548
Developed a thin OLED displays based on graphene electrodes
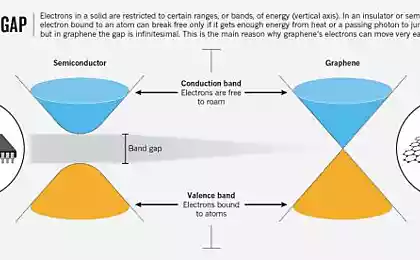
With the refinement and facilitation of displays are increasingly reminded about graphene — a promising material, which the researchers have already found dozens of theoretical applications. He is considered a good conductor of heat and electricity, and many scientists are trying to use it in displays. The fact that the currently used transparent electrodes made of indium-tin oxides — substances which are becoming scarce. Different scientists have offered to replace it, for example, silver.

A group of Korean scientists announced the creation of a technology that will allow OLED panels to replace the electrodes made of indium-tin on graphene. The reason for the replacement not only in increasing the deficit. Existing electrodes are very fragile, graphene also provides strength and resistance to chipping. By the way, that is why he is often said to be the basis for flexible displays.
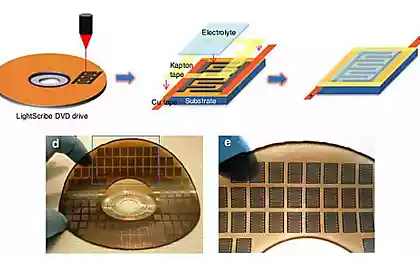
A team of scientists have used graphene to create the most big OLED panels on earth — 370 mm in length, 470 mm in width. The thickness of the graphene electrodes was only 5 nm. Scientists have also developed a special process of formation of a graphene substrate, which can become the basis for flexible smart devices of the future.
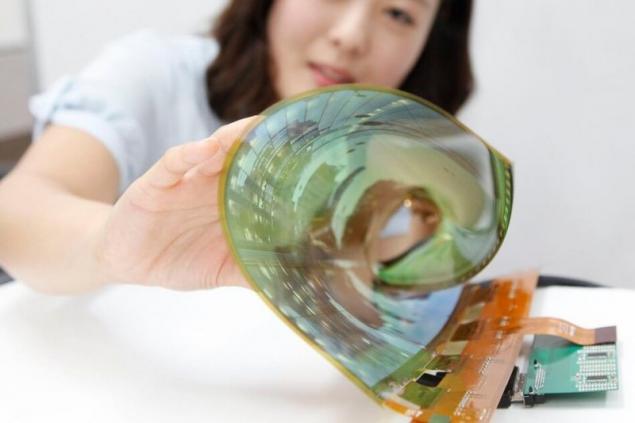
Technology, said scientists should provide South Korea with a big separation from competitors in the creation of graphene OLED panels, particularly from China. A couple of years, the team managed to increase the size of the panels dozens of times. In 2015, they presented a display about the size of a coin, a year later increased it 10 times, now has the largest grafenauer OLED display, which is planning to commercialize in the near future.
But not a single graphene live industry of the future displays. Recently those Korean scientists have created the first tissue OLED display. German scientists have applied to create a new type of monitor to fluorescent proteins. And thanks to the work of Stephanie Malek and her colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania to create the world's first elastic holographic display. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //hightech.fm/2017/04/12/oled_display

A group of Korean scientists announced the creation of a technology that will allow OLED panels to replace the electrodes made of indium-tin on graphene. The reason for the replacement not only in increasing the deficit. Existing electrodes are very fragile, graphene also provides strength and resistance to chipping. By the way, that is why he is often said to be the basis for flexible displays.
A team of scientists have used graphene to create the most big OLED panels on earth — 370 mm in length, 470 mm in width. The thickness of the graphene electrodes was only 5 nm. Scientists have also developed a special process of formation of a graphene substrate, which can become the basis for flexible smart devices of the future.

Technology, said scientists should provide South Korea with a big separation from competitors in the creation of graphene OLED panels, particularly from China. A couple of years, the team managed to increase the size of the panels dozens of times. In 2015, they presented a display about the size of a coin, a year later increased it 10 times, now has the largest grafenauer OLED display, which is planning to commercialize in the near future.
But not a single graphene live industry of the future displays. Recently those Korean scientists have created the first tissue OLED display. German scientists have applied to create a new type of monitor to fluorescent proteins. And thanks to the work of Stephanie Malek and her colleagues from the University of Pennsylvania to create the world's first elastic holographic display. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: //hightech.fm/2017/04/12/oled_display