167
Teach my son to find the area of the polygon in a minute without a draft
How to find the area of a polygon depicted on checkered paper? And is it possible to do this in 20 seconds without coordinates, tangents and complex calculations? And solving problems on the exam, and, for example, calculating the area of the tile floor will facilitate the formula of the Austrian mathematician Georg Peake.

In school, we were taught that a complex figure should fit into a rectangle. Then find the area of all the additional figures, the area of the rectangle itself and subtract the amount of additional areas from it.

For example, the area S of the triangle ABC can be calculated by subtracting from the area of the rectangle areas S1, S2 and S3. But if the polygon is complex, and there are many additional figures, then this method becomes quite tedious.

To simplify the task and do without formulas, you can count all the cells. However, some of them are only half inside the figure. In our triangle of 36 cells, the full ones are 15 and the incomplete ones are 21. Conditionally, 2 incomplete cells can be taken as 1 complete. Then the area of the triangle will be 15 + 21/2 = 25.5 cells.
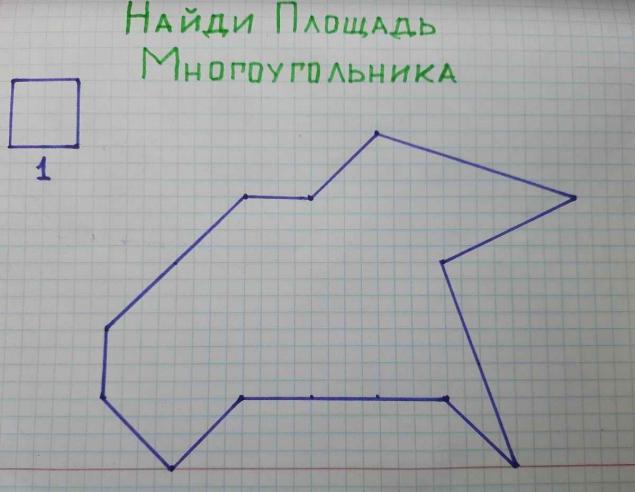
But that's a rough estimate. It is easier and more accurate to calculate. Peak's theoremIn school, teachers don’t tell everyone. It sounds like this: the area of a polygon with vertices in the nodes of the grid can be found by the formula
S = N - 1 + M/2
N is the number of nodes within the polygon
M is the number of lattice nodes at the polygon boundary
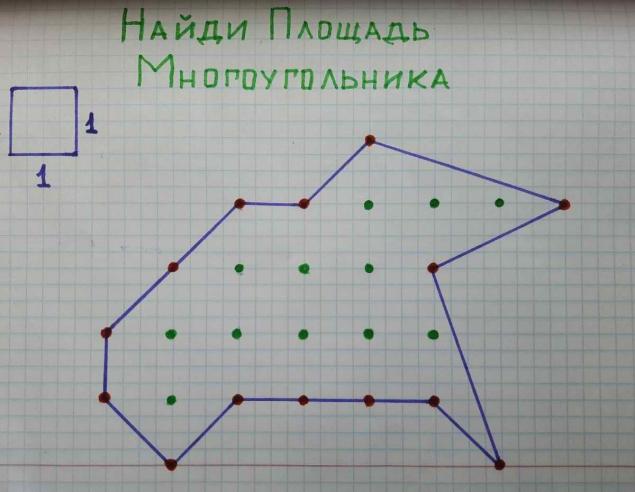
In our case, for clarity, we take a square with sides in 4 cells as a grid cell. Then inside the figure 12 nodes of the lattice (green dots), and on the border of the polygon 14 nodes (red dots). N = 12 and M = 14. Substitute the formula: S = 12 - 1 + 14/2 = 18

To consolidate the skill, try to count the area of another figure and share the result in the comments, and at the same time recheck it in the traditional way. Obviously, the effort and time expended are incommensurable.
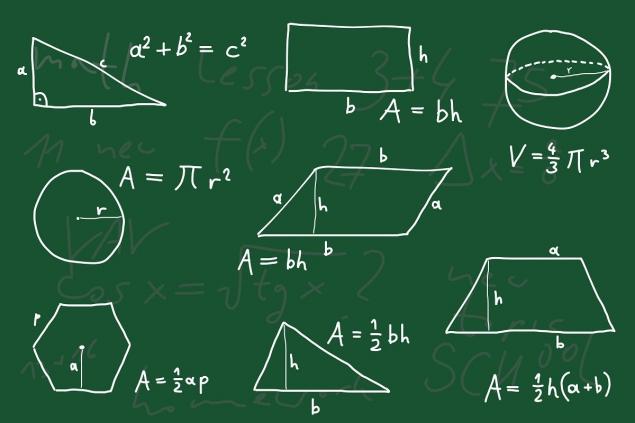
Note that the Peak formula works only for polygons, the vertices of which are located in the nodes of the coordinate grid. Completely replace the usual formulas for calculating the area, unfortunately, will not work, so you should not forget them in any case. As you can see, mathematics can be interesting. And to attract young students will help a selection of 7 fascinating books, which we offer to our readers.

In school, we were taught that a complex figure should fit into a rectangle. Then find the area of all the additional figures, the area of the rectangle itself and subtract the amount of additional areas from it.

For example, the area S of the triangle ABC can be calculated by subtracting from the area of the rectangle areas S1, S2 and S3. But if the polygon is complex, and there are many additional figures, then this method becomes quite tedious.

To simplify the task and do without formulas, you can count all the cells. However, some of them are only half inside the figure. In our triangle of 36 cells, the full ones are 15 and the incomplete ones are 21. Conditionally, 2 incomplete cells can be taken as 1 complete. Then the area of the triangle will be 15 + 21/2 = 25.5 cells.

But that's a rough estimate. It is easier and more accurate to calculate. Peak's theoremIn school, teachers don’t tell everyone. It sounds like this: the area of a polygon with vertices in the nodes of the grid can be found by the formula
S = N - 1 + M/2
N is the number of nodes within the polygon
M is the number of lattice nodes at the polygon boundary

In our case, for clarity, we take a square with sides in 4 cells as a grid cell. Then inside the figure 12 nodes of the lattice (green dots), and on the border of the polygon 14 nodes (red dots). N = 12 and M = 14. Substitute the formula: S = 12 - 1 + 14/2 = 18

To consolidate the skill, try to count the area of another figure and share the result in the comments, and at the same time recheck it in the traditional way. Obviously, the effort and time expended are incommensurable.

Note that the Peak formula works only for polygons, the vertices of which are located in the nodes of the coordinate grid. Completely replace the usual formulas for calculating the area, unfortunately, will not work, so you should not forget them in any case. As you can see, mathematics can be interesting. And to attract young students will help a selection of 7 fascinating books, which we offer to our readers.
Fisherman from Murmansk pleads not to make shameful mistakes in salting red fish
Do Spanish hostess add strawberries to gazpacho and is it worth it?