635
When the Sun makes the Earth uninhabitable?
Well, quite a long time we're hanging in there on the Ground. Since then, as 4.5 billion years ago formed our Sun, followed by our proto-Earth was born in the inner Solar system, and the combination of initial conditions and the late heavy bombardment gave rise to our first oceans and atmosphere that we feel here is quite good. More than four billion years the Sun always shone and life was flourishing. But it won't last forever. One day the Sun will exhaust its fuel, which will lead to our demise.
Born an interesting question...
Reduced if nuclear energy of the Sun or remain stable? How long we can survive on Earth, if the "nuclear potential" of the Sun slowly fade?

If we assume that there will be no disasters caused by the Land itself (e.g. the volcano, which will cover the entire planet or destroy the biosphere) or the Universe (sterilizing gamma-ray burst or supernova explosion nearby), the Sun will one day destroy all life on Earth.
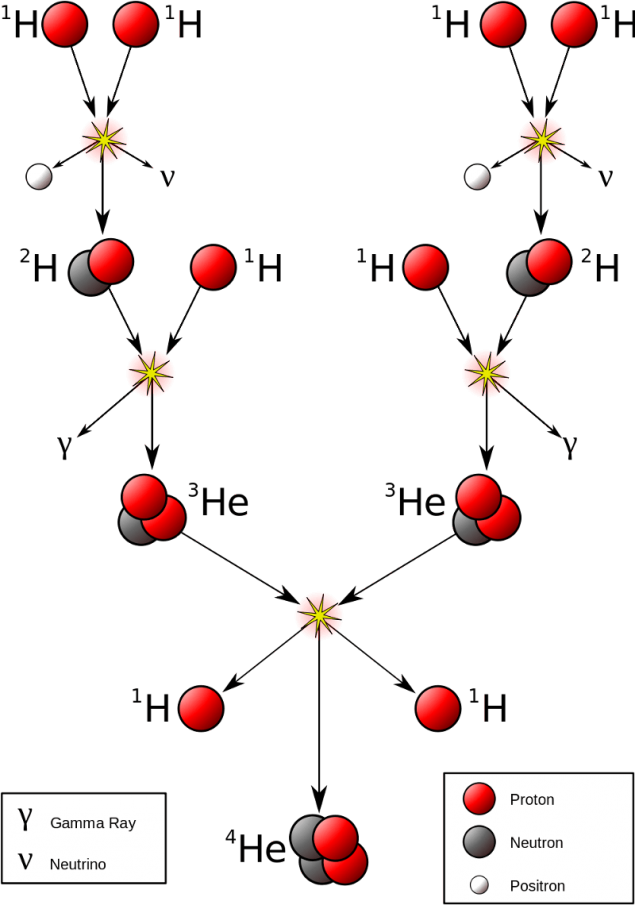
You see, stars like our Sun live at the expense of nuclear fusion: due to the synthesis of the lightest and most common element in the Universe (hydrogen) in the second lightest and most abundant element (helium) in the course of a chain reaction. Chain reaction, through which the Sun receives most of its energy, includes:
This is the most common source of solar energy, where a total of 0.7% of the initial mass of the four protons is converted into energy during the reaction according to the formula of Einstein:
E = mc2.
Every second, 4 x 1038 protons to synthesize helium-4, releasing about 4 x 1026 Watts of energy on an ongoing basis.
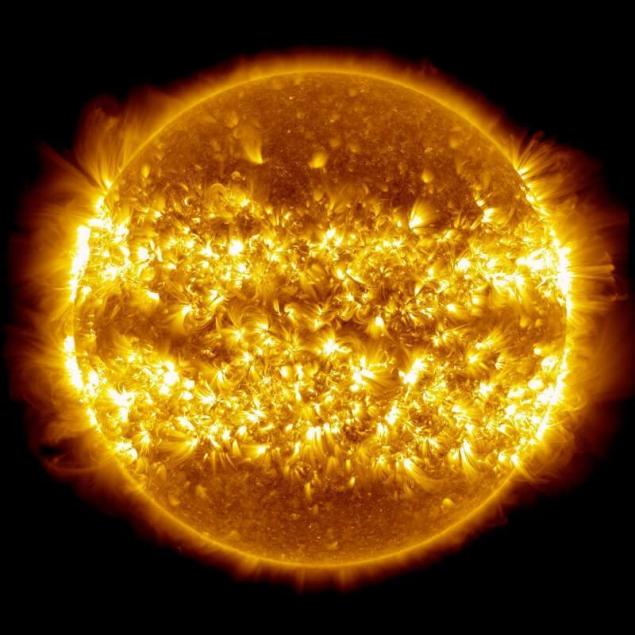

The sun is huge and massive, and consists of about 1057 particles. But how else was this number,the total amount of solar fuel is limited, and give it time — it will end.
Even more pressing issue is that hydrogen is fused only in the core of the Sun where the temperature is the highest. The very first protons are not synthesized until you pass more than halfway to the center of the Sun and does not detect the temperature of 4 million degrees Celsius. And only in the deepest part of the Sun where the temperature reaches 10 million (or 15 million) degrees and is 99% of the Sun's energy.
This means that over time, in the deepest bowels of the Sun's fuel runs out faster, because that's where it burns hydrogen to form helium.
You would think that eventually the Sun will become dim, since the fuel for its heat will burn out. But in the absence of such reactions occurring inside the nucleus, it will start to shrink and the gravitational compression will release more energy that will increase the internal temperature. The synthesis starts flowing faster and wider. It turns out, over time the output energy of the Sun will increase. Actually, this happened for more than four billion years.
When our Sun was a young star, it burned 75-80% of the capacity of the current its luster. Due to the presence of flora, fauna, the ocean and atmosphere on our planet, we were able to adapt to a steady rise in temperature. But there is a limit: at some point, the luminosity of the Sun will increase so that the Earth at its present distance from the Sun will become hot enough that the oceans will boil. When this happens, our planet will suffer the fate of Venus — a thick layer of clouds will envelop her — and life will cease to exist.

It is possible that some life forms learn to survive in the upper layers of clouds. It's also possible that humanity will be able to understand how to survive in such conditions. But this will happen long before the core of the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel. In 5-7 billion years our Sun will pass through the following stages:
But after one or two billion years (according to most estimates) the Sun will become hot enough to evaporate the oceans.
Also interesting: there Shines in the summer the Sun is brighter
The sun is the source of heat and electricity for residential buildings in Alaska
By the time we have to find a new home.
In the end it is only this global warming would make sense.published
Author: Ilya Hel
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru/space/kogda-solnce-sdelaet-zemlyu-neprigodnoj-dlya-zhizni.html
Born an interesting question...
Reduced if nuclear energy of the Sun or remain stable? How long we can survive on Earth, if the "nuclear potential" of the Sun slowly fade?

If we assume that there will be no disasters caused by the Land itself (e.g. the volcano, which will cover the entire planet or destroy the biosphere) or the Universe (sterilizing gamma-ray burst or supernova explosion nearby), the Sun will one day destroy all life on Earth.

You see, stars like our Sun live at the expense of nuclear fusion: due to the synthesis of the lightest and most common element in the Universe (hydrogen) in the second lightest and most abundant element (helium) in the course of a chain reaction. Chain reaction, through which the Sun receives most of its energy, includes:
- the merger of the two protons, together with the formation of deuterium, positrons (which annihilate with an electron and produces high-energy photons), neutrinos, and free energy;
- then the fusion of deuterium with a proton to form helium-3, a high-energy photon and free energy;
- and then the fusion of two nuclei of helium-3 together to form helium-4, two free protons and even more free energy.
This is the most common source of solar energy, where a total of 0.7% of the initial mass of the four protons is converted into energy during the reaction according to the formula of Einstein:
E = mc2.
Every second, 4 x 1038 protons to synthesize helium-4, releasing about 4 x 1026 Watts of energy on an ongoing basis.

The sun is huge and massive, and consists of about 1057 particles. But how else was this number,the total amount of solar fuel is limited, and give it time — it will end.
Even more pressing issue is that hydrogen is fused only in the core of the Sun where the temperature is the highest. The very first protons are not synthesized until you pass more than halfway to the center of the Sun and does not detect the temperature of 4 million degrees Celsius. And only in the deepest part of the Sun where the temperature reaches 10 million (or 15 million) degrees and is 99% of the Sun's energy.
This means that over time, in the deepest bowels of the Sun's fuel runs out faster, because that's where it burns hydrogen to form helium.
You would think that eventually the Sun will become dim, since the fuel for its heat will burn out. But in the absence of such reactions occurring inside the nucleus, it will start to shrink and the gravitational compression will release more energy that will increase the internal temperature. The synthesis starts flowing faster and wider. It turns out, over time the output energy of the Sun will increase. Actually, this happened for more than four billion years.
When our Sun was a young star, it burned 75-80% of the capacity of the current its luster. Due to the presence of flora, fauna, the ocean and atmosphere on our planet, we were able to adapt to a steady rise in temperature. But there is a limit: at some point, the luminosity of the Sun will increase so that the Earth at its present distance from the Sun will become hot enough that the oceans will boil. When this happens, our planet will suffer the fate of Venus — a thick layer of clouds will envelop her — and life will cease to exist.

It is possible that some life forms learn to survive in the upper layers of clouds. It's also possible that humanity will be able to understand how to survive in such conditions. But this will happen long before the core of the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel. In 5-7 billion years our Sun will pass through the following stages:
- the kernel will run out of hydrogen;
- the sun will expand to a very bright subgiants stars, while hydrogen will burn in a shell around the core;
- when the temperature reaches a critical limit, the core will start to synthesize helium;
- the sun will expand to red giant this;
- and die, blowing their outer layers into a planetary nebula and the core will shrink to a white dwarf state.
But after one or two billion years (according to most estimates) the Sun will become hot enough to evaporate the oceans.
Also interesting: there Shines in the summer the Sun is brighter
The sun is the source of heat and electricity for residential buildings in Alaska
By the time we have to find a new home.
In the end it is only this global warming would make sense.published
Author: Ilya Hel
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru/space/kogda-solnce-sdelaet-zemlyu-neprigodnoj-dlya-zhizni.html