768
The muscle fiber types and rules for their training
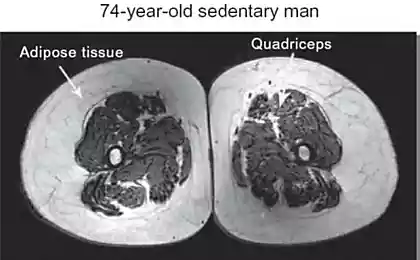
Understanding how the physiology of the body adapts to the exercises will help to develop effective training programs for your fitness goals.
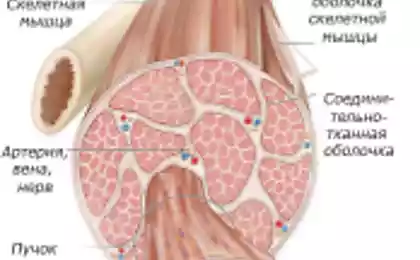
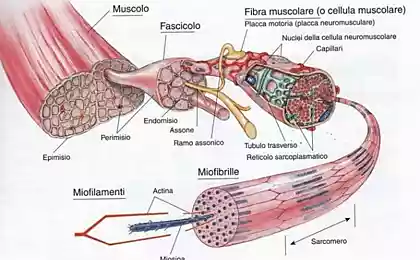
The human body consists of different types of muscle fibers that are classified by how produce energy. Different muscle fibers must be trained with special exercises, which should focus on how energy is produced or generated power. Although there were identified many types of muscle fibers, differing in (I, IC, IIC, IIA, IIB, IIA and IIX), they are usually divided into two groups: slow-twitch and fast-twitch.
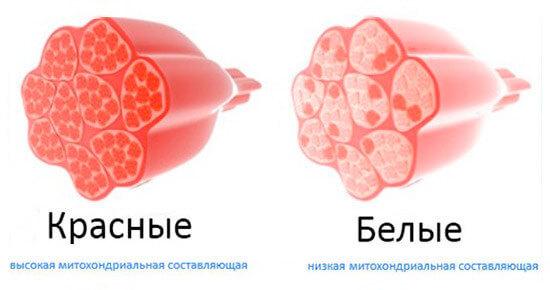
Slow-twitch muscle fibers (I-type) 1. Slow-twitch fibers contain large amounts of mitochondria — organelles that use oxygen to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a chemical which acts as a fuel for muscle contraction. Therefore, these reductions are considered to be aerobic.
2. Slow fibers are also called red fibers. They are intensively supplied with blood, which delivers myoglobin, which creates a red color.
3. As they provide their own source of energy, you can maintain a sufficient power level for an extended period of time. But slow-twitch muscle fibers themselves are not able to generate high levels of force.
4. Slow fibers have low activation threshold, that is, the first involved with physical activities. If they can't generate the necessary power levels required for this type of activity, the work of connecting the fast-twitch fibers.
5. The muscles responsible for maintaining a certain body position, mostly it consist of slow-twitch fibers.
6. Static endurance training help to increase mitochondrial density, which in turn leads to increased efficiency, since the body will use more oxygen for ATP production.
As can be seen from the above, especially slow-twitch fibers is caused by the way they operate. This means that their training will be the most effective program of aerobic exercise.

Training methods for slow-twitch fibers:
— Exercises that involve prolonged isometric contraction with slight movement, help to improve the ability of slow-twitch fibres use oxygen for energy production. Examples of exercises: plank, side plank, balance on one foot (horizontal).
— Resistance exercise using light weights, performed at a slow pace, but with lots of reps (15 and above), make slow-twitch fibers use aerobic metabolism to support activity.
— Circuit training using light weight, which involves the transition from one exercise to another with minimal rest (or do without), are able to challenge the slow-twitch fibers.
— Exercise with own body weight and a large number of repetitions well stimulate the aerobic metabolism, which will make slow-twitch fibers more efficient.
— During exercise with its own weight or with a slight extra weight use short rest intervals (about 30 seconds between sets). This will provide a challenge to slow-twitch fibers and force them to use aerobic metabolism as fuel for exercise.

Fast twitch muscle fibers ( II-type)1. Fast twitch fibers are divided into 2 groups:
2. Fast-twitch fibers have a high activation threshold, so off to work only when the demand for power will more than slow-twitch fibers.
3. Fast fibers requires less time to achieve peak power. To the same they can generate more force than slow fibers.
4. Although they generate more power but get tired more quickly.
5. The muscles responsible for the creation of the movement, largely composed of fast fibers.
6. Training for power and strength increases the amount of fast twitch muscle fibers involved in a particular movement.
7.Fast-twitch fibers are responsible for the size and expressiveness of the muscles.
8. Fast type fibers called "white fibers", as poorly supplied with blood and has a rich color, like the second type.
As can be seen from the above, the characteristics of fast-twitch fibers require training on power and strength, and develop explosive power. If you want to make maximum use of fast fiber in their training to enhance strength and durability, here are a few specific methods that can help in this.
Training methods for fast twitch fibers:
— Workout with a heavy weight forcing the muscles to activate more muscle fibers. The heavier the weight, the more fast twitch fibers will be involved in the work.
— Responsible for explosive movements and strength exercises using a barbell, kettlebell or dumbbell, will provide more muscle fibers.
— Fast-twitch fibers tire quickly. So you should focus on using heavy weights, but only up to a certain number of repetitions (e.g., two to six) to achieve maximum effect.
Since the fast fibers quickly drain your energy during workouts require longer rest periods to the muscles-the engines had enough time to recover and replenish ATP. Therefore, any explosive or power exercises is to pause for a duration of 60-90 seconds.

Genetics determines the number of each type of muscle fibers in our body. However, knowing which fast - or slow-twitch, type is dominant will help to build the correct training program. So, if you find that, as a rule, stick to endurance, and they are relatively easy to you give you are probably the owner of a large number of slow-twitch fibers. Conversely, if you prefer physical activity, which involves short explosive movements or exercises with high weight — your body is dominated by fast-twitch type fibers.
The exercise program that applies the correct strategies of workouts for your muscle fibers will help to maximize the efficiency of the loads.published
The table of characteristics of muscle fiber types
Features
Slow-twitch
Fast twitch IIa
Fast twitch IIb
Generating power
Low level
The average level
A high level
Speed reduction
Low level
A high level
A high level
Stavelot
Low level
The average level
A high level
Glycolytic capacity
Low level
A high level
A high level
Oxidative ability
A high level
The average level
Low level
Cabaiesti blood
A high level
The average level
Low level
Mitochondrial density
A high level
The average level
Low level
Endurance
A high level
The average level
Low level
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: fitfixed.com/training/advise/tipy-myshechnyh-volokon-i-pravila-ih-trenirovki/
The human body consists of different types of muscle fibers that are classified by how produce energy. Different muscle fibers must be trained with special exercises, which should focus on how energy is produced or generated power. Although there were identified many types of muscle fibers, differing in (I, IC, IIC, IIA, IIB, IIA and IIX), they are usually divided into two groups: slow-twitch and fast-twitch.

Slow-twitch muscle fibers (I-type) 1. Slow-twitch fibers contain large amounts of mitochondria — organelles that use oxygen to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a chemical which acts as a fuel for muscle contraction. Therefore, these reductions are considered to be aerobic.
2. Slow fibers are also called red fibers. They are intensively supplied with blood, which delivers myoglobin, which creates a red color.
3. As they provide their own source of energy, you can maintain a sufficient power level for an extended period of time. But slow-twitch muscle fibers themselves are not able to generate high levels of force.
4. Slow fibers have low activation threshold, that is, the first involved with physical activities. If they can't generate the necessary power levels required for this type of activity, the work of connecting the fast-twitch fibers.
5. The muscles responsible for maintaining a certain body position, mostly it consist of slow-twitch fibers.
6. Static endurance training help to increase mitochondrial density, which in turn leads to increased efficiency, since the body will use more oxygen for ATP production.
As can be seen from the above, especially slow-twitch fibers is caused by the way they operate. This means that their training will be the most effective program of aerobic exercise.

Training methods for slow-twitch fibers:
— Exercises that involve prolonged isometric contraction with slight movement, help to improve the ability of slow-twitch fibres use oxygen for energy production. Examples of exercises: plank, side plank, balance on one foot (horizontal).
— Resistance exercise using light weights, performed at a slow pace, but with lots of reps (15 and above), make slow-twitch fibers use aerobic metabolism to support activity.
— Circuit training using light weight, which involves the transition from one exercise to another with minimal rest (or do without), are able to challenge the slow-twitch fibers.
— Exercise with own body weight and a large number of repetitions well stimulate the aerobic metabolism, which will make slow-twitch fibers more efficient.
— During exercise with its own weight or with a slight extra weight use short rest intervals (about 30 seconds between sets). This will provide a challenge to slow-twitch fibers and force them to use aerobic metabolism as fuel for exercise.

Fast twitch muscle fibers ( II-type)1. Fast twitch fibers are divided into 2 groups:
- fast twitch IIa — fast oxidative (uses oxygen to convert the glycogen into ATP);
- fast twitch IIb — fast glycolytic (using ATP stored in muscle cells as glycogen to produce energy).
2. Fast-twitch fibers have a high activation threshold, so off to work only when the demand for power will more than slow-twitch fibers.
3. Fast fibers requires less time to achieve peak power. To the same they can generate more force than slow fibers.
4. Although they generate more power but get tired more quickly.
5. The muscles responsible for the creation of the movement, largely composed of fast fibers.
6. Training for power and strength increases the amount of fast twitch muscle fibers involved in a particular movement.
7.Fast-twitch fibers are responsible for the size and expressiveness of the muscles.
8. Fast type fibers called "white fibers", as poorly supplied with blood and has a rich color, like the second type.
As can be seen from the above, the characteristics of fast-twitch fibers require training on power and strength, and develop explosive power. If you want to make maximum use of fast fiber in their training to enhance strength and durability, here are a few specific methods that can help in this.
Training methods for fast twitch fibers:
— Workout with a heavy weight forcing the muscles to activate more muscle fibers. The heavier the weight, the more fast twitch fibers will be involved in the work.
— Responsible for explosive movements and strength exercises using a barbell, kettlebell or dumbbell, will provide more muscle fibers.
— Fast-twitch fibers tire quickly. So you should focus on using heavy weights, but only up to a certain number of repetitions (e.g., two to six) to achieve maximum effect.
Since the fast fibers quickly drain your energy during workouts require longer rest periods to the muscles-the engines had enough time to recover and replenish ATP. Therefore, any explosive or power exercises is to pause for a duration of 60-90 seconds.

Genetics determines the number of each type of muscle fibers in our body. However, knowing which fast - or slow-twitch, type is dominant will help to build the correct training program. So, if you find that, as a rule, stick to endurance, and they are relatively easy to you give you are probably the owner of a large number of slow-twitch fibers. Conversely, if you prefer physical activity, which involves short explosive movements or exercises with high weight — your body is dominated by fast-twitch type fibers.
The exercise program that applies the correct strategies of workouts for your muscle fibers will help to maximize the efficiency of the loads.published
The table of characteristics of muscle fiber types
Features
Slow-twitch
Fast twitch IIa
Fast twitch IIb
Generating power
Low level
The average level
A high level
Speed reduction
Low level
A high level
A high level
Stavelot
Low level
The average level
A high level
Glycolytic capacity
Low level
A high level
A high level
Oxidative ability
A high level
The average level
Low level
Cabaiesti blood
A high level
The average level
Low level
Mitochondrial density
A high level
The average level
Low level
Endurance
A high level
The average level
Low level
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Join us in Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: fitfixed.com/training/advise/tipy-myshechnyh-volokon-i-pravila-ih-trenirovki/
Greenhouse thermos – unique energy-saving technology
4 Council of the ancient philosophers that will make You happier