205
How thyroid problems can affect your mental health
The thyroid gland is a tiny organ in the neck, which, despite its small size, plays a key role in the work of the entire body. With improper thyroid work (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism), you can not only worsen your mood, but also develop depression, as well as increase anxiety. In this article, we will discuss how thyroid dysfunction can affect mental health and what to do about it.

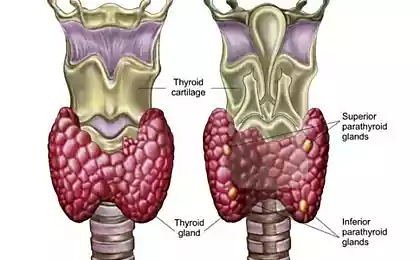
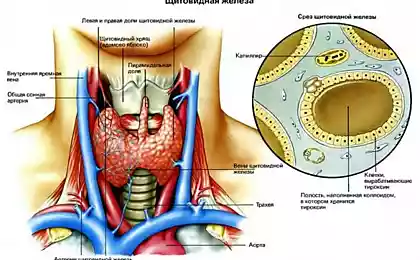
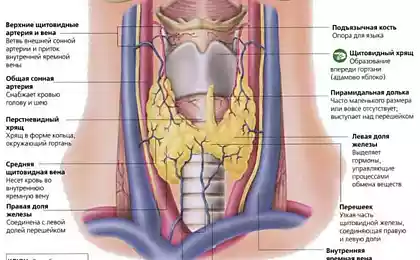
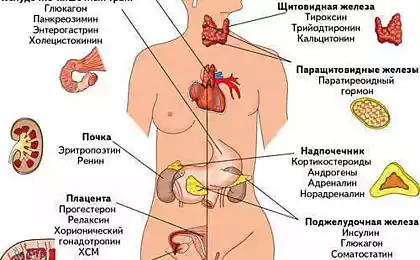
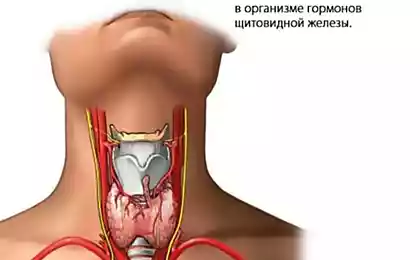
The role of the thyroid in the body
The main function of the thyroid gland is the production of hormones that regulate metabolism, body temperature, energy level, and indirectly affect the emotional state. Impaired production of these hormones can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, insomnia, changes in appetite, and even sudden mood swings.
“Sometimes the root of mental problems lies not in psychological trauma but in physiological dysfunction. ?

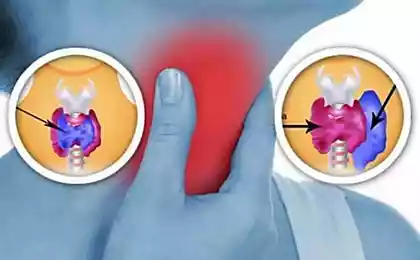
Hypothyroidism: depression and apathy
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones. This can lead to:
Hyperthyroidism: anxiety and irritability
Hyperthyroidism, on the contrary, is characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones. This can be expressed in:

Why it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner
If you suspect that thyroid problems are affecting your emotional state, you should consult an endocrinologist and psychotherapist. Here are a few reasons why this is important:
Tips for maintaining mental health
In addition to medical intervention, some simple tips can help maintain a stable emotional state:
Conclusion
Thyroid problems can significantly affect your mood and overall mental health. When symptoms of depression, anxiety, chronic fatigue and irritability appear, it is important not to postpone a visit to the doctor. Timely diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment will help improve the quality of life and cope with possible emotional disorders.

The role of the thyroid in the body
The main function of the thyroid gland is the production of hormones that regulate metabolism, body temperature, energy level, and indirectly affect the emotional state. Impaired production of these hormones can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, insomnia, changes in appetite, and even sudden mood swings.
“Sometimes the root of mental problems lies not in psychological trauma but in physiological dysfunction. ?

Hypothyroidism: depression and apathy
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones. This can lead to:
- Depression: People with hypothyroidism often complain of depression, lack of interest in life and increased tearfulness.
- Apathy: Decreased energy, constant fatigue and a feeling of indifference to what is happening around.
- Cognitive impairment: Difficulty concentration and memory impairment.
Hyperthyroidism: anxiety and irritability
Hyperthyroidism, on the contrary, is characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones. This can be expressed in:
- Increased anxiety: Excessive excitability, a sense of panic and anxiety.
- Irritability: Excessive reaction to the slightest stimuli and mood swings.
- Sleep problems: Difficulty falling asleep and restless sleep, leading to additional fatigue and emotional instability.

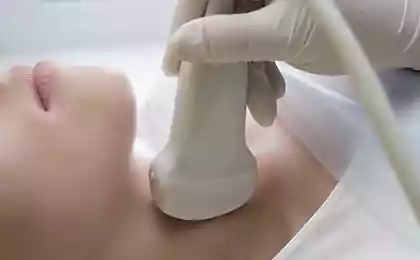
Why it is important to contact a specialist in a timely manner
If you suspect that thyroid problems are affecting your emotional state, you should consult an endocrinologist and psychotherapist. Here are a few reasons why this is important:
- Accurate diagnosis: Only hormone tests and ultrasound will help pinpoint the problem.
- Adequate treatment: Taking medications that regulate the work of the thyroid gland often improves well-being and mental state.
- Complex therapy: Sometimes a combination of medication, psychotherapy and lifestyle changes (nutrition, sleep, physical activity) are required.
Tips for maintaining mental health
In addition to medical intervention, some simple tips can help maintain a stable emotional state:
- Follow the daily routine: Regular sleep and a clear schedule help stabilize hormonal levels.
- Watch your food: Eat foods rich in minerals and vitamins that support the work of the thyroid gland (for example, iodine, selenium).
- Maintain physical activity: Moderate exercise, yoga or outdoor walks improve blood circulation and mood.
- Contact a psychologist or therapist: Talk therapy can help to cope with anxiety and depression associated with hormonal imbalance.
Conclusion
Thyroid problems can significantly affect your mood and overall mental health. When symptoms of depression, anxiety, chronic fatigue and irritability appear, it is important not to postpone a visit to the doctor. Timely diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment will help improve the quality of life and cope with possible emotional disorders.
10 Types of People You Should Maintain Strict and Inviolable Borders With
Disadvantages and weaknesses that prevent you from taking advantage of opportunities