763
The skills of the peoples of the world (17 photos)
For thousands of years, that tribal peoples held in close communion with nature, taught them surprisingly accurately read her slightest signs: to feel climate change, well oriented in the forest and the sea, to predict the displacement of ice blocks, to find food and water.
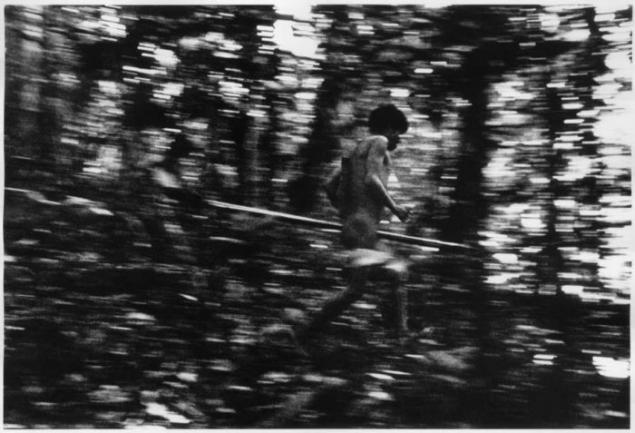

I - some of these places - says Davi Yanomami. I was born in the forest and know him well.
During drought people dzharava uses as a source of moisture rattan palm juice. When they need to collect wild honey, they sprinkle the juice of this plant is a hive of bees and fly away.
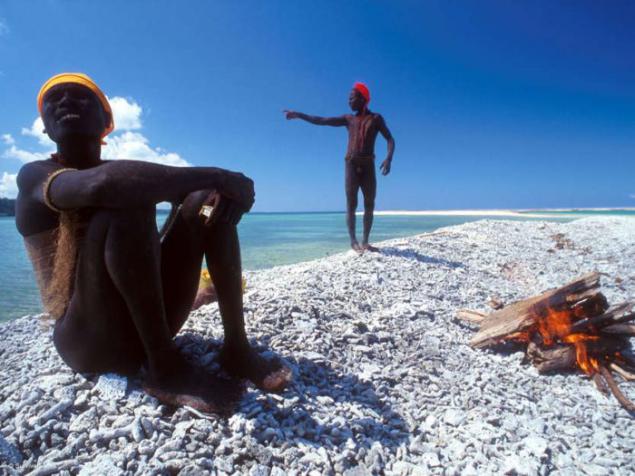

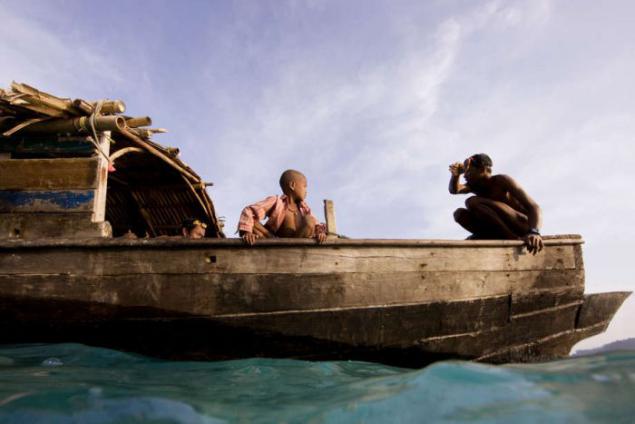
"Sea Gypsies" of the Moken people that live on the shores of the Andaman Sea, have developed an amazing ability to see well under water, so that can find food on the sea floor. Seeing these people more acute than the Europeans by about 50 percent.
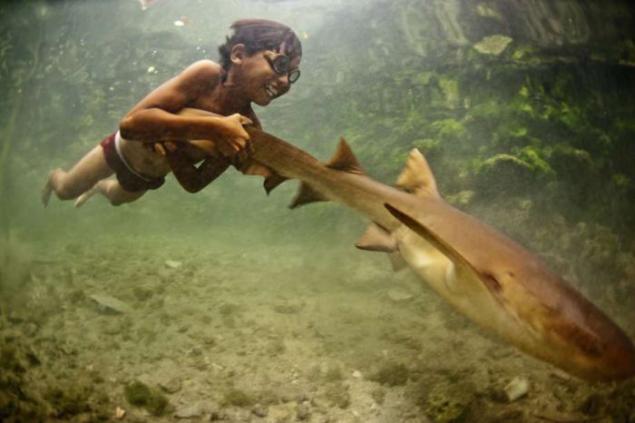

History of the Moken is transmitted orally from one generation to another. These tales are full of deep knowledge of the sea, the winds and lunar cycles.
In one legend, for example, refers to the sinister la bun - "wave that eats people." Before coming la bun, the sea starts to back away in fear.
When the front of the devastating 2004 tsunami, the water receded, the elders of the village in Thailand Moken recognized the evil omen and took their fellow with tourists is close to a nearby hill.

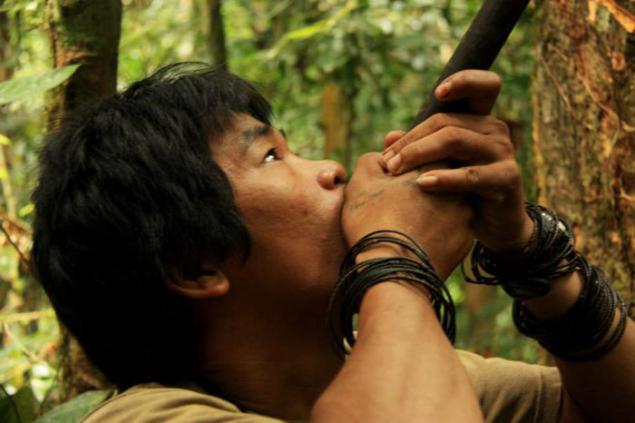
In the tropical forests of Borneo tribe lives foam. These people hunted wild boar using brass tubes hardwood from which they blow darts soaked poisonous sap of a local tree.
From this poison paralyzes the animal, we can only take it home. Sami blowguns are longer than two meters.

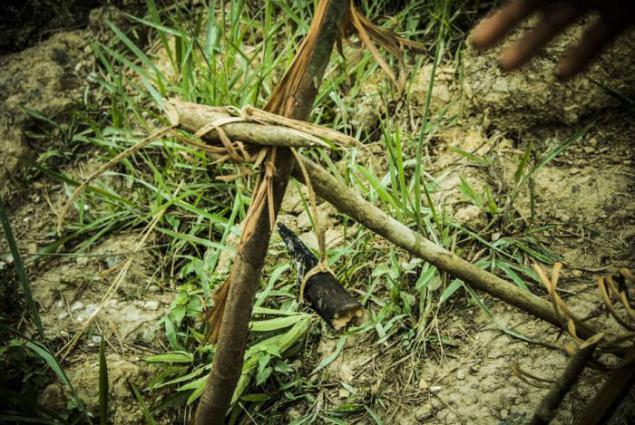
Until the 1960s, people Pena led a nomadic life, communicating in the woods on the way a light signal system, which includes symbols of sticks and leaves, called yell. With yell could tell, for example, that the past is a person is sick or hungry.

In the 1970s, on the ground that the people served many generations of foam came white men - have cut down the forest, planted oil palm plantations, and had a gas pipeline built hydroelectric dams.
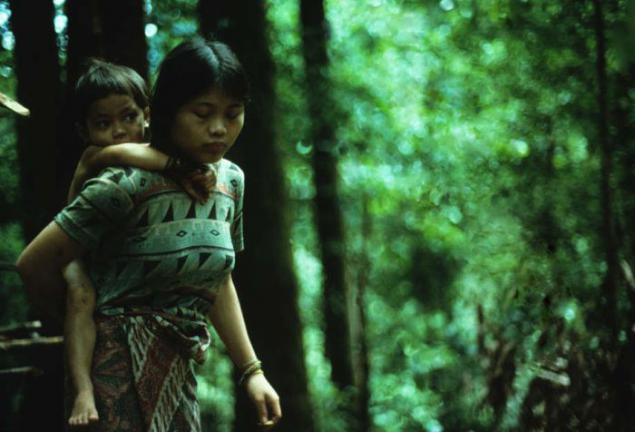

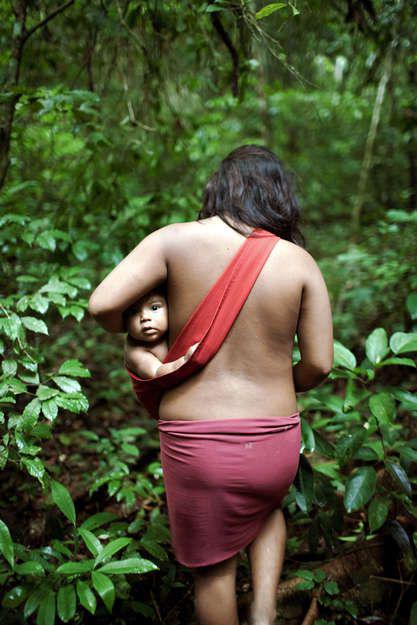
Many people living in tribes possess encyclopedic knowledge of animals, various fruits and herbs. Yanomami, for example, is used in the daily life of nearly 500 species of plants. And representatives of the people of West Papua Yali distinguish at least 49 varieties of sweet potato, and 13 varieties of bananas.
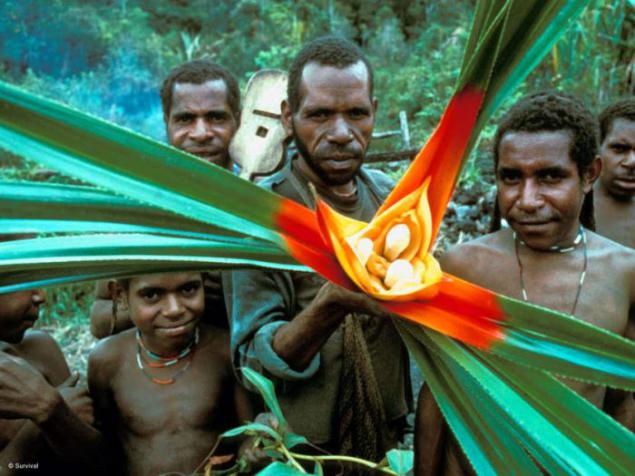

Over time, the tribe has developed a complex and integrated system of healing. Cora Copiah County, for example, is used to treat eye infections, wine from the juice of acacia Gregg used for diarrhea and flavor pounded leaves is inhaled for colds and nausea.
Many drugs of modern medicine were developed through observation and experience of these people and saved millions of lives. For example, the poison curare, which Yanomami hunters used to paralyze their prey used in Western medicine as a muscle relaxant.
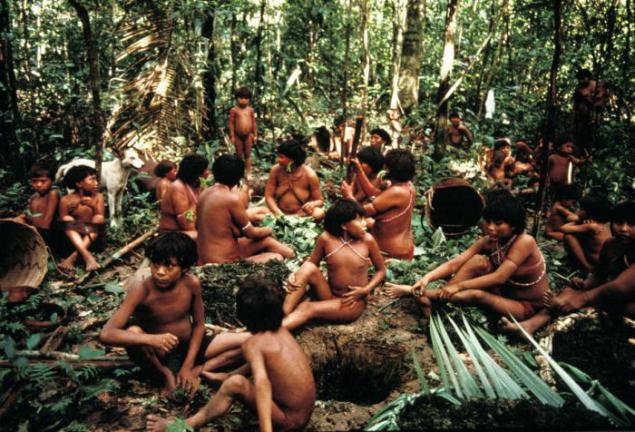

Most of the tribes living people wonder sensitively perceive the behavior of animals. Pygmies so accurately mimic the sounds of antelope in distress that can easily lure the animal out of the shelter. A Siberian hunters are able to perfectly imitate the cry of the northern fawn.
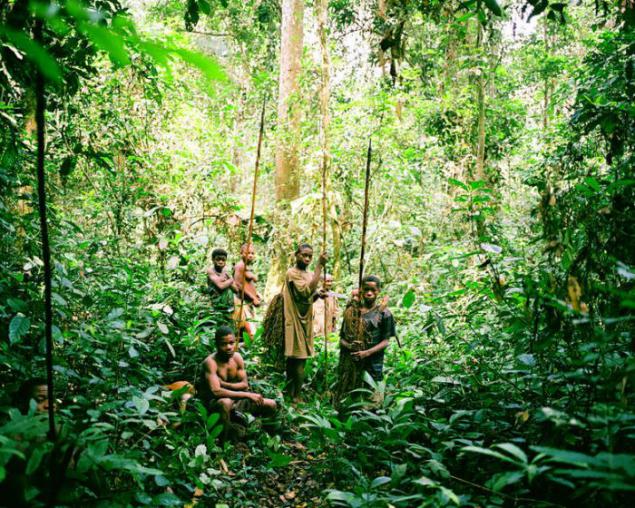

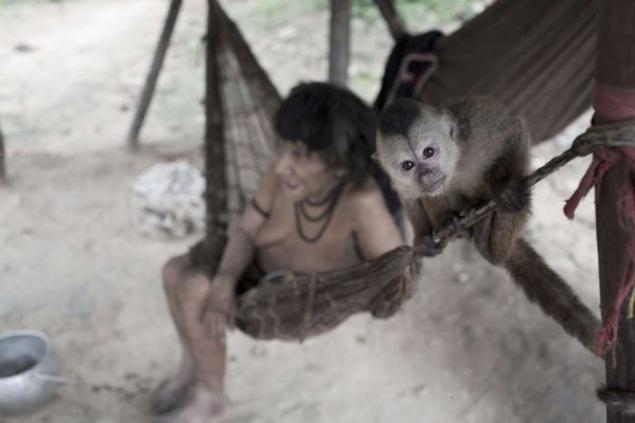
The women of the tribe of Av assume care of orphaned cubs monkeys including howler and Capuchin; often they suckle milk their animals.

Women collect resin Av Brazilian mahogany, with which illuminate their homes in the evening.

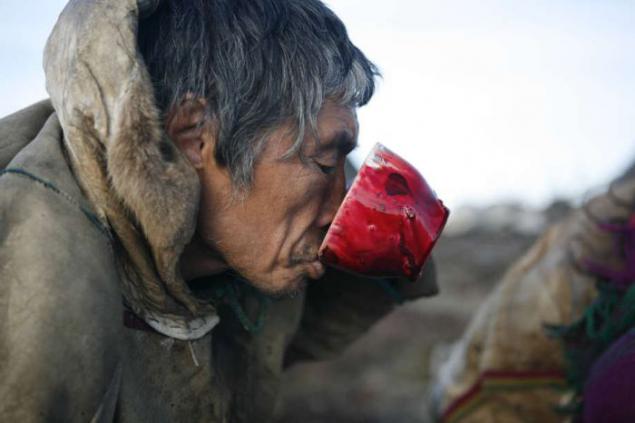
Reindeer meat - the most important part of the diet of the Nenets. It is eaten raw, frozen or boiled, together with the blood of freshly slaughtered animal, containing many valuable vitamins. Milk fat deer is 22 percent - six times more than the cow.

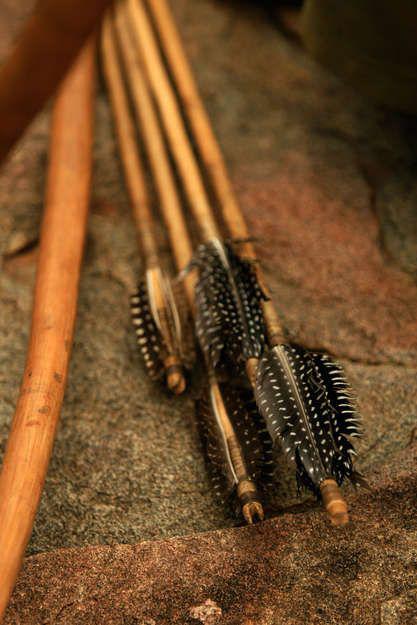
Bowstring for their bows representatives Hadza tribe of Tanzania made from animal ligaments. Arrows painstakingly machined from wood kongoroko and then fledge in using guinea fowl feathers. Tip smeared poison Adenium.

The people Hadza particularly close relationship with birds medoukazchikami that lead them to the hives of wild bees. People are whistling, the birds they meet, flying from tree to tree closer to honey. So, calling, they get to the hive, which usually hangs from the branches of the baobab.
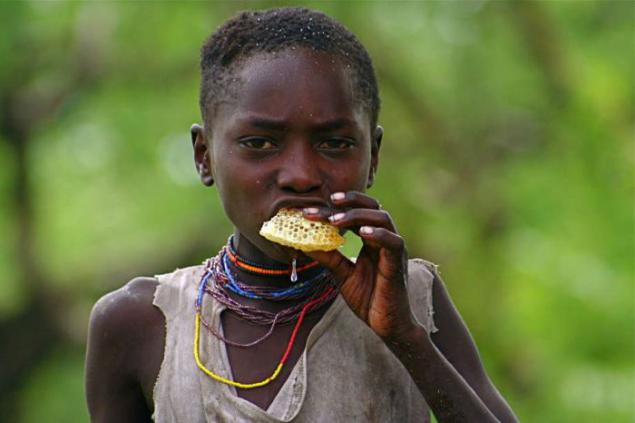

Then Hadza climb a tree with a bunch of smoldering herbs, smoke bees and collect honey. Bird remains remains of the feast.

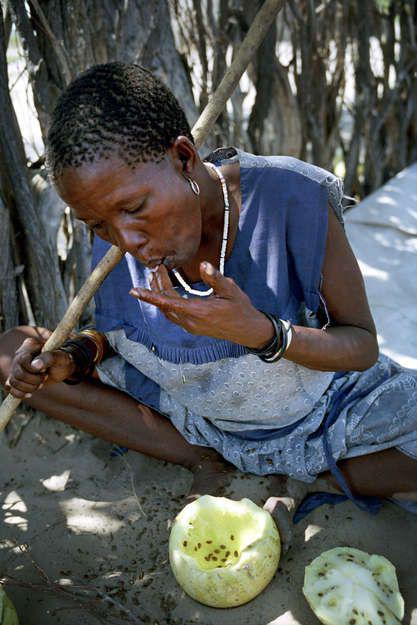
Bushman woman from Botswana tries melon pulp for juiciness. Typically, the Bushmen get moisture from the depressions in the ground that fills the rain or from plants. Water extraction technique perfected by thousands of years of life in the desert.


I - some of these places - says Davi Yanomami. I was born in the forest and know him well.
During drought people dzharava uses as a source of moisture rattan palm juice. When they need to collect wild honey, they sprinkle the juice of this plant is a hive of bees and fly away.

"Sea Gypsies" of the Moken people that live on the shores of the Andaman Sea, have developed an amazing ability to see well under water, so that can find food on the sea floor. Seeing these people more acute than the Europeans by about 50 percent.

History of the Moken is transmitted orally from one generation to another. These tales are full of deep knowledge of the sea, the winds and lunar cycles.
In one legend, for example, refers to the sinister la bun - "wave that eats people." Before coming la bun, the sea starts to back away in fear.
When the front of the devastating 2004 tsunami, the water receded, the elders of the village in Thailand Moken recognized the evil omen and took their fellow with tourists is close to a nearby hill.

In the tropical forests of Borneo tribe lives foam. These people hunted wild boar using brass tubes hardwood from which they blow darts soaked poisonous sap of a local tree.
From this poison paralyzes the animal, we can only take it home. Sami blowguns are longer than two meters.

Until the 1960s, people Pena led a nomadic life, communicating in the woods on the way a light signal system, which includes symbols of sticks and leaves, called yell. With yell could tell, for example, that the past is a person is sick or hungry.

In the 1970s, on the ground that the people served many generations of foam came white men - have cut down the forest, planted oil palm plantations, and had a gas pipeline built hydroelectric dams.

Many people living in tribes possess encyclopedic knowledge of animals, various fruits and herbs. Yanomami, for example, is used in the daily life of nearly 500 species of plants. And representatives of the people of West Papua Yali distinguish at least 49 varieties of sweet potato, and 13 varieties of bananas.

Over time, the tribe has developed a complex and integrated system of healing. Cora Copiah County, for example, is used to treat eye infections, wine from the juice of acacia Gregg used for diarrhea and flavor pounded leaves is inhaled for colds and nausea.
Many drugs of modern medicine were developed through observation and experience of these people and saved millions of lives. For example, the poison curare, which Yanomami hunters used to paralyze their prey used in Western medicine as a muscle relaxant.

Most of the tribes living people wonder sensitively perceive the behavior of animals. Pygmies so accurately mimic the sounds of antelope in distress that can easily lure the animal out of the shelter. A Siberian hunters are able to perfectly imitate the cry of the northern fawn.

The women of the tribe of Av assume care of orphaned cubs monkeys including howler and Capuchin; often they suckle milk their animals.

Women collect resin Av Brazilian mahogany, with which illuminate their homes in the evening.

Reindeer meat - the most important part of the diet of the Nenets. It is eaten raw, frozen or boiled, together with the blood of freshly slaughtered animal, containing many valuable vitamins. Milk fat deer is 22 percent - six times more than the cow.

Bowstring for their bows representatives Hadza tribe of Tanzania made from animal ligaments. Arrows painstakingly machined from wood kongoroko and then fledge in using guinea fowl feathers. Tip smeared poison Adenium.

The people Hadza particularly close relationship with birds medoukazchikami that lead them to the hives of wild bees. People are whistling, the birds they meet, flying from tree to tree closer to honey. So, calling, they get to the hive, which usually hangs from the branches of the baobab.

Then Hadza climb a tree with a bunch of smoldering herbs, smoke bees and collect honey. Bird remains remains of the feast.

Bushman woman from Botswana tries melon pulp for juiciness. Typically, the Bushmen get moisture from the depressions in the ground that fills the rain or from plants. Water extraction technique perfected by thousands of years of life in the desert.