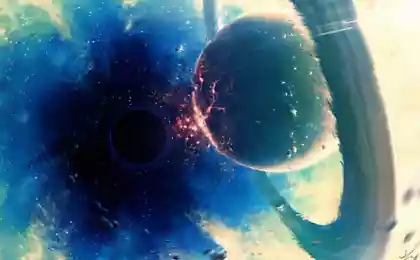3000
The biggest black hole in the known Universe
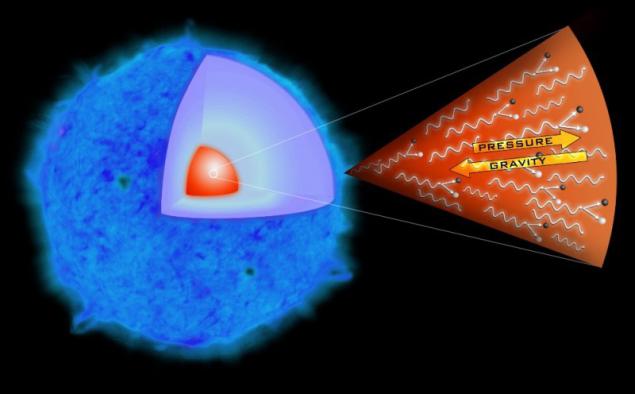
The black hole is the result of the collapse of a supermassive star, which ends in the core "fuel" for the nuclear reaction. As the compression core temperature rises and photons with energies above 511 keV, colliding to form electron-positron pairs, which leads to a catastrophic decline of pressure and further collapse of the star under the influence of its own gravity.
Astrophysicist Ethan Siegel (Ethan Siegel) published an article «Крупнейшая black hole in the known Universe », which collected information on the mass of black holes in different galaxies. Just wondering: where is the most massive of them?
Since the most dense clusters of stars - at the center of galaxies, now almost in the center of each galaxy is a massive black hole, formed after the merger of many others. For example, in the center of the Milky Way's black hole has a mass of about 0, 1% of our galaxy that is 4 million times the mass of the sun.
Determine the presence of a black hole is very easy by examining the trajectory of the stars, which are affected by the gravity of the invisible body.
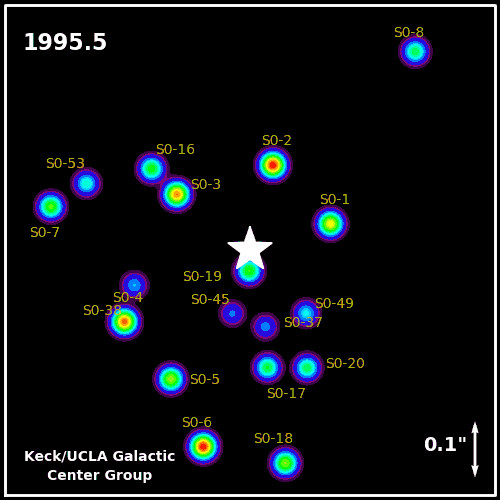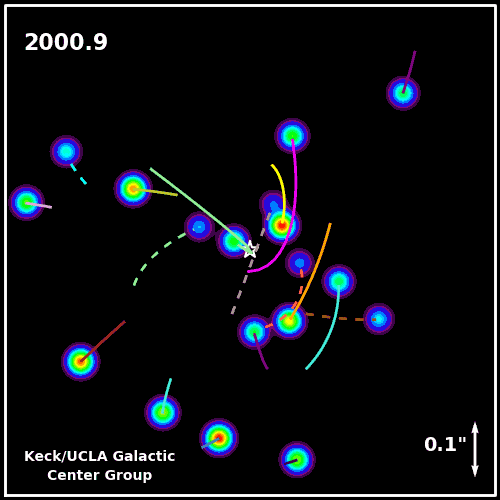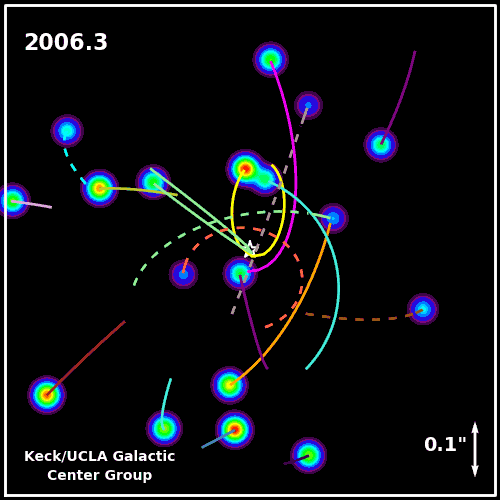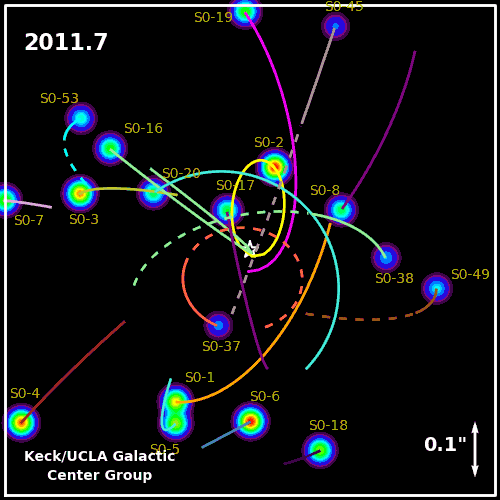
But the Milky Way - a relatively small galaxy that does not have at the biggest black hole. For example, not far from us in the Virgo cluster is a giant galaxy Messier 87 - it is about 200 times larger than ours.
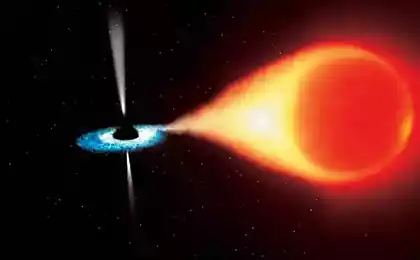
So, from the center of this galaxy breaks the flow of matter in length about 5,000 light-years (see photo). It's a crazy anomaly, writes Ethan Siegel, but looks very nice.
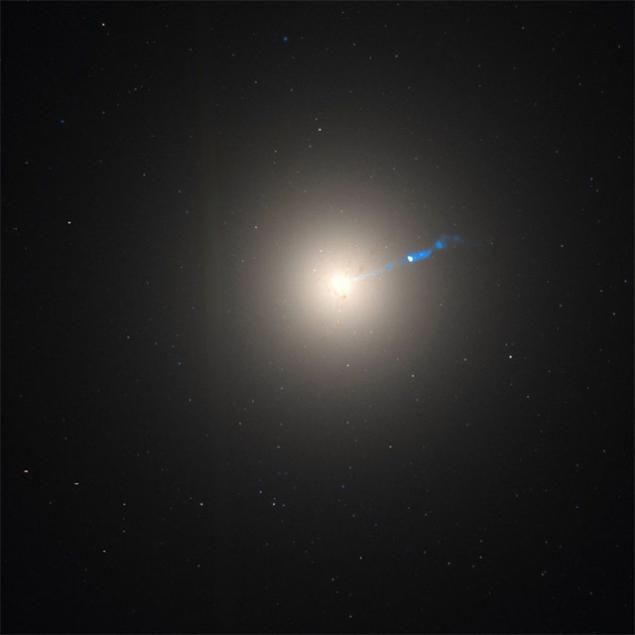

Scientists believe that the explanation of this "eruption" from the center of the galaxy can only be a black hole. Calculation shows that the mass of the black hole somewhere in 1500 times greater than the mass of the black hole in the Milky Way, which is about 6, 6 billion solar masses.
But where in the universe is the biggest black hole? Assuming the rate of that in the center of almost every galaxy has an object with a mass of 0, 1% of the mass of the galaxy, then you need to find the most massive galaxies. Scientists can give an answer to this question.
The most massive of the known - galaxy IC 1101 in the center of the cluster Abell 2029, which lies on the Milky Way is 20 times farther than cluster Virgo.
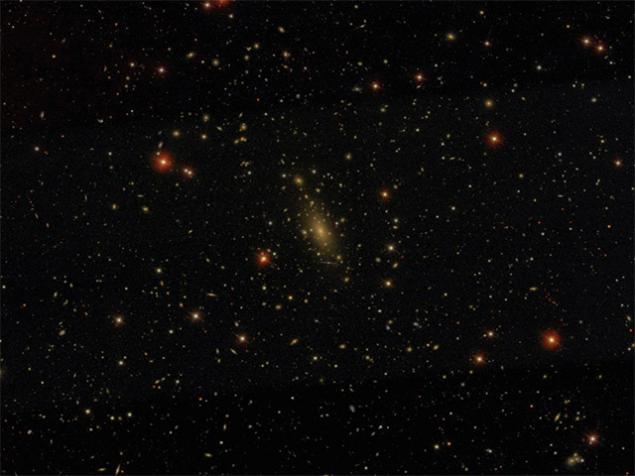

In IC 1101 distance from the center to the farthest edge - about 2 million light-years. Its size is twice that distance from the Milky Way to our nearest galaxy Andromeda. Weight almost equals that of the total stellar cluster Virgo!
If the center of the IC 1101 has a black hole (and it should be there), then it may be the most massive in the known universe.
Ethan Siegel says he can make mistakes. The reason - a unique galaxy NGC 1277. This galaxy is too much, a little less than ours. But the analysis of its rotation showed incredible result: a black hole in the center is 17 billion solar masses and is already 17% of the total mass of the galaxy. This is a record for the ratio of the black hole mass to the mass of the galaxy.

There is another candidate for the biggest black hole in the known universe. It is shown in the next photo.
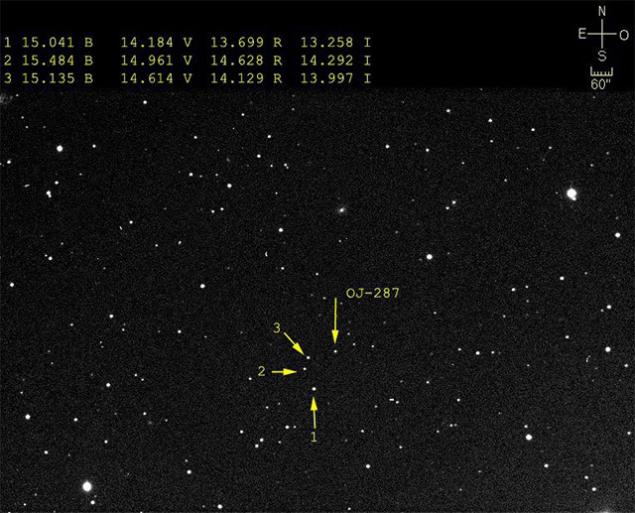
Strange object OJ 287 is called blazar < / a>. Blazars - a special class of extragalactic objects, a kind of quasars. They have a very powerful radiation, which in OJ 287 varies with a cycle of 11-12 years (double peak).
According astrophysicists, OJ 287 includes a central supermassive black hole, which revolves in its orbit another black hole smaller. The central black hole 18 billion solar masses - the largest known to date.
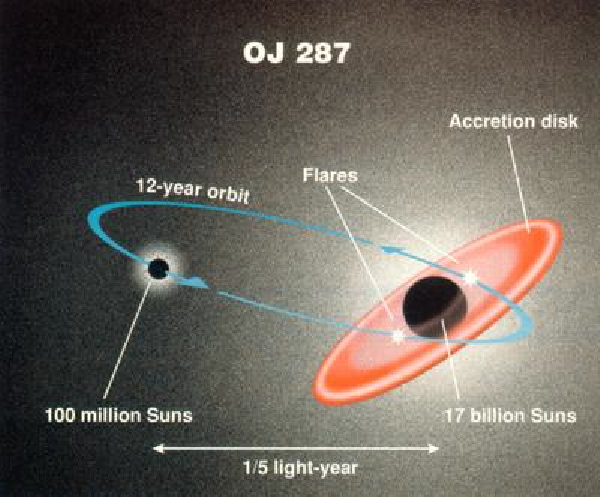
The pair of black holes will be one of the best experiments to test general relativity - namely, the deformation of space-time as described in GR.
Due to relativistic effects perihelion black holes, that is closest to the central black hole point of the orbit, be offset by 39 ° in one turn! For comparison, the perihelion of Mercury shifted by only 43 arcseconds per century.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/226411/
Follow the World Cup? You know that the International Space Station is the size of the stadium?
Intel demonstrated "floating" display