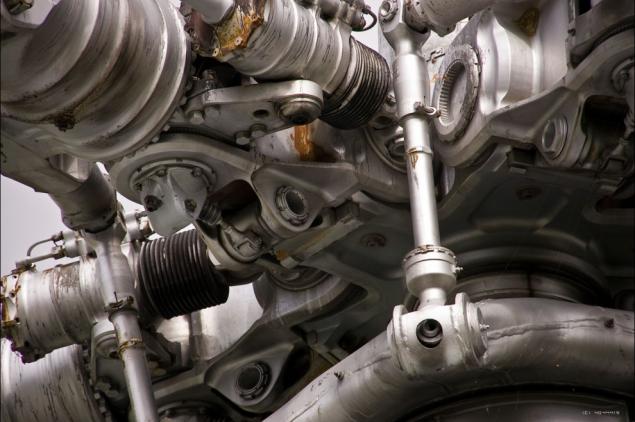

33) One of the curious modification of the Mi-6 is a variant of the fire Mi-6PZH.

34) It can be seen in the Air Force Museum in Monino.
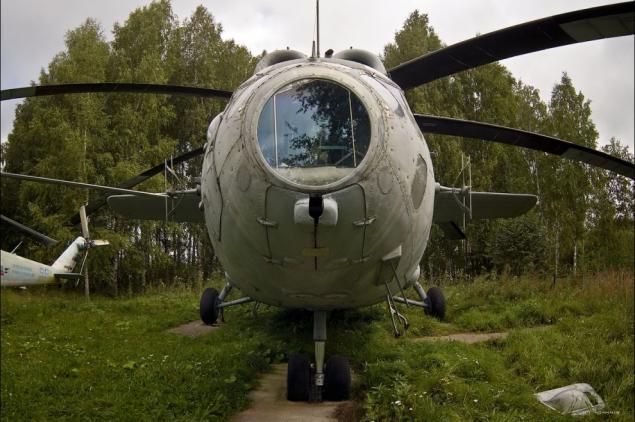

35) Ka-25 (Hormone - according to NATO classification) - Soviet shipborne ASW helicopter. Is the first domestic helicopter was originally designed for combat use and became the first anti-submarine and the first combat helicopter initially USSR. On this basis, a large number of modifications.
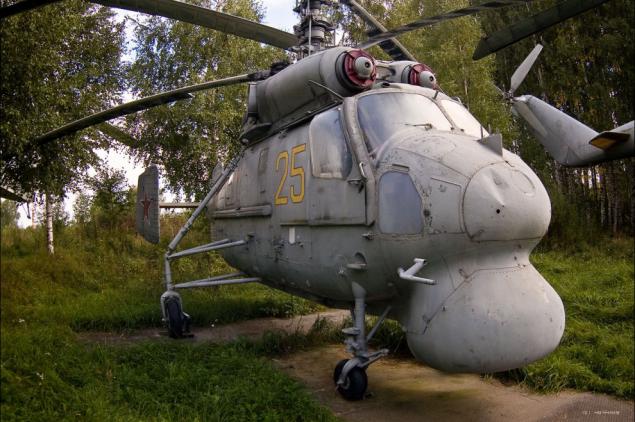

36) The crew is 2 people. The helicopter could carry 12 passengers. Cruising speed - 185 km / h.

Source:
The museum contains samples of all helicopters ever absorbed in the 344th Center. And given the special status of the military unit (the 344th and Center BP PLC is preparing highly qualified crews of helicopters), it's safe to say that it's almost the entire fleet of military and naval helicopters, produced in the USSR.
36 photos via 4,044,415 and bigpicture
1) The exposition of the museum opens Mi-1 (Hare - according to NATO classification). This multi-purpose Soviet helicopter Mil developed in the late 1940s. Originally designated as GM-1 (helicopter Mil 1). First flew in 1948 and became the first Soviet serial helicopter.

2) In addition to the basic version, designed for the pilot and three passengers were released and the other versions and modifications - health with lateral detachable gondolas, postal with hanging containers, ferry with additional fuel tanks, agricultural spraying and dusting, with floats, military training and others.

3) One of these helicopters, made in a version of "luxury", the President of Finland enjoyed. Two further equipped with Mi-1T used as a base for Arctic icebreakers.

4) Attack of the Mi-1 began to build in 1958 on the basis of the modification of the Mi-1mu. On each side of the machine secured 2 cassettes 12 rockets. Some modifications were equipped with machine guns, 100 kg bombs, anti-tank missiles "Phalanx" and "Baby". Also offers the option to install large-aviapulemetov in the side pods. An attempt was made to use the Mi-1 as an anti-submarine helicopter, but its engine was not enough to carry the search and bomb equipment.

5) Military Mi-1B actively used in China in police operations. Egypt and Syria used the Mi-1 in the conflict with Israel. The helicopter was also used in the civil war in North Yemen, Iraq to crush Kurdish revolts in Cuba to eliminate armed opposition. Today, this car can be found only rarely as an exhibit in a museum or a monument.

6) The crew - 1 persons + 3 passengers. Cruising speed - 145 km / h. Radius - 360 km. The ceiling - 1220 m.

7) Mi-2 (Hoplite - according to NATO classification) - Soviet multi-purpose helicopter, which is used in military and civil aviation since the 1960's. Even today, the Mi-2 is actively taking part in tenders in competition with the new helicopters. It is simple to operate, nepriholivaya and reliable machine, which for many helicopter was the first training. It is believed that if you can manage Mi-2, so you can pick up any helicopter in the air. His crew - 10 people + 1 passengers. Speed - 194 km / h. Flight range - 580 km. The ceiling - 4000 m.

8) Mi-4 (Hound - according to NATO classification) - another Soviet multipurpose helicopter. Widely used for civilian traffic in the national economy and in the armed forces until the appearance of the Mi-8.

9) The crew of the Mi-4 consisted of 3 people. Mi-4 transport up to 16 passengers, a car or a cannon, could be equipped with floats.

10) Cruising speed - 140 km / h. Flight range - 465 km. The ceiling - 1200 m.

11) Mi-8 (Hip - according to NATO classification) - a multi-purpose helicopter, developed in the early 1960s. Is the most popular twin-engined helicopter in the world, and is also included in the list of the most popular helicopters in the history of aviation. Widely used for the moment to perform a variety of civilian and military tasks.

12) The history of the Mi-8 has a huge variety of modifications and upgrades. This variety of options for passenger helicopters, transport, agricultural, anti, mine layers, with night-vision equipment, flying workshop, refueling-tanker towing trawl, sea life, headquarters, command post, an artillery spotter helicopter remote surveillance systems, radio-chemical reconnaissance, air hospital, the helicopter radio-electronic countermeasures jammer, transport and assault, etc.

13) Mi-24 (Hind - according to NATO classification) is presented at the Museum 3 machines. This Soviet military transport helicopter, production of which began in 1971. It has a lot of modifications, was exported to many countries. Actively used in many armed conflicts and wars. Its unofficial name - "Crocodile".

14) Mi-24 first modification (Mi-24A) had a "rectangular" glazing. Designated pilot and radio operator-arrow located next to, not in tandem.

15) The nose Mi-24A was mounted mobile machine-gun installation FCC-1 with the gun A-12.7 (ammo - 900 rounds). Pole - units of unguided rockets and anti-tank missiles 4 "Falanga-M."

16) Such cars have been built about 250 units.

17) Mi-24V (export version - Mi-35) - the most mass modification of the helicopter. Cabs were arranged in tandem is already isolated.

18) Instead of nizkoskorostrelnogo A-12.7 machine gun was installed chetyrehstvolny Yakushev-Borzov, a new missile and bomb weapons, new guidance systems and engines.

19) Like the Mi-8, Mi-24 helicopter of the history of their time to participate in the operation of a large number of armed conflicts in many parts of the world.

20) In addition to the basic functions of combat transport helicopter, were also options: minesweeper, anti-tank, reconnaissance and correction, sea (draft), night, patrol and rescue, reconnaissance, and other high-rise.

21) The crew of the Mi-24 - 3 person + 8 paratroopers.

22) Mi-10 (Harke - according to NATO classification) - a military transport helicopter "flying crane", created on the basis of the Mi-6. His civil modification to perform construction and installation works - Mi-10K.

23) The crew was 5 people. The main objective of the design was the ability to carry cruise and ballistic missiles. Cargo can be transported on the outside of the platform or by means of hydraulic grips.

24) In view of the fact that these helicopters were released in limited edition, would lead them to live even in the museums - a rarity.

25) Mi-18 - one of the experimental versions of the Mi-8. It features a stretched fuselage (technical requirements demand more capacity), removing the side fuel tanks, enhanced rigidity and strength of the fuselage.

26) Since the rate of the Mi-18 was supposed to increase to 270 km / h, was the installation of low-retractable landing gear. The tail rotor moved from right to left, set the screen-exhaust suppression devices IR engines. Number of side doors increased to two.

27) In connection with a number of different factors, the Soviet Air Force refused to finance further rarabotku Mi-18, determined to manage the existing fleet of Mi-8.

28) Two samples of the Mi-18 were as visual aids in the training centers (one right here, Torzhok). Spent on the Mi-18, the new design elements and equipment were subsequently introduced in other production Mi-8.

29) The third car of the Mi-24 at the Museum of PPI-344 and PLC - unique. In 1992, the female crew (pilot - G.Rastorgueva navigator - L.Polyanskaya) on a specially prepared Mi-24B realized flight Torzhok - Miami (USA), dedicated to the 500th anniversary of the discovery of America and the 50th anniversary of the Lend-Lease.

30) After this exciting trip the car was handed over to the museum.

31) Mi-6 (Hook - according to NATO classification) - a heavy military transport helicopter. it was built in 1964 as a series of major military and civil versions.

32) The crew of the helicopter were 5 people. Speed - 300 km / h. Payload - 12 tons.

33) One of the curious modification of the Mi-6 is a variant of the fire Mi-6PZH.

34) It can be seen in the Air Force Museum in Monino.

35) Ka-25 (Hormone - according to NATO classification) - Soviet shipborne ASW helicopter. Is the first domestic helicopter was originally designed for combat use and became the first anti-submarine and the first combat helicopter initially USSR. On this basis, a large number of modifications.

36) The crew is 2 people. The helicopter could carry 12 passengers. Cruising speed - 185 km / h.

Source: