7
9 Types of Physical Pain That Beget Stress: When Your Body Cries for Help

Imagine: You wake up in the morning after a full eight-hour nap, but you feel like you've been unloading trucks all night. The neck aches, the head hums like an orchestra before tuning the instruments, the back refuses to keep you straight. Familiar? Welcome to the amazing world of psychosomatics, a place where our unspoken emotions turn into physical symptoms with the precision of a Swiss watch.
Modern medicine has finally recognized what ancient healers have known for millennia: The body and mind are not separate apartments in the same house, but a single ecosystem.. When we ignore stress signals, the body turns on the “emergency mode” and begins to talk to us in the language of pain.
Science: Why Stress Turns into Pain
Studies show that chronic stress triggers a cascade of biochemical reactions. Cortisol, the main "stress hormone," begins to circulate in the blood as an angry guard who can't find the source of danger. As a result, the muscles are in constant tension, blood circulation is disturbed, and inflammatory processes are activated.
Dr. John Sarno, author of the revolutionary book Healing Back Pain, stated, Most back pain is psychological. The subconscious uses physical pain as a distraction from emotional problems.

Pain Map: 9 SOS Signals From Your Body
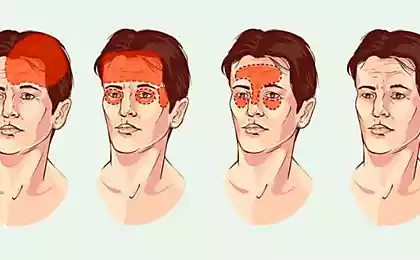
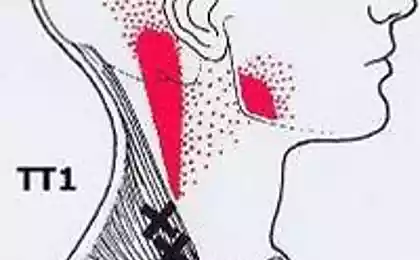
1. Neck pain – when grievances become physical
Symptoms: pulling pain, stiffness during turns, a feeling of "shot through"
Decision: Write a letter to the offender and burn him. Practice forgiveness techniques, not for others, but for your own neck.
2. Headaches – when the brain overheats from thoughts
Symptoms: Temporal pressure, heaviness in the forehead, dull pain in the back of the head
Decision: Practice the 5-minute rule – take a five-minute break every hour without thinking about work.
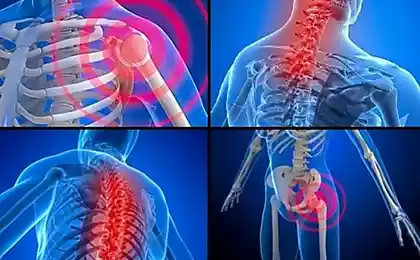
3. Pain in the shoulders - "Everything rests on me" syndrome
Symptoms: stony muscles, constant whining, a feeling of heaviness
Decision: Learn to delegate. Even Atlas sometimes had to shift the celestial sphere.
4. Lower back pain - fear of losing ground under your feet
Symptoms: aching pain, stiffness, exacerbations under stress
Decision: Create a “stability plan” – concrete steps to build confidence in the future.
5. Chest pain – when the heart shrinks from the unspoken
Symptoms: feeling of compression, "lump" in the chest, difficulty breathing
Attention! Chest pain can indicate serious illness. Be sure to consult a cardiologist.
Decision: Allow yourself to be vulnerable. Talking about feelings out loud is not weakness but courage.

6. Abdominal pain - the second nervous system rebels
Symptoms: spasms, bloating, digestive disorders, loss of appetite
Scientific fact: There are about 500 million neurons in the gut – more than in the spinal cord!
Decision: Practice “diaphragmatic breathing” and keep an emotional diary to track the link between stress and digestion.
7. Pain in the legs - when you want to run away, but scary
Symptoms: aching sensations, fatigue without physical exertion, “cotton” legs
Decision: Ask yourself, “Where am I not allowing myself to go?” Make a plan of small steps to the desired changes.
8. Stiffness in the jaw is the anger we chew
Symptoms: grinding of teeth, grinding at night, tension of facial muscles
Decision: Find healthy ways to let out anger — from aggressive cleaning to pillow-beating.
9. General muscle tension - the red code of the body
Symptoms: pain throughout the body, as after a marathon, fatigue, irritability
Decision: Enter the ritual of “exhaling” – 15 minutes daily without tasks, tasks and obligations.
️ Practical recovery strategies
STOP technique
- S. - Stop (stop)
- T Take a breath (take a deep breath)
- Oh. Observe (watch your body sensations)
- P. Proceed (act consciously)
Emergency methods of stress relief:
- Cold water: Wash your face or hold your hands under cold water – the parasympathetic nervous system is activated
- Technique 4-7-8: inhale by 4 counts, delay by 7, exhale by 8
- Progressive muscle relaxation: consistent tension and relaxation of muscle groups
Research: Evidence for a link between stress and pain
A study conducted in 2023 by the American Psychological Association found that 78% of people People with chronic pain have a history of prolonged stress. Moreover, participants who underwent psychotherapy along with medical treatment showed an improvement in symptoms. 60% fasterthan the control group.
A 2024 Harvard Medical School study found that stress reduction techniques can reduce the intensity of chronic pain by 40-60% in just 8 weeks of regular practice.
Conclusion: Your body is a wise teacher
Physical pain from stress is not an enemy to be destroyed by painkillers. This is a wise teacher who is trying to convey an important message: It’s time to stop and take care of yourself..
Keep in mind that mental health is not a luxury, but a necessity. Your body deserves the same attention and care as your most important projects.
Glossary of terms
Psychosomatics - direction in medicine and psychology, studying the influence of mental factors on the occurrence and course of somatic (body) diseases.
cortisol Stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands. With a prolonged increase, it causes inflammation, violates immunity and contributes to the development of various diseases.
vagus nerve The longest cranial nerve connecting the brain to internal organs. Responsible for parasympathetic reactions (relaxation, digestion, recovery).
Diaphragmatic breathing Deep breathing technique involving the diaphragm that activates the parasympathetic nervous system and promotes relaxation.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation - a method of stress relief, in which alternately strain and relax different muscle groups to achieve deep relaxation.
Parasympathetic nervous system The part of the autonomic nervous system responsible for the processes of recovery, digestion and relaxation (“rest and digestion”).
Gut microbiome - a set of microorganisms that inhabit the intestine. It affects digestion, immunity and even mood through the gut-brain axis.