1127
Pre-revolutionary Vladivostok (27 photos)
Excellent retro pictures.
Peter the Great Bay, which is located on the coast of Vladivostok, became known in Europe only in 1852 thanks to the members of the crew of the French whaling ship accidentally committed wintering in the Bay of poset. According to some reports, the same whalers in 1851 and attended the Golden Horn.
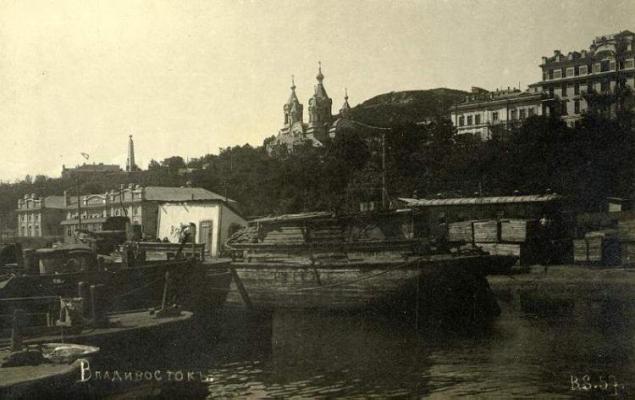

In 1856, the British ship "Winchester" from the Anglo-French squadron, look for the Russian squadron during the Crimean War, visited the Golden Horn. The British called it Port Mae.
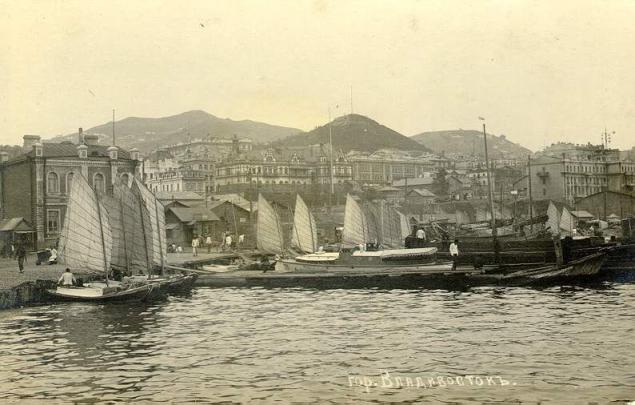


In 1859, Governor-General of Eastern Siberia Nikolai Muravyov-Amur, bypassing the ship shore Peter the Great Bay, drew attention to the well-sheltered bay. It resembled the Golden Horn in Constantinople, and the Governor-General proposed to call it the same way, and on the shores of the bay ordered to establish a military post which he is a named Vladivostok.

Another option. The bay stretches from west to east. If you look at the bay at sunrise or sunset, the bay is clearly visible reflection of the sun in the form of horns. Golden Horn.
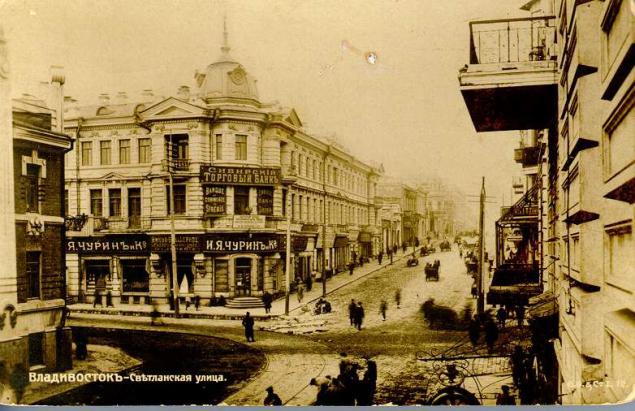


June 20 (July 2, New Style), 1860 military transport "Manchuria", under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Alexei Karlovich Shefner founded a military post, which is now officially received the name of Vladivostok.

In the logbook "Manchu" of the event was the following inscription: "this number is sent to the bank - one chief officer, two non-commissioned officer and 37 privates 4th Line Battalion for the position."
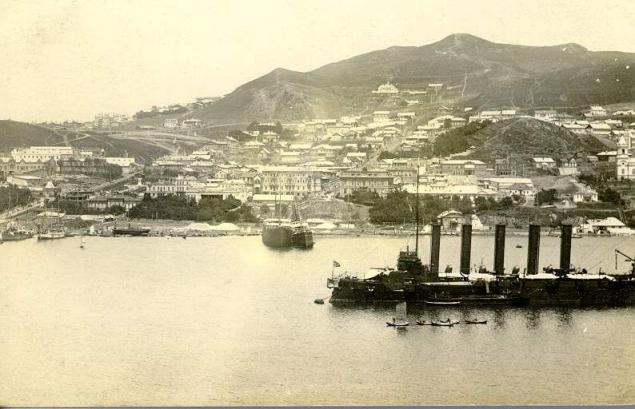

Soldiers and sailors under the command of Ensign Komarova have started construction of the post. This day is officially the day of foundation of the city.

One month after the first landing in the Golden Horn came screw corvette "Griden" under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Hans Egersheld. Corvette has been tasked to guard the post of Vladivostok and to provide garrison necessary supplies.
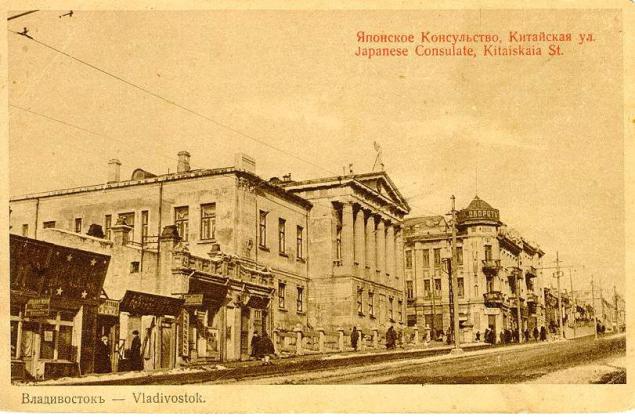

In 1862 a military post was renamed the port, and to increase the volume of foreign trade it was given the status of a free port (free port).

The first child was born in Vladivostok in May 1863. (Hope Podorozhkina)
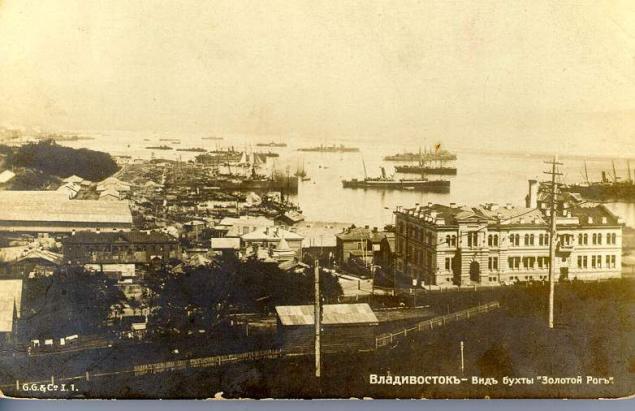

In 1871 Vladivostok has been translated (from Nikolaevsk-on-Amur) the main base of the Siberian Flotilla, the residence of the military governor and other marine facilities. In the same year the underwater telegraph cable connected Vladivostok to Shanghai and Nagasaki.
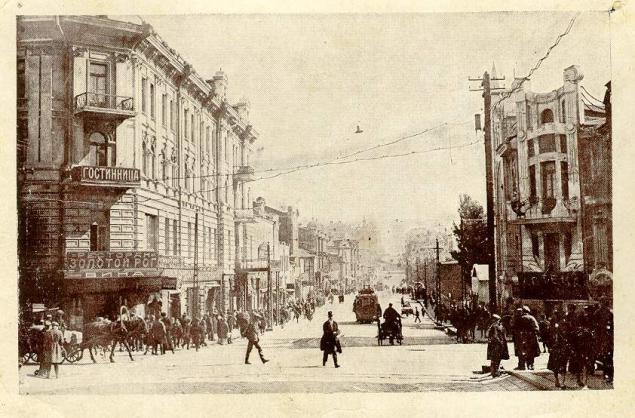
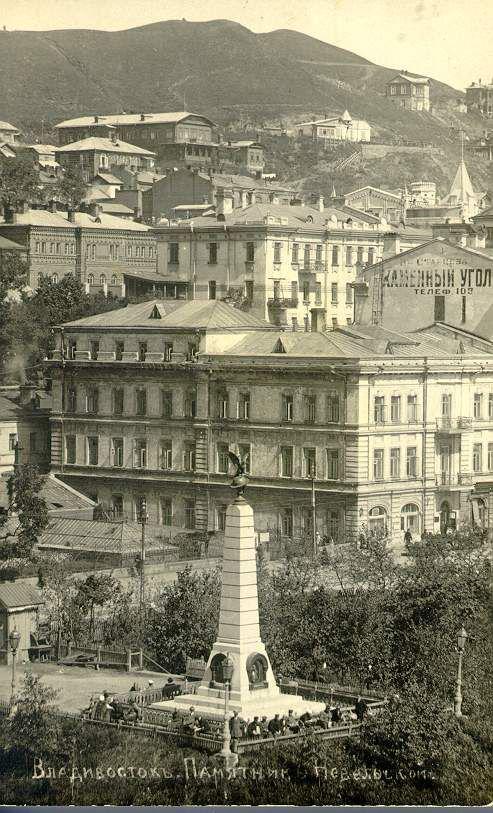


Permanent steamship line connected Vladivostok to St. Petersburg and Odessa in 1879.
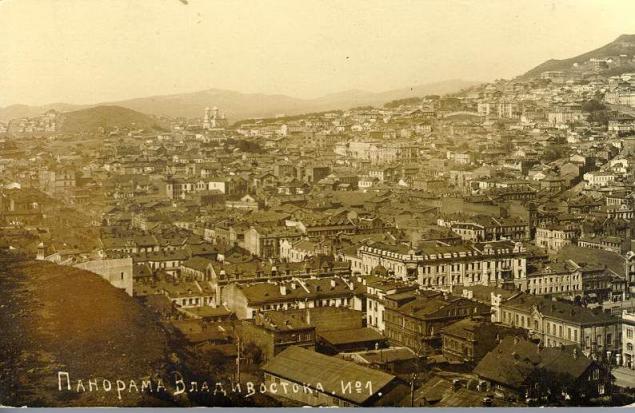
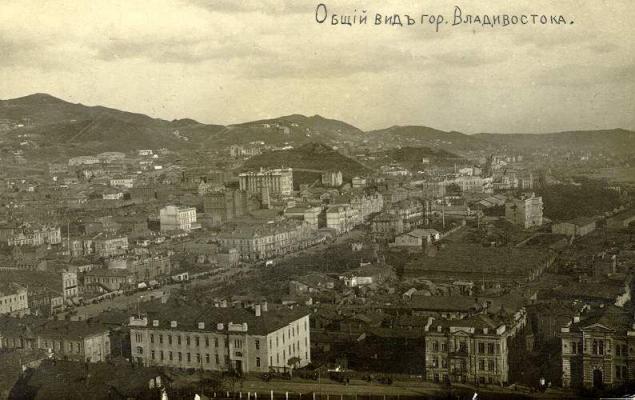


In 1880 Vladivostok (Amur Peninsula ants and Russian island) was identified as a "military governor" and was granted city status.
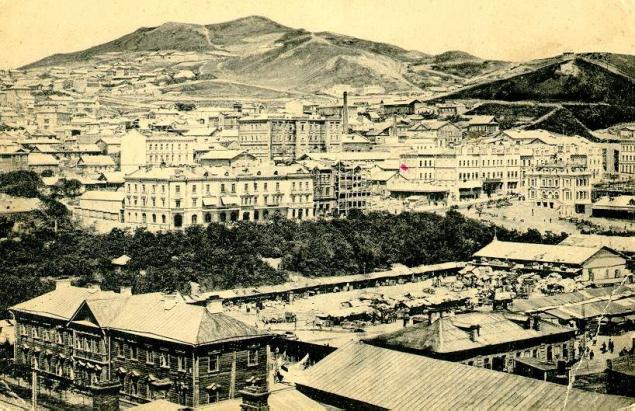

March 16, 1883 Alexander III approved the first coat of arms of the city.
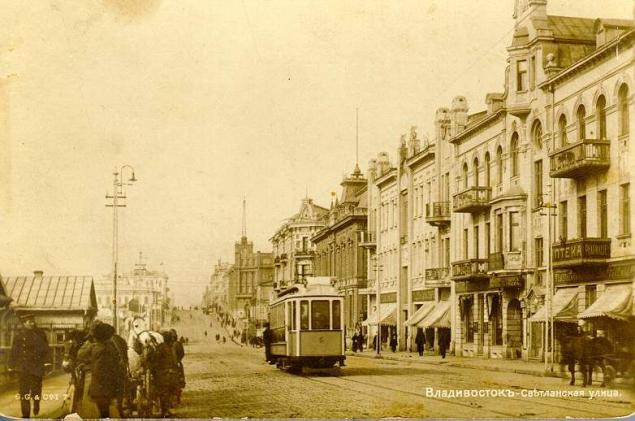


In July 1886 the city was visited group of warships of the Chinese Beiyang Fleet - it was the first visit of the Chinese naval forces in Russia.
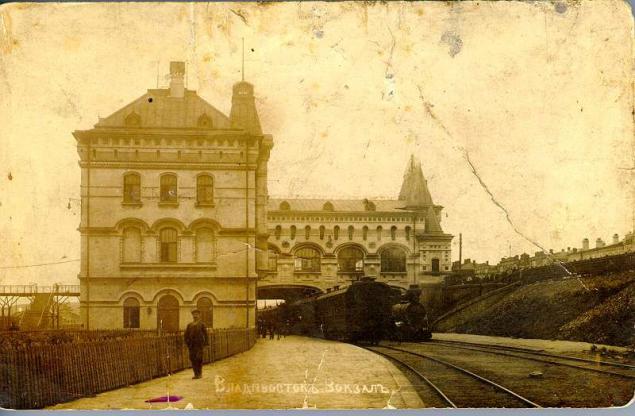

In 1888, Vladivostok became the center of the Maritime region.

In May 1891, visited Vladivostok Tsarevich Nicholas, the future Emperor Nicholas II. He was returning from a trip to Eastern countries, and the first Russian city on his return became Vladivostok. During his visit, the crown prince laid the railway station with a stone, a dry dock for repairs of ships and a monument to Admiral Nevelsky.

In 1893 opened railway traffic between Vladivostok and Nikolsky (Ussuriisk), in 1897 the railway was built Khabarovsk - Vladivostok, and in 1903 opened a direct rail link with Moscow on the Trans-Siberian Railway.

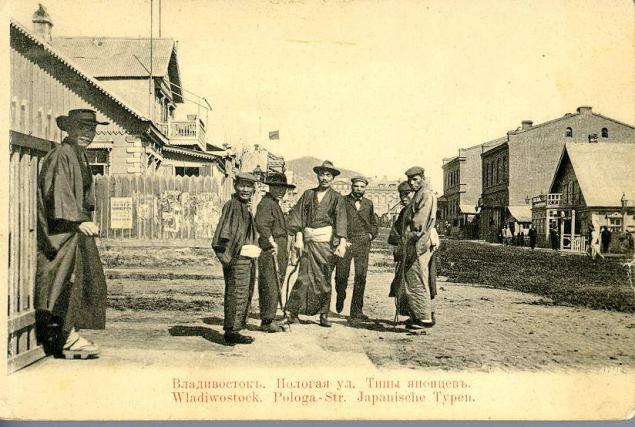
In the 1890s. Vladivostok gradually transformed into a place of concentration of Russian culture in the Far East. Vladivostok was organizing center of expeditions of Russian travelers and scientists NM Przewalski, Makarov, VK Arsenyev, VL Komarov (later president of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR) and others. In 1899 he opened in Vladivostok East Institute.

After the establishment of Soviet power in 1917 in the city repeatedly changed the government, military landings of Japanese, British, French and American invaders.
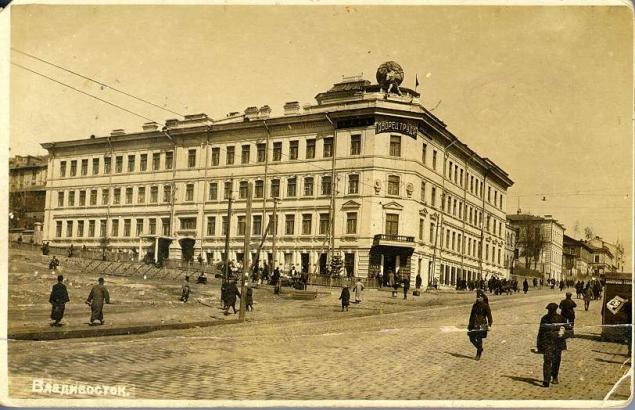

In 1920-1921 Vladivostok - as part of the Far Eastern Republic. In 1921-1922 - the capital of the independent Republic of the Amur region.
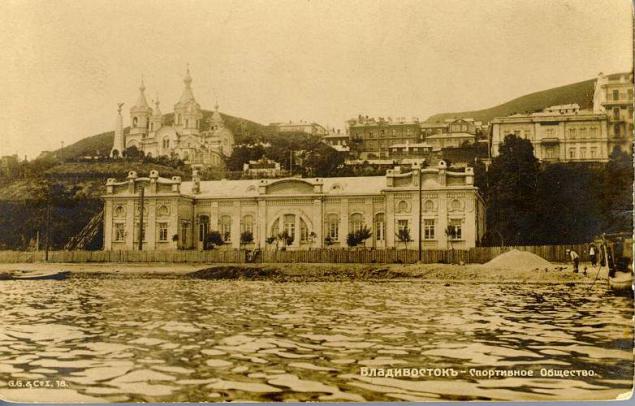

Since 1938 - the center of Primorsky Krai.

Peter the Great Bay, which is located on the coast of Vladivostok, became known in Europe only in 1852 thanks to the members of the crew of the French whaling ship accidentally committed wintering in the Bay of poset. According to some reports, the same whalers in 1851 and attended the Golden Horn.

In 1856, the British ship "Winchester" from the Anglo-French squadron, look for the Russian squadron during the Crimean War, visited the Golden Horn. The British called it Port Mae.


In 1859, Governor-General of Eastern Siberia Nikolai Muravyov-Amur, bypassing the ship shore Peter the Great Bay, drew attention to the well-sheltered bay. It resembled the Golden Horn in Constantinople, and the Governor-General proposed to call it the same way, and on the shores of the bay ordered to establish a military post which he is a named Vladivostok.

Another option. The bay stretches from west to east. If you look at the bay at sunrise or sunset, the bay is clearly visible reflection of the sun in the form of horns. Golden Horn.


June 20 (July 2, New Style), 1860 military transport "Manchuria", under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Alexei Karlovich Shefner founded a military post, which is now officially received the name of Vladivostok.

In the logbook "Manchu" of the event was the following inscription: "this number is sent to the bank - one chief officer, two non-commissioned officer and 37 privates 4th Line Battalion for the position."

Soldiers and sailors under the command of Ensign Komarova have started construction of the post. This day is officially the day of foundation of the city.

One month after the first landing in the Golden Horn came screw corvette "Griden" under the command of Lieutenant-Commander Hans Egersheld. Corvette has been tasked to guard the post of Vladivostok and to provide garrison necessary supplies.

In 1862 a military post was renamed the port, and to increase the volume of foreign trade it was given the status of a free port (free port).

The first child was born in Vladivostok in May 1863. (Hope Podorozhkina)

In 1871 Vladivostok has been translated (from Nikolaevsk-on-Amur) the main base of the Siberian Flotilla, the residence of the military governor and other marine facilities. In the same year the underwater telegraph cable connected Vladivostok to Shanghai and Nagasaki.


Permanent steamship line connected Vladivostok to St. Petersburg and Odessa in 1879.


In 1880 Vladivostok (Amur Peninsula ants and Russian island) was identified as a "military governor" and was granted city status.

March 16, 1883 Alexander III approved the first coat of arms of the city.


In July 1886 the city was visited group of warships of the Chinese Beiyang Fleet - it was the first visit of the Chinese naval forces in Russia.

In 1888, Vladivostok became the center of the Maritime region.

In May 1891, visited Vladivostok Tsarevich Nicholas, the future Emperor Nicholas II. He was returning from a trip to Eastern countries, and the first Russian city on his return became Vladivostok. During his visit, the crown prince laid the railway station with a stone, a dry dock for repairs of ships and a monument to Admiral Nevelsky.

In 1893 opened railway traffic between Vladivostok and Nikolsky (Ussuriisk), in 1897 the railway was built Khabarovsk - Vladivostok, and in 1903 opened a direct rail link with Moscow on the Trans-Siberian Railway.

In the 1890s. Vladivostok gradually transformed into a place of concentration of Russian culture in the Far East. Vladivostok was organizing center of expeditions of Russian travelers and scientists NM Przewalski, Makarov, VK Arsenyev, VL Komarov (later president of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR) and others. In 1899 he opened in Vladivostok East Institute.

After the establishment of Soviet power in 1917 in the city repeatedly changed the government, military landings of Japanese, British, French and American invaders.

In 1920-1921 Vladivostok - as part of the Far Eastern Republic. In 1921-1922 - the capital of the independent Republic of the Amur region.

Since 1938 - the center of Primorsky Krai.