1374
Black holes continue to surprise us
1. Our ancestors could easily see a black hole in the Milky Way
About 2 million. Years ago in the center of our galaxy broke a supermassive black hole. Our ancestors most likely were able to observe the luminous object. Now this black hole is not lit, but then she was an active galactic nucleus (AGN), ie a compact center of the galaxy, producing energy and illuminates everything around. The black hole can be a source of AGN because its gravitational field attracts matter, forming a disk, which heats up and glows.

2. Not every "space generator" is a black hole
For decades, many scientists believed that ultramoschnye X-ray sources (ULX) - is the result of absorption of black holes of stars or other matter. The larger the black hole, the more it consumes, the more powerful radiation. That was the theory. Then, in a nearby galaxy M82, astronomers discovered accidentally pulsating source ULX. The problem is that the pulse is not black holes, pulsars and (rotating neutron stars). But pulsars in the galaxy M82 is 100 times brighter than in accordance with their weight (physical principle "Eddington limit"). It can not be a source of ULX. Therefore, astronomers do not consider that each source ULX or "cosmic generator" is a black hole.

3. Black holes are more "gluttonous" than expected
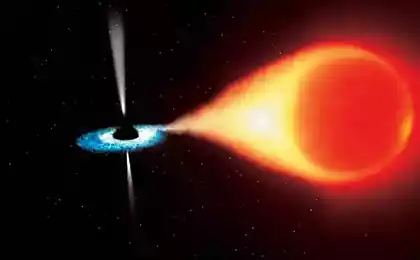
Until recently, scientists believed that the size of the black hole is determined by the maximum rate at which it can absorb / produce radiation ("Eddington limit"). Already found a black hole in the galaxy P13 NGC7793, which revolves around the supergiant star, absorbing it. P13 gas facility attracts its companion star is 10 times faster than previously thought. It is believed that the black hole is 15 times smaller than the Sun, but a million times brighter. As the pulsar M82, P13 is ULX, which is not only contrary to the "Eddington limit", but it completely denies.
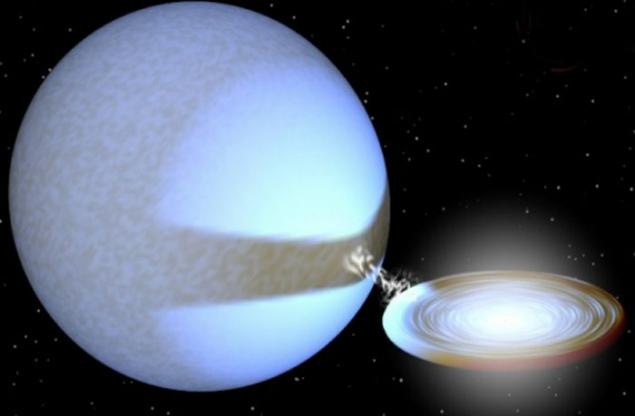

4. Supermassive black holes are more numerous than we thought
Black holes come in various sizes, from the size of a single atom to the massive (with masses greater than one million suns within the boundaries of the solar system). In rare cases, there are supermassive black holes. It was once thought that they can exist only in large galaxies, but astronomers have recently found that many dwarf galaxies have their massive black holes in the center. Then, astronomers announced that they had discovered a supermassive black hole in the ultra-compact dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1. The mass of this central black is 21 Million Suns (15% of the total mass of the entire galaxy).
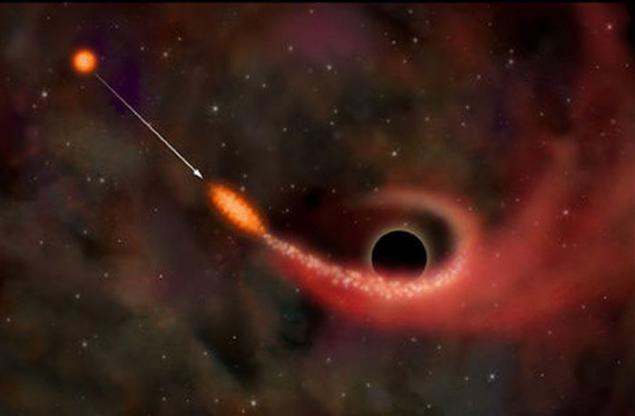

5. The rapid growth of mass black holes
Quasars - is the most luminous centers of distant galaxies. They are considered supermassive black holes with accretion disks, emit powerful X-rays. Scientists have long puzzled over the question of how a black hole can grow with such incredible speed. Now researchers believe that existed in the early universe cold gas flows, which were much denser than the current flows. Young black hole quickly and chaotically moving, pulling the next matter. As they grow and build mass black hole becomes more "greedy".
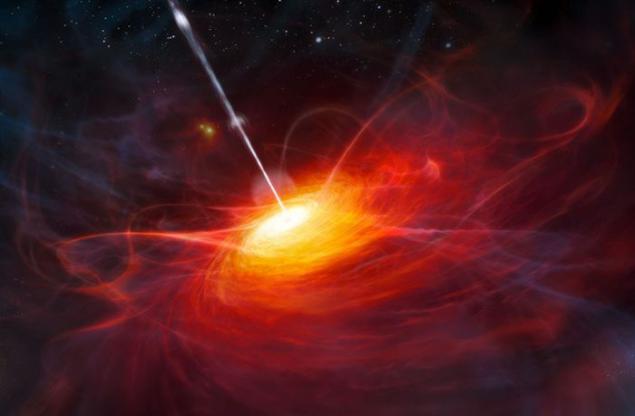

6. Black holes may prevent the formation of stars
In mature galaxies massive black holes can stop the development of young stars emitting particles emitting radio waves. Moving at the speed of light, they do not give the hot gas in galaxy cool and turn into new stars. Why is the black hole in the middle-aged, elliptical galaxies begin to emit particles? It was later found several compact, young, but dying galaxies. Astronomers came to the conclusion that the rapid onset of star formation begins with the collision of two galaxies with lots of cold gas. The energy from this process can blow any remaining gas, which stops the formation of stars.

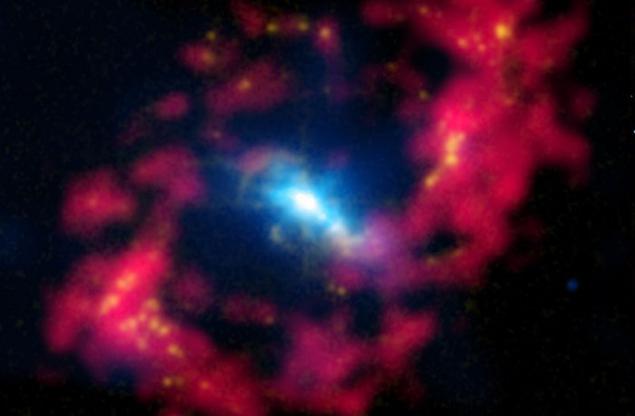
7. Eye of Sauron proves that black holes weigh more
Astronomers think that supermassive black holes in the centers of galaxies is 40% heavier than previously thought. This explains why the "Eddington limit" does not work with some calculations by weight. The researchers used a geodetic technique to measure the distance to the galaxy NGC 4151, whose active area is called the "Eye of Sauron", and get results with an accuracy of 90%, calculate the distance between the black hole and the dust ring on its orbit, and then to the eye of Sauron ( 62 million. light-years). This now makes it possible to more accurately measure the mass of a supermassive black hole.

8. An explanation of why the bumblebee flies
Until recently, most researchers believed gravity that space-time can not be turbulent. This was refuted by three scientists who decided to test whether gravity behave like a liquid and began to study rapidly spinning black holes. Space-time was less viscous around them, which increases the possibility of turbulence. The research results can also help to understand the turbulence in the world, including the nature of hurricanes, wind shear motion and even aircraft Flight of the Bumblebee.
9. The mystery of the disappearance of the center of the galaxy
Some astronomers believe that one of the secrets of the cosmos - is the transformation of pulsars in the small black holes. At least 50 of these stars have to be dead in the center of the Milky Way. However, astronomers have found only one pulsar. One theory involves dark matter, considering that the gravity of the pulsar can attract some dark matter particles, resulting in a dark matter "inflates" the pulsar to enormous size, and then turning it into a black hole. Pulsar becomes so large that punches a hole in the fabric of space-time and disappears.

10. Our universe may be the brainchild of 4-D black hole
Doubts about the Big Bang theory lies in the fact that our universe comes from the singularity, infinitely dense point that "not playing" by the rules of physics. Physicists do not understand the singularity and can not explain what caused the big bang. Proposed a new, well-founded theory. Scientists say that our universe - is the outer material of the deceased supernova 4-D star, whose inner layer is turned into a black hole. Researchers are still improving this theory, arguing that our thinking is limited to a 3-D world, but because we only see the tip of the reality.

About 2 million. Years ago in the center of our galaxy broke a supermassive black hole. Our ancestors most likely were able to observe the luminous object. Now this black hole is not lit, but then she was an active galactic nucleus (AGN), ie a compact center of the galaxy, producing energy and illuminates everything around. The black hole can be a source of AGN because its gravitational field attracts matter, forming a disk, which heats up and glows.

2. Not every "space generator" is a black hole
For decades, many scientists believed that ultramoschnye X-ray sources (ULX) - is the result of absorption of black holes of stars or other matter. The larger the black hole, the more it consumes, the more powerful radiation. That was the theory. Then, in a nearby galaxy M82, astronomers discovered accidentally pulsating source ULX. The problem is that the pulse is not black holes, pulsars and (rotating neutron stars). But pulsars in the galaxy M82 is 100 times brighter than in accordance with their weight (physical principle "Eddington limit"). It can not be a source of ULX. Therefore, astronomers do not consider that each source ULX or "cosmic generator" is a black hole.

3. Black holes are more "gluttonous" than expected
Until recently, scientists believed that the size of the black hole is determined by the maximum rate at which it can absorb / produce radiation ("Eddington limit"). Already found a black hole in the galaxy P13 NGC7793, which revolves around the supergiant star, absorbing it. P13 gas facility attracts its companion star is 10 times faster than previously thought. It is believed that the black hole is 15 times smaller than the Sun, but a million times brighter. As the pulsar M82, P13 is ULX, which is not only contrary to the "Eddington limit", but it completely denies.

4. Supermassive black holes are more numerous than we thought
Black holes come in various sizes, from the size of a single atom to the massive (with masses greater than one million suns within the boundaries of the solar system). In rare cases, there are supermassive black holes. It was once thought that they can exist only in large galaxies, but astronomers have recently found that many dwarf galaxies have their massive black holes in the center. Then, astronomers announced that they had discovered a supermassive black hole in the ultra-compact dwarf galaxy M60-UCD1. The mass of this central black is 21 Million Suns (15% of the total mass of the entire galaxy).

5. The rapid growth of mass black holes
Quasars - is the most luminous centers of distant galaxies. They are considered supermassive black holes with accretion disks, emit powerful X-rays. Scientists have long puzzled over the question of how a black hole can grow with such incredible speed. Now researchers believe that existed in the early universe cold gas flows, which were much denser than the current flows. Young black hole quickly and chaotically moving, pulling the next matter. As they grow and build mass black hole becomes more "greedy".

6. Black holes may prevent the formation of stars
In mature galaxies massive black holes can stop the development of young stars emitting particles emitting radio waves. Moving at the speed of light, they do not give the hot gas in galaxy cool and turn into new stars. Why is the black hole in the middle-aged, elliptical galaxies begin to emit particles? It was later found several compact, young, but dying galaxies. Astronomers came to the conclusion that the rapid onset of star formation begins with the collision of two galaxies with lots of cold gas. The energy from this process can blow any remaining gas, which stops the formation of stars.

7. Eye of Sauron proves that black holes weigh more
Astronomers think that supermassive black holes in the centers of galaxies is 40% heavier than previously thought. This explains why the "Eddington limit" does not work with some calculations by weight. The researchers used a geodetic technique to measure the distance to the galaxy NGC 4151, whose active area is called the "Eye of Sauron", and get results with an accuracy of 90%, calculate the distance between the black hole and the dust ring on its orbit, and then to the eye of Sauron ( 62 million. light-years). This now makes it possible to more accurately measure the mass of a supermassive black hole.

8. An explanation of why the bumblebee flies
Until recently, most researchers believed gravity that space-time can not be turbulent. This was refuted by three scientists who decided to test whether gravity behave like a liquid and began to study rapidly spinning black holes. Space-time was less viscous around them, which increases the possibility of turbulence. The research results can also help to understand the turbulence in the world, including the nature of hurricanes, wind shear motion and even aircraft Flight of the Bumblebee.

9. The mystery of the disappearance of the center of the galaxy
Some astronomers believe that one of the secrets of the cosmos - is the transformation of pulsars in the small black holes. At least 50 of these stars have to be dead in the center of the Milky Way. However, astronomers have found only one pulsar. One theory involves dark matter, considering that the gravity of the pulsar can attract some dark matter particles, resulting in a dark matter "inflates" the pulsar to enormous size, and then turning it into a black hole. Pulsar becomes so large that punches a hole in the fabric of space-time and disappears.

10. Our universe may be the brainchild of 4-D black hole
Doubts about the Big Bang theory lies in the fact that our universe comes from the singularity, infinitely dense point that "not playing" by the rules of physics. Physicists do not understand the singularity and can not explain what caused the big bang. Proposed a new, well-founded theory. Scientists say that our universe - is the outer material of the deceased supernova 4-D star, whose inner layer is turned into a black hole. Researchers are still improving this theory, arguing that our thinking is limited to a 3-D world, but because we only see the tip of the reality.