707
The universe: end of the world in scientific interpretation
When albert Einstein developed his General theory of relativity (GTR), formulated in 1916, he proceeded from the fact that the universe is stationary. That is, she is what she is, a well-defined volume, finite but without boundaries, as there are no boundaries at the surface of the ball.

This view, developed by the early twentieth century, in fact, was not based on anything but logic and the absence of any data to refute this logic. But all were materialists because they believed in the eternal existence of matter; believed in Divine creation, because they saw no reason why the world was created is changeable.
In 1922-1924 mathematician Alexander Friedman on the basis of Einstein's equations, created the model of expanding Universe suggested that the universe had a beginning about 10 billion years ago. Friedman's work is little noticed, but in 1927 (Friedman died in 1925 from typhoid fever) this model "rediscovered" a Belgian Catholic priest, astronomer and mathematician Georges Lemaitre, who proposed the hypothesis that the universe originated from protostome.



Alexander Friedman (1888-1925); Georges Lemaitre (1894-1966); Edwin Hubble (1889-1953)
Einstein didn't believe either one, considering that from a mathematical point of view, the expanding universe has a right to exist, but to physics, and hence to reality is irrelevant. However, in 1929 the American astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered the law of red shift, a shift in the far red region of the spectrum of radiation of remote objects. According to this law, a distant galaxy is receding from us at a speed proportional to the distance to them. In other words, the farther from us a galaxy is, the faster it is removed. This picture is fully consistent with the model of the expanding Universe. And if the universe is expanding, it means that somewhere in the past she was very little, that is, when she was supposed to start.
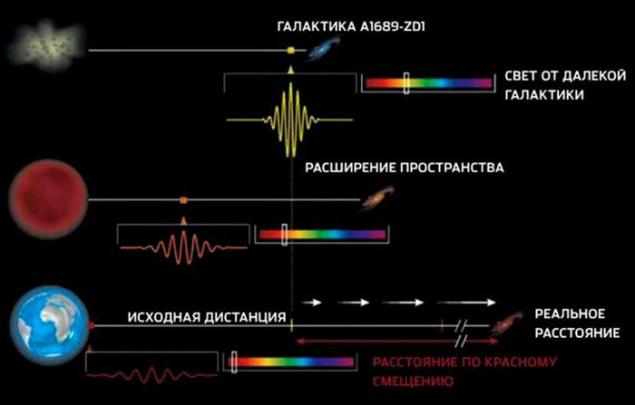
The red shift
However, Hubble made a mistake in the calculations: according to him the age of the Universe was almost less than the age of the Earth. Therefore, doubts about the origin of the Universe still remained until the 60-ies, when the possibility of astronomical observations came to a new level and was obtained updated parameters of the redshift. The scientific community finally acknowledged that fifteen to twenty billion years ago our world came out of something very small. In 1948, American physicist and astronomer of Russian origin, George Gamow proposed a model of the Universe, now called the hot Big Bang. In the framework of this model it was predicted the existence of background or CMB, left over from this explosion. In 1965 it was discovered. This is a very weak radiation in the radio frequency range and with a temperature of 2.7 ° K (if someone is forgotten, the reading on the Kelvin scale starts from absolute zero, that is, the 2.7 º K = — 270,45 º C). However, this radiation is uniformly distributed throughout the Universe and in the aggregate, has a very great energy. Figuratively we can say that the CMB is old and tired of billions of years of wandering photons are trying to tell us about the wild days of their youth, the hot stage of the early Universe. Although actually there was a clock there, what we talked about in the last article, and these billions of years for them does not exist, but in space they still had to poskitatsya.
In 1965 thanks to the work of Stephen Hawking and Roger Penrose became more or less clear that the universe arose from a singularity, that is, a region where the end of all sorts known to us the laws of this world. Actually, this is not an area at all, but the point, as no volume in our space-time it occupies. In the initial singularity, according to modern ideas, were concentrated infinite energy and perhaps infinite density.
With the idea of an expanding Universe, and therefore, that time and space have a beginning, for many decades, there was a rather fierce fight. By assumption, the same Hawking, the thought of it "many people do not like the fact that it has a hint of the intervention of divine forces" (Stephen Hawking, "a brief history of time"). The most consistent fighters against this idea was, of course, in the Soviet Union. In magazine "Questions of philosophy" in 1948, someone Karpov in his article "On the philosophical views of A. Einstein" wrote (op. CIT. by Ivan Lupandin. Lectures on the history of natural philosophy) :
In 1946, Einstein published the book "The Meaning of Relativity", which declares himself a supporter of the reactionary theory of the expanding world. In this book he tries to "scientifically prove" priestly dogma of the creation of the world [...] One of the typical speculations on the theory of relativity, in its doctrine of the so-called four-dimensional world is the denial of the three-dimensional real space, the preaching of the fourth dimension with all its attendant mysticism and devilry. The class instinct did not let down the organizers of the ideological support of Soviet science. The scientific picture of our world in the continuation of the XX century is rapidly approaching the Biblical description. Physics and astronomy of the Soviet school in question the birth of the Universe kept to the last. Only in 1970 was published a famous Soviet physicist Evgeny Lifshitz, Isaac Khalatnikov and Vladimir Belinsky, not only recognized the Big Bang theory, but also to some extent have enriched it. Imagining the decision-making mechanism in the Soviet Union, I venture to suggest that the decision to publish this work was taken at the level of the Politburo. Apparently, the accumulated scientific knowledge was not given to the Soviet ideology no way to contain the recognition is obvious to the rest of the world theory. Nevertheless, until the late 80-ies in all Soviet universities continued to study dialectical materialism, which, as you know, claimed that the universe is eternal and infinite.

In 80-e years there was the so-called inflationary model of the Universe. First, the Russian physicist Alexei Starobin and parallel Professor Massachusetts Institute of technology, Alan Guth, and then Andrei Linde, Professor at Stanford University, developed some modification of the theory of the Big Bang. The essence of the inflationary model is that at a very early stage in its development the universe is extremely fast, exponentially expanded by: Linda, for 10-35 seconds, the universe expanded at 101012 times (Andrei Linde, a lecture. Inflation, quantum cosmology and the anthropic principle). And expanded not hot stuff, but a scalar field, physical field, have a certain energy, but this energy doesn't manifest itself to the casual observer, as it has no direction. And then, this field has produced the first elementary particles of matter, both particles and antiparticles, and then we started the hot phase of the Universe.

Alexei Starobin
Earlier this year one of the research collaborations it was reported about the detection of primary gravitational waves. If this discovery becomes a discovery, then there will be confirmed by other independent scientists, it will be a direct proof that the universe really passed the stage of inflation. And there the developers of the inflation model and to the Nobel prize close! Let me remind you that the Nobel prize in physics can be awarded only to a theory confirmed experimentally. While this model explains, in particular, why is our universe so homogeneous and isotropic, i.e. identical in its properties in all directions, and also why it looks flat. And our universe really is remarkably uniform. Stars are grouped into star clusters, star clusters in galaxies, galaxies in clusters of galaxies, which, in turn, form superclusters. And if anyone managed to look at our Universe from a great height, he could see something resembling a rather elegant woven multi-layer web.
This little 7-minute film, presented to the public this spring, a compilation of the largest and most comprehensive to date, computer simulation of the evolution of the Universe from 12 million years after the Big Bang to the present day. Moreover, the model covers the formation of the macroscopic structure of the Universe and individual galaxies. The project was called Illustris. Very nice!
Moreover, this web, according to modern scientific views, is something like the surface swelling of a balloon or stretching a rubber plane. The exact configuration of the Universe remains a controversial issue, although we observed its part of the requirements of Euclidean geometry, that is, parallel lines do not intersect, therefore it is close to flat. The universe is expanding but has no center, no highlighted point from which this expansion can be measured. Each galaxy is removed from all the surrounding galaxies, as points of the pattern on the surface of the flaring ball will be removed from each other.

The balloon is inflated, the distance between the points of its surface increases
The reason for the uniformity and flatness of the Universe remains a mystery in standard model Big Bang, as if exploded, the substance of today's universe was supposed to look different. The inflationary model addresses occurred on this occasion bewilderment. According to Linda, all heterogeneity in the time of inflation were stretched in the same 101012 times, that is to become virtually invisible.
Least understood in this model there remain two questions: why inflation started, and probably the most important — why did it end? But if it's not slowed down, neither of which galaxies in our Universe, and about any substance in its present form of speech would not go. In the best case we would have (not very clear who is the "we") are scattered subatomic particles are scattered light-years from one another.
Model Andrei Linde suggests that the universe is much bigger than the part that we see. And that perhaps in other parts of the laws of physics can be quite different, in fact we are talking about many universes with different properties. But this is megamerge how about other variations on this theme, we will talk separately. Meantime, let's say that in one degree or another with this model ready to accept the majority of those scientists who has any relevance to cosmology.
Our universe continues to expand. And, as it turned out in 1998, again with acceleration. Until 1998, when scientific observations are reliably confirmed this accelerated expansion, cosmologists considered three possible scenarios for the behavior of the Universe, which at the time offered Alexander Friedman. First — the universe is expanding infinitely, and the rate of expansion will never tend to zero, so this speed would not decrease but may increase. Second, the universe expands forever, but the rate of expansion tends to zero, that is, the expansion will slow down, but to the end and will not stop. And the third universe to a point in expanding, but then starts to shrink to the original point. The third scenario was the basis of the so-called theory of pulsating Universe, one of the varieties of ideas about an eternal Universe: it is, according to supporters, always pulsing, then shrinking, then expanding. To date, this script apparently has lost its relevance.
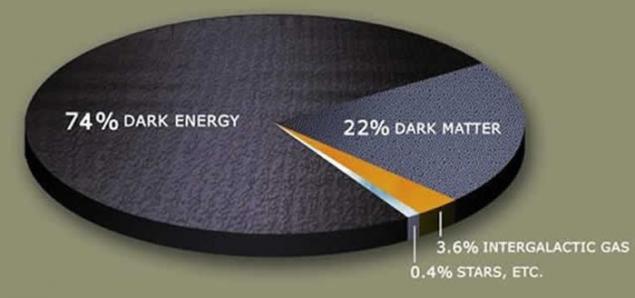
The fact of the accelerated expansion of the Universe, which again after a period of braking began about 5 billion years ago, the scientific world linked with the existence of dark energy. The calculations made by scientists, showed that the structure of the observable part of our world is as follows: approximately 74% of it consists of dark energy, the nature of which is not known, 22% is dark matter, whose existence scientists have known already some time ago, but its nature is not clear, and less than 5% is familiar to us the visible matter. And dark energy is not very large, but negative pressure, that is, it pushes the substance, thus forcing the galaxy to rapidly scatter. It is uniformly distributed throughout the space, including all directly surrounding us and ourselves. On this basis, have built scenarios for the future of the Universe in which all matter will be torn to tiny shreds.
So what do we know about the Universe, if more than 95% of it is "dark mass"?
The adjective "dark" in relation to energy and matter (sometimes referred to as dark mass, although their nature is obviously different) means that they practically do not interact with ordinary matter, from which we are all highly complex scientific instruments created by mankind. So they do not manifest themselves before us, except for their gravitational properties. However, in the case of dark energy, perhaps, worthwhile to say anti-gravity.
But back to the story about singularities, which I mentioned just above. STO, in contrast to General relativity, does not take into account gravitational effects. In our history, with the exploding star, discussed in the previous article, we talked about these effects is not even mentioned, although astronomers discovered a distant star, most likely in some way to account for them in their calculations. But in our reasoning gravity is unlikely to be made significant changes.
And in the story of the singularities without gravity we already can not do. The greatest discovery of albert Einstein is that he by some incredible instinctively realized that gravity leads to curvature of space-time. Usually, to show how it looks like, popularizers of science give an example of a massive body (e.g. very big weight) on the trampoline.
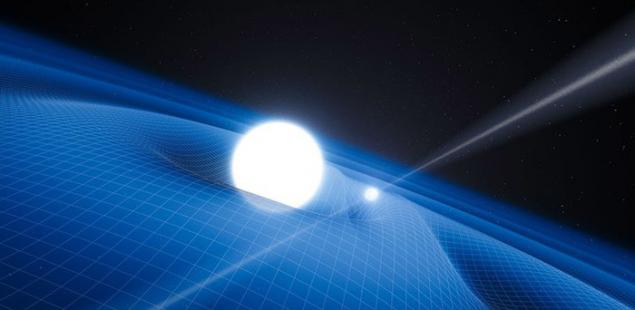
Gravity bends space
This body pushes the elastic surface of the trampoline, and if on a curved surface is to put a small ball, he would simply slide to the weight. Of course, in our reality we are not dealing with a plane, which is a stretched trampoline, and the three-dimensional space or, more precisely, with four-dimensional geometry of space-time. Imagine all this clearly is almost impossible.
Therefore, we can just believe that, for example, our Earth in space-time is moving not on a curve around the Sun and tries to fly past the Sun in a straight line. But the Sun his weight so warps space-time in three-dimensional space the Earth moves in a circular orbit. And light rays in gravitational fields also apply for, and geodetic lines (as on the surface of the Earth). And time near massive bodies is slower than at a distance: all navigation systems using satellite, including the currently fashionable car navigation, this effect should be considered, otherwise the error can amount to several kilometers.
But the more massive a body is, the more it warps space-time, the more attracts nearby matter, causing only increases its own mass. And at some point the gravitational influence of the body begins to tend to infinity, in and by itself: this body is trying to shrink to a point. This happens with a massive (just a few times the mass of our Sun, and it is considered to be very small, compact and cozy, you might say, home) stars. In the initial phases of matter desperately resists the impending collapse: the first is a thermonuclear reaction, then some quantum effects that do not allow the star to die easily. But sooner or later, any massive star, reaching incredible, from our ordinary point of view, density, heats up with up to tremendous temperatures and explode. This is called a supernova explosion. At the same time in the surrounding area will be ejected large amounts of matter and energy, but if after such a weight it weight will be more than just a few times the mass of our Sun, alas, most likely, this place becomes a black hole.
In other words, such a star collapses into a point, which will not remain even a tiny place in our space. But this does not mean that she will completely disappear in this world. This is not so. But the curvature of space-time at this point is so strong that the space-time here will be destroyed. This point and called space-time singularity. There was nothing to see and not to measure. Contact with human consciousness then is interrupted. However, the singularity of black holes is fundamentally different from the singularity, the beginning of our Universe, and about it we will talk in more detail, discussing such a thing as entropy.
Now note that the impact of the singularity of a black hole on the surrounding space is maintained despite the fact that the point itself will be actually outside of our space-time. Around it will be a realm in which because of the extraordinary strength of the gravitational field cannot escape, even light. Because of that, this region is called a black hole. A conditional that can not escape the captive light is called the event horizon of a black hole. And here, on this horizon, time behaves quite unusual for us. For example, for an external observer an object falling into a black hole, forever(!) will crash on this line. It is dangerous along the horizon, but never, I repeat, never cross: the time from the point of view of an external observer, will stop. Although he is falling into the hole object even if it is a sentient being, say, an astronaut in the first moments no change either in ourselves or around ourselves won't notice (if, of course, by that time will not die from the sheer overload). And his watch will continue to go the usual way.

So with black holes so...
Naturally, outside of its event horizon black holes have an intense gravitational field, although light is already able to escape from them. Because of this they can be observed: glowing tongues heated to very high temperatures swallow their substance. Black holes are greedy and try to absorb everything that approaches them. Their weight continues to increase, which in turn increases their appetite.
Every self-respecting galaxy, as scientists believe, must have a massive black hole in the center. It is believed that our galaxy, the milky way — such a hole is a cosmic object "Sagittarius a*". Its mass is estimated at about 4 million solar masses. Apparently, there are in our galaxy and other black holes, the mass is smaller, according to some estimates, almost tens of millions of such holes. Due to the fact that, with its incredible mass black holes have a relatively small size, and the force of gravity with distance (proportional to the square of the distance) is substantially reduced, they didn't absorb until now, all matter in the galaxy. But the business goes slowly. The most likely scenario for the future evolution of the Universe is that in ten or twenty billion years we are now all visible galaxies will turn into black holes. Nearby pre-merge into a single galaxy. Long-term, if the expansion of the Universe will not stop, will break the speed of light to infinity, and then, as black holes will evaporate because of the so-called Hawking radiation of many trillions and trillions of years until they are completely gone. Or there will be a Large gap — this is when all matter will be torn apart by the dark energy, as I mentioned just above. But if for some reason the extension will cease and the universe will start to shrink, it ends the so-called Big crunch. As you can see, all terms have already been prepared. That is, all matter (= energy) again collapses to a single singular point.
Any of these scenarios means the end of our Universe. The end of the world in scientific interpretation. The end of forever, without any hope. The whole social optimism cosmologists is that perhaps our world is not the only one. And it is possible that somewhere, sometime in other worlds, which, however, we do not and cannot be any connection may occur or has already occurred the conditions are suitable for sustaining other forms of life, and hence, perhaps, and mind. About the kind of models I will talk a little later, at least in order to not give too much cause for accusations of bias. But they are unlikely to bring significant additions to the argument: our world is not left by any chance. And it is the use of entropy — his curse.
The inglorious end of the Universe. Even black holes will evaporate, and will remain isolated photons, electrons and even number of elementary particles not interacting with each other. Most likely, such a universe will continue to expand forever, but, in fact, she's already dead. Kazimir Malevich, I think, meant something else, though... posted
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.cablook.com/universe/vselennaya-konets-sveta-v-nauchnoj-interpretatsii/

This view, developed by the early twentieth century, in fact, was not based on anything but logic and the absence of any data to refute this logic. But all were materialists because they believed in the eternal existence of matter; believed in Divine creation, because they saw no reason why the world was created is changeable.
In 1922-1924 mathematician Alexander Friedman on the basis of Einstein's equations, created the model of expanding Universe suggested that the universe had a beginning about 10 billion years ago. Friedman's work is little noticed, but in 1927 (Friedman died in 1925 from typhoid fever) this model "rediscovered" a Belgian Catholic priest, astronomer and mathematician Georges Lemaitre, who proposed the hypothesis that the universe originated from protostome.



Alexander Friedman (1888-1925); Georges Lemaitre (1894-1966); Edwin Hubble (1889-1953)
Einstein didn't believe either one, considering that from a mathematical point of view, the expanding universe has a right to exist, but to physics, and hence to reality is irrelevant. However, in 1929 the American astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered the law of red shift, a shift in the far red region of the spectrum of radiation of remote objects. According to this law, a distant galaxy is receding from us at a speed proportional to the distance to them. In other words, the farther from us a galaxy is, the faster it is removed. This picture is fully consistent with the model of the expanding Universe. And if the universe is expanding, it means that somewhere in the past she was very little, that is, when she was supposed to start.

The red shift
However, Hubble made a mistake in the calculations: according to him the age of the Universe was almost less than the age of the Earth. Therefore, doubts about the origin of the Universe still remained until the 60-ies, when the possibility of astronomical observations came to a new level and was obtained updated parameters of the redshift. The scientific community finally acknowledged that fifteen to twenty billion years ago our world came out of something very small. In 1948, American physicist and astronomer of Russian origin, George Gamow proposed a model of the Universe, now called the hot Big Bang. In the framework of this model it was predicted the existence of background or CMB, left over from this explosion. In 1965 it was discovered. This is a very weak radiation in the radio frequency range and with a temperature of 2.7 ° K (if someone is forgotten, the reading on the Kelvin scale starts from absolute zero, that is, the 2.7 º K = — 270,45 º C). However, this radiation is uniformly distributed throughout the Universe and in the aggregate, has a very great energy. Figuratively we can say that the CMB is old and tired of billions of years of wandering photons are trying to tell us about the wild days of their youth, the hot stage of the early Universe. Although actually there was a clock there, what we talked about in the last article, and these billions of years for them does not exist, but in space they still had to poskitatsya.
In 1965 thanks to the work of Stephen Hawking and Roger Penrose became more or less clear that the universe arose from a singularity, that is, a region where the end of all sorts known to us the laws of this world. Actually, this is not an area at all, but the point, as no volume in our space-time it occupies. In the initial singularity, according to modern ideas, were concentrated infinite energy and perhaps infinite density.
With the idea of an expanding Universe, and therefore, that time and space have a beginning, for many decades, there was a rather fierce fight. By assumption, the same Hawking, the thought of it "many people do not like the fact that it has a hint of the intervention of divine forces" (Stephen Hawking, "a brief history of time"). The most consistent fighters against this idea was, of course, in the Soviet Union. In magazine "Questions of philosophy" in 1948, someone Karpov in his article "On the philosophical views of A. Einstein" wrote (op. CIT. by Ivan Lupandin. Lectures on the history of natural philosophy) :
In 1946, Einstein published the book "The Meaning of Relativity", which declares himself a supporter of the reactionary theory of the expanding world. In this book he tries to "scientifically prove" priestly dogma of the creation of the world [...] One of the typical speculations on the theory of relativity, in its doctrine of the so-called four-dimensional world is the denial of the three-dimensional real space, the preaching of the fourth dimension with all its attendant mysticism and devilry. The class instinct did not let down the organizers of the ideological support of Soviet science. The scientific picture of our world in the continuation of the XX century is rapidly approaching the Biblical description. Physics and astronomy of the Soviet school in question the birth of the Universe kept to the last. Only in 1970 was published a famous Soviet physicist Evgeny Lifshitz, Isaac Khalatnikov and Vladimir Belinsky, not only recognized the Big Bang theory, but also to some extent have enriched it. Imagining the decision-making mechanism in the Soviet Union, I venture to suggest that the decision to publish this work was taken at the level of the Politburo. Apparently, the accumulated scientific knowledge was not given to the Soviet ideology no way to contain the recognition is obvious to the rest of the world theory. Nevertheless, until the late 80-ies in all Soviet universities continued to study dialectical materialism, which, as you know, claimed that the universe is eternal and infinite.

In 80-e years there was the so-called inflationary model of the Universe. First, the Russian physicist Alexei Starobin and parallel Professor Massachusetts Institute of technology, Alan Guth, and then Andrei Linde, Professor at Stanford University, developed some modification of the theory of the Big Bang. The essence of the inflationary model is that at a very early stage in its development the universe is extremely fast, exponentially expanded by: Linda, for 10-35 seconds, the universe expanded at 101012 times (Andrei Linde, a lecture. Inflation, quantum cosmology and the anthropic principle). And expanded not hot stuff, but a scalar field, physical field, have a certain energy, but this energy doesn't manifest itself to the casual observer, as it has no direction. And then, this field has produced the first elementary particles of matter, both particles and antiparticles, and then we started the hot phase of the Universe.

Alexei Starobin
Earlier this year one of the research collaborations it was reported about the detection of primary gravitational waves. If this discovery becomes a discovery, then there will be confirmed by other independent scientists, it will be a direct proof that the universe really passed the stage of inflation. And there the developers of the inflation model and to the Nobel prize close! Let me remind you that the Nobel prize in physics can be awarded only to a theory confirmed experimentally. While this model explains, in particular, why is our universe so homogeneous and isotropic, i.e. identical in its properties in all directions, and also why it looks flat. And our universe really is remarkably uniform. Stars are grouped into star clusters, star clusters in galaxies, galaxies in clusters of galaxies, which, in turn, form superclusters. And if anyone managed to look at our Universe from a great height, he could see something resembling a rather elegant woven multi-layer web.
This little 7-minute film, presented to the public this spring, a compilation of the largest and most comprehensive to date, computer simulation of the evolution of the Universe from 12 million years after the Big Bang to the present day. Moreover, the model covers the formation of the macroscopic structure of the Universe and individual galaxies. The project was called Illustris. Very nice!
Moreover, this web, according to modern scientific views, is something like the surface swelling of a balloon or stretching a rubber plane. The exact configuration of the Universe remains a controversial issue, although we observed its part of the requirements of Euclidean geometry, that is, parallel lines do not intersect, therefore it is close to flat. The universe is expanding but has no center, no highlighted point from which this expansion can be measured. Each galaxy is removed from all the surrounding galaxies, as points of the pattern on the surface of the flaring ball will be removed from each other.

The balloon is inflated, the distance between the points of its surface increases
The reason for the uniformity and flatness of the Universe remains a mystery in standard model Big Bang, as if exploded, the substance of today's universe was supposed to look different. The inflationary model addresses occurred on this occasion bewilderment. According to Linda, all heterogeneity in the time of inflation were stretched in the same 101012 times, that is to become virtually invisible.
Least understood in this model there remain two questions: why inflation started, and probably the most important — why did it end? But if it's not slowed down, neither of which galaxies in our Universe, and about any substance in its present form of speech would not go. In the best case we would have (not very clear who is the "we") are scattered subatomic particles are scattered light-years from one another.
Model Andrei Linde suggests that the universe is much bigger than the part that we see. And that perhaps in other parts of the laws of physics can be quite different, in fact we are talking about many universes with different properties. But this is megamerge how about other variations on this theme, we will talk separately. Meantime, let's say that in one degree or another with this model ready to accept the majority of those scientists who has any relevance to cosmology.
Our universe continues to expand. And, as it turned out in 1998, again with acceleration. Until 1998, when scientific observations are reliably confirmed this accelerated expansion, cosmologists considered three possible scenarios for the behavior of the Universe, which at the time offered Alexander Friedman. First — the universe is expanding infinitely, and the rate of expansion will never tend to zero, so this speed would not decrease but may increase. Second, the universe expands forever, but the rate of expansion tends to zero, that is, the expansion will slow down, but to the end and will not stop. And the third universe to a point in expanding, but then starts to shrink to the original point. The third scenario was the basis of the so-called theory of pulsating Universe, one of the varieties of ideas about an eternal Universe: it is, according to supporters, always pulsing, then shrinking, then expanding. To date, this script apparently has lost its relevance.
The fact of the accelerated expansion of the Universe, which again after a period of braking began about 5 billion years ago, the scientific world linked with the existence of dark energy. The calculations made by scientists, showed that the structure of the observable part of our world is as follows: approximately 74% of it consists of dark energy, the nature of which is not known, 22% is dark matter, whose existence scientists have known already some time ago, but its nature is not clear, and less than 5% is familiar to us the visible matter. And dark energy is not very large, but negative pressure, that is, it pushes the substance, thus forcing the galaxy to rapidly scatter. It is uniformly distributed throughout the space, including all directly surrounding us and ourselves. On this basis, have built scenarios for the future of the Universe in which all matter will be torn to tiny shreds.

So what do we know about the Universe, if more than 95% of it is "dark mass"?
The adjective "dark" in relation to energy and matter (sometimes referred to as dark mass, although their nature is obviously different) means that they practically do not interact with ordinary matter, from which we are all highly complex scientific instruments created by mankind. So they do not manifest themselves before us, except for their gravitational properties. However, in the case of dark energy, perhaps, worthwhile to say anti-gravity.
But back to the story about singularities, which I mentioned just above. STO, in contrast to General relativity, does not take into account gravitational effects. In our history, with the exploding star, discussed in the previous article, we talked about these effects is not even mentioned, although astronomers discovered a distant star, most likely in some way to account for them in their calculations. But in our reasoning gravity is unlikely to be made significant changes.
And in the story of the singularities without gravity we already can not do. The greatest discovery of albert Einstein is that he by some incredible instinctively realized that gravity leads to curvature of space-time. Usually, to show how it looks like, popularizers of science give an example of a massive body (e.g. very big weight) on the trampoline.

Gravity bends space
This body pushes the elastic surface of the trampoline, and if on a curved surface is to put a small ball, he would simply slide to the weight. Of course, in our reality we are not dealing with a plane, which is a stretched trampoline, and the three-dimensional space or, more precisely, with four-dimensional geometry of space-time. Imagine all this clearly is almost impossible.
Therefore, we can just believe that, for example, our Earth in space-time is moving not on a curve around the Sun and tries to fly past the Sun in a straight line. But the Sun his weight so warps space-time in three-dimensional space the Earth moves in a circular orbit. And light rays in gravitational fields also apply for, and geodetic lines (as on the surface of the Earth). And time near massive bodies is slower than at a distance: all navigation systems using satellite, including the currently fashionable car navigation, this effect should be considered, otherwise the error can amount to several kilometers.
But the more massive a body is, the more it warps space-time, the more attracts nearby matter, causing only increases its own mass. And at some point the gravitational influence of the body begins to tend to infinity, in and by itself: this body is trying to shrink to a point. This happens with a massive (just a few times the mass of our Sun, and it is considered to be very small, compact and cozy, you might say, home) stars. In the initial phases of matter desperately resists the impending collapse: the first is a thermonuclear reaction, then some quantum effects that do not allow the star to die easily. But sooner or later, any massive star, reaching incredible, from our ordinary point of view, density, heats up with up to tremendous temperatures and explode. This is called a supernova explosion. At the same time in the surrounding area will be ejected large amounts of matter and energy, but if after such a weight it weight will be more than just a few times the mass of our Sun, alas, most likely, this place becomes a black hole.
In other words, such a star collapses into a point, which will not remain even a tiny place in our space. But this does not mean that she will completely disappear in this world. This is not so. But the curvature of space-time at this point is so strong that the space-time here will be destroyed. This point and called space-time singularity. There was nothing to see and not to measure. Contact with human consciousness then is interrupted. However, the singularity of black holes is fundamentally different from the singularity, the beginning of our Universe, and about it we will talk in more detail, discussing such a thing as entropy.
Now note that the impact of the singularity of a black hole on the surrounding space is maintained despite the fact that the point itself will be actually outside of our space-time. Around it will be a realm in which because of the extraordinary strength of the gravitational field cannot escape, even light. Because of that, this region is called a black hole. A conditional that can not escape the captive light is called the event horizon of a black hole. And here, on this horizon, time behaves quite unusual for us. For example, for an external observer an object falling into a black hole, forever(!) will crash on this line. It is dangerous along the horizon, but never, I repeat, never cross: the time from the point of view of an external observer, will stop. Although he is falling into the hole object even if it is a sentient being, say, an astronaut in the first moments no change either in ourselves or around ourselves won't notice (if, of course, by that time will not die from the sheer overload). And his watch will continue to go the usual way.

So with black holes so...
Naturally, outside of its event horizon black holes have an intense gravitational field, although light is already able to escape from them. Because of this they can be observed: glowing tongues heated to very high temperatures swallow their substance. Black holes are greedy and try to absorb everything that approaches them. Their weight continues to increase, which in turn increases their appetite.
Every self-respecting galaxy, as scientists believe, must have a massive black hole in the center. It is believed that our galaxy, the milky way — such a hole is a cosmic object "Sagittarius a*". Its mass is estimated at about 4 million solar masses. Apparently, there are in our galaxy and other black holes, the mass is smaller, according to some estimates, almost tens of millions of such holes. Due to the fact that, with its incredible mass black holes have a relatively small size, and the force of gravity with distance (proportional to the square of the distance) is substantially reduced, they didn't absorb until now, all matter in the galaxy. But the business goes slowly. The most likely scenario for the future evolution of the Universe is that in ten or twenty billion years we are now all visible galaxies will turn into black holes. Nearby pre-merge into a single galaxy. Long-term, if the expansion of the Universe will not stop, will break the speed of light to infinity, and then, as black holes will evaporate because of the so-called Hawking radiation of many trillions and trillions of years until they are completely gone. Or there will be a Large gap — this is when all matter will be torn apart by the dark energy, as I mentioned just above. But if for some reason the extension will cease and the universe will start to shrink, it ends the so-called Big crunch. As you can see, all terms have already been prepared. That is, all matter (= energy) again collapses to a single singular point.
Any of these scenarios means the end of our Universe. The end of the world in scientific interpretation. The end of forever, without any hope. The whole social optimism cosmologists is that perhaps our world is not the only one. And it is possible that somewhere, sometime in other worlds, which, however, we do not and cannot be any connection may occur or has already occurred the conditions are suitable for sustaining other forms of life, and hence, perhaps, and mind. About the kind of models I will talk a little later, at least in order to not give too much cause for accusations of bias. But they are unlikely to bring significant additions to the argument: our world is not left by any chance. And it is the use of entropy — his curse.
The inglorious end of the Universe. Even black holes will evaporate, and will remain isolated photons, electrons and even number of elementary particles not interacting with each other. Most likely, such a universe will continue to expand forever, but, in fact, she's already dead. Kazimir Malevich, I think, meant something else, though... posted
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.cablook.com/universe/vselennaya-konets-sveta-v-nauchnoj-interpretatsii/