574
Strength, size and all about the number of reps
Myofibrillar hypertrophy
Myofibril — cylindrical filaments with a thickness of 1 — 2 µm, running along from one end of muscle fiber to another. Myofibril – the contractile elements of the muscle cells, decreasing with the help of ATP.
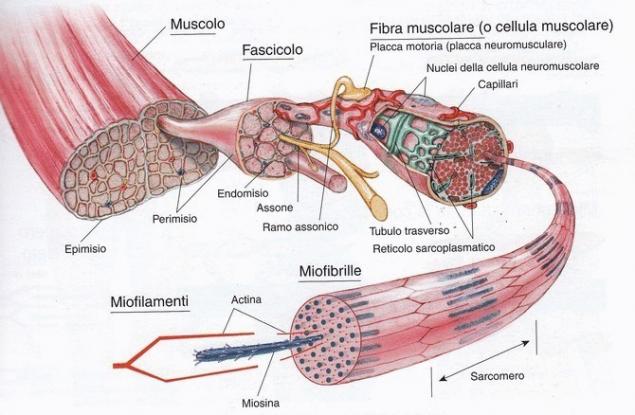
Myofibrillar hypertrophy, or “power” hypertrophy, leads to an increase in the content of actin and myosin, which are contractile proteins in the myofibrils (IIa and IIb muscle fiber types or “bystrosokhnuschie” muscle fibers). In more simple terms, when you lift heavy weights and make muscles experience a new stress (progressive overload increasing weights every workout for obtaining myofibrillar hypertrophy), your body will respond by improving the contractility of the muscles.
The use of muscle fibers (motor units) in the exercises increases with hypertrophy of myofibrils, which increases the strength of muscle contractions, enhanced strength allows you to progressively increase the load, resulting in greater hypertrophy of the myofibrils bystrosokhnuschie muscle fibers.
The stronger your bystrosokhnuschie muscle fibers, the stronger the neuromuscular response and therefore more weight you can take in the exercises.
Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy
Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy leads to an increase in the number of sarcoplasm in your muscle tissue. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm (the nutrient fluid) that surrounds the myofibrils in the muscle fiber. The sarcoplasm contains substrates such as ATP, glycogen, creatine phosphate and water. Simply put, when you work on hypertrophy sarcoplasm, the amount of fluid in muscles is greatly increased, creating a large muscle volume.
This type of hypertrophy is being developed through slow, controlled movements to put the muscles in a longer stress and activate the muscle fibers of both types, simultaneously depleting energy substrates.
Note that increased muscle size does not need to increase in contractile muscle proteins in the myofibrils (read — myofibrillar hypertrophy), it means that the increase in size is not necessarily related to increased strength. At the same time, the strength can be greatly increased without significant increase in muscle mass.
How am I supposed to train for the development of these types of hypertrophy?
Neuromuscular training increases the activation of muscle fibers the nervous system, as well as the amount of contractile proteins in the myofibrils. These workouts are based on heavy weights (85-100% of your 1RM) and consist of quick, explosive movements from 1 to 40 seconds per set. Rest periods between sets can vary from 90 seconds to 5 minutes.
Metabolic training is based on increasing the amount of energy substrates in muscle fibers. It is important to use average weight (60-75% of your 1RM), to perform the exercises slowly and keep the muscle under load for 40-70 seconds. The recommended rest time from 30 to 60 seconds.
You may notice that there is a space at 10% of 1RM between these types of training. This is because in this period the most benefit from both measures, i.e. the strength and muscle volume.
How can I determine my 1RM and relative percentage of the 1RM?
Fortunately, we have many opportunities to calculate it the easy way. Available below, the website calculator will help you calculate the interest based on your current reps/weight in exercises.
How can I determine the time under load for optimal myofibrillar/sarcoplasmic hypertrophy?
The simplest way to help you is to follow a scheme of repetitions. Usually when you perform a small number of repetitions, your muscles are under load a short time and the weight will be close to the maximum (and therefore building strength through neuromuscular training). On the other hand, when you finish the set with a high number of repetitions, your muscles need more time under load and weight will be quite small compared to the maximum. This will increase training volume and consequently muscle size through this training. It is recommended not to rest more than 60 seconds.
Below shows the number of repetitions that allows you to change the direction of your workouts:
• 1-5 reps 85-100% More myofibrillar training, closer to 5 repetitions – moderate growth in sarcoplasma.
• 6-8 Reps 75-85% the Golden mean. Almost the same development as myofibrillar hypertrophy and sarcoplasmic.
• 9-12 Reps 70-75 More sarcoplasmic training, myofibrillar and a bit weak on endurance.
• 13-15 Reps 65-70% Almost only sarcoplasmic, a little stamina and very little effect on the hypertrophy of the myofibrils.
• 15+ Reps* 65% More endurance, a lot sarcoplasmic hypertrophy.
*Note that the more you increase the number of repetitions after 15, the more your workouts become endurance training and down almost to nothing hypertrophy.
How do I use this information to adjust training under him?
Firstly decide what your goal is. If you want to add muscle volume or want to increase strength? Or do you want both?
Mainly training for strength is a goal which has several advantages, especially if you are satisfied with your current volume. This way, you will very slowly gain muscle mass, but very quickly will raise the power, if you recover properly. But be careful! Heavy strength training has a strong stress on the Central nervous system, so you can easy earn overtraining. If you want to train for strength, use such schemes like 5x5, 6x4, 8x3 with decent rest time between sets. Start to lift weight within 85% of your 1RM, then increase the weight and decrease the reps with each set.
Training for strength is a goal that has its advantages but is not without drawbacks. If you are training for mass and you are a beginner, eventually you will rest against a plateau after a rapid compilation of a number of muscle mass. This will happen due to lack of power. So you have to some extent to focus on the development of the force (that's why the power of the program is recommended for the beginners). The lower your strength, the faster you will get to a plateau.
If you want to train mostly for mass, use such training methods as 3х15, 4х12 and 5x9 with a small rest period between sets (no more than 60-90 seconds). Supersets (performing two exercises for the muscles – antagonists with no rest between sets) can also be a strong Supplement to the training ground. Lift 65-70% of your 1RM, increasing the percentage and decreasing repetitions in each following set.
Training and power and to ground, in my opinion, is the right to let for building big muscle size. There are two methods that I recommend you to do this:
• 1. Regular training on the simultaneous development of sarcoplasmic/myofibrils
Use as many sets/reps like 4x8, 5x7 or 6x6 with an average rest period of approximately 60-120 seconds. Raise 75% of your 1RM for 8 reps, 80% for 7 and ~85% for 6 reps.
• 2. The method of linear periodization.
The method of linear periodization allows you to explore versatile and power and ground for the various “periods”.
Two schemes of linear periodization:
• Weeks 1-4: 3x15 reps 65% of 1RM
• Weeks 5-8: 4x10 reps at 72% 1RM
• Weeks 9-12: 5x5 reps 85% of 1RM
• Weeks 1-4: 4x12 reps 70% of 1RM
• Weeks 5-8: 5x7 reps 80% of 1RM
• Weeks 9-12 6x3 reps 90% of 1RM
You can use any scheme of periodization, as almost all of them work well.
If you want to gain more muscle mass with time, the best way to do this is to develop both the myofibrils and the sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasm is responsible for quick growth, which, however, quickly slowed down, as they limit the hypertrophy of myofibrils and your strength.
The results
I really hope this information will be useful for you and will give you a rough direction in order to enable you to easier realize their goals. Remember that training is only one element of the equation that nutrition and recovery are another important part of the growth of the mass, it will help you maximize the effectiveness of the effect of training. I wish you great gains in muscle mass and strength to each of you!
The article did not reflect reality 100%, as even 3 repetitions still cause a small sarcoplasmic hypertrophy and for a relatively untrained person, all the schemes and on the power and ground will work, giving a significant increase in strength and mass.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: vk.com/sport_stat?z=photo-25740422_371941214%2Falbum-25740422_00%2Frev
Myofibril — cylindrical filaments with a thickness of 1 — 2 µm, running along from one end of muscle fiber to another. Myofibril – the contractile elements of the muscle cells, decreasing with the help of ATP.

Myofibrillar hypertrophy, or “power” hypertrophy, leads to an increase in the content of actin and myosin, which are contractile proteins in the myofibrils (IIa and IIb muscle fiber types or “bystrosokhnuschie” muscle fibers). In more simple terms, when you lift heavy weights and make muscles experience a new stress (progressive overload increasing weights every workout for obtaining myofibrillar hypertrophy), your body will respond by improving the contractility of the muscles.
The use of muscle fibers (motor units) in the exercises increases with hypertrophy of myofibrils, which increases the strength of muscle contractions, enhanced strength allows you to progressively increase the load, resulting in greater hypertrophy of the myofibrils bystrosokhnuschie muscle fibers.
The stronger your bystrosokhnuschie muscle fibers, the stronger the neuromuscular response and therefore more weight you can take in the exercises.
Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy
Sarcoplasmic hypertrophy leads to an increase in the number of sarcoplasm in your muscle tissue. The sarcoplasm is the cytoplasm (the nutrient fluid) that surrounds the myofibrils in the muscle fiber. The sarcoplasm contains substrates such as ATP, glycogen, creatine phosphate and water. Simply put, when you work on hypertrophy sarcoplasm, the amount of fluid in muscles is greatly increased, creating a large muscle volume.
This type of hypertrophy is being developed through slow, controlled movements to put the muscles in a longer stress and activate the muscle fibers of both types, simultaneously depleting energy substrates.
Note that increased muscle size does not need to increase in contractile muscle proteins in the myofibrils (read — myofibrillar hypertrophy), it means that the increase in size is not necessarily related to increased strength. At the same time, the strength can be greatly increased without significant increase in muscle mass.
How am I supposed to train for the development of these types of hypertrophy?
Neuromuscular training increases the activation of muscle fibers the nervous system, as well as the amount of contractile proteins in the myofibrils. These workouts are based on heavy weights (85-100% of your 1RM) and consist of quick, explosive movements from 1 to 40 seconds per set. Rest periods between sets can vary from 90 seconds to 5 minutes.
Metabolic training is based on increasing the amount of energy substrates in muscle fibers. It is important to use average weight (60-75% of your 1RM), to perform the exercises slowly and keep the muscle under load for 40-70 seconds. The recommended rest time from 30 to 60 seconds.
You may notice that there is a space at 10% of 1RM between these types of training. This is because in this period the most benefit from both measures, i.e. the strength and muscle volume.
How can I determine my 1RM and relative percentage of the 1RM?
Fortunately, we have many opportunities to calculate it the easy way. Available below, the website calculator will help you calculate the interest based on your current reps/weight in exercises.
How can I determine the time under load for optimal myofibrillar/sarcoplasmic hypertrophy?
The simplest way to help you is to follow a scheme of repetitions. Usually when you perform a small number of repetitions, your muscles are under load a short time and the weight will be close to the maximum (and therefore building strength through neuromuscular training). On the other hand, when you finish the set with a high number of repetitions, your muscles need more time under load and weight will be quite small compared to the maximum. This will increase training volume and consequently muscle size through this training. It is recommended not to rest more than 60 seconds.
Below shows the number of repetitions that allows you to change the direction of your workouts:
• 1-5 reps 85-100% More myofibrillar training, closer to 5 repetitions – moderate growth in sarcoplasma.
• 6-8 Reps 75-85% the Golden mean. Almost the same development as myofibrillar hypertrophy and sarcoplasmic.
• 9-12 Reps 70-75 More sarcoplasmic training, myofibrillar and a bit weak on endurance.
• 13-15 Reps 65-70% Almost only sarcoplasmic, a little stamina and very little effect on the hypertrophy of the myofibrils.
• 15+ Reps* 65% More endurance, a lot sarcoplasmic hypertrophy.
*Note that the more you increase the number of repetitions after 15, the more your workouts become endurance training and down almost to nothing hypertrophy.
How do I use this information to adjust training under him?
Firstly decide what your goal is. If you want to add muscle volume or want to increase strength? Or do you want both?
Mainly training for strength is a goal which has several advantages, especially if you are satisfied with your current volume. This way, you will very slowly gain muscle mass, but very quickly will raise the power, if you recover properly. But be careful! Heavy strength training has a strong stress on the Central nervous system, so you can easy earn overtraining. If you want to train for strength, use such schemes like 5x5, 6x4, 8x3 with decent rest time between sets. Start to lift weight within 85% of your 1RM, then increase the weight and decrease the reps with each set.
Training for strength is a goal that has its advantages but is not without drawbacks. If you are training for mass and you are a beginner, eventually you will rest against a plateau after a rapid compilation of a number of muscle mass. This will happen due to lack of power. So you have to some extent to focus on the development of the force (that's why the power of the program is recommended for the beginners). The lower your strength, the faster you will get to a plateau.
If you want to train mostly for mass, use such training methods as 3х15, 4х12 and 5x9 with a small rest period between sets (no more than 60-90 seconds). Supersets (performing two exercises for the muscles – antagonists with no rest between sets) can also be a strong Supplement to the training ground. Lift 65-70% of your 1RM, increasing the percentage and decreasing repetitions in each following set.
Training and power and to ground, in my opinion, is the right to let for building big muscle size. There are two methods that I recommend you to do this:
• 1. Regular training on the simultaneous development of sarcoplasmic/myofibrils
Use as many sets/reps like 4x8, 5x7 or 6x6 with an average rest period of approximately 60-120 seconds. Raise 75% of your 1RM for 8 reps, 80% for 7 and ~85% for 6 reps.
• 2. The method of linear periodization.
The method of linear periodization allows you to explore versatile and power and ground for the various “periods”.
Two schemes of linear periodization:
• Weeks 1-4: 3x15 reps 65% of 1RM
• Weeks 5-8: 4x10 reps at 72% 1RM
• Weeks 9-12: 5x5 reps 85% of 1RM
• Weeks 1-4: 4x12 reps 70% of 1RM
• Weeks 5-8: 5x7 reps 80% of 1RM
• Weeks 9-12 6x3 reps 90% of 1RM
You can use any scheme of periodization, as almost all of them work well.
If you want to gain more muscle mass with time, the best way to do this is to develop both the myofibrils and the sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasm is responsible for quick growth, which, however, quickly slowed down, as they limit the hypertrophy of myofibrils and your strength.
The results
I really hope this information will be useful for you and will give you a rough direction in order to enable you to easier realize their goals. Remember that training is only one element of the equation that nutrition and recovery are another important part of the growth of the mass, it will help you maximize the effectiveness of the effect of training. I wish you great gains in muscle mass and strength to each of you!
The article did not reflect reality 100%, as even 3 repetitions still cause a small sarcoplasmic hypertrophy and for a relatively untrained person, all the schemes and on the power and ground will work, giving a significant increase in strength and mass.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: vk.com/sport_stat?z=photo-25740422_371941214%2Falbum-25740422_00%2Frev