1368
Excursion to the Kursk nuclear
Kursk Nuclear Power Plant is located 40 kilometers west of the city of Kursk, on the banks of the river Seim. 3 km away is the city of Kurchatov. The decision to build the station was made in the mid 60s. Start of construction - 1971. The need for energy facilities was caused by rapidly developing industrial-economic complex of the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly.
Kursk NPP - the Single-station type: the steam supplied to the turbine, is formed directly in the reactor at boiling coolant passing through it. As the coolant used ordinary purified water circulating in a closed circuit. To cool the exhaust steam in the turbine condenser uses water cooling pond. Mirror area of the reservoir - 21, 5 square. km.
33 photos via russos
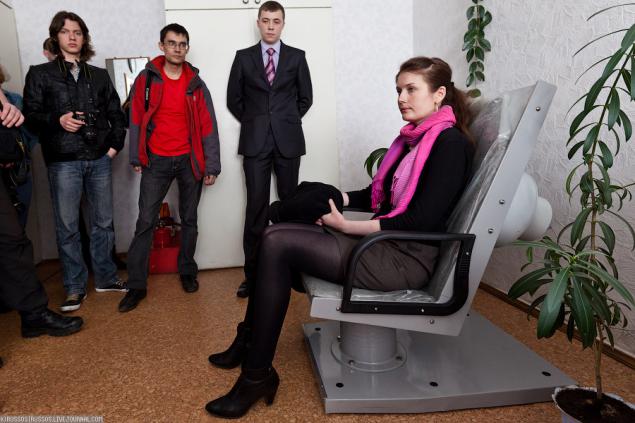
1. Before visiting the station, we have our general measures the background (I'm not sure that the word of background here is correct, but in another way I do not know how to say it). To do this, sit in a chair a couple of minutes. Just do and at the end of the tour.

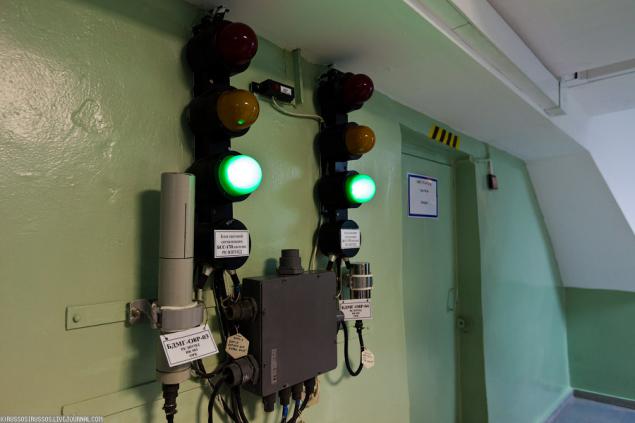
2. In all the rooms are hung station alarm system with a set of sensors. In short, the green means that all is well. Yellow - should tick. Red - in general, to hurry it is not necessary. In fact, this three-level radiation, and each level has its own rules and actions.

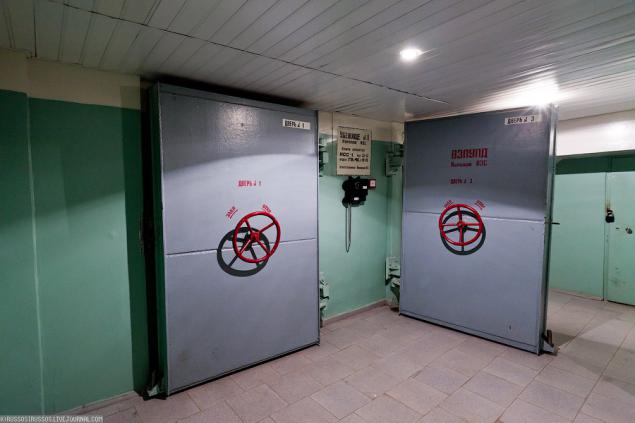
3. The headquarters is located in the shelter of GO № 1.

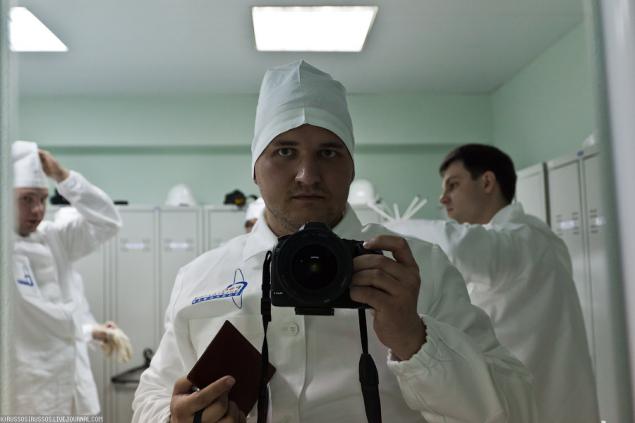
4. E ... onion, sorry, a self-portrait in uniform, which we were given. We are divided, again, sorry to his shorts, leaving with him the most important thing: a passport and a camera.

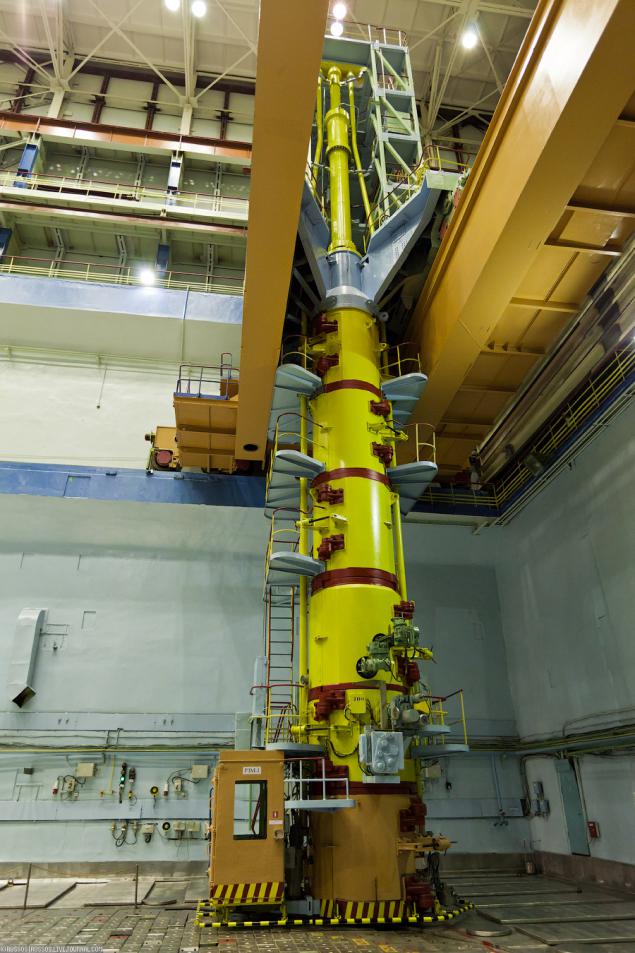
5. RBMK-1000 - high-power channel reactor. Who wants to read about them in more detail, you can do it on Wikipedia or visit Kursk NPP.

6. unloading-loading machine designed for refueling. The process may occur as the reactor is stopped, and the running.

7. Before the Chernobyl accident in the Soviet Union there were extensive plans for RBMK reactors, but after the accident, plans for the construction of the reactors at new sites were stopped. Since 1986, were put into operation two RBMK: RBMK-1000 Smolensk Nuclear Power Plant (1990) and the RBMK-1500 Ignalina NPP (1987) (the station is located in Lithuania and is now fully decommissioned). Another reactor RBMK-1000 5th unit of Kursk NPP is under completion. On the operating reactors was carried out comprehensive reconstruction and modernization, greatly increasing their safety.

8. The central hall is designed to accommodate complex systems, transport and manufacturing equipment and facilities for the assembly and storage of fresh fuel, transhipment and storage of spent fuel, repair and replacement of reactor equipment. In the central hall located equipment and technological systems of the Plateau of the reactor, closed assembly; Storage Pools (BV) of spent fuel and waste fuel channels; Unloading-loading machine (REM); Balcony with a stand hanging fresh fuel; Crane CH and knee-mobile crane; Exercise stand; Node deactivation suspension fuel assemblies (FA), etc.
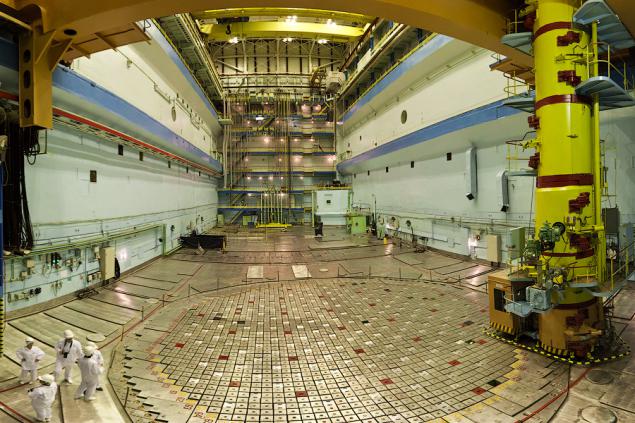

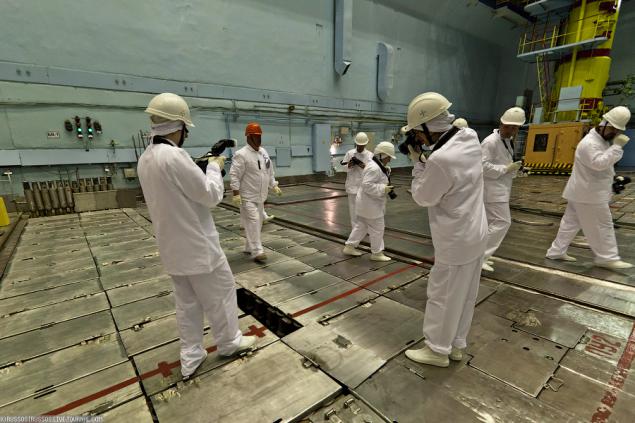
9. Each of the central hall there are two storage pools for spent nuclear fuel. Each BV is filled with water to cool the spent fuel assemblies and biological defense personnel. This is a traditional frame glow fuel rod under water.

10. We all take pictures of a hole in which nearly collapsed Enigma. He stepped on another metal figovinu that covers pool. A cover made somersault and flew in black siniyu depth. Enigma was at the top, a little surprised. Then we quickly left the roof of the storage pool.

11. One of the many control rooms.
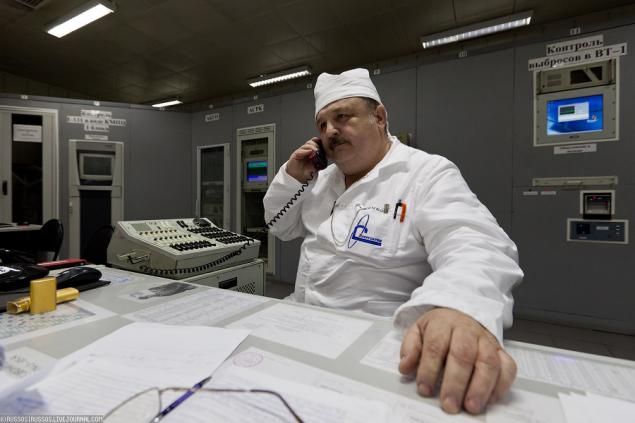

12. dosimeters.

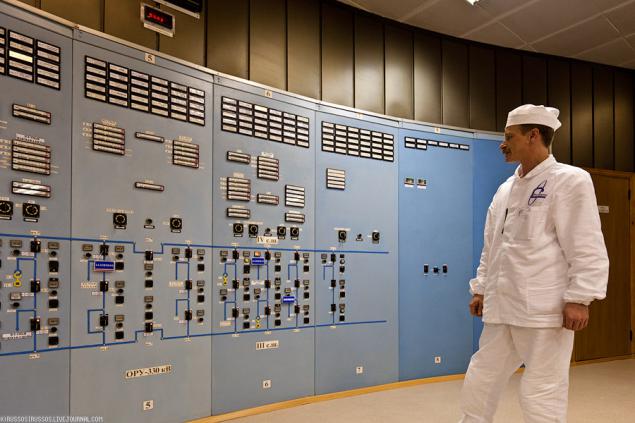
13. Dispatching ORU.

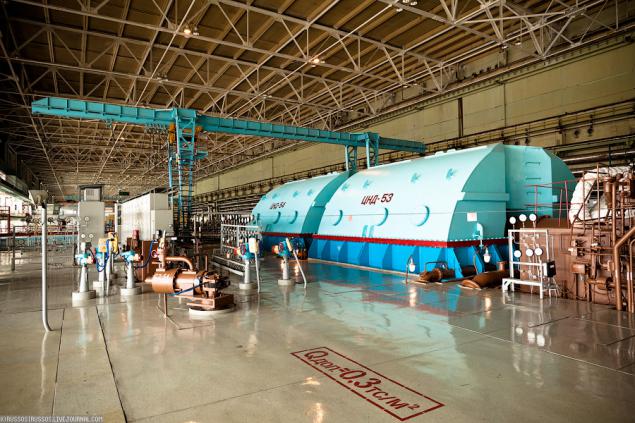
14. I quote: "Each energy unit of Kursk NPP has two turbines K-500-65 / 3000-2 with generators of 500 MW each. The turbines are single-shaft, dual-branch one high pressure cylinder (HPC) and four low-pressure cylinder (LPC). In the CVP and low-pressure cylinder mounted separator-superheater (NGN). Generators three-phase, water and hydrogen-cooled. Turbine generator block are connected to the public power substation. The energy for own needs come from nuclear power auxiliary transformer. "

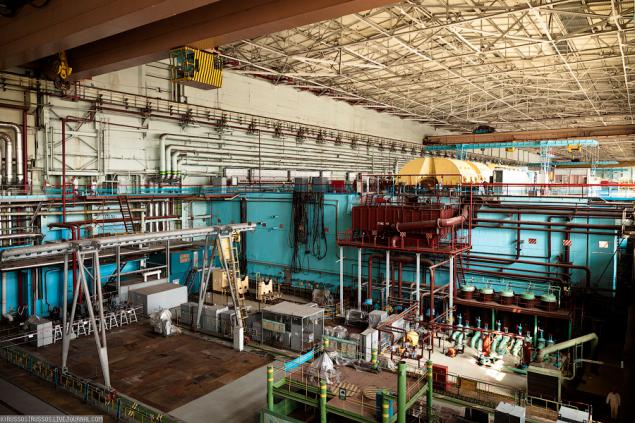
15. The huge machine room, common to all four units.

16.
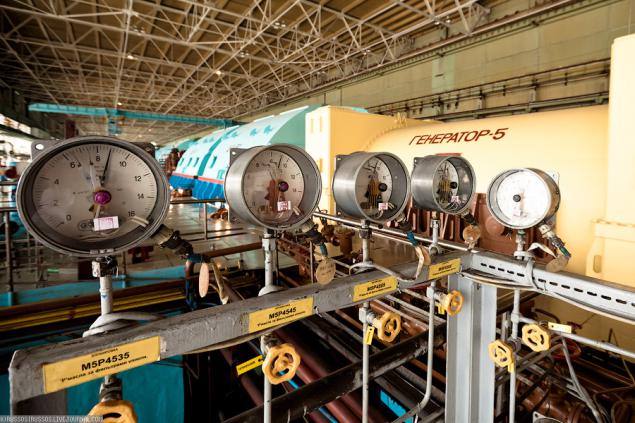

17. Mushroom Glade - electric motor for automatic drive of various valves.
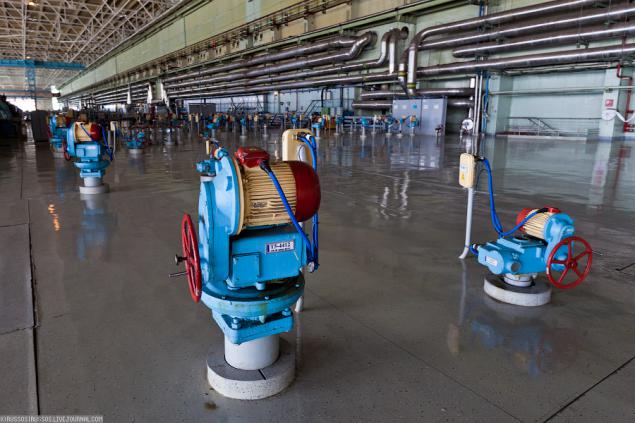

18. To remove it was possible only in the halls and in the rooms. At the time of passage through the corridors we were asked to close the lens cap. If someone she was not, or was dish soap, then he picks up the camera and gave a security guard in the next room, where you can shoot.

19. Block control room.
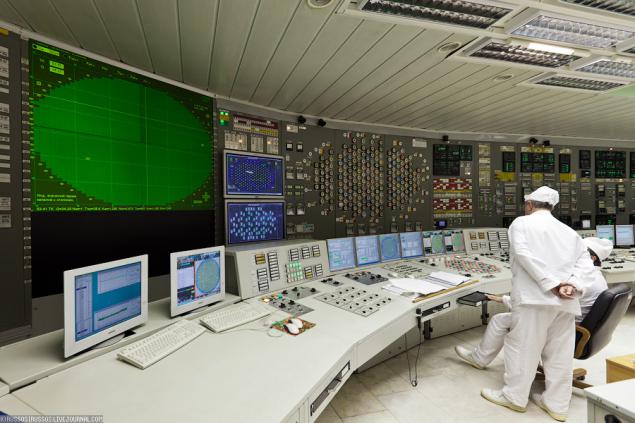

20.
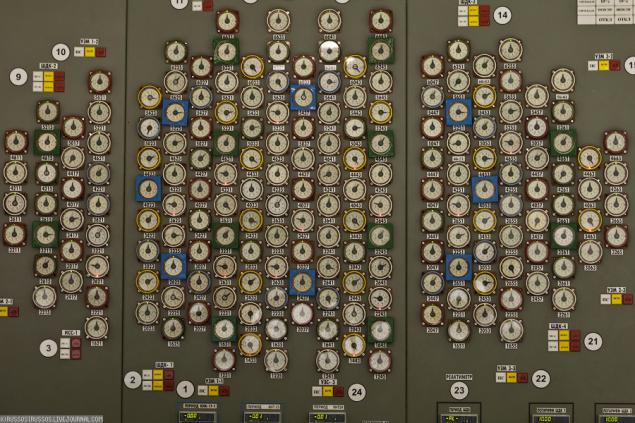

21. Our escort - Vasily Zubov. He can talk for hours about the station. Only manage to ask.
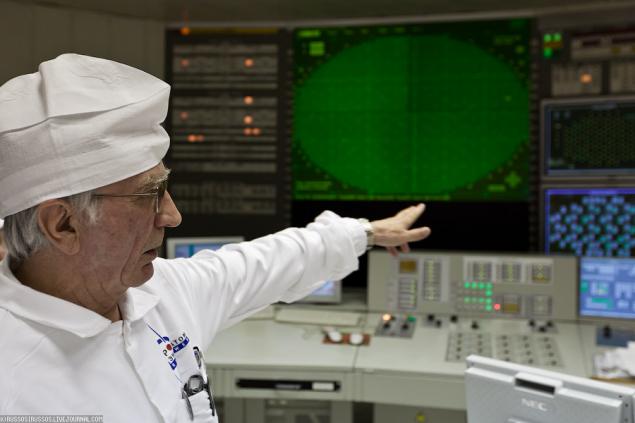

22. Incidentally, the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was built according to the plans of the Kursk. And in the photo - one of the corridors, where there are lockers with individual dosimeters.
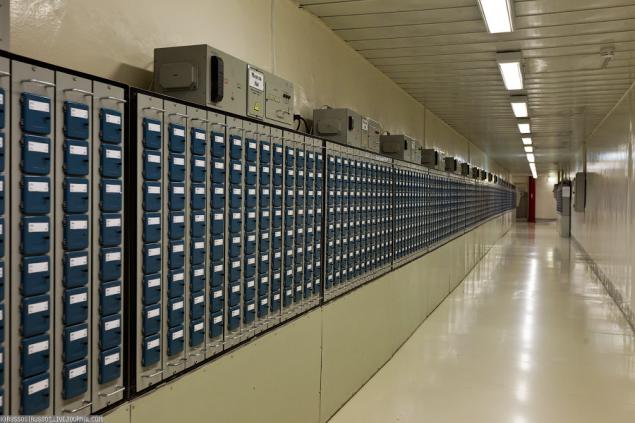

23. Exit. All net - the green signal.

24. spray pond on a background of units. Pool is used to cool the water that circulates in the cooling system of diesel engines. To pool does not grow, it bred fish: catfish, carp and the Japanese carp.

25. The power unit № 5 Kursk NPP - the third generation of a block with the most sophisticated nuclear-physical characteristics, equipped with reliable systems of control and protection. Its construction was started on 1 December 1985, after 90 it continued intermittently in the mid-2000s, was finally stopped, despite the fact that the unit has already had a high degree of readiness - the equipment of the reactor department installed 70%, the basic equipment RBMK - 95% of the turbine shop - 90%. In March 2011 it became known that the introduction of the 5th unit of Kursk NPP may require 3, 5 years and 45 billion rubles excluding VAT in 2009 prices, and that the final decision on the continuation of the construction will be taken in 2012. We also consider the option of using the new VVER-1200 at the 5th power unit that, in fact, require a complete change in the project.
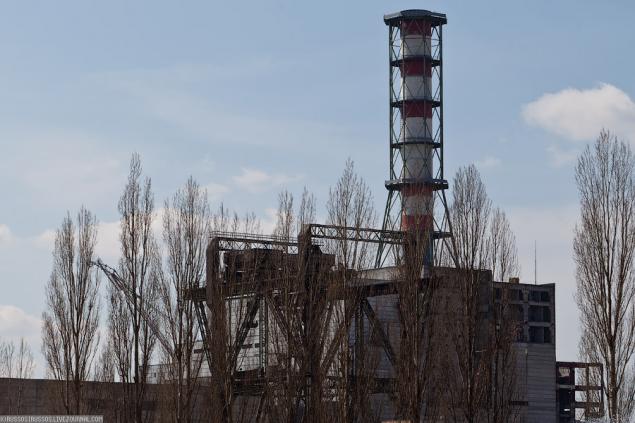

26. One of diesel engines for emergency power supply.

27.

28. Cocoon block TUK-109, designed for storage and transportation of spent nuclear fuel RBMK-1000 reactors.

29. A special device ("cap") for the operation of the overhead crane with the container.
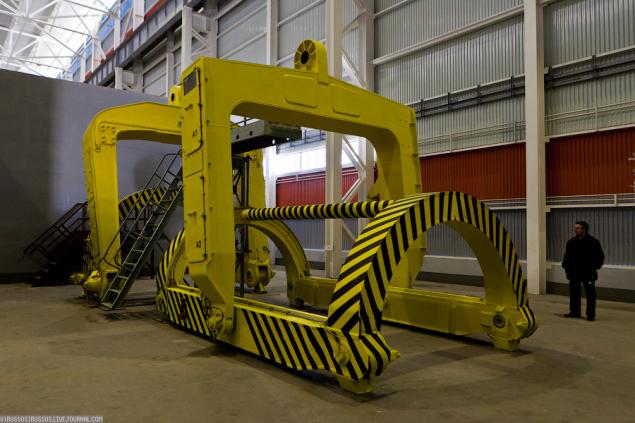

30. Training block control panel.
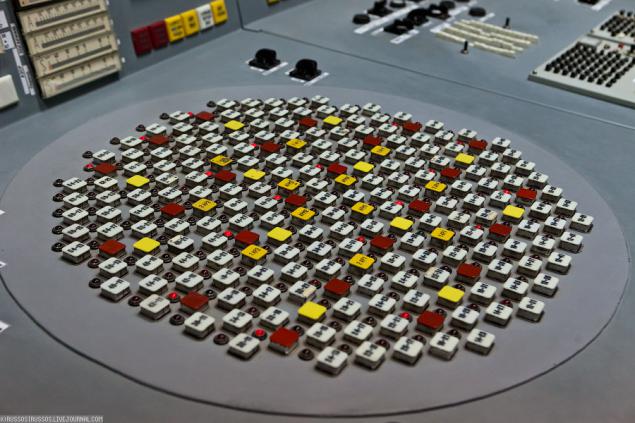

31.
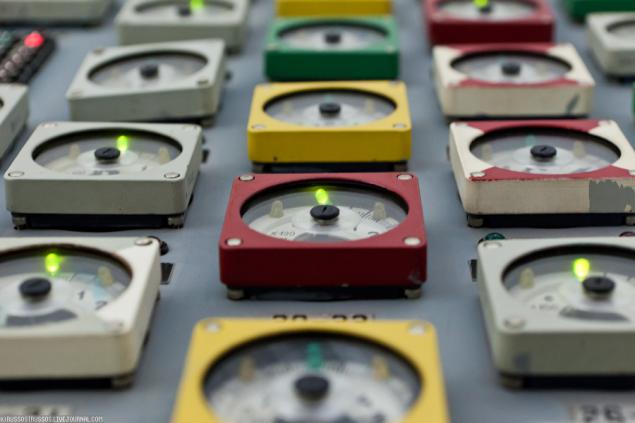

32. A full analogue of a control room at the station.
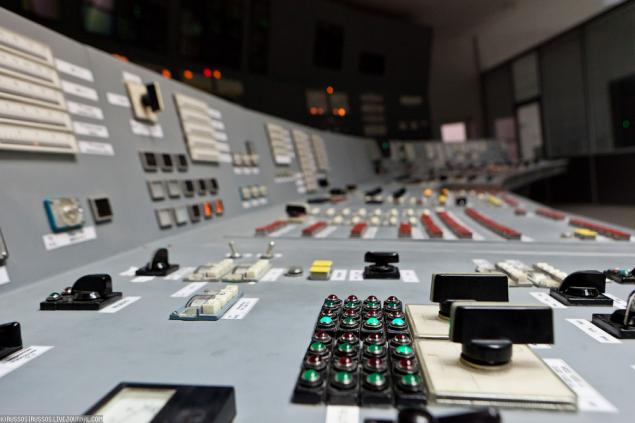

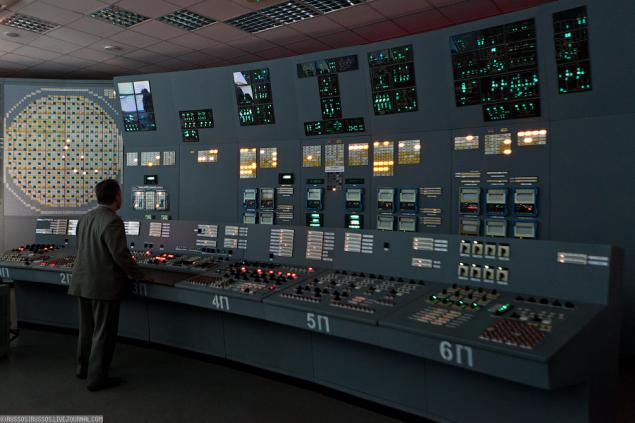
33. Instructors played Fukushima scenario (complete loss of power) and to cope with a drill.

Source:
Kursk NPP - the Single-station type: the steam supplied to the turbine, is formed directly in the reactor at boiling coolant passing through it. As the coolant used ordinary purified water circulating in a closed circuit. To cool the exhaust steam in the turbine condenser uses water cooling pond. Mirror area of the reservoir - 21, 5 square. km.
33 photos via russos
1. Before visiting the station, we have our general measures the background (I'm not sure that the word of background here is correct, but in another way I do not know how to say it). To do this, sit in a chair a couple of minutes. Just do and at the end of the tour.

2. In all the rooms are hung station alarm system with a set of sensors. In short, the green means that all is well. Yellow - should tick. Red - in general, to hurry it is not necessary. In fact, this three-level radiation, and each level has its own rules and actions.

3. The headquarters is located in the shelter of GO № 1.

4. E ... onion, sorry, a self-portrait in uniform, which we were given. We are divided, again, sorry to his shorts, leaving with him the most important thing: a passport and a camera.

5. RBMK-1000 - high-power channel reactor. Who wants to read about them in more detail, you can do it on Wikipedia or visit Kursk NPP.

6. unloading-loading machine designed for refueling. The process may occur as the reactor is stopped, and the running.

7. Before the Chernobyl accident in the Soviet Union there were extensive plans for RBMK reactors, but after the accident, plans for the construction of the reactors at new sites were stopped. Since 1986, were put into operation two RBMK: RBMK-1000 Smolensk Nuclear Power Plant (1990) and the RBMK-1500 Ignalina NPP (1987) (the station is located in Lithuania and is now fully decommissioned). Another reactor RBMK-1000 5th unit of Kursk NPP is under completion. On the operating reactors was carried out comprehensive reconstruction and modernization, greatly increasing their safety.

8. The central hall is designed to accommodate complex systems, transport and manufacturing equipment and facilities for the assembly and storage of fresh fuel, transhipment and storage of spent fuel, repair and replacement of reactor equipment. In the central hall located equipment and technological systems of the Plateau of the reactor, closed assembly; Storage Pools (BV) of spent fuel and waste fuel channels; Unloading-loading machine (REM); Balcony with a stand hanging fresh fuel; Crane CH and knee-mobile crane; Exercise stand; Node deactivation suspension fuel assemblies (FA), etc.

9. Each of the central hall there are two storage pools for spent nuclear fuel. Each BV is filled with water to cool the spent fuel assemblies and biological defense personnel. This is a traditional frame glow fuel rod under water.

10. We all take pictures of a hole in which nearly collapsed Enigma. He stepped on another metal figovinu that covers pool. A cover made somersault and flew in black siniyu depth. Enigma was at the top, a little surprised. Then we quickly left the roof of the storage pool.

11. One of the many control rooms.

12. dosimeters.

13. Dispatching ORU.

14. I quote: "Each energy unit of Kursk NPP has two turbines K-500-65 / 3000-2 with generators of 500 MW each. The turbines are single-shaft, dual-branch one high pressure cylinder (HPC) and four low-pressure cylinder (LPC). In the CVP and low-pressure cylinder mounted separator-superheater (NGN). Generators three-phase, water and hydrogen-cooled. Turbine generator block are connected to the public power substation. The energy for own needs come from nuclear power auxiliary transformer. "

15. The huge machine room, common to all four units.

16.

17. Mushroom Glade - electric motor for automatic drive of various valves.

18. To remove it was possible only in the halls and in the rooms. At the time of passage through the corridors we were asked to close the lens cap. If someone she was not, or was dish soap, then he picks up the camera and gave a security guard in the next room, where you can shoot.

19. Block control room.

20.

21. Our escort - Vasily Zubov. He can talk for hours about the station. Only manage to ask.

22. Incidentally, the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was built according to the plans of the Kursk. And in the photo - one of the corridors, where there are lockers with individual dosimeters.

23. Exit. All net - the green signal.

24. spray pond on a background of units. Pool is used to cool the water that circulates in the cooling system of diesel engines. To pool does not grow, it bred fish: catfish, carp and the Japanese carp.

25. The power unit № 5 Kursk NPP - the third generation of a block with the most sophisticated nuclear-physical characteristics, equipped with reliable systems of control and protection. Its construction was started on 1 December 1985, after 90 it continued intermittently in the mid-2000s, was finally stopped, despite the fact that the unit has already had a high degree of readiness - the equipment of the reactor department installed 70%, the basic equipment RBMK - 95% of the turbine shop - 90%. In March 2011 it became known that the introduction of the 5th unit of Kursk NPP may require 3, 5 years and 45 billion rubles excluding VAT in 2009 prices, and that the final decision on the continuation of the construction will be taken in 2012. We also consider the option of using the new VVER-1200 at the 5th power unit that, in fact, require a complete change in the project.

26. One of diesel engines for emergency power supply.

27.

28. Cocoon block TUK-109, designed for storage and transportation of spent nuclear fuel RBMK-1000 reactors.

29. A special device ("cap") for the operation of the overhead crane with the container.

30. Training block control panel.

31.

32. A full analogue of a control room at the station.

33. Instructors played Fukushima scenario (complete loss of power) and to cope with a drill.

Source: