403
Behavior and DNA

Recent studies of the bees showed that the behavior and activity lead to changes in DNA. All bees are born equal, but after birth, some become Queens and live long, while others become ordinary bees live about 40 days. Moreover, this process of transformation is reversible. The difference in lifetimes depending on the activities and the corresponding epigenetic maps are especially noticeable in bees. Among bees, there are workers of different professions." They start out as nurses, taking care of the livelihood of the uterus and larvae. Then, upon reaching 15 to 18 days of age, they become a forager and leave the hives in search of pollen and nectar.
The researchers argue that the role of the worker bees in the hive accompanied by subtle changes in their DNA. Moreover, these changes are reversible when changing activity. When the worker bees perekvalifitsiruetsya from forager to nurse, the set of individual external and internal signs of their body (called phenotype) is also changed. Such transformations are called epigenetic changes.
Generally, epigenetic changes are irreversible. However, a study published in Nature Neuroscience, provides the first example of reversible changes in the DNA directly related to the behavior: after a bee returns to the duties of the nurse, characteristics of methylation of its DNA changed again.
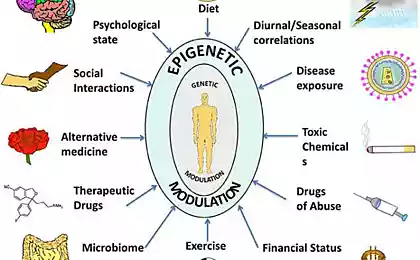
The interaction with the environment and the human response to external factors generate changes in the activity of genes. DNA changing mechanisms of information processing due to epigenetic mechanisms. Attached to the genes of the methyl group and it becomes less active. If the methyl group leaves the gene, he aktiviziruyutsya. The body is very sensitive from the point of view of epigenetic mechanisms to the events occurring around them. Typically, in healthy cells, oncogenes that initiate the process of formation of the cancerous tumor off. But scientists have proved that acetaldehyde alcohol gives methyl groups to join DNA. The result includes "sleeping" oncogenes and begin to work, turning healthy cells into cancer cells.
Thus, it is clear that human behavior may trigger the development of cancer or make it more difficult for diseases and prolong life.
Researcher Marcus Pembrey of the Institute of child health at the University of London found that if a man started Smoking before 11 years of age, his future sons have an increased risk of obesity. The reason is that tobacco also disrupts the delicate balance of gene regulation. In 2007, researchers from the Institute BMC Genomics compared lung tissue taken from those who quit smokers and in people who never smoked. It was established about 600 altered genes that would not work properly. Fortunately, most of them returned to normal, if you quit Smoking – the sooner the better. But still about 120 genes remain altered even after 10 years after refusal of cigarettes.
First established indisputable fact that behavior change leads to a change of samples of DNA methylation.
The study of epigenetic mechanisms to influence the behavior of social animals will help in understanding some aspects of human biology, but also opens up new ways to change human behavior. Epigenetic effects are manifested in human behavior based on its learning and memory, stress reactions and mood changes.
Greg hunt, the study of bees, says: “the Structure of the human nervous system to a large extent similar to the nervous system of bees”. Therefore, by studying bees we can find out what connection exists between genes and human behavior. The ability to reverse the appearance of epigenetic effects responsible for the physiological and mental illness, could be very interesting.
Not only harmful substances but also our actions are recorded by epigenetic mechanisms in the activity of genes programming our fate, exposure and disease.
published
Source: www.quantumcristal.com/povedenie-i-dna/