280
5 Suggestions on How Humanity Will Evolve
4,4007176
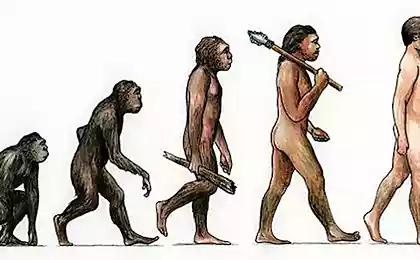
Human evolution has not stopped; it continues right now, shaping our future.
Human evolution is not over. Contrary to popular belief, natural selection and other evolutionary mechanisms continue to operate, altering the human genome even today. But more importantly, we are on the cusp of an era in which technology is actively interfering with evolutionary processes, accelerating and directing them. What will the people of the future be like? How will our body, mind and society change? Let’s take a look at the five most interesting science-based hypotheses.
1. Genetic adaptation to modern conditions
We often think of evolution as something that happened in the distant past, but genetic studies in recent years show that the human genome continues to change. The modern environment, with its unique challenges – from climate change to digitalization – is shaping new evolutionary pressures.
What's changing right now:
- Immune system: Pandemics and new pathogens cause rapid adaptations in the genes responsible for the immune response. Studies show that after each large-scale epidemic, certain genetic variants provide better protection in the human population.
- Metabolism: Changing diet and lifestyle leads to the selection of genes associated with nutrient absorption. So, in populations with a long history of agriculture, there is a higher frequency of genes associated with the effective absorption of starch.
- Cognitive abilities: The information age creates pressures in favor of certain cognitive abilities, including multitasking, fast information processing, and specific types of memory.
According to research by geneticists from Stanford University, over the past 5,000 years, the human genome has changed more than in the previous 50,000 years. If current trends continue several centuries from now, we can see people genetically adapted to urban life, resistant to modern diseases and able to function effectively in an information-rich environment.
2. Technological expansion of human capabilities

Integrating technology into the human body – from implants to neural interfaces – could be the next stage in our evolution.
The technological evolution of man is much faster than biological evolution. Unlike genetic changes that take generations to fix, technological extensions can be introduced and modified within a single person’s lifetime.
Key directions of cyborgization of mankind:
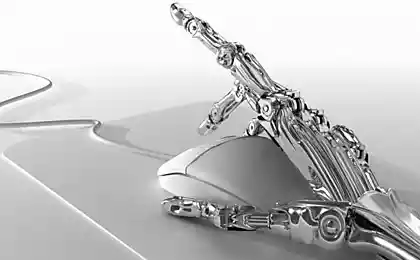
- Neurointerfaces: Directly connecting the brain to computers and networks could radically alter our cognitive abilities. Companies like Neuralink are already working on implants that allow you to control devices with the power of thought, and in the future – directly exchange thoughts and memories.
- Exoskeletons and prosthetics: The gradual merging of man with mechanical amplifiers can lead to the emergence of people with radically improved physical abilities. Modern bionic prostheses are already superior in some aspects to natural limbs.
- Internal implants: From organ regulators to nanobots in the bloodstream, internal body modification technologies can provide unprecedented control over physiology.
Futurologists suggest that in 100-200 years, a significant part of humanity may have some technological modifications. Many researchers, including the famous futurist Ray Kurzweil, believe that by 2100, the line between man and machine can largely blur, leading to the emergence of a new form of “techno-man”.
3. Genetic modification and directed evolution
Unlike natural evolution, which acts slowly and blindly, genetic editing technologies allow humanity to take control of evolutionary processes. CRISPR-Cas9 technologies and their more advanced variants open the door to an era where humans can consciously modify their genetic code.
Probable development scenarios:
- Therapeutic modifications: The first widespread genetic changes aimed at eliminating hereditary diseases and defects. Clinical trials of gene therapy are already underway to treat conditions such as sickle cell anemia, hemophilia, and some forms of blindness.
- Improvement modifications: The next step could be to introduce genetic changes that improve basic human qualities, from immunity and strength to cognitive ability and life expectancy.
- Radical modifications: In the long run, people with fundamentally new abilities are possible – from resistance to radiation and extreme temperatures to fundamentally improved senses.
Professor George Church, a leading geneticist at Harvard University, suggests that during the twenty-first century, humanity may be able to “reprogram” itself, eliminating genetic predispositions to disease and possibly extending life expectancy by decades. And by the end of the century, humans may emerge with unique genetic modifications that adapt them to life in extreme conditions, including space missions.
4. Divergence of the evolutionary paths of mankind
For most of their history, Homo sapiens were a single species with a high degree of genetic exchange between populations. However, future technologies of genetic modification, colonization of other planets and social stratification may lead to unprecedented divergence of evolutionary paths.

Different habitats and technological choices can lead to a divergence of mankind into several evolutionary branches.
Potential factors of divergence:
- Planetary colonization: Humans living in low-gravity Mars or in an atmosphere with a different composition will be subject to entirely new evolutionary pressures. Adaptation to these conditions can lead to significant physiological changes over several generations.
- Cultural choice: Different communities and cultures may choose different types of genetic or technological modification based on their values and priorities.
- Economic inequality: Access to advanced human enhancement technologies can be unevenly distributed, creating a gap between modified and unmodified populations.
Anthropologist Scott Solomon, in his book The Future of Human Evolution, suggests that colonization of Mars could lead to the emergence of the first new human species in just 300-500 years. Martian colonists can develop denser bones to compensate for low gravity, improved resistance to radiation, and an altered cardiovascular system. With the development of genetic engineering, these differences can be amplified deliberately to better adapt people to specific habitats.
5. Symbiosis with Artificial Intelligence
Perhaps the most radical change in human evolution will not be a biological or genetic transformation, but a symbiosis with artificial intelligence. As AI and neurotechnology advance, the boundaries between human and artificial intelligence may be blurring.
Possible forms of symbiosis:
- Cognitive expansion: AI systems can complement the human mind by providing instant access to information, increasing memory capacity and computing ability. We are already seeing the beginnings of this process through the use of smartphones and other devices.
- Co-evolution: Human intelligence and AI can evolve in interdependent tandem, creating a fundamentally new form of intelligence that transcends both human and artificial intelligence separately.
- Consciousness loading: In the long run, a partial or complete digitization of human consciousness is possible, which could lead to a radical revision of the concepts of life, death and human identity.
Neuroscientist David Eagleman suggests that 100 to 200 years from now, human cognition may exist in a "distributed" form, partly in a biological brain, partly in cloud-based AI systems. Philosopher and futurist Nick Bostrom goes further, suggesting that the final stage of human evolution could be a "post-biological" civilization where consciousness exists predominantly in digital form.
What can we do today?
While many of these scenarios are far in the future, we can now take steps to prepare us for evolutionary change.
- Invest in genetic literacy. Understanding the basics of genetics and evolution will help make better decisions about future human modification technologies.
- Promote digital hygiene. As the symbiosis with technology deepens, it is important to learn to maintain a healthy balance between analog and digital experiences.
- Participate in ethical discussions. Human change technologies require careful ethical analysis and extensive public discussion.
- Practice adaptability. In a rapidly changing world, the ability to adapt to new conditions becomes a key evolutionary advantage.
- Develop emotional intelligence. As AI takes on more analytical tasks, uniquely human qualities such as empathy and creativity can become our biggest asset.
Conclusion: Evolution as a Choice
For the first time in the history of life on Earth, a species has been able to direct its own evolution. Each of these trends, from genetic modification to symbiosis with AI, represents not an inevitable fate, but a potential path that humanity can choose or reject.
The coming centuries promise to be the most dynamic and transformative period in the history of the human species. Instead of passively submitting to evolutionary processes, we have an unprecedented ability to shape our future. The main question is not whether humanity will evolve, but what path of evolution we will choose and what values will guide this choice.
Glossary
CRISPR-Cas9 is a revolutionary genome editing technology that allows for precise changes in the DNA of living organisms. It works as "genetic scissors" capable of cutting, inserting or replacing specific pieces of DNA.
A neural interface is a system that creates a direct channel of information exchange between the brain and an external device (computer, prosthetic, etc.), bypassing traditional paths such as voice or gesture input.
An exoskeleton is an external framework worn on the human body and increases its physical capabilities, such as strength, endurance or speed of movement.
Genetic adaptation is the process of changing the genetic makeup of a population in response to changes in the environment, resulting in better matching organisms to their living conditions.
Mind uploading is a hypothetical process of transferring or copying a person’s consciousness from the brain to a computer system.
Transhumanism is a philosophical movement that argues that humanity should strive to overcome current biological limitations with the help of technologies that expand physical and mental abilities.
Divergence (in evolution) is the process of divergence of characteristics in related groups of organisms, leading to the formation of new species.
Cyborgization is the process of integrating technological elements into the human body in order to enhance its capabilities or compensate for lost functions.
How to Stop Being Guilty for Everything That Happens in Your Life
What is cluster thinking and how not to give in to false choices