765
Black holes
Despite the fact that the whole of these interesting objects is still very little is known, "the mysterious" they can already be called a stretch.
The term black hole is an object, gravity along the border and inside of which is so great that leave this facility may not even photons. In other words, not even light is able to break out of the black holes, hence this tragic-poetic name. The border, after crossing which is no longer possible to leave the black hole is called the event horizon. Equally poetic, is not it? Strictly speaking, there is no black hole surface or some other real border. What happens to the substance inside the event horizon, nobody knows, so it can be conditionally considered as "surface."
5 photos

Modern science believes that there are three kinds of black holes:
Microscopic - quantum - BH
Supermassive black hole (10 ^ 5-10 ^ 10 solar masses) which are cores of most galaxies
BH stellar masses (3-100 solar masses)
Some time ago, also spoke about the "middle" of the black hole, but their existence is hotly debated: in particular, found a satisfactory explanation of the mechanism of their formation. In this article, we will focus on "regular" and the supermassive black holes, the existence of which is considered to be completely vindicated.
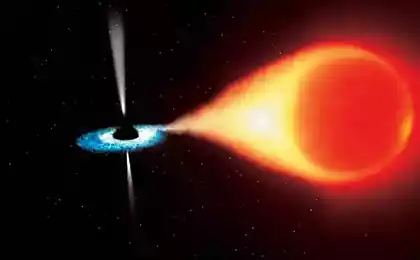
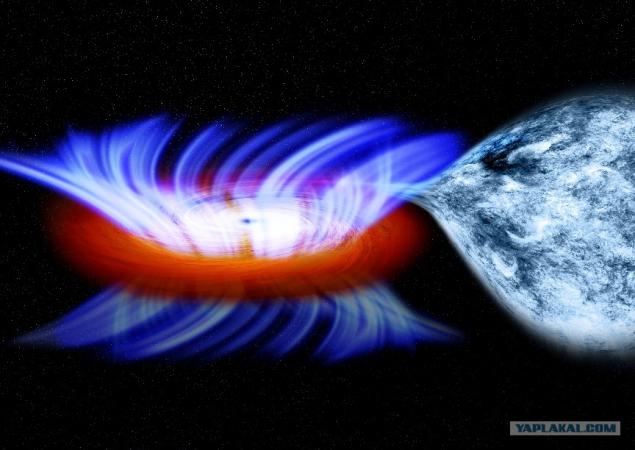
Formally, themselves black hole totally invisible (just because even light can not escape their limits). However, due to the gravitational pull of the giant black hole surrounded by an accretion disk, consisting of interstellar gas, dust and other failures occurred near objects.
In the process of falling accumulated matter of which it consists disc is twisted helically around BH gaining a tremendous speed and heats, whereby accretion disk emits ultraviolet and X-ray spectrum. It can detect radiation and black holes in the depths of space.
In the minds of many black holes are mysterious and overwhelming epitome infernal abyss. But not all matter orbiting a black hole, it is absorbed. Part of the accretion disk of matter emitted in the form of cosmic wind as a result of intense heat and high speeds. For example, in 2011, it was found that the stellar black hole IGR J17091-3624 periodically emits the fastest known today like "the wind": its speed reaches about 30 million km / h, which is 3% of the speed of light.
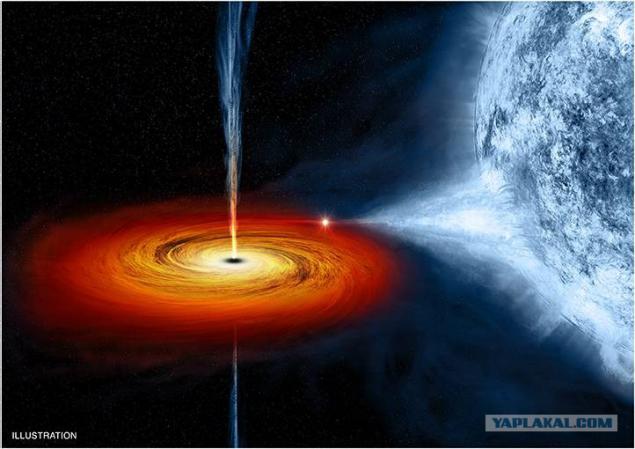
In addition, black holes also have the property of emitting substance in the form of plasma emission narrowly focused, aimed at both poles of the "rotation perpendicular to the plane of the accretion disk. It looks like the axis on which the planted disk. These emissions are called jets [Eng. jet], or relativistic jets. The mechanism of their formation is still poorly understood. In supermassive black holes power jets of radiation such that it can stop the flow of interstellar gas in the galactic center of the cluster. The rate of emission of jets several times higher speed "wind».

Statistically, the black holes of stellar mass should be the most common kind in the universe. In fact, it is a form of post-mortem existence of cooled stars. However, not every star after his death, is transformed into an infinite sink of all things. Theoretical calculations predict that only if the star has a mass of at least 3-6 times more solar, then it has a chance to become the standard absorbent.
The mechanism of degeneration of stars in a black hole takes place, according to the scientists, the following scenario. On the matter inside the star are two opposite forces: compression (gravity) and expansion (thermonuclear reaction). In fact, any star of the time in a state of precarious equilibrium in which gravitational compression is compensated by a constant fusion "wildness." However, with the passage of time, the concentration of substances that serve as fuel for nuclear fusion in the core of the star falls. The balance of power is broken, and the nucleus begins to rapidly shrink and condense. The outer layer, "burn out" and begins to shrink, actually falling into the nucleus. Here history may go different ways - it depends on, inter alia, by weight of the star. One of these ways is the explosion of a star as a result of the fall in the core and the shell becoming a supernova. With the explosion of the star finally compressed to a diameter of 20-30 km, while gaining tremendous density. The resulting object has such a strong gravitational field that near the event horizon is curved space-time. It should be manifested, for example, the bending of light rays.
According to Schwarzschild solution of Birkhoff's theorem, the radius of a spherical horse in a vacuum spherical event horizon of the black star is determined by the formula:
R = 2GM / c2, where G - gravitational constant, M - mass of the star, c - the speed of light.
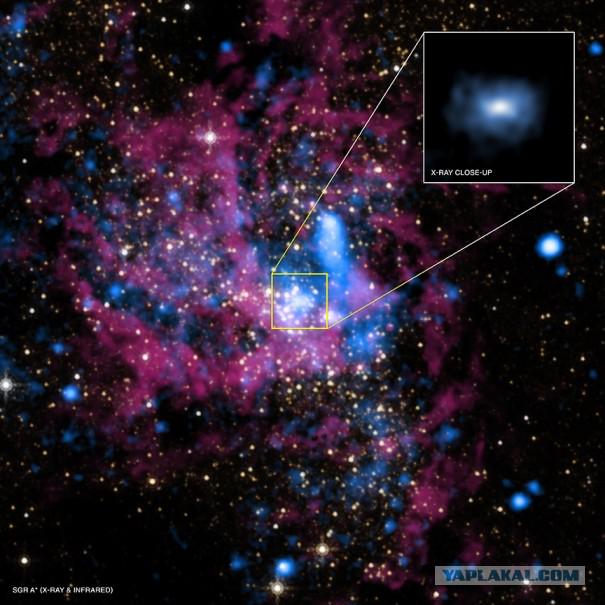
Thus, to our sun turned into a black hole, it must be compressed to 6 km in diameter (instead of 1 392 000 km). As you know, this black star of the newborn has an incredible density. However, with increasing mass density decreases, with this dependence is nonlinear. If "normal" black star is compressed to a state of "core to the core", the supermassive black holes weighing 105-1010, is at the core of galactic clusters, have a density comparable to the most common substances known to us. For example, a black hole with a mass of 1 billion solar (and this is not the champion in the heavyweight division!) Will have a density of about 18, 5 kg / m3, which is only 10 times the density of air. Sagittarius A * (Sagittarius A *), located 26 000 light-years away. Presumably, this is the supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Weight - about 4 million solar. The density is about 100 times higher than the density of lead.
M84, a massive galaxy in the constellation Virgo located 55 million light-years away. Here you can see an example of the work jets supermassive black hole.
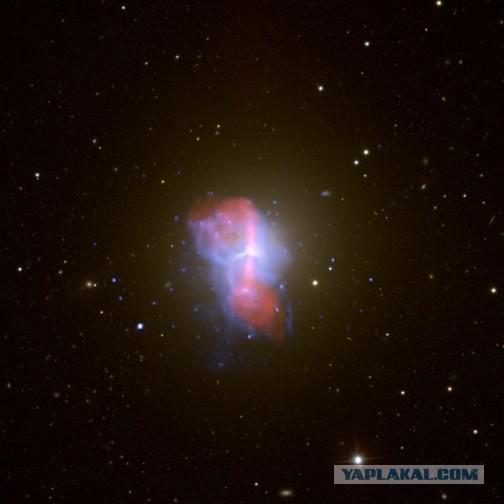

NGC 6240, a dual system of supermassive black holes in the process of merging. While there is no solid hypotheses of what happens in such cases, as opposed to, say, the collision of stars and supermassive black holes. It is believed that at the time of the merger of massive black holes appear the strongest gravitational waves in the universe.
Posted in [mergetime] 1378710143 [/ mergetime]
How does fall into a black hole? Logic dictates that if an object falls just one day disappear in the darkness of the event horizon. However, it is not. When approaching the event horizon of the object is elongated in the radial direction and contract in a transverse direction. Having reached the point of no return, the object is extremely elongated, slow down and fall asleep. This is due to the fact that no radiation, including in the optical range is not able to move beyond the event horizon. For most falling body fall subjectively never come in connection with an infinite time dilation.
Recent studies of Stephen Hawking say that nothing lasts forever in terms of quantum physics, black holes still lose energy by themselves, and not only due to collisions of accretion disks. This hypothetical effect is called Hawking radiation. If the theory is correct, then, in the absence of feeding matter, eventually the black hole must be faster to lose energy and eventually explode. However, the quantum theory as a whole is worked so superficial that the theory of Hawking generally creates more questions than assumptions.
All ...

Source:
The term black hole is an object, gravity along the border and inside of which is so great that leave this facility may not even photons. In other words, not even light is able to break out of the black holes, hence this tragic-poetic name. The border, after crossing which is no longer possible to leave the black hole is called the event horizon. Equally poetic, is not it? Strictly speaking, there is no black hole surface or some other real border. What happens to the substance inside the event horizon, nobody knows, so it can be conditionally considered as "surface."
5 photos

Modern science believes that there are three kinds of black holes:
Microscopic - quantum - BH
Supermassive black hole (10 ^ 5-10 ^ 10 solar masses) which are cores of most galaxies
BH stellar masses (3-100 solar masses)
Some time ago, also spoke about the "middle" of the black hole, but their existence is hotly debated: in particular, found a satisfactory explanation of the mechanism of their formation. In this article, we will focus on "regular" and the supermassive black holes, the existence of which is considered to be completely vindicated.
Formally, themselves black hole totally invisible (just because even light can not escape their limits). However, due to the gravitational pull of the giant black hole surrounded by an accretion disk, consisting of interstellar gas, dust and other failures occurred near objects.
In the process of falling accumulated matter of which it consists disc is twisted helically around BH gaining a tremendous speed and heats, whereby accretion disk emits ultraviolet and X-ray spectrum. It can detect radiation and black holes in the depths of space.
In the minds of many black holes are mysterious and overwhelming epitome infernal abyss. But not all matter orbiting a black hole, it is absorbed. Part of the accretion disk of matter emitted in the form of cosmic wind as a result of intense heat and high speeds. For example, in 2011, it was found that the stellar black hole IGR J17091-3624 periodically emits the fastest known today like "the wind": its speed reaches about 30 million km / h, which is 3% of the speed of light.
In addition, black holes also have the property of emitting substance in the form of plasma emission narrowly focused, aimed at both poles of the "rotation perpendicular to the plane of the accretion disk. It looks like the axis on which the planted disk. These emissions are called jets [Eng. jet], or relativistic jets. The mechanism of their formation is still poorly understood. In supermassive black holes power jets of radiation such that it can stop the flow of interstellar gas in the galactic center of the cluster. The rate of emission of jets several times higher speed "wind».

Statistically, the black holes of stellar mass should be the most common kind in the universe. In fact, it is a form of post-mortem existence of cooled stars. However, not every star after his death, is transformed into an infinite sink of all things. Theoretical calculations predict that only if the star has a mass of at least 3-6 times more solar, then it has a chance to become the standard absorbent.
The mechanism of degeneration of stars in a black hole takes place, according to the scientists, the following scenario. On the matter inside the star are two opposite forces: compression (gravity) and expansion (thermonuclear reaction). In fact, any star of the time in a state of precarious equilibrium in which gravitational compression is compensated by a constant fusion "wildness." However, with the passage of time, the concentration of substances that serve as fuel for nuclear fusion in the core of the star falls. The balance of power is broken, and the nucleus begins to rapidly shrink and condense. The outer layer, "burn out" and begins to shrink, actually falling into the nucleus. Here history may go different ways - it depends on, inter alia, by weight of the star. One of these ways is the explosion of a star as a result of the fall in the core and the shell becoming a supernova. With the explosion of the star finally compressed to a diameter of 20-30 km, while gaining tremendous density. The resulting object has such a strong gravitational field that near the event horizon is curved space-time. It should be manifested, for example, the bending of light rays.
According to Schwarzschild solution of Birkhoff's theorem, the radius of a spherical horse in a vacuum spherical event horizon of the black star is determined by the formula:
R = 2GM / c2, where G - gravitational constant, M - mass of the star, c - the speed of light.
Thus, to our sun turned into a black hole, it must be compressed to 6 km in diameter (instead of 1 392 000 km). As you know, this black star of the newborn has an incredible density. However, with increasing mass density decreases, with this dependence is nonlinear. If "normal" black star is compressed to a state of "core to the core", the supermassive black holes weighing 105-1010, is at the core of galactic clusters, have a density comparable to the most common substances known to us. For example, a black hole with a mass of 1 billion solar (and this is not the champion in the heavyweight division!) Will have a density of about 18, 5 kg / m3, which is only 10 times the density of air. Sagittarius A * (Sagittarius A *), located 26 000 light-years away. Presumably, this is the supermassive black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Weight - about 4 million solar. The density is about 100 times higher than the density of lead.

M84, a massive galaxy in the constellation Virgo located 55 million light-years away. Here you can see an example of the work jets supermassive black hole.

NGC 6240, a dual system of supermassive black holes in the process of merging. While there is no solid hypotheses of what happens in such cases, as opposed to, say, the collision of stars and supermassive black holes. It is believed that at the time of the merger of massive black holes appear the strongest gravitational waves in the universe.
Posted in [mergetime] 1378710143 [/ mergetime]
How does fall into a black hole? Logic dictates that if an object falls just one day disappear in the darkness of the event horizon. However, it is not. When approaching the event horizon of the object is elongated in the radial direction and contract in a transverse direction. Having reached the point of no return, the object is extremely elongated, slow down and fall asleep. This is due to the fact that no radiation, including in the optical range is not able to move beyond the event horizon. For most falling body fall subjectively never come in connection with an infinite time dilation.
Recent studies of Stephen Hawking say that nothing lasts forever in terms of quantum physics, black holes still lose energy by themselves, and not only due to collisions of accretion disks. This hypothetical effect is called Hawking radiation. If the theory is correct, then, in the absence of feeding matter, eventually the black hole must be faster to lose energy and eventually explode. However, the quantum theory as a whole is worked so superficial that the theory of Hawking generally creates more questions than assumptions.
All ...

Source: