963
Punk in Russia 80-90 years
Punk punks (Eng. Punk) - a youth subculture that emerged in the mid-70s in the UK, USA, Canada and Australia, the characteristic feature of which is the love of music punk rock, a critical attitude to society and politics. Punk itself is composed of many smaller subcultures, such as a street punk, horror punk, oi-punk, heavy punk and others. Punk maintains a close relationship with other subcultures such as gothic and psihobiliti; supporters of the movement opposed to the commercialization, which is one of the basic mechanisms of capitalism.

Initially, it had negative connotations. The Concise Oxford English Dictionary "punk" means:
- Ustari. moll (1596);
- Amer. rotten wood or wood mold is used in dry form for kindling the fires; tinder, punk (1707).

The Anglo-Russian dictionary Mueller VK (Wiley, 2000), the word & quot; punk & quot; Russian values are as follows:
- A worthless person;
- Smth. unnecessary, useless, nonsense;
-amer. Punk, "bastard" punks;
-amer. fledgeling, simp

In the middle of the XX century the word "Punk" was an American slang term for certain youth groups at the social bottom, like a tramp (hoboes) and black prisoners-homosexuals.

As for the music, the term was first applied to the so-called "garage rock" (1964-1967) - Musical youth movements in the United States. The word "punk" in the sense of 'rot' was used as a metaphor in relation to the American group, which affected in their songs taboo topics and behaved most obscene, singing about sexual perversion, growing drug use, social exclusion, violence society, full of hopelessness and disappointment in the future among the young.

Background of punk
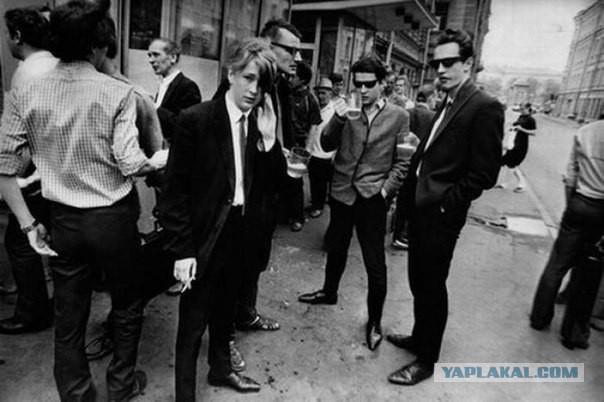

In the mid-1970s in the United States did not have the conditions that provoked the counterculture of the 1960s ("New Left", hippies, beatniks, et al.). In the UK the 1970s - a time of the biggest youth unemployment, this was just before the war. World energy crisis that resulted in economic difficulties, further worsened the already distant from the welfare situation of young people of Great Britain. This has contributed to heighten the atmosphere of social despair and spiritual hopelessness, which led, in turn, spread among young people moods of despair and hopelessness, which could not find expression in the pacifist, non-aggressive hippie subculture. It is this point, according to Ted Polimusa became rallying for the punk subculture, despite its social diversity: "Punks were not (as commonly believed) completely slum dwellers from the working class. Some were, but most - children from the middle class, as well as teenagers affluent suburban areas. They are all united by hatred of hippies, "" sluggish, lazy and boring »

Another important prerequisite for the emergence of punk rock was a change of status, which by the mid-1970s from the music of child rebels turned into a "music for the parents." In other words, the rock for the most part lost its countercultural quality and became a product of mass culture. Rock brought huge profits to producers, performers, music corporations. Success and wealth isolated rock Rupp from a simple youth. Now it was inaccessible idol "entertainers" who came to the concerts in luxury limousines under police protection. Punks sharply broke with this tradition. Punk countered commercial music in two ways: first, it boycotted the major record corporations, secondly, changed the process of creating music, proclaiming "this can do everyone!" "Professionalism was considered the commercial trappings of rock
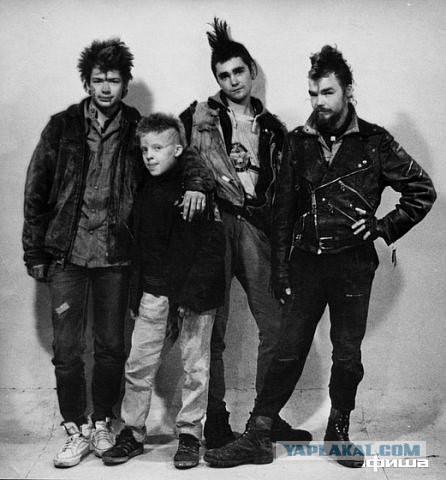
Now the most important thing. Punk in the Soviet Union.

Punk was one of the few musical trends, which came to the Soviet Union with the minimum delay. In 1976, punk rock emerged in England, and in 1977 in Leningrad, Moscow, Siberia, young people interested in Western music purchased from black marketeers plate »Sex Pistols & quot ;, & quot; Clash & quot; and other British punk bands, music programs caught by the "Voice of America", the Air Force Seva Novgorodtsev, read Soviet newspapers and magazines, which have been quick to respond to the emergence of a new youth movements as a "build-up on the rotting body of bourgeois culture."

If rock music in the Soviet Union was in the underground, punk was the ": underground underground & quot; He was already a counterculture because of its prohibition and opposed the system, bringing new values, not revolt and protest like the English punk.

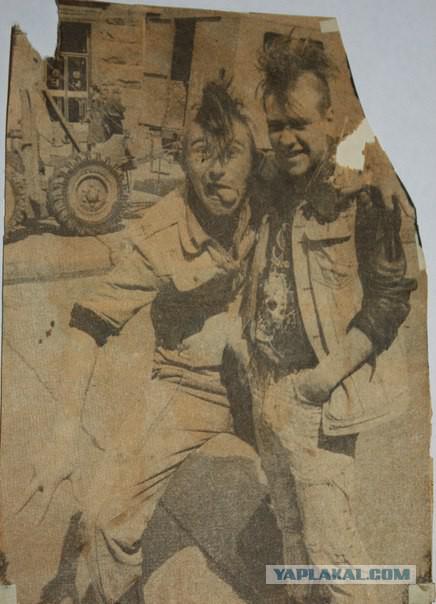
Soviet punk culture of the 1980s, initially focusing on the West for organically rethink its intertwined with national roots. The result is a completely original phenomenon, generated primarily not imitation, and a desire to express themselves and somehow oppose each other, are not so much for the music as social and intellectual. In the Soviet Union was the punk counterculture because of their forbidden, so he resisted the system, even if in a punk songs did not have direct political implications.
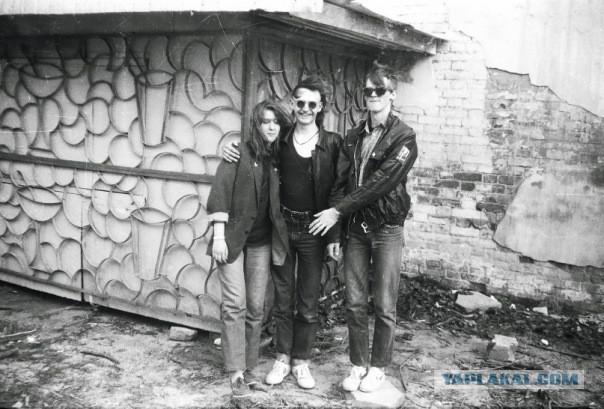

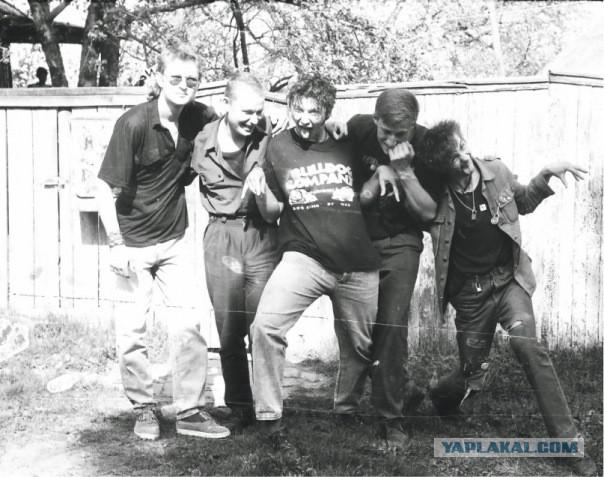
Since the mid-1990s, the Russian punk scene begins to focus on the relevant Western ideals namely: & quot; Green Day & quot; and other Californian pop punk band. (In the face of such groups, such as the Moscow "Cockroaches!" And St. Petersburg "The King and the Clown").

,,,
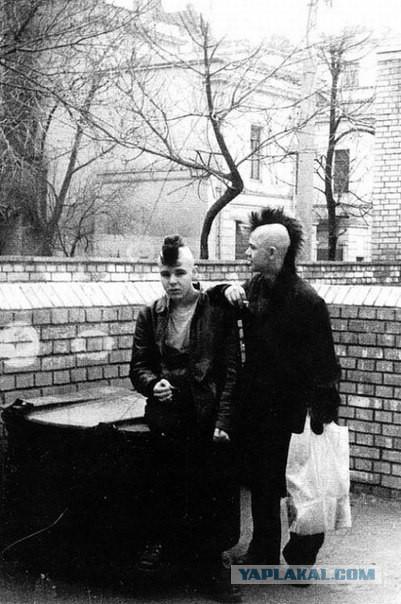

A couple of clippings,, zhurnashlyuh the time

,,,

,,,

,,,
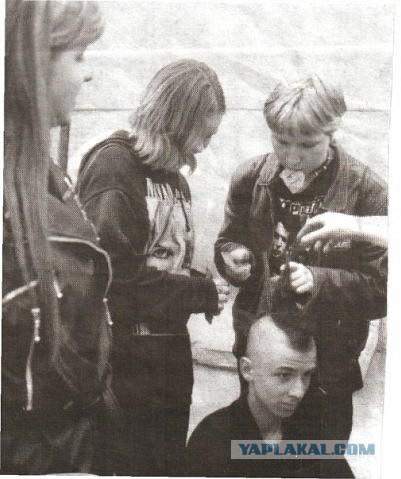

16 more and all.

...
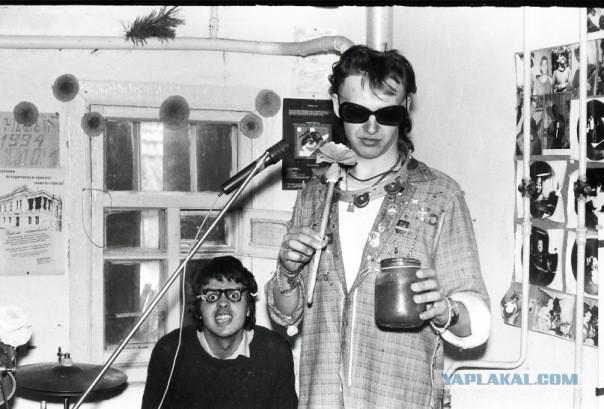

...

...
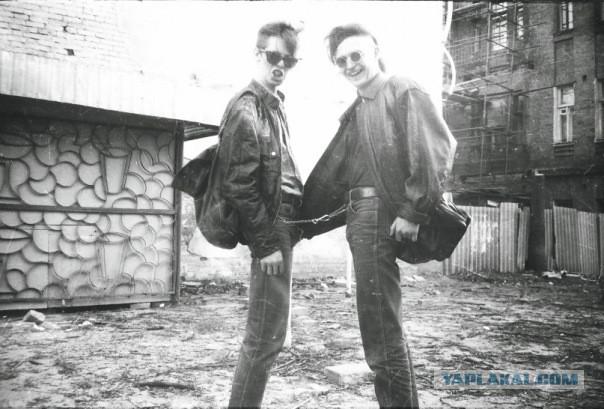

...

...
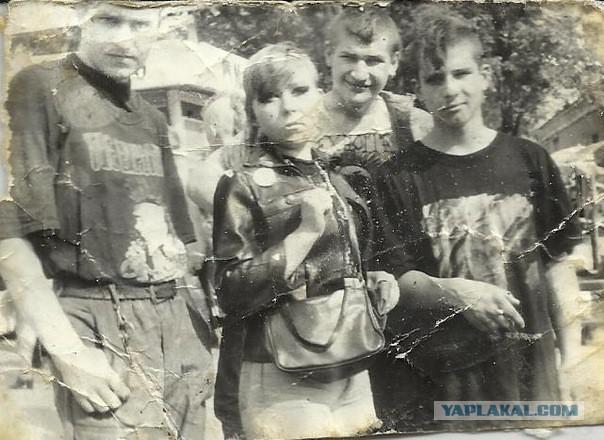

...

Another 3-4)
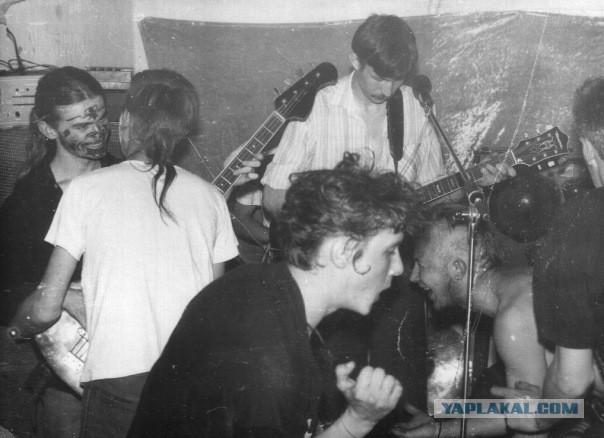

,,,
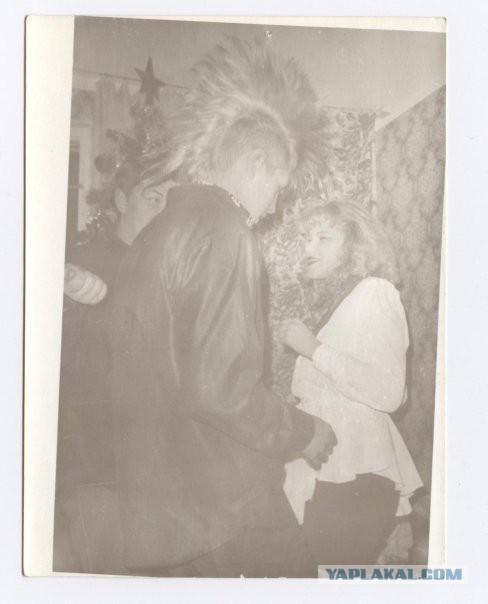

,,,

All

Source:

Initially, it had negative connotations. The Concise Oxford English Dictionary "punk" means:
- Ustari. moll (1596);
- Amer. rotten wood or wood mold is used in dry form for kindling the fires; tinder, punk (1707).

The Anglo-Russian dictionary Mueller VK (Wiley, 2000), the word & quot; punk & quot; Russian values are as follows:
- A worthless person;
- Smth. unnecessary, useless, nonsense;
-amer. Punk, "bastard" punks;
-amer. fledgeling, simp

In the middle of the XX century the word "Punk" was an American slang term for certain youth groups at the social bottom, like a tramp (hoboes) and black prisoners-homosexuals.

As for the music, the term was first applied to the so-called "garage rock" (1964-1967) - Musical youth movements in the United States. The word "punk" in the sense of 'rot' was used as a metaphor in relation to the American group, which affected in their songs taboo topics and behaved most obscene, singing about sexual perversion, growing drug use, social exclusion, violence society, full of hopelessness and disappointment in the future among the young.

Background of punk

In the mid-1970s in the United States did not have the conditions that provoked the counterculture of the 1960s ("New Left", hippies, beatniks, et al.). In the UK the 1970s - a time of the biggest youth unemployment, this was just before the war. World energy crisis that resulted in economic difficulties, further worsened the already distant from the welfare situation of young people of Great Britain. This has contributed to heighten the atmosphere of social despair and spiritual hopelessness, which led, in turn, spread among young people moods of despair and hopelessness, which could not find expression in the pacifist, non-aggressive hippie subculture. It is this point, according to Ted Polimusa became rallying for the punk subculture, despite its social diversity: "Punks were not (as commonly believed) completely slum dwellers from the working class. Some were, but most - children from the middle class, as well as teenagers affluent suburban areas. They are all united by hatred of hippies, "" sluggish, lazy and boring »

Another important prerequisite for the emergence of punk rock was a change of status, which by the mid-1970s from the music of child rebels turned into a "music for the parents." In other words, the rock for the most part lost its countercultural quality and became a product of mass culture. Rock brought huge profits to producers, performers, music corporations. Success and wealth isolated rock Rupp from a simple youth. Now it was inaccessible idol "entertainers" who came to the concerts in luxury limousines under police protection. Punks sharply broke with this tradition. Punk countered commercial music in two ways: first, it boycotted the major record corporations, secondly, changed the process of creating music, proclaiming "this can do everyone!" "Professionalism was considered the commercial trappings of rock

Now the most important thing. Punk in the Soviet Union.

Punk was one of the few musical trends, which came to the Soviet Union with the minimum delay. In 1976, punk rock emerged in England, and in 1977 in Leningrad, Moscow, Siberia, young people interested in Western music purchased from black marketeers plate »Sex Pistols & quot ;, & quot; Clash & quot; and other British punk bands, music programs caught by the "Voice of America", the Air Force Seva Novgorodtsev, read Soviet newspapers and magazines, which have been quick to respond to the emergence of a new youth movements as a "build-up on the rotting body of bourgeois culture."

If rock music in the Soviet Union was in the underground, punk was the ": underground underground & quot; He was already a counterculture because of its prohibition and opposed the system, bringing new values, not revolt and protest like the English punk.

Soviet punk culture of the 1980s, initially focusing on the West for organically rethink its intertwined with national roots. The result is a completely original phenomenon, generated primarily not imitation, and a desire to express themselves and somehow oppose each other, are not so much for the music as social and intellectual. In the Soviet Union was the punk counterculture because of their forbidden, so he resisted the system, even if in a punk songs did not have direct political implications.

Since the mid-1990s, the Russian punk scene begins to focus on the relevant Western ideals namely: & quot; Green Day & quot; and other Californian pop punk band. (In the face of such groups, such as the Moscow "Cockroaches!" And St. Petersburg "The King and the Clown").

,,,

A couple of clippings,, zhurnashlyuh the time

,,,

,,,

,,,

16 more and all.

...

...

...

...

...

...

Another 3-4)

,,,

,,,

All

Source: