746
The most famous modern scientist Stephen Hawking about his relationship with God

Stephen Hawking ©Getty Images "for Centuries it was thought that such as I, that is, people with disabilities are cursed of God. I think that I someone now upset, but personally, I think that can all be explained differently, namely laws of nature" are words of the most famous scientist of our time, British astrophysicist Stephen Hawking. They reveal the essence of Hawking's relationship with God. Don't need to be a psychologist to understand that Hawking's entire life struggling with God because he never "punished". But maybe it was the opposite – the Creator of "punished" scientist because, even as a young man, before his illness, he decided to fathom his secret? The irony of this paradox can be compared with the irony of the Universe, closed on itself, which is finite in extent but has no boundary. Such antinomies exist on the border of physics and philosophy. But from the point of view of laws of nature – is there a Creator? We will tell you what he thinks about it Stephen Hawking. Science and religion
These opposites are fighting each other for nearly three thousand years. In 1277 Pope John XXI was so scared of the fact that there are laws of nature, declared them heresy. But, alas, he could not deny even one of them – gravity. A few months later, the Palace roof collapsed directly to the Pope on the head.
However, religion, with its plastic logic immediately found a solution to all problems. She quickly declared the laws of nature are the handiwork of God, who will change these laws at any time, as only a "want". And the fire – someone who will think more.
It later emerged that are a little more complicated. Humble the Church was ready for this. In 1985, at a conference on cosmology in the Vatican, Pope John Paul II said that there is nothing wrong in studying the Universe. "But we – said the Pope – do not have to wonder about its origins, as it was the handiwork of the Creator." But Stephen Hawking is still set.
To answer this question, according to Hawking, it is necessary to understand the nature of all three ingredients "dish of the Universe": matter, energy and space. But where did they come from this "kitchen"? The response to this gave Einstein. But he "stood on the shoulders of giants", so everything in order.

Giordano Bruno before the court of the Inquisition / ©Wikimedia Commons
Aristotle, Newton and Galileo
In the framework of its laws of motion for Newton as you know, put measurements of Galileo. Recall that in the experiments of the last the body would roll down an inclined plane under the action of a constant force, which gave him constant acceleration. So, it has been shown that the actual effect of force – change the speed of the body, and not bringing it in motion, as was considered before. Still it followed that until the body is exposed to any force, it moves in a straight line with constant speed (Newton's First law).
In addition to the laws of motion, work, Newton described and the determination of the specific type of force – gravity. According to the Law of universal gravitation, any two bodies attract each other with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses.
The main difference between the views of Aristotle on the one hand and ideas of Galileo and Newton on the other is that Aristotle believed the peace of the natural state of any body to which it is committed, if not under action of some force. Aristotle, for example, believed that the Earth remains at rest. But from Newton's laws should be: no rest, no. Everything is in motion. And Earth, and the train going through it.
What? No absolute "standard of rest" for physics had the same effect as for the pupils of the parochial school – admission to the University. From this it followed that it is impossible to determine, happened whether two events happened at different times in the same place. And it already means nothing, as the absence of absolute, fixed space. Newton is strongly discouraged, because it does not accord with his idea of the absolute God. In the end, he actually refused this conclusion, which was a consequence of they also open laws.
But from Aristotle, and Newton found a General "sedative": a belief in absolute time. They believed that it is possible to measure the frequency interval between the two events, and the resulting figure will be the same, no matter who measured (if you use an accurate clock, of course). Unlike absolute space, absolute time really even got along with Newton's laws, and most people today thought it was consistent with common sense. But then there was Einstein...

Isaac Newton / ©The Royal Society
3 is equal to 2
Who called himself "the Gypsy and the hobo", the great Einstein found that two components of the Universe – matter and energy are essentially one and the same, like two sides of the same coin. His famous E = mc2 (where E is energy, m is body mass, c – speed of light in vacuum) means that mass can be regarded as a form of energy and Vice versa. Thus, the Universe should be regarded as "cake", consisting of just two components: energy and space. But how he came to that?
Same subject – for example, flying ping-pong – can be attributed to a different speed. It all depends on which reference frame this speed measure. If the ball is thrown in a moving train, its speed can be calculated relative to the train and relative to the earth on which the train travels, and which also moves around its axis and around the Sun which itself is moving... and so on, without end.
If you believe the laws of Newton, the same should apply to light. But thanks to Maxwell science became known that the speed of light is constant, how would we neither measured. To reconcile the theory of Maxwell with the mechanics of Newton, was adopted the hypothesis that everywhere, even in vacuum, there is a certain medium, called "ether". According to the theory of the ether, light waves (and we know that light simultaneously has the properties of waves and particles) is spread in the same way as sound waves in the air, and their speed must be measured relative to this ether. In this case, different observers recorded the different values of the speed of light, but relative to the ether it would have remained constant.
However, the famous Michelson-Morley experiment, held in 1887, has forced scientists to abandon the idea of the ether forever. To the great surprise of the experimenters, they were able to prove that the speed of light never changes relative to what would it was not measured.
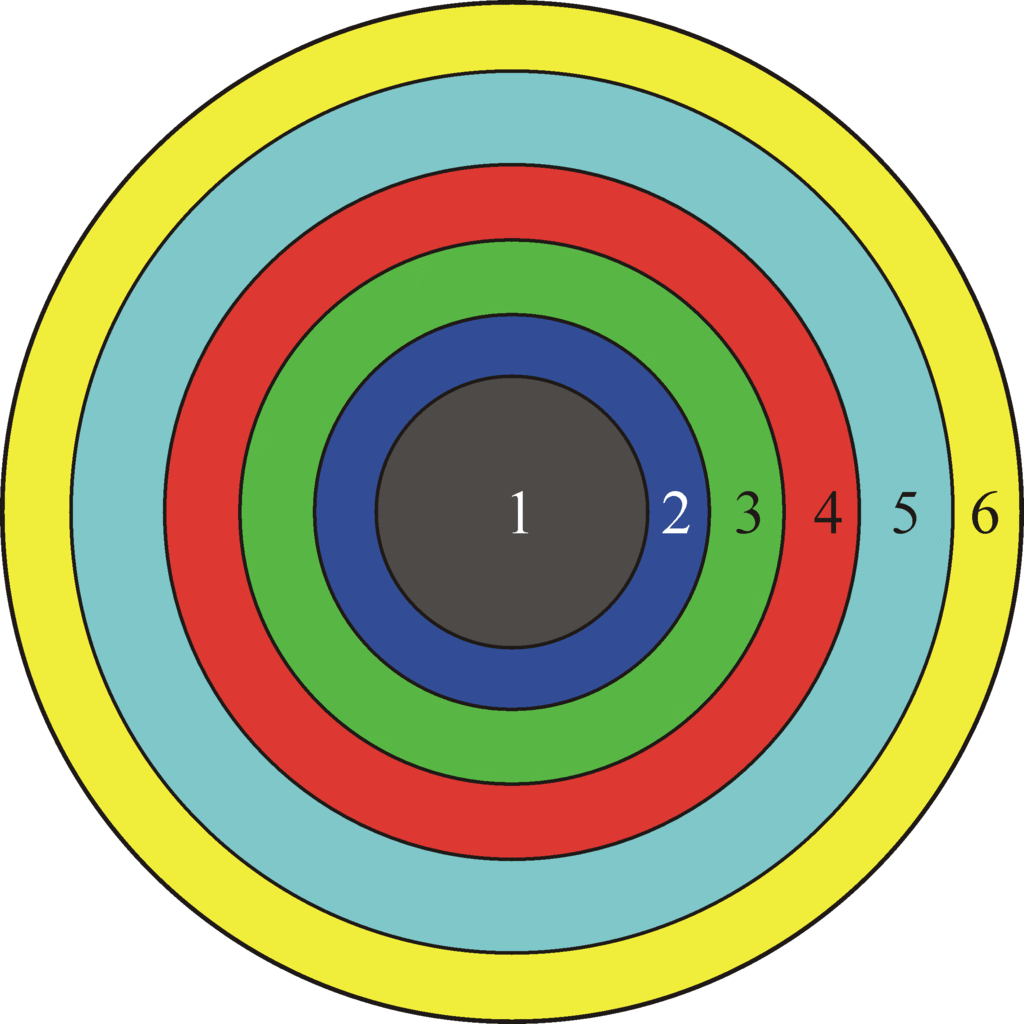
The structure of the Universe according to Aristotle. The figures indicate the spheres: earth (1), water (2) air (3) fire (4), ether (5), Prime Mover (6). Not to scale.
©Wikimedia Commons
The principle of relativity States that the laws of physics must be the same for all freely moving systems, regardless of their speed. This was true for the laws of motion of Newton, but now Einstein extended his hypothesis and the theory of Maxwell.
This means that the velocity of light is constant, then any freely moving observer must record the same value that would not depend on the speed with which it approaches the light source or away from it. This simple conclusion explained the emergence of the speed of light in Maxwell's equations without the involvement of air or some other privileged system of reference. But the same conclusion followed a number of other incredible discoveries. And, above all, changing ideas about time.
For example, according to the Special theory of relativity, a person traveling on the train, and the one standing on the platform, diverge in the assessment of the distance traveled by the light from a single source. And since speed is distance divided by time, the only way for observers to come to a common conclusion about the speed of light is to disperse in time evaluation. So the theory of relativity has done away with the idea of absolute time!
Another conclusion STO is the inseparability of time and space, which constitute a kind of community, space-time.
Developing the ideas of a HUNDRED in the General theory of relativity, Einstein showed that gravity is not a magnetic force, and due to the fact that space-time is curved by mass and energy that are in him.

Albert Einstein / ©AP
In this respect, back to the destroyed before the Foundation of the illusion of absolute time. Einstein proved that near massive bodies, such as, for example, the Land needs to slow down and the passage of time (speaking roughly, this is due to the curvature of space, and therefore time – some of them stretching around the massive body). The more weight, the slower its environs will flow time and Vice versa.
As you know, orbiting the earth time flows faster than on the planet, so the astronauts come home a little younger than it could be if I chose another profession, and there'd always be on the Ground. However, this "youthfulness" of the astronauts is almost impossible to observe. First, because of the proximity of the earth's orbit to the Earth, and secondly, because short-term stay of astronauts in orbit. But if one of them managed to go to space travel on the ship to reach speeds close to the speed of light, and return after a year, he certainly would not have found in living not only one from their loved ones, but also many generations of his grandchildren and great-grandchildren.
Model of the geocentric system of the world according to Ptolemy / ©national library of France
The big Bang
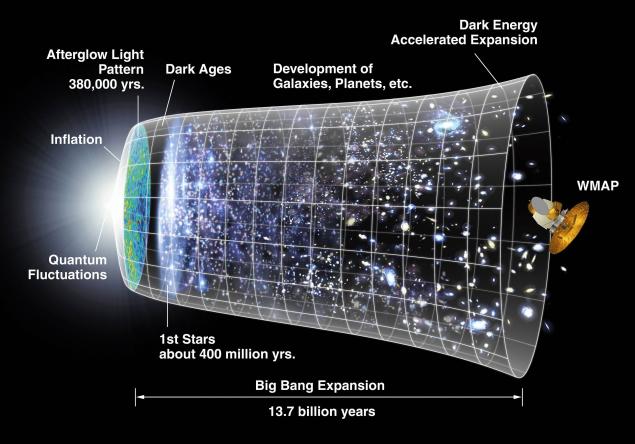
Go back to the other two ingredients, of which "cooked" the universe: energy and space. Where did they? Today, scientists say: they appeared in the Big Bang. But what is the Big Bang?
Approximately 13.7 billion years ago the universe was compressed into one incredibly small point. This is evidenced not only in the famous red shift, but all the solutions of Einstein's equations. Sometime in the past the distance between neighboring galaxies was zero. The universe had to be compressed into a point of zero size, the sphere with zero radius. The density of the Universe and the curvature of space-time in these glorious days had to be infinite. They have ceased to be such only at the Big Bang.
Another infinite value in the era of the infancy of the universe had to be temperature. It is believed that in the moment of the Big Bang, the universe was infinitely hot. To the extent that, as the universe expanded, decreased, and temperature. This is the origins of what we call matter. The fact that at such high temperatures as were in the Universe at the dawn of time, could not be formed not only atoms, but also subatomic particles. But with decreasing energy they began to connect with each other. So there was substance.
Approximately 100 seconds after the Big Bang, the universe cooled to one billion degrees (the temperature of the subsoil the hottest stars). Under these conditions, the energy of protons and neutrons is not enough to overcome the strong nuclear interaction. They begin to fuse, forming a deuterium nucleus (heavy hydrogen) consisting of a proton and neutron. And then the deuterium nucleus by adding protons and neutrons could turn into a helium nucleus. The other elements are born later in the thermonuclear synthesis in a hydrogen-helium stars.
After all this truly "hot" bustle about a million years the universe continued to expand, and nothing much happened. But when the temperature dropped to a few thousand degrees, the kinetic energy of electrons and nuclei was insufficient to overcome the force of electromagnetic attraction, and they began to coalesce into atoms. So the matter came in the usual sense of the word.
But what about antimatter? What is it and where did it? According to the laws of physics, there is negative energy. In order to understand what it is, here is an analogy. Imagine that someone wants to build a big hill on a flat landscape. Hill is our universe. To create a hill that someone digs a big hole. Pit – this is the "negative version" of the hill. What was in the pit, has now become a hill, so the balance is fully preserved. The same principle was the basis of the "construction" and our Universe. When the Big Bang was created by a large number of positive energy is simultaneously formed the same amount of negative energy. But where is she? Answer: everywhere in space. "The pit" – is our space, and all matter, to which we are accustomed, that you can see, that is what the universe is "hill".
A brief history of the Big Bang / ©NASA
Quantum mechanics
In the moment of the Big Bang, the universe was compressed into an unimaginably tiny point. And it is at this subatomic level is failing the General theory of relativity, as his time was a fiasco Newton's laws, when they tried to apply the traffic light. At the subatomic level are entirely different, truly fantastic laws, which have no analogues in our everyday life. Therefore, the science that studies the laws dealing with phenomena that occur at very small scale – quantum mechanics – is so difficult to understand. The universe in the Big Bang is a place where the laws of quantum mechanics.
But, wanting to add up all the puzzles of the universe, Stephen Hawking holds our best hope for creating a unified theory of the functioning of the Universe – the theory of quantum gravity. She needs to reconcile General relativity with quantum mechanics.
God plays dice
Quantum mechanics based on so-called uncertainty principle. It says that particles do not possess individually precisely defined positions and velocities. But they have the so-called quantum state, a combination of characteristics that are known only within the boundaries permitted by the uncertainty principle.
Quantum mechanics in a moment dashed all hopes that the Universe and all processes can be predicted. She has made science the worst – an accident. The laws of quantum mechanics offer a number of possible outcomes of something, say, how likely is each of them. That is why Einstein up to the end of his life never accepted quantum mechanics. Their attitude he expressed with the famous phrase: "God does not play dice".
One of the most important consequences of the uncertainty principle is that in some ways particles behave like waves. They do not have specific provisions, but "smeared" over space, in accordance with the probability distribution. And yet, in accordance with the laws of quantum mechanics, particles are not a specific "story", that is, the trajectories in space-time. Instead, the particle moves within a certain range over all possible trajectories, that is, paradoxically, in several places at the same time.
This can be understood only by the brain, calculations and equations, feelings and logic to make it virtually impossible. In our everyday life, the Cup of coffee in the morning doesn't simply appear. To on our the table any drink you need to take a coffee beans, sugar, water and milk. But if you look at the coffee deeper into the subatomic level, you can witness real magic. And all because at this level, particles operate according to the laws of quantum mechanics. They suddenly appear, exist for some time, just as suddenly disappear – and appear again.

Stephen Hawking at the lecture / ©Getty Images
All of nothing
But where did the unimaginably small point – our universe – the moment of the Big Bang? From the same place and a Cup of coffee: nothing. Like vanishing and emerging protons in the coffee beverage, the universe appeared out of nothing and the Big Bang was caused by... nothing!
However, in the next second after this event, something wonderful happened: they started. Therefore, to go back in time before the Big Bang is impossible – it simply did not exist. And then, there was no causes of the Universe, because the existence of a causal connection also takes time. God just didn't have time to create the cause of the Universe. For the Stephen Hawking all of this means the impossibility of creation and of the Creator, because it also didn't have time.
In addition, in the quantum theory of space-time may be finite in extent (to begin at the moment of the Big Bang), but do not have singularities that form a boundary or edge. The universe is thus "closed" on itself, it has no boundaries, it is completely isolated and does not interact with anything outside of yourself. But if this is so, according to Hawking, there is no need to figure out how does the space-time boundary does not need to know the initial state of the Universe. It, according to Hawking, you can neither create nor destroy. It's just there.
"While we believed that the universe had a beginning, the role of the Creator seemed clear, writes Hawking in his book "the Shortest history of time". But if the universe is really completely Autonomous, has no boundaries, no edges, no beginning and no end, the answer to the question of the role of the Creator ceases to be obvious."
Source:Naked Science
Source: /users/1077